1. 前言
之前一直看别人的源码,虽然对自己提升比较大,但毕竟不是自己写的,很容易遗忘。这段时间准备自己造一些轮子,主要目的还是为了提升自身实力,总不能一遇到问题就Google

。
之前写i博客园客户端的时候,经常会遇到JSON数据转Model的功能。一般遇到这种问题我都是自己在对应Model类中定义一个+ (instance)initWithAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes函数来将NSDictionary*数据转化为对应Model。
下面是i博客园中ICUser的部分代码,其中就使用了initWithAttributes。
// ICUser.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
extern NSString *const kUserId;
extern NSString *const kUserBlogId;
extern NSString *const kUserDisplayName;
extern NSString *const kUserAvatarURL;
@interface ICUser : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *userId;
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger blogId;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *displayName;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSURL *avatarURL;+ (instancetype)initWithAttributes:(NSDictionary *
)attributes;
@end
// ICUser.m
#import "ICUser.h"
NSString *const kUserId = @"UserId";
NSString *const kUserBlogId = @"BlogId";
NSString *const kUserDisplayName = @"DisplayName";
NSString *const kUserAvatarURL = @"Avatar";
@implementation ICUser+ (instancetype)initWithAttributes:(NSDictionary *
)attributes
{
ICUser *user = [[ICUser alloc] init]; user.userId = attributes[kUserId];
user.blogId = [attributes[kUserBlogId] integerValue];
user.displayName = attributes[kUserDisplayName];
user.avatarURL = [NSURL URLWithString:attributes[kUserAvatarURL]];
return user;
}
@end如果我们需要处理的情况符合下面两个要求:
- Model类的个数比较少
- 每个Model的成员不是很复杂
这种情况下使用上述方法还可以接受。但是一旦Model这一层急剧膨胀,这时候就会让人苦不堪言:
- initWithAttributes函数容易写错,而且出错后不方便排查。
- 机械性的代码会比较多,不利于提高效率。
考虑到手动转JSON为Model的种种不便,我决定自己写一个JSON转Model的库。虽然网上已经有很多这方面的第三方库,但是我还是想自己造轮子,目的是为了更深入地学习iOS。
2. 设计思路
1.首先要考虑到输入输出是什么?
输入:NSDictionary类型的数据
这里我们先从简,一般我们使用到解析JSON的场合是在网络请求。服务器端返回JSON格式的数据,我们需要转化成本地的Model(此处不讨论直接使用NSDictionary好还是转化为Model好)。并且本篇文章只假设我们网络请求获取到的JSON数据已经在客户端处理成了NSDictionary类型的数据(比较常见)。
输出:Model类型的数据
Model类型的数据。
举例:
目前我实现的一个简单的例子:
#pragma mark - PJXUser
@interface PJXUser : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* username; // 用户名
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* password; // 密码
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* avatarImageURL; // 头像的URL地址
@end
- (void)runSimpleSample
{
NSDictionary *userDict = @{@"username" :@"shuaige",
@"password" :@"",
@"avatarImageURL":@"http://www.example.com/shuaige.png"};
PJXUser *user = [[PJXUser alloc] initWithAttributes:userDict];;
NSLog(@"username:%@\n",user.username);
NSLog(@"password:%@\n",user.password);
NSLog(@"avatarImageURL:%@\n",user.avatarImageURL);
}这个例子的输入就是userDict这个NSDictionary数据,输出则是一个PJXUser类的对象user。不知道大家有没有注意到,attributes中的key必须和Model中的property的名称一致,比如上例中PJXUser的username、password等属性(当然,你可以使用一个映射表解决这个问题,不过我们先暂时不想那么多)。
2. 核心算法怎么做(输入转输出)?
核心算法部分其实就是调用initWithAttributes:这个函数。那这个函数该如何设计呢?
既然我们需要所有的Model类都可以调用这个initWithAttributes:来完成JSON转Model的工作。那么我们首先想到的就是将这个函数添加到NSObject的category中,并要求所有Model类都继承自NSObject。
所以我首先新建了一个NSObject+Extension的category。并在其中添加了- (instancetype)initWithAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes方法。下面我简单阐述下该函数的实现。
其实我的实现思路基本参照的YYKit(传送门)中的YYModel(传送门)部分。其最核心的部分就是调用Model中每个属性的setter方法,并且将传入的attributes中每个元素的value作为setter的参数。
好的,到此为止最核心的部分已经讲完了。可能大家会有很多疑问,比如说如何获取到属性的setter方法,获取后又如何调用setter方法,毕竟此时的操作是在NSObject这个父类中进行的,并没有具体子类的信息。这里我简单提一下,既然编译期我们无法解决上述问题,那么我们就需要借助于OC的runtime机制了。当然,下面会具体讲解如何实现。
3. 具体实现
根据上面的核心思路,我觉得实现起来还存在一些问题:
如何获取每个属性的setter方法?如果现在获取到了每个属性的setter方法(注意是SEL类型),怎么给每个属性调用此方法?
现在是在NSObject中操作,所以不指望使用obj.username = attributes[@"username"]。所以需要使用runtime中的objc_msgSend,使用方法举例如下:
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)self, NSSelectorFromString(@"setUsername:"), @"shuaige");
可以看到我们只需要把其中的@"setUsername"和@"shuaige"替换成我们自己的变量就行。具体怎么替换呢?这时候我们就需要创建一些数据结构来处理和保存相关的属性信息。当然,这些数据结构也是我在实现过程中不断修正的结果。至于中间如何修正,就不细说了,直接上结果。
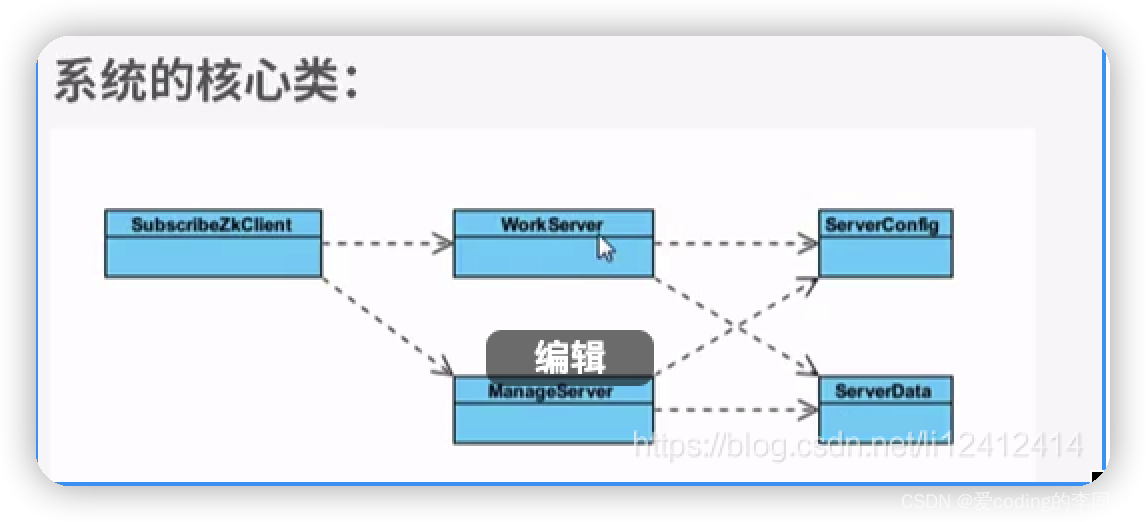
数据结构的构建其实也很符合我们的思考习惯。既然我们需要对某个类进行处理,不可避免的,我们需要新建一个类来存储Class信息(PJXClassInfo),而每个Class是由property、ivar和method组成的,所以针对不同组成,我们需要定义三个类来存储property、ivar、method。但是此处我们只需要property信息,所以只建立了property相关的类(PJXPropertyInfo)。
我首先创建了一个PJXClassInfo的类。这个类目前只存放了一个NSMutableDictionary类型的propertyInfos属性,该属性是用来存储这个Class的property信息。而propertyInfos中每个元素其实就是一个个PJXPropertyInfo对象。而每个PJXPropertyInfo保存的就是property的name,setter方法等等,当然,后期会根据需求为PJXPropertyInfo添加新的属性。
这两个类的关系如下:

下面我们看看具体代码如何实现,如下:
PJXPropertyInfo代码
/**
* @brief 存储Model中每个property的信息
* @param property 是一个objc_property_t类型变量
* @param name 表示该property的名称
* @param setter 是一个SEL类型变量,表示该property的setter方法
*/
@interface PJXPropertyInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) objc_property_t property;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) SEL setter;
@end
@implementation PJXPropertyInfo
- (instancetype)initWithPropertyInfo:(objc_property_t)property
{
self = [self init];
if (self) {
// 以备不时之需
_property = property;
// 使用property_getName获取到该property的名称
const char *name = property_getName(property);
if (name) {
_name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
}
// 目前不考虑自定义setter方法,只考虑系统默认生成setter方法
// 也就是说属性username的setter方法为setUsername:
NSString *setter = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@%@", [_name substringToIndex:].uppercaseString, [_name substringFromIndex:]];
_setter = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"set%@:", setter]);
}
return self;
}
@endPJXClassInfo代码
/**
* @brief 存储Model的Class信息,不过目前只存储Class的property信息
* @param propertyInfos 是一个NSMutableDictionary类型的变量,key存储property的名称,value存储对应的PJXPropertyInfo对象
*/
@interface PJXClassInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary *propertyInfos;
@end
@implementation PJXClassInfo
- (instancetype)initWithClassInfo:(Class)cls
{
self = [self init];
// 使用class_copyPropertyList获取到Class的所有property(objc_property_t类型)
unsigned int propertyCount = ;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(cls, &propertyCount);
_propertyInfos = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
// 遍历properties数组
// 根据对应的objc_property_t信息构建出PJXPropertyInfo对象,并给propertyInfos赋值
if (properties) {
for (unsigned int i = ; i < propertyCount; i++) {
PJXPropertyInfo *propertyInfo = [[PJXPropertyInfo alloc] initWithPropertyInfo:properties[i]];
_propertyInfos[propertyInfo.name] = propertyInfo;
}
// 注意释放空间
free(properties);
}
return self;
}
@end现在我们回到之前的问题,即如何获取setter并应用?可以看到有了这两个数据结构,我们就已经解决了如何获取到每个property的setter的问题(使用PJXClassInfo的propertyInfos的属性)。剩下的事情就简单了,调用setter方法进行赋值。这里参考YYModel中的方式,使用了一个Core Foundation函数CFDictionaryApplyFunction。
void CFDictionaryApplyFunction(CFDictionaryRef theDict, CFDictionaryApplierFunction applier, void *context);
该函数的作用是对于theDict每个key-value元素都应用applier函数。
所以我们来看看这个applier函数应该怎么设计。
注意这种C语言的applier回调函数不能设计为成员函数,因为成员函数隐藏了一个self参数。此处我们将该回调函数设计成static,并且命名为PropertyWithDictionaryFunction。
// 注意我传入的dictionary就是用户提供的JSON数据
// 比如此处传入的key==@"username",value==@"shuaige"
static void PropertyWithDictionaryFunction(const void *key, const void *value, void *context)
{
// 先将key和value转化到Cocoa框架下
NSString *keyStr = (__bridge NSString *)(key);
id setValue = (__bridge id)(value);
// modelSelf其实就是self,不过我这里用的是static函数,所以没有默认参数self
// 此时我们需要借助context参数来获取到这个self
// 所以我设计了一个PJXModelContext,用来存储self信息
// 另外,此函数的参数中也没有保存每个property信息,也得靠context这个参数来传递
// 所以PJXModelContext还需要存储PJXClassInfo对象信息
PJXModelContext *modelContext = context;
id modelSelf = (__bridge id)(modelContext->modelSelf);
PJXClassInfo *classInfo = (__bridge PJXClassInfo *)(modelContext->modelClassInfo);
PJXPropertyInfo *info = classInfo.propertyInfos[keyStr];
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, info.setter, setValue);
}最后一步就是在我们的initWithAttributes:函数中构建PJXModelContext并应用到上述函数。
typedef struct {
void *modelSelf;
void *modelClassInfo;
}PJXModelContext;
- (instancetype)initWithAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes
{
self = [self init];
if (self) {
// 初始化PJXClassInfo对象,并给modelContext赋值
PJXModelContext modelContext = {};
modelContext.modelSelf = (__bridge void *)(self);
PJXClassInfo *classInfo = [[PJXClassInfo alloc] initWithClassInfo:[self class]];
modelContext.modelClassInfo = (__bridge void *)classInfo;
// 应用该函数,将得到JSON->Model后的Model数据
CFDictionaryApplyFunction((CFDictionaryRef)attributes, PropertyWithDictionaryFunction, &modelContext);
}
return self;
}4. 测试结果
在2.设计思路这一部分,我们举了一个案例。现在我们运行下,看看NSLog的结果:
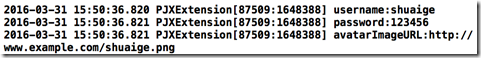
成功了!
5. 存在问题
目前的函数整体才100来行,还是存在很多问题没有考虑到。
比如:
- 没有考虑用户传入的JSON数据的key值和property的名称不一致
- 没有考虑用户传入的JSON数据有嵌套
- 没有考虑JSON数据的value值不一定是NSString类型
- 没有考虑JSON数据并不一定是NSDictionary类型
- 没有考虑用户自定义了Model属性的setter方法