关于System.nanoTime
System.currentTimeMills与System.nanoTime实际都是时间间隔,只不过两个时间的起始时间衡量不一致。
我们比较常用的,实际是System.currentTimeMills(),这个时间是以1970-01-01起始,到系统显示时间的间隔。
所以,只要改系统时间,这个方法的返回时间就会相应改变。
而System.nanoTime,与系统设置时间无关,同一个jvm中,System.nanoTime的起始是一致的。因此,改变系统时间,也不会改变System.nanoTime,此外,System.nanoTime的时间精度更高。适合用于计算时间间隔。
而在okio中的超时机制,就是使用System.nanoTime来进行计算的。
Timeout
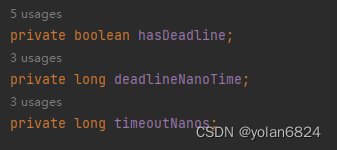
Timeout是一个类,只有3个成员变量需要关注。
- timeoutNanos:超时时间,相当于duration
- deadlineNanoTime:最终超时时间点,相当于System.nanoTime+timeout=dealineNanoTime
- hasDeadLine:是否有deadLine,一般设置了第二个参数,第三个参数就自动为true。
AsyncTimeout
Timeout的子类。
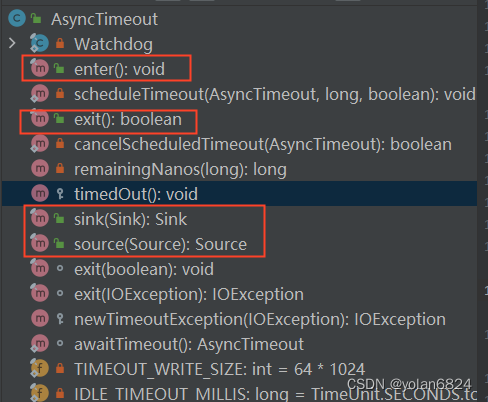
只有4个public方法。enter和exit方法都是在sink和source方法调用的。
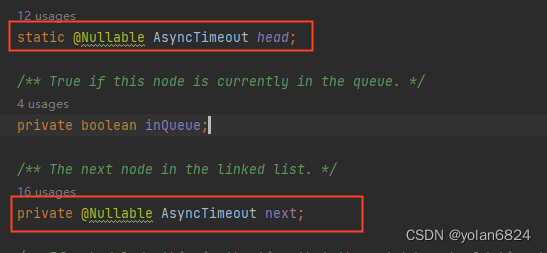
有一个静态变量head,还有一个next指针,说明AsyncTimeout维护了一个AsyncTimeout类型的链表。
由于4个public方法中,enter和exit方法都是被source和sink方法调用的,source和sink又是概念相似的方法,所以下面只介绍source方法。
source
public final Source source(final Source source) {
return new Source() {
@Override public long read(Buffer sink, long byteCount) throws IOException {
boolean throwOnTimeout = false;
enter();// 调用enter
try {
long result = source.read(sink, byteCount);// 读取数据
throwOnTimeout = true;
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw exit(e);
} finally {
exit(throwOnTimeout);// 检查是否超时,超时抛异常
}
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
boolean throwOnTimeout = false;
try {
source.close();
throwOnTimeout = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw exit(e);
} finally {
exit(throwOnTimeout);
}
}
@Override public Timeout timeout() {
return AsyncTimeout.this;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "AsyncTimeout.source(" + source + ")";
}
};
}source方法很简单,只是在read方法之前,调用enter方法,在read方法之后,调用了exit方法。
enter
public final void enter() {
if (inQueue) throw new IllegalStateException("Unbalanced enter/exit");
long timeoutNanos = timeoutNanos();
boolean hasDeadline = hasDeadline();
if (timeoutNanos == 0 && !hasDeadline) {
return; // No timeout and no deadline? Don't bother with the queue.
}
inQueue = true;// 标记入队列了
scheduleTimeout(this, timeoutNanos, hasDeadline);// 静态方法
}enter方法只标记了inQueue为true和调用了scheduleTimeout方法。
private static synchronized void scheduleTimeout(
AsyncTimeout node, long timeoutNanos, boolean hasDeadline) {
// Start the watchdog thread and create the head node when the first timeout is scheduled.
if (head == null) {// 创建head指针
head = new AsyncTimeout();
new Watchdog().start();// 开启一个线程监听队列中超时的节点
}
long now = System.nanoTime();
if (timeoutNanos != 0 && hasDeadline) {
// Compute the earliest event; either timeout or deadline. Because nanoTime can wrap around,
// Math.min() is undefined for absolute values, but meaningful for relative ones.
node.timeoutAt = now + Math.min(timeoutNanos, node.deadlineNanoTime() - now);
} else if (timeoutNanos != 0) {
node.timeoutAt = now + timeoutNanos;
} else if (hasDeadline) {
node.timeoutAt = node.deadlineNanoTime();
} else {
throw new AssertionError();
}// 求出当前节点的最终超时时间点
// Insert the node in sorted order.
long remainingNanos = node.remainingNanos(now);// 求出当前节点的剩余时间
// 按剩余时间,按顺序插入链表
for (AsyncTimeout prev = head; true; prev = prev.next) {
if (prev.next == null || remainingNanos < prev.next.remainingNanos(now)) {
node.next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
if (prev == head) {
AsyncTimeout.class.notify(); // Wake up the watchdog when inserting at the front.
}
break;
}
}
}总结下scheduleTimeout方法:
- 调用enter方法时,如果head为null,就创建一个head,并开启一个WatchDog线程(后面会讲)。
- 求出当前节点的deadline时间点,和剩余时间。
- 根据剩余时间,按序插入链表。
- 如果当前链表只有自己一个有效节点(prev == head),就调用AsyncTimeout.class.notify(后面会讲为什么要调用notify)。
WatchDog
private static final class Watchdog extends Thread {
Watchdog() {
super("Okio Watchdog");
setDaemon(true);// 守护线程。不影响JVM退出
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
AsyncTimeout timedOut;
synchronized (AsyncTimeout.class) {
timedOut = awaitTimeout();
// Didn't find a node to interrupt. Try again.
if (timedOut == null) continue;
// The queue is completely empty. Let this thread exit and let another watchdog thread
// get created on the next call to scheduleTimeout().
// 如果等了60s,返回的还是head,就直接不等了,等下一个节点插入的时候,再开始一个新的watchdog线程
if (timedOut == head) {
head = null;
return;
}
}
// Close the timed out node.
timedOut.timedOut();// 调用超时节点的timeout方法
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}总结下WatchDog线程:
- WatchDog是一个demon线程,即守护线程。当虚拟机中用户线程数为0时,虚拟机就会退出。而守护线程是不会影响虚拟机退出的。
- 调用awaitTimeout获取一个超时的节点,如果节点为null,continue,再重新获取节点。
- 如果超时节点为head,就说明当前队列为空,直接退出线程。
- 如果超时节点不为空,且不为head,调用节点的timeout方法。
下面看下awaitTimeout是怎么获取一个超时节点的:
static @Nullable AsyncTimeout awaitTimeout() throws InterruptedException {
// Get the next eligible node.,head不是一个有效节点,head.next才是第一个有效节点
AsyncTimeout node = head.next;
// The queue is empty. Wait until either something is enqueued or the idle timeout elapses.
if (node == null) {
long startNanos = System.nanoTime();
// 等待60s,只有调用enter()的时候才会调用notify,所以这里是检查到没有有效节点的时候,
// 就等待60s,看有没有新节点插入
AsyncTimeout.class.wait(IDLE_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
return head.next == null && (System.nanoTime() - startNanos) >= IDLE_TIMEOUT_NANOS
? head // The idle timeout elapsed. 超时了
: null; // The situation has changed. 插入了新的节点,返回null,触发WatchDog调用continue,重新回到这个方法
}
long waitNanos = node.remainingNanos(System.nanoTime());
// The head of the queue hasn't timed out yet. Await that.
if (waitNanos > 0) {
// Waiting is made complicated by the fact that we work in nanoseconds,
// but the API wants (millis, nanos) in two arguments.
long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L;
waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L);
AsyncTimeout.class.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos);// 等待剩余时间,返回null,重新触发调用该方法
return null;
}
// 这个节点的deadLine已经过了,从链表中移除这个节点
// The head of the queue has timed out. Remove it.
head.next = node.next;
node.next = null;
return node;
}- 如果队列中只有head,即没有有效节点的时候,等待60s。
- 当线程被唤醒时,只有两种可能,一种是插入了一个新的节点(即上面scheduleTimeout中的AsyncTimeout.class.notify方法),返回null,告诉WatchDog重新获取一遍节点;一种是超时,这时候,head.next还是null,返回head,告诉WatchDog不要再等了,直接退出线程。
- 如果head.next不为空
- 获取节点的剩余时间:remainingNanos
- 如果remainingNanos>0,就调用wait方法,并再次返回null。
- 否则就将节点移出队列,并且调用节点的timeout方法。
所以再次总结下,WatchDog干的事情就是,顺序遍历AysncTimeout链表(这大概就是为啥叫AsyncTimeout,开启了个线程专门监听有谁超时了)。如果遍历到有节点超时了,就调用节点的timeout方法。如果没有超时,就调用wait方法,等待节点的剩余时间,再去看链表中有没有超时的节点。
exit
前面介绍的source方法中,enter方法已经介绍完了。enter主要干的事情就是,如果head为空,就创建一个head,并开启一个WatchDog线程监听队列中的超时节点,如果有超时节点,就调用节点的timeout方法。如果head不为空,就获取当前节点的剩余时间,并按顺序插入链表。
这时候再想下,超时节点调用timeout方法很正常,但按WatchDog这么个遍历方法,链表中的所有节点都得超时。所以肯定有个机制,没有超时的节点,要及时移出队列。
所以这就是为什么source.read方法,前有一个enter方法,后有一个exit方法。
final void exit(boolean throwOnTimeout) throws IOException {
boolean timedOut = exit();
if (timedOut && throwOnTimeout) throw newTimeoutException(null);
}
public final boolean exit() {
if (!inQueue) return false;
inQueue = false;
return cancelScheduledTimeout(this);
}
private static synchronized boolean cancelScheduledTimeout(AsyncTimeout node) {
// Remove the node from the linked list.
for (AsyncTimeout prev = head; prev != null; prev = prev.next) {
if (prev.next == node) {
prev.next = node.next;
node.next = null;
return false;
}
}
// The node wasn't found in the linked list: it must have timed out!
return true;
}cancelScheduledTimeout方法,如果队列有这个节点(说明还没超时),就移出这个节点,并返回false,否则返回true。
exit方法,根据cancelScheduledTimeout方法的返回值,如果返回true,会抛出newTimeoutException中定义的exception。
实例:socket
public static Source source(Socket socket) throws IOException {
if (socket == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("socket == null");
if (socket.getInputStream() == null) throw new IOException("socket's input stream == null");
AsyncTimeout timeout = timeout(socket);// 调用timeout方法。
Source source = source(socket.getInputStream(), timeout);
return timeout.source(source);
}private static AsyncTimeout timeout(final Socket socket) {
return new AsyncTimeout() {
// 定义newTimeoutExeception
@Override protected IOException newTimeoutException(@Nullable IOException cause) {
InterruptedIOException ioe = new SocketTimeoutException("timeout");
if (cause != null) {
ioe.initCause(cause);
}
return ioe;
}
// 这个方法会在WatchDog检测到已经到达deadline的时候,调用
// 调用socket.close之后,socket对应的inputStream和outputStream都会被调用close
// 当inputStream.read方法过程中,inputStream被关闭了,会抛出IOException
@Override protected void timedOut() {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to close timed out socket " + socket, e);
} catch (AssertionError e) {
if (isAndroidGetsocknameError(e)) {
// Catch this exception due to a Firmware issue up to android 4.2.2
// https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=54072
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to close timed out socket " + socket, e);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
};
}上面一直说,如果WatchDog检测到节点超时了,会调用节点的timeout方法。下面看下timeout方法是如何阻断整个链路的。
在这个socket的示例方法中,timedout方法中调用了socket.close方法。
根据socket.close方法的注释,如果socket被关闭了,socket的inputStream和outputStream都会被调用close方法。
而inputStream被调用close,那么一直等待服务端的inputStream.read方法会被中断,直接抛出IOException。
再看回上面的一个方法source方法:
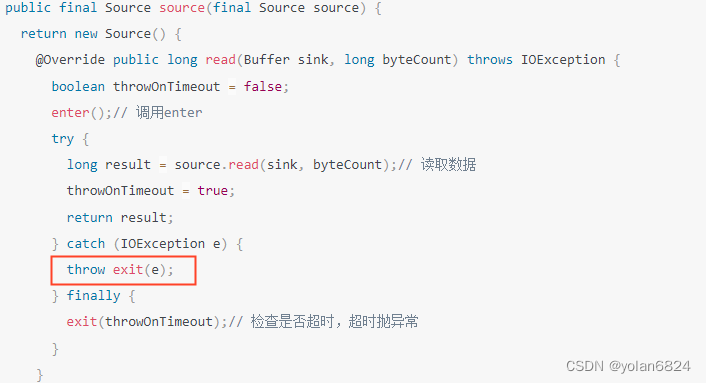
如果socket被调用close,source.read方法会抛出IOException。
抛出IOException的时候,会再次调用exit方法。大家应该还记得exit方法,是用来看节点还在不在队列中(节点是否超时),如果不在会抛出newTimeoutException方法定义的异常。
所以,通过上面的例子,就可以知道Source中的timeout方法是用来调用一些关闭资源的方法的。
最后的最后,总结一下:
- 当调用AsyncTimeout.source方法时,相当于在原来的source.read方法前后,分别调用了enter和exit方法。enter方法相当于创建了一个节点插入AsyncTimeout维护的超时链表中。而exit方法则是用来将自己从链表中移除。
- AsyncTimeout中的WatchDog线程会顺序遍历链表中的节点,如果超时,会调用节点的timeout方法。
- Source的timedout方法中,一般会调用close方法,阻断source.read方法。

![K8S管理系统项目实战[API开发]-2](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/27e2b8811f3645d5b5e29dcbc1715515.png)


![JavaWeb07(MVC应用01[家居商城]连接数据库)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ae1e3e29d924f06b6dc6eb4e4570fee.png)