1. 前言
上一篇《【疯狂造轮子-iOS】JSON转Model系列之一》实现了一个简陋的JSON转Model的库,不过还存在很多问题。下面我会尝试一个个去解决。
2. 存在问题及解决思路
2.1 没有考虑JSON数据并不一定是NSDictionary类型
有时候JSON并不一定是NSDictionary类型,可能是一个字符串,也可能是NSData类型的数据。不过不管是哪种类型,统统先将其转化为NSData数据,然后使用+[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:options:error:]来转化。所以我在initWithAttributes:上面又封装了一层。
- (instancetype)initWithJSONData:(id)json
{
NSDictionary *dict = [self pjx_dictionaryWithJSON:json];
return [self initWithAttributes:dict];
}
/**
* @brief 将NSString和NSData格式的json数据转化为NSDictionary类型
*/
- (NSDictionary *)pjx_dictionaryWithJSON:(id)json
{
if (!json) {
return nil;
}
// 若是NSDictionary类型,直接返回
if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
return json;
}
NSDictionary *dict = nil;
NSData *jsonData = nil;
if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
// 如果是NSString,就先转化为NSData
jsonData = [(NSString*)json dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
} else if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSData class]]) {
jsonData = json;
}
if (jsonData && [jsonData isKindOfClass:[NSData class]]) {
// 如果时NSData类型,使用NSJSONSerialization
NSError *error = nil;
dict = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:jsonData options: error:&error];
if (error) {
NSLog(@"pjx_dictionaryWithJSON error:%@", error);
return nil;
}
if (![dict isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
return nil;
}
}
return dict;
}为此,我在ViewController添加了两个sample。分别用来解析NSString类型的JSON数据和NSData类型的JSON数据。
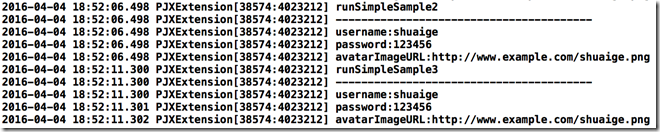
// NSString类型的JSON数据
- (void)runSimpleSample2
{
NSString *userStr = @" \
{ \
\"username\" : \"shuaige\", \
\"password\" : \"123456\", \
\"avatarImageURL\" : \"http://www.example.com/shuaige.png\" \
}";
PJXUser *user = [[PJXUser alloc] initWithJSONData:userStr];
NSLog(@"runSimpleSample2\n");
NSLog(@"----------------------------------------");
NSLog(@"username:%@\n",user.username);
NSLog(@"password:%@\n",user.password);
NSLog(@"avatarImageURL:%@\n",user.avatarImageURL);
}
// NSData类型的JSON数据
- (void)runSimpleSample3
{
NSString *userInfoFilePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"UserInfo" ofType:@"txt"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:userInfoFilePath];
PJXUser *user = [[PJXUser alloc] initWithJSONData:data];
NSLog(@"runSimpleSample3\n");
NSLog(@"----------------------------------------");
NSLog(@"username:%@\n",user.username);
NSLog(@"password:%@\n",user.password);
NSLog(@"avatarImageURL:%@\n",user.avatarImageURL);
}输出结果也是正确的:
2.2 没有考虑用户传入的JSON数据的key值和property的名称不一致
我第一反应是使用一个映射表。也就是说用户使用时需要自定义一套property和key的映射表。YYModel中使用了一个+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper函数,用户可以自定义该函数达到映射表的效果,而这个函数是放在一个protocol中的。我挺认同这种设计的,因为modelCustomPropertyMapper这种函数和Model是一种组合关系,可有可无(optional),所以设计成协议更合适。但是作者在设计protocol又说了一句:
// There's no need to add '<YYModel>' to your class header.
@protocol YYModel <NSObject>
什么意思呢,就是说你自定义一个NSObject子类(如YYBook)时,如果想实现自定义的property映射关系,只需要实现modelCustomPropertyMapper函数即可,而不需要写成@interface YYBook : NSObject <YYModel>。作者的意思是你遵不遵循YYModel这个protocol都没事,反正你只要在YYBook实现了modelCustomPropertyMapper即可。具体解释,大家请参考这个issue。
这种设计我不是很赞同,我是有洁癖的人,要不然你就别定义YYModel这个protocol,说明文档里面着重说明一下就行。所以此处我还是选择判断NSObject的子类是否遵循protocol,也就是说只有遵循了这个protocol,才能自定义property映射关系。
首先我们看如何使用自定义propertyMapper。我先建立一个PJXUserPropertyMapper类,遵循了JSONProtocol协议,并实现了propertyMapper协议函数。
// 遵循JSONProtocol协议,这个JSONProtocol中定义的就是我的propertyMapper协议函数
@interface PJXUserPropertyMapper : NSObject <JSONProtocol>
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* username; // 用户名
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* password; // 密码
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* avatarImageURL; // 头像的URL地址
@end
@implementation PJXUserPropertyMapper
// 实现propertyMapper这个协议方法
+ (NSDictionary *)propertyMapper
{
return @{@"Username" : @"username",
@"Password" : @"password",
@"AvatarImageURL" : @"avatarImageURL"};
}
@end随后我定义了一个example。
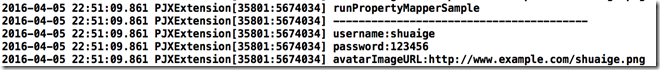
#pragma mark - PropertyMapper Sample
- (void)runPropertyMapperSample
{
NSDictionary *userDict = @{@"Username" : @"shuaige",
@"Password" : @"",
@"AvatarImageURL" : @"http://www.example.com/shuaige.png"};
PJXUserPropertyMapper *user = [[PJXUserPropertyMapper alloc] initWithJSONData:userDict];
NSLog(@"runPropertyMapperSample\n");
NSLog(@"----------------------------------------");
NSLog(@"username:%@\n",user.username);
NSLog(@"password:%@\n",user.password);
NSLog(@"avatarImageURL:%@\n",user.avatarImageURL);
}是不是感觉调用上和之前的非property映射没什么区别?那是因为我们需要在initWithJSONData中增加一些东西。
具体的做法是在PropertyWithDictionary函数增加了一个查表操作。
// 注意我传入的dictionary就是用户提供的JSON数据
// 比如此处传入的key==@"username",value==@"shuaige"
static void PropertyWithDictionaryFunction(const void *key, const void *value, void *context)
{
NSString *keyStr = (__bridge NSString *)(key);
......
// 如果使用了JSONProtocol,并且自定义了propertyMapper,那么还需要将keyStr转化下
if ([modelSelf conformsToProtocol:@protocol(JSONProtocol)] && [[modelSelf class] respondsToSelector:@selector(propertyMapper)]) {
keyStr = [[[modelSelf class] propertyMapper] objectForKey:keyStr];
}
......
}
这样就可以啦.我们看看效果:
2.3 没有考虑JSON数据的value值不一定是NSString类型
开始的时候,挺担心我这种写法会不会不兼容别的数据类型。不过我觉得应该没什么问题,毕竟我使用的setter方法本质上没啥问题,我的类型全用id来代替了(事实上,我的想法大错特错):
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, info.setter, setValue);不过本着不怕一万,就怕万一的心态。我还是做了一个example来试验一下:
@interface PJXUserVariousType : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *blogTitle; // 博客标题
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSURL *blogURL; // 博客网址
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger blogIndex; // 博客索引值
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *postDate; // 博客发布时间
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *friends; // 我的好友名称
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSSet *collections; // 我的收藏
@end
@implementation PJXUserVariousType
@end
#pragma mark - VariousType Sample
- (void)runVariousTypeSample
{
NSDictionary *userDict = @{@"blogTitle" : @"iOS developer",
@"blogURL" : @"http://www.example.com/blog.html",
@"blogIndex" : @,
@"postDate" : [NSDate date],
@"friends" : @[@"meinv1", @"meinv2", @"meinv3"],
@"collections" : @[@"shuaige1", @"shuaige2", @"shuaige3"]};
PJXUserVariousType *user = [[PJXUserVariousType alloc] initWithJSONData:userDict];
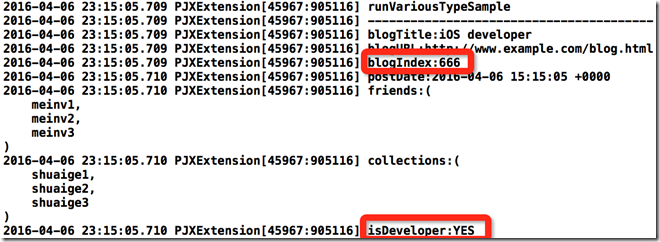
NSLog(@"runVariousTypeSample\n");
NSLog(@"----------------------------------------");
NSLog(@"blogTitle:%@\n",user.blogTitle);
NSLog(@"blogURL:%@\n",user.blogURL);
NSLog(@"blogIndex:%ld\n",user.blogIndex);
NSLog(@"postDate:%@\n",user.postDate);
NSLog(@"friends:%@\n",user.friends);
NSLog(@"collections:%@\n",user.collections);
}你猜输出啥?
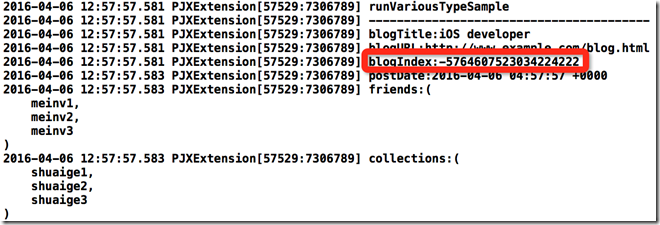
其他都正确,唯独我们的blogIndex出错了。这里确实是我欠考虑了,类似NSInteger,BOOL这些NSNumber类型(我暂时只考虑这些常用类型)需要单独处理一下。这一部分看起来容易,但是为了处理这种特殊情况确实要下很大功夫。比如你得先判断该属性是不是double或int这种类型,只有判断除了该属性是double还是int,你才能正确使用setter方法,而此处的调用方式也要单独写一个,因为和之前调用方式有一些些区别,需要判断Number的类型是double,是int,还是BOOl…….
对此我在PJXPropertyInfo中定义了两个函数,一个叫isNumber,用来判断该属性是不是一个Number,另一个叫setNumberValue:withModelSelf:,用来给是Number类型的属性赋值。另外,我仿照YYModel(比YYModel简化很多了)建了一个PJXEncodingType的enum类型,用来存储Number的类型(int?double?BOOL?……),与之配套的还有一个PJXGetEncodingType函数,来获取当前属性的类型(是int?double?BOOL?),具体怎么做还挺复杂的,后面会详细说明。
代码如下:
// Number类型
typedef NS_ENUM(NSUInteger, PJXEncodingType) {
PJXEncodingTypeUnknown = , ///< unknown
PJXEncodingTypeBool = 1, ///< bool
PJXEncodingTypeInt8 = 2, ///< char / BOOL
PJXEncodingTypeUInt8 = 3, ///< unsigned char
PJXEncodingTypeInt16 = 4, ///< short
PJXEncodingTypeUInt16 = 5, ///< unsigned short
PJXEncodingTypeInt32 = 6, ///< int
PJXEncodingTypeUInt32 = 7, ///< unsigned int
PJXEncodingTypeInt64 = 8, ///< long long
PJXEncodingTypeUInt64 = 9, ///< unsigned long long
PJXEncodingTypeFloat = 10, ///< float
PJXEncodingTypeDouble = 11, ///< double
PJXEncodingTypeLongDouble = 12, ///< long double
};
// 根据objc_property_attribute_t可以获取到property的类型PJXEncodingType
// 参考YYModel
PJXGetEncodingType(const char *encodingType) {
char *type = (char *)encodingType;
if (!type) return PJXEncodingTypeUnknown;
size_t len = strlen(type);
if (len == ) return PJXEncodingTypeUnknown;
switch (*type) {
case 'B': return PJXEncodingTypeBool;
case 'c': return PJXEncodingTypeInt8;
case 'C': return PJXEncodingTypeUInt8;
case 's': return PJXEncodingTypeInt16;
case 'S': return PJXEncodingTypeUInt16;
case 'i': return PJXEncodingTypeInt32;
case 'I': return PJXEncodingTypeUInt32;
case 'l': return PJXEncodingTypeInt32;
case 'L': return PJXEncodingTypeUInt32;
case 'q': return PJXEncodingTypeInt64;
case 'Q': return PJXEncodingTypeUInt64;
case 'f': return PJXEncodingTypeFloat;
case 'd': return PJXEncodingTypeDouble;
case 'D': return PJXEncodingTypeLongDouble;
default: return PJXEncodingTypeUnknown;
}
}
/**
* @brief 存储Model中每个property的信息
* ......
* @param type 是一个PJXEncodingType类型变量,为了存储该属性是哪种Number(int?double?BOOL?)
*/
@interface PJXPropertyInfo : NSObject
......
@property (nonatomic, assign) PJXEncodingType type;
@end
@implementation PJXPropertyInfo
- (instancetype)initWithPropertyInfo:(objc_property_t)property
{
self = [self init];
if (self) {
......
// 判断属性类型
unsigned int attrCount;
// 关于objc_property_attribute_t,这里有一篇文章介绍的很好
// http://www.henishuo.com/runtime-property-ivar/
objc_property_attribute_t *attrs = property_copyAttributeList(property, &attrCount);
for (unsigned int i = ; i < attrCount; i++) {
switch (attrs[i].name[]) {
case 'T': {// EncodingType
if (attrs[i].value) {
//NSLog(@"attrs[%d].value = %s", i, attrs[i].value);
// 可以根据value获取到property类型
_type = PJXGetEncodingType(attrs[i].value);
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
......
}
return self;
}
// 根据propertyInfo中存储的type判断其是否为Number
- (BOOL)isNumber
{
switch (self.type) {
case PJXEncodingTypeBool:
case PJXEncodingTypeInt8:
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt8:
case PJXEncodingTypeInt16:
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt16:
case PJXEncodingTypeInt32:
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt32:
case PJXEncodingTypeInt64:
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt64:
case PJXEncodingTypeFloat:
case PJXEncodingTypeDouble:
case PJXEncodingTypeLongDouble:
return YES;
default:
return NO;
break;
}
}
// 使用objc_msgSend调用modelSelf中该属性对应的setter方法
- (void)setNumberValue:(NSNumber *)number withModelSelf:(id)modelSelf
{
switch (self.type) {
case PJXEncodingTypeBool:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.boolValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeInt8:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.charValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt8:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.unsignedCharValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeInt16:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.shortValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt16:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.unsignedShortValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeInt32:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.intValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt32:
((void (*)(id, SEL, BOOL))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.unsignedIntValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeInt64:
((void (*)(id, SEL, uint64_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.longLongValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeUInt64:
((void (*)(id, SEL, uint64_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.unsignedLongLongValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeFloat:
((void (*)(id, SEL, float))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.floatValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeDouble:
((void (*)(id, SEL, double))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.doubleValue);
break;
case PJXEncodingTypeLongDouble:
((void (*)(id, SEL, long double))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, self.setter, number.doubleValue);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
@end有了上述的几个方法,后面就好办了,只需在PropertyWithDictionaryFunction函数中添加一个Number的判断就行:
static void PropertyWithDictionaryFunction(const void *key, const void *value, void *context)
{
......
// 如果该属性是Number,那么就用Number赋值方法给其赋值
if ([info isNumber]) {
[info setNumberValue:setValue withModelSelf:modelSelf];
} else {
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)(modelSelf, info.setter, setValue);
}
}这下终于成功了:
2.4 没有考虑用户自定义了Model属性的setter方法
这个其实比较简单,只需要对property的attribute(objc_property_attribute_t)进行判断即可:
- (instancetype)initWithPropertyInfo:(objc_property_t)property
{
......
BOOL isCustomSetter = NO;
// 判断属性类型
unsigned int attrCount;
// 关于objc_property_attribute_t,这里有一篇文章介绍的很好
// http://www.henishuo.com/runtime-property-ivar/
objc_property_attribute_t *attrs = property_copyAttributeList(property, &attrCount);
for (unsigned int i = ; i < attrCount; i++) {
switch (attrs[i].name[]) {
case 'T': { // EncodingType
if (attrs[i].value) {
//NSLog(@"attrs[%d].value = %s", i, attrs[i].value);
// 可以根据value获取到property类型
_type = PJXGetEncodingType(attrs[i].value);
}
break;
}
case 'S': { // 自定义setter方法
if (attrs[i].value) {
isCustomSetter = YES;
_setter = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithUTF8String:attrs[i].value]);
}
} break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (!isCustomSetter) {
// 如果没有自定义setter方法,只考虑系统默认生成setter方法
// 也就是说属性username的setter方法为setUsername:
NSString *setter = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@%@", [_name substringToIndex:].uppercaseString, [_name substringFromIndex:]];
_setter = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"set%@:", setter]);
}
}
return self;
}使用下面这个例子测试:
@interface PJXUserCustomSetter : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy, setter=setCustomUserName:) NSString* username; // 用户名
@property (nonatomic, copy, setter=setCustomBirthday:) NSDate* birthday; // 生日
@end
@implementation PJXUserCustomSetter
- (void)setCustomUserName:(NSString *)username
{
_username = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"My name is %@", username];
}
- (void)setCustomBirthday:(NSDate *)birthday
{
NSTimeInterval timeInterval = **; // 过一天
_birthday = [NSDate dateWithTimeInterval:timeInterval sinceDate:birthday];
}
@end
#pragma mark - Custom Setter Sample
- (void)runCustomSetterSample
{
NSDateFormatter *dateFormatter = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init];
[dateFormatter setDateFormat:@"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"];
NSDate *birthday = [dateFormatter dateFromString:@"2016-04-07 00:20:03"];
NSDictionary *userDict = @{@"username" : @"shuaige",
@"birthday" : birthday};
PJXUserCustomSetter *user = [[PJXUserCustomSetter alloc] initWithJSONData:userDict];
NSLog(@"runCustomSetterSample\n");
NSLog(@"----------------------------------------");
NSLog(@"username:%@\n",user.username);
NSLog(@"birthday:%@\n",user.birthday);
}得到的结果为:

成功了.
2.5 没有考虑用户传入的JSON数据有嵌套
我个人感觉这个应该没什么问题,为什么这么说呢?因为我嵌套的无非也是一个NSObject类型,那么就调用其自身的setter方法就OK啊.不过还是以防万一,我构造了一下案例:
@interface PJXBlog : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *title; // 博客名称
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *postDate; // 博客发表日期
@property (nonatomic, copy) PJXUser *author; // 博客作者
@end
@implementation PJXBlog
@end
#pragma mark - Nest Sample
- (void)runNestSample
{
NSDictionary *blogDict = @{@"title" : @"how to convert JSON to Model?",
@"postDate" : [NSDate date],
@"author" : @{@"username" : @"shuaige",
@"password" : @"",
@"avatarImageURL":@"http://www.example.com/shuaige.png"}};
PJXBlog *blog = [[PJXBlog alloc] initWithJSONData:blogDict];
NSLog(@"runNestSample\n");
NSLog(@"----------------------------------------");
NSLog(@"title:%@\n",blog.title);
NSLog(@"postDate:%@\n",blog.postDate);
NSLog(@"author:%@\n",blog.author);
}
输出结果如下:

结果没什么问题.不过这样说可能不是很负责任,但是目前我也想不到反例.暂时先当做成功了.
3. 总结
以我的能力,目前只能将JSON转化Model实现到这个地步了.总体来说,实现的难度不是很大(因为我考虑的情况还是比较少的,另外还有些功能没添加),不过涉及的知识点还是挺多的,挺不错的一个练手项目:).