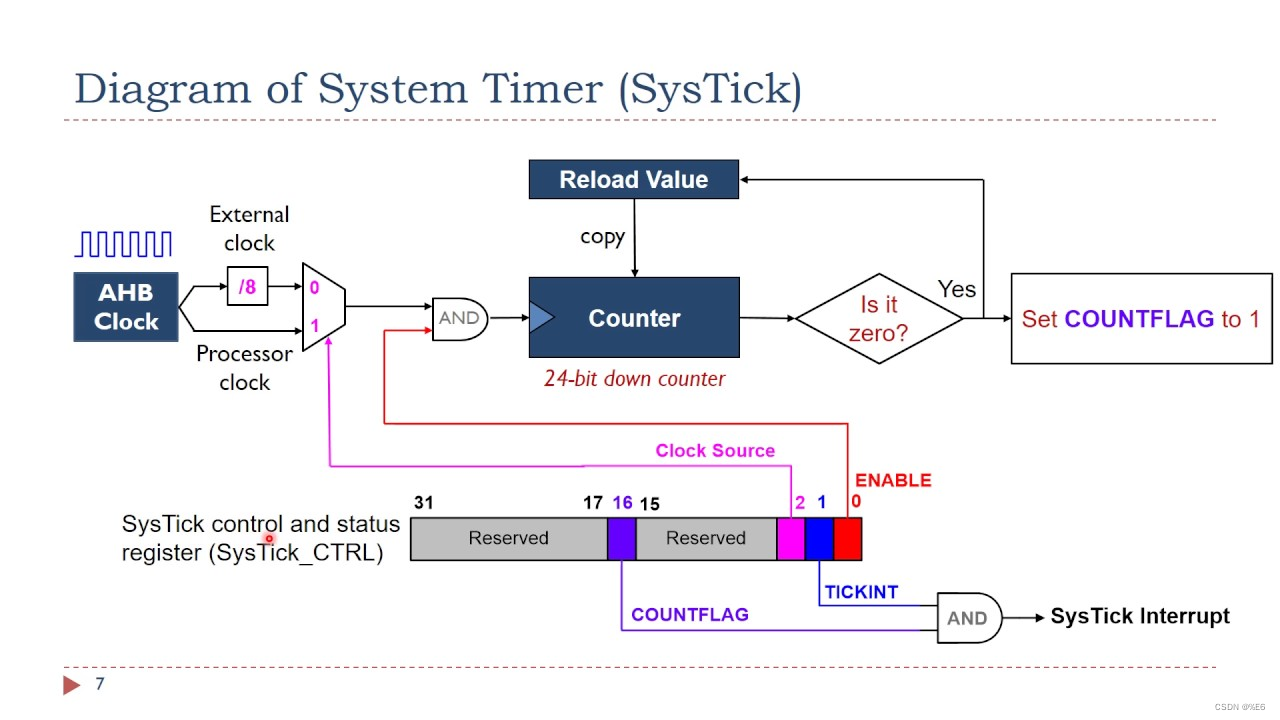
线程池&单例模式
- 一、什么是线程池
- 二、设计思路
- 三、代码实现
- 四、基于线程池的单例模式
- 4.1 懒汉模式设计思路
- 五、读者写者问题及读写锁
一、什么是线程池
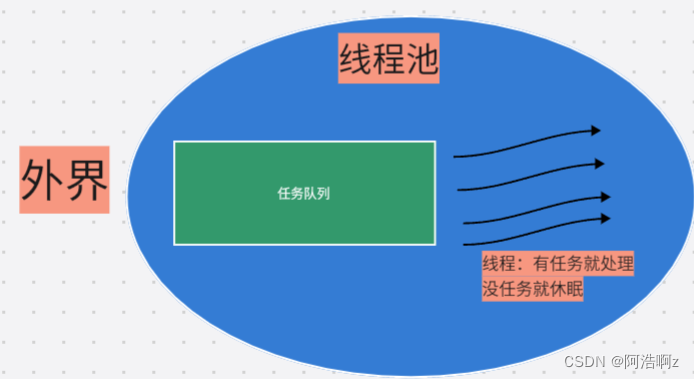
线程池: 一种线程使用模式。线程过多会带来调度开销,进而影响缓存局部性和整体性能。而线程池维护着多个线程,等待着监督管理者分配可并发执行的任务。这避免了在处理短时间任务时创建与销毁线程的代价。线程池不仅能够保证内核的充分利用,还能防止过分调度。可用线程数量应该取决于可用的并发处理器、处理器内核、内存、网络sockets等的数量。
线程池的应用场景:
- 需要大量的线程来完成任务,且完成任务的时间比较短。
- 对性能要求苛刻的应用,比如要求服务器迅速响应客户请求。
- 接受突发性的大量请求,但不至于使服务器因此产生大量线程的应用。
二、设计思路
三、代码实现
注:由于我个人不注意,将ThreadPool写成了ThredaPool!!!
//Thread.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cassert>
namespace ThreadCat
{
typedef std::function<void *(void *)> func_t;
const int num = 1024;
class Thread
{
private:
// 使用静态方法
static void *start_rountine(void *args)
{
Thread *this_ = static_cast<Thread *>(args);
return this_->callback();
}
public:
Thread()
{
char namebuffer[num];
snprintf(namebuffer, sizeof namebuffer, "thread-%d", thread_num++);
_name=namebuffer;
}
void start(func_t func, void *args=nullptr)
{
_func=func;
_args=args;
int n = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, start_rountine, this);
assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
}
void join()
{
int n = pthread_join(_tid, nullptr);
assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
}
std::string threadname()
{
return _name;
}
void *callback()
{
return _func(_args);
}
~Thread(){}
private:
std::string _name;
pthread_t _tid;
func_t _func;
void *_args;
static int thread_num;
};
int Thread::thread_num=1;
}
//Task.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
class Task//计算任务
{
public:
using func_t =std::function<int(int,int,char)>;
Task(){}
Task(int x,int y,char op,func_t callback)
:x_(x),y_(y),op_(op),callback_(callback)
{
}
std::string operator()()
{
int result=callback_(x_,y_,op_);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof buffer,"%d %c %d=%d",x_,op_,y_,result);
return buffer;
}
std::string toTaskString()
{
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof buffer,"%d %c %d=?",x_,op_,y_);
return buffer;
}
private:
int x_;
int y_;
char op_;
func_t callback_;
};
const std::string oper = "+-*/%";
int mymath(int x,int y,char op)
{
int result = 0;
switch (op)
{
case '+':
result = x + y;
break;
case '-':
result = x - y;
break;
case '*':
result = x * y;
break;
case '/':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "div zero error!" << std::endl;
result = -1;
}
else
result = x / y;
}
break;
case '%':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "mod zero error!" << std::endl;
result = -1;
}
else
result = x % y;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
//lockguard.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
class Mutex
{
public:
Mutex(pthread_mutex_t * lock_p=nullptr)
:lock_p_(lock_p)
{}
void lock()
{
if(lock_p_) pthread_mutex_lock(lock_p_);
}
void unlock()
{
if(lock_p_) pthread_mutex_unlock(lock_p_);
}
~Mutex(){}
private:
pthread_mutex_t* lock_p_;
};
//RAII思想管理资源
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(pthread_mutex_t* lock_p)//用传过来的锁去初始化Mutex
:mutex(lock_p)
{
mutex.lock();
}
~LockGuard()
{
mutex.unlock();
}
private:
Mutex mutex;
};
//ThreadPool.hpp
#pragma once
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "lock_guard.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ThreadCat;
const int gnum = 5;
template <class T>
class ThredaPool;
template <class T>
class ThreadData
{
public:
ThreadData(ThredaPool<T> *tp, const std::string &n)
: threadpool(tp), name(n)
{
}
public:
ThredaPool<T> *threadpool;
std::string name;
};
template <class T>
class ThredaPool
{
private:
static void *handlerTask(void *args)
{
ThreadData<T> *td = static_cast<ThreadData<T> *>(args);
while (true)
{
T t;
{
LockGuard lock(td->threadpool->mutex());
//td->threadpool->lockQueue();
while (td->threadpool->isQueueEmpty())
{
td->threadpool->threadWait();
}
// pop本质,就是把任务从公共队列中拿到当前线程独立的栈中
t = td->threadpool->pop();
//td->threadpool->unlockQueue();
}
std::cout << td->name << "获取了一个" << t.toTaskString() << "并处理完成,结果是" << t() << std::endl;
}
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
public:
void lockQueue() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_); }
void unlockQueue() { pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_); }
bool isQueueEmpty() { return task_queue_.empty(); }
void threadWait() { pthread_cond_wait(&cond_, &mutex_); }
T pop()
{
T t = task_queue_.front();
task_queue_.pop();
return t;
}
pthread_mutex_t* mutex()
{
return &mutex_;
}
public:
ThredaPool(const int &num = gnum) : num_(num)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&cond_, nullptr);
for (int i = 0; i < num_; ++i)
{
//创建多个线程并传递参数,由于在类内调用,需要用静态方法
threads_.push_back(new Thread());
}
}
void run()
{
for (const auto &t : threads_)
{
ThreadData<T> *td = new ThreadData<T>(this, t->threadname());
t->start(handlerTask, td);
std::cout << t->threadname() << std::endl;
}
}
void push(const T &in)
{
LockGuard lock(&mutex_);
//pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_);
task_queue_.push(in);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_);
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_);
}
~ThredaPool()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_);
for (const auto &t : threads_)
{
delete t;
}
}
private:
int num_;
std::vector<Thread *> threads_;
std::queue<T> task_queue_;
pthread_mutex_t mutex_;
pthread_cond_t cond_;
};
//main.cc
#include "ThreadPool.hpp"
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <memory>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
std::unique_ptr<ThredaPool<Task>> tp(new ThredaPool<Task>());
tp->run();
srand((size_t)time(0) ^ 0x22116652);
int x, y;
char op;
while (true)
{
x = rand() % 10 + 1;
y = rand() % 5 + 1;
op = oper[rand() % oper.size()];
Task t(x, y, op, mymath);
tp->push(t);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
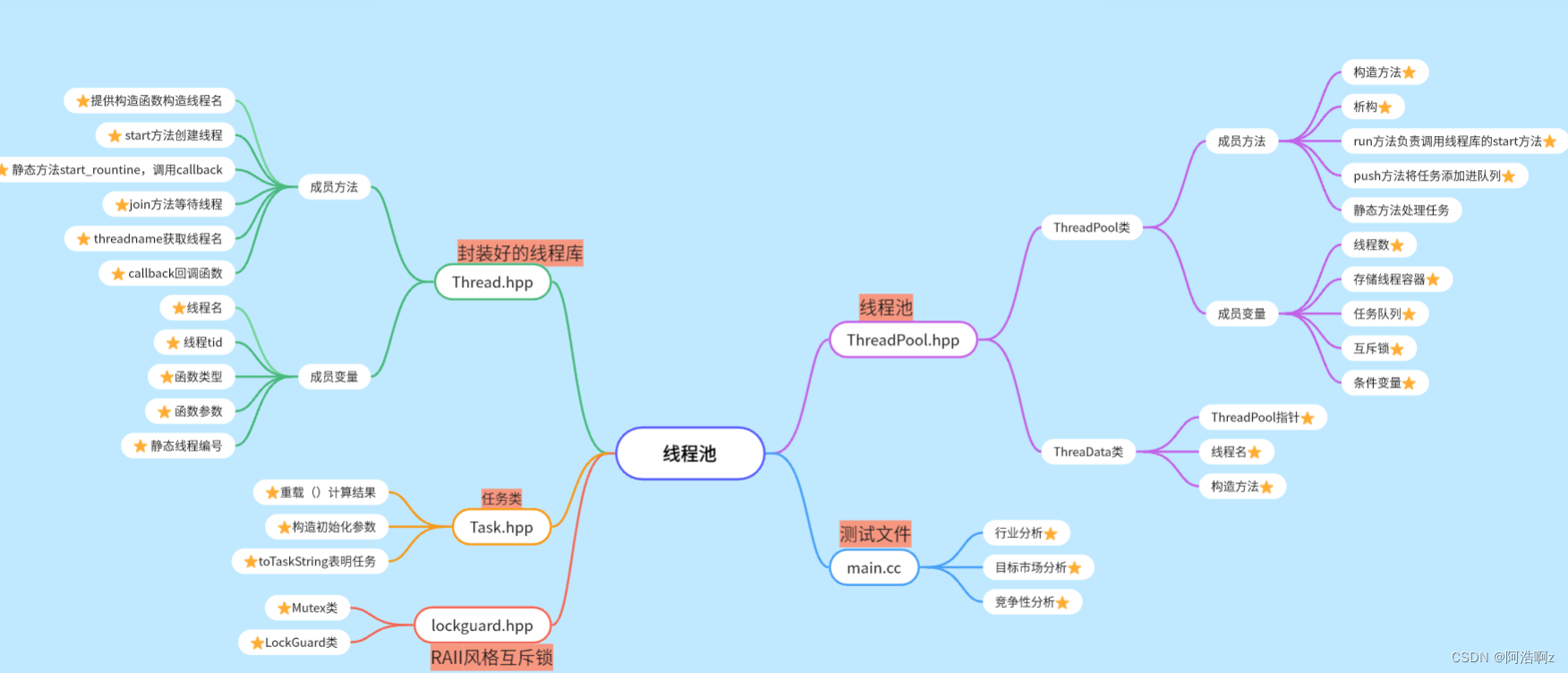
在以上代码中,我们首先封装好了线程库Thread,任务类Task,以及RAII风格的锁,然后编写ThreadPool文件。当我们在main.cc启动的时候,首先创建一个线程池对象然后调用其run方法,run方法中会调用线程库中的start方法,传递线程要执行的函数(handlerTask)以及喂给函数的参数(ThreadData *);在Thread库中,start方法会用pthread_create()创建一个线程,并实现回到函数,(其实这里绕了一圈就是为了解决调用类内方法存在this指针的问题,我们需要把方法设置成静态的,但是静态的方法无法使用非静态成员,需要一个大号结构体(ThreadData)包含一个ThreadPool的对象)。接下来主线程往任务队列中不断push任务,线程池中的线程执handlerTask函数,判断有无任务(无任务阻塞等待)有任务就从公共队列中拿到自己独立的栈中去执行。
四、基于线程池的单例模式
单例模式是一种创建型设计模式,它确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供了全局访问点来访问这个实例。这种模式通常用于控制资源的访问,例如数据库连接、线程池等等。单例模式的核心思想是将一个类的实例化过程限制在单个对象中,并提供一个全局的访问点来获取该对象。这个访问点通常是一个静态方法,可以在程序的任何地方调用。
单例模式的优点包括:
-
确保类只有一个实例,可以节省系统资源。
-
提供了全局访问点,方便程序的调用和管理。
-
保证了对象的一致性,避免了多个实例造成的数据不一致问题。
-
可以对实例化过程进行控制,保证对象的安全性和正确性。
4.1 懒汉模式设计思路
- 私有化构造函数,禁止拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载
- 在线程池基础上增加成员变量:静态互斥锁,静态线程池指针()
- 在线程池基础上增加静态方法:负责获取唯一对象
#include <mutex>
const int gnum = 5;
template <class T>
class ThreadPool;
template <class T>
class ThreadData
{
public:
ThreadData(ThreadPool<T> *tp, const std::string &n)
: threadpool(tp), name(n)
{
}
public:
ThreadPool<T> *threadpool;
std::string name;
};
template <class T>
class ThreadPool
{
private:
ThreadPool(const int &num = gnum) : num_(num)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&cond_, nullptr);
for (int i = 0; i < num_; ++i)
{
// 创建多个线程并传递参数,由于在类内调用,需要用静态方法
threads_.push_back(new Thread());
}
}
ThreadPool &operator=(const ThreadPool &) = delete;
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool &) = delete;
static void *handlerTask(void *args)
{
ThreadData<T> *td = static_cast<ThreadData<T> *>(args);
while (true)
{
T t;
{
LockGuard lock(td->threadpool->mutex());
// td->threadpool->lockQueue();
while (td->threadpool->isQueueEmpty())
{
td->threadpool->threadWait();
}
// pop本质,就是把任务从公共队列中拿到当前线程独立的栈中
t = td->threadpool->pop();
// td->threadpool->unlockQueue();
}
std::cout << td->name << "获取了一个" << t.toTaskString() << "并处理完成,结果是" << t() << std::endl;
}
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
public:
void lockQueue() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_); }
void unlockQueue() { pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_); }
bool isQueueEmpty() { return task_queue_.empty(); }
void threadWait() { pthread_cond_wait(&cond_, &mutex_); }
T pop()
{
T t = task_queue_.front();
task_queue_.pop();
return t;
}
pthread_mutex_t *mutex()
{
return &mutex_;
}
public:
void run()
{
for (const auto &t : threads_)
{
ThreadData<T> *td = new ThreadData<T>(this, t->threadname());
t->start(handlerTask, td);
std::cout << t->threadname() << std::endl;
}
}
void push(const T &in)
{
LockGuard lock(&mutex_);
// pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_);
task_queue_.push(in);
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_);
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_);
}
~ThreadPool()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_);
for (const auto &t : threads_)
{
delete t;
}
}
static ThreadPool<T> *GetInstance()
{
if (tp == nullptr)
{
//std::lock_guard<mutex> lock(siglock);
siglock.lock();
if (nullptr == tp)
{
tp = new ThreadPool<T>();
}
siglock.unlock();
}
return tp;
}
private:
int num_;
std::vector<Thread *> threads_;
std::queue<T> task_queue_;
pthread_mutex_t mutex_;
pthread_cond_t cond_;
volatile static ThreadPool<T> *tp;
static std::mutex siglock;
};
template <class T>
ThreadPool<T> *ThreadPool<T>::tp = nullptr;
template <class T>
std::mutex ThreadPool<T>::siglock;
//main.cc
ThreadPool<Task>::GetInstance()->run();
五、读者写者问题及读写锁
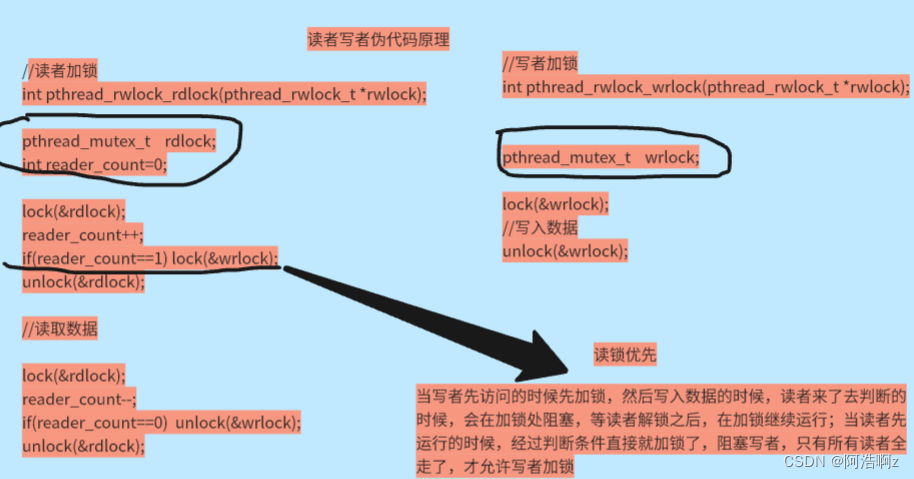
在编写多线程的时候,有一种情况是十分常见的。那就是,有些公共数据修改的机会比较少。相比较改写,它们读的机会反而高的多。通常而言,在读的过程中,往往伴随着查找的操作,中间耗时很长。给这种代码段加锁,会极大地降低我们程序的效率。
321原则也适用于读者写者问题
3种关系:读者与写者互斥&&同步,读者与读者没有关系,写者与写者互斥
2种角色:读者与写者
1个交易场所
读者写者问题和生产者消费者模型的本质区别就是消费者会取走数据,而读者不会取走数据。
读写锁的行为
| 当前锁状态 | 读锁请求 | 写锁请求 |
|---|---|---|
| 无锁 | 可以 | 可以 |
| 读锁 | 可以 | 阻塞 |
| 写锁 | 阻塞 | 阻塞 |
//初始化读写锁
pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr);
//销毁读写锁
pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
//读者加锁
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
//写者加锁
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
//解除锁
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
感谢阅读,linux系统编程到此结束,接下来将慢慢更新网络编程及C++方面的博客。



![[ tool ] Xpath选择器和selenium工具基本使用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/81b649f93a2d8784c4a232fa8697a7fc.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)