目录
一、throws
一、基本说明
二、使用细节
二、自定义异常
一、 基本概念
编辑二、自定义异常的步骤
三、实例
四、练习
三、throw和throws的区别
四、本章作业
第一道
第二题
第三题
第四题
一、throws
一、基本说明

package com.hspedu.throws_;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Throws01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{
f1();
}
public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException,NullPointerException,ClassCastException {
//创建了一个文件流对象
//1.这里的异常是一个FileNotFoundException 编译异常,必须要明确的处理
//2.使用前面讲过的try-catch-finally
//3.使用 throws ,抛出异常,让调用f1方法的调用者处理
//4.throws可以抛出方法中产生的异常类型:FileNotFoundException,也可以抛出其父类Exception
//5.throws 关键字后也可以是 异常列表,即可以抛出多个异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.jpg");
}
}
二、使用细节

package com.hspedu.throws_;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ThrowsDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
f2();//运行异常,默认throws处理
}
public static void f2() {
//1.对于编译异常, 程序中必须处理, 比如 try-catch 或者 throws
//2.对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理, 默认就是 throws 的方式处理
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
double res = n1 / n2;
}
public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException {
//在f1()中调用方法f3(), f3()抛出一个编译异常: FileNotFoundException
//编译异常必须要显式的处理,两种:t-c-f/throws
f3();
}
public static void f3() throws FileNotFoundException {//编译异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.jpg");
}
public static void f4() {
//1.在此处调用f5()是OK的
//2.f5()抛出的是一个运行异常
//3.运行异常有默认处理机制,并不要求显式处理
f5();
}
public static void f5() throws ArithmeticException {//运行异常
}
}
class Father {
public void method() throws RuntimeException {
}
}
class Son extends Father {
//3.子类重写父类的方法时,抛出的异常类型要么和父类一致,或者是父类异常类型的子类型
//子类抛出的异常类型 范围 <= 父类
//4. 在 throws 过程中, 如果有方法 try-catch , 就相当于处理异常, 就可以不必 throws
@Override
//如果是throws Exception就会报错
//如果是throws FileNotFoundException 也会报错因为这是编译异常,跟运行异常之间不存在继承关系
public void method() throws NullPointerException {//NullPointerException是RuntimeException的子类
}
}
二、自定义异常
一、 基本概念

二、自定义异常的步骤

三、实例
package com.hspedu.customexception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class CustomException {
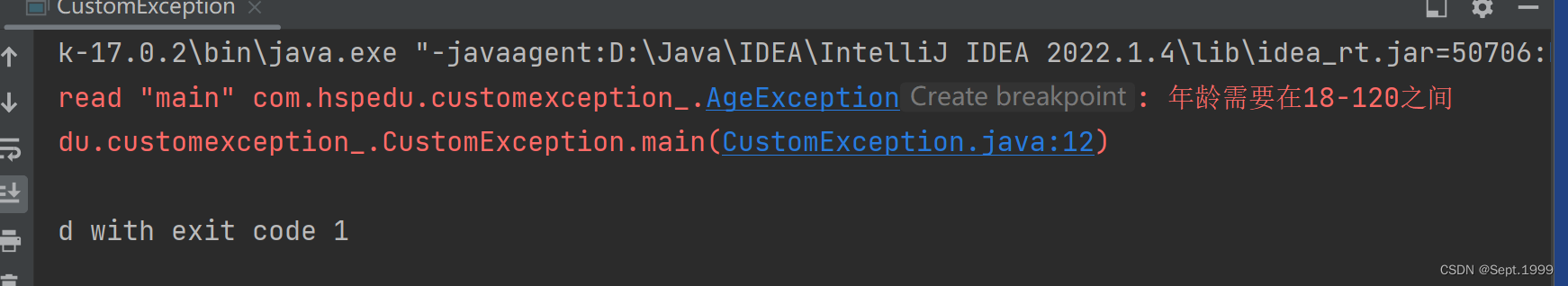
public static void main(String[] args)/*throws Exception*/{
int age = 124;
if(!(age >= 18 && age <= 120)){
//可以通过构造器,设置打印出的信息
throw new AgeException("年龄需要在18-120之间");
}
System.out.println("年龄范围正确...");//如果只是扔出异常而没有catch,则不会执行此语句
}
}
//自定义一个异常
//一般情况下,自定义异常是继承自RuntimeException
//2.即把自定义异常做成运行时异常,好处是: 我们可以使用默认的处理机制
//3.如果写成是extends Exception,则是编译异常,
// 4.就必须在main方法中显式的抛出异常 throws Exception,或者使用t-c-f
class AgeException extends RuntimeException{
public AgeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
} 
四、练习
package com.hspedu.customexception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class CustomExceptionExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
ReturnExceptionDemo.methodA();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
ReturnExceptionDemo.methodB();
}
}
class ReturnExceptionDemo{
static void methodA(){
try {
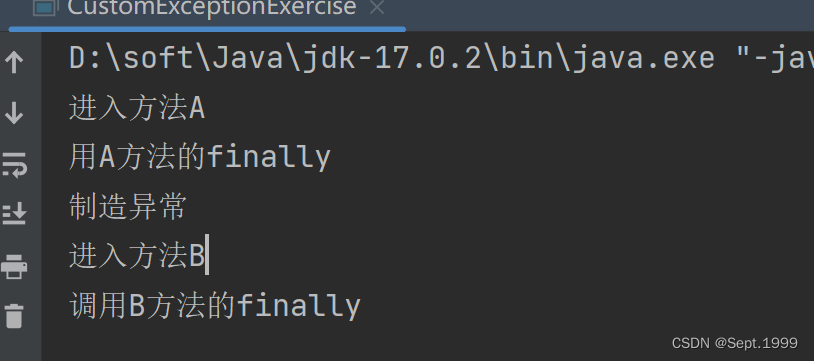
System.out.println("进入方法A");
throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");
}finally {
System.out.println("用A方法的finally");
}
}
static void methodB(){
try {
System.out.println("进入方法B");
return;
} finally{
System.out.println("调用B方法的finally");
}
}
}考察知识点:如果抛出了异常throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");,或者是出现了return语句就表示要结束此方法,剩余的代码不会再执行,但是如果有finally,那么finally中的代码必须执行,所以此时就会优先执行finally中的代码
三、throw和throws的区别

四、本章作业
第一道

我的代码
package com.hspedu.homework;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class EcmDef {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
编写应用程序EcmDef.java,接收命令行的两个参数(整数),计算两数相除。
计算两个数相除,要求使用方法 cal(int n1,int n2)
对数据格式不正确、缺少命令行参数、除0 进行异常处理
数据格式不正确:NumberFormatException
缺少命令行参数:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
除0:ArithmeticException
*/
try {
//如果用这个循环条件的话,即使传入了3个参数也不会报错
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
cal(n1,n2);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
throw new NumberFormatException("数据格式不正确");
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("缺少命令行参数");
}catch (ArithmeticException e) {
throw new ArithmeticException("被除数为0,运算异常");
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行...");
}
public static void cal(int n1 ,int n2){
System.out.println("res = " + n1 / n2);
}
}
代码问题:

在命令行输入参数时,数组args的数据就已经传入到main方法中了,所以
就算没有发生异常,此循环也会被执行 参数的个数 次,此时循环次数就是3
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
cal(n1,n2);
}
运行结果
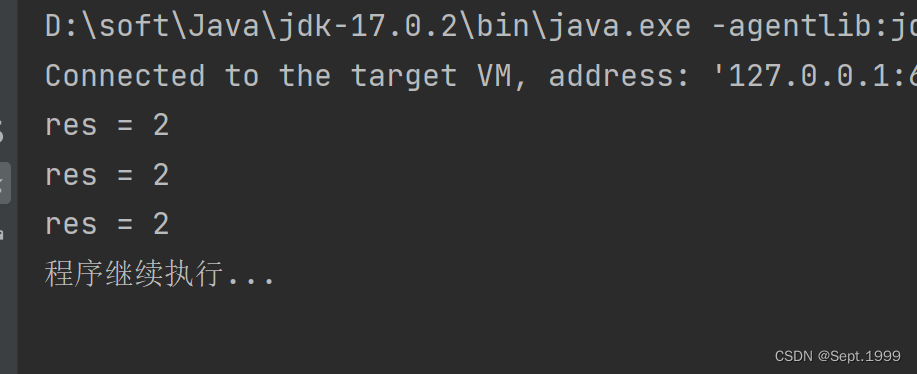
并且此代码只在 命令行参数只有一个的时候 会抛出异常,不能判断命令行参数 为多个或者0个的情况
正确代码
package com.hspedu.homework;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class EcmDef02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//首先对传入的参数个数进行判断
try {
if(args.length != 2){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("参数个数不正确");//扔出异常后需要用try-catch来捕获异常
}
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
cal(n1,n2);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("数字类型转换异常");
}catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("数学运算异常(除数为0)");
}
System.out.println("继续执行程序...");
}
public static void cal(int n1, int n2){
System.out.println("res=" + n1 / n2);
}
}

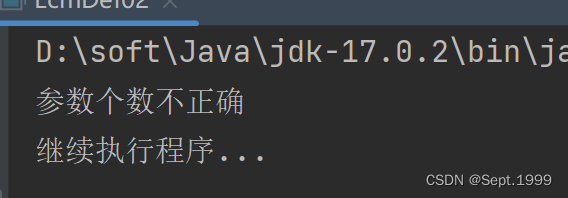
第二题

package com.hspedu.homework;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HomeWork02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String[] args是一个空数组,里面没有存储任何数据
System.out.println(args.length);
//由于args是一个空数组,这里会发生ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
//发生异常后,下面的代码都不会执行
if(args[4].equals("john")){
System.out.println("BB");
}else{
System.out.println("AA");
}
Object o= args[2];//ok,String是Object的子类
Integer i =(Integer)o;//ClassCastException,Integer和String没有继承关系
//String i =(String)o;//OK
}
}
第三题
package com.hspedu.homework;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HomeWork03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
func();
System.out.println("A");//在try中如果抛出了异常,剩余代码块就不执行,所以此处不输出
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("C");//捕获异常并打印 即第三步 C
}
System.out.println("D");//由于异常已经被捕获,所以可以正常输出 D,结果就是BCD
}
public static void func() {//静态方法
try {
//第一步是抛出异常,但是一旦抛出异常,就不会执行剩余代码
//但是finally中的代码必须执行,所以先输出B,再抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException();//第二步
} finally {
System.out.println("B");//第一步 B
}
}
}
第四题
package com.hspedu.homework;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HomeWork04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
showExce();//调用此方法后抛出一个异常,剩余代码不再执行
System.out.println("A");
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("B");
} finally{
System.out.println("C");
}
System.out.println("D");
}
public static void showExce() throws Exception{
throw new Exception();//抛出异常
}
}