单链表的定义
由于顺序表存在以下缺陷,所以衍生出了链表,而链表种类有很多种,今天我们讲的是单链表。
顺序表存在的问题如下
1.中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2. 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到
200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
链表就像开火车一样,火车头代表开始,后面链接着运送货物的车厢。
链表的分类:实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构。
虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们实际中最常用还是两种结构:无头单向非循环链表和带头双向循环链表。
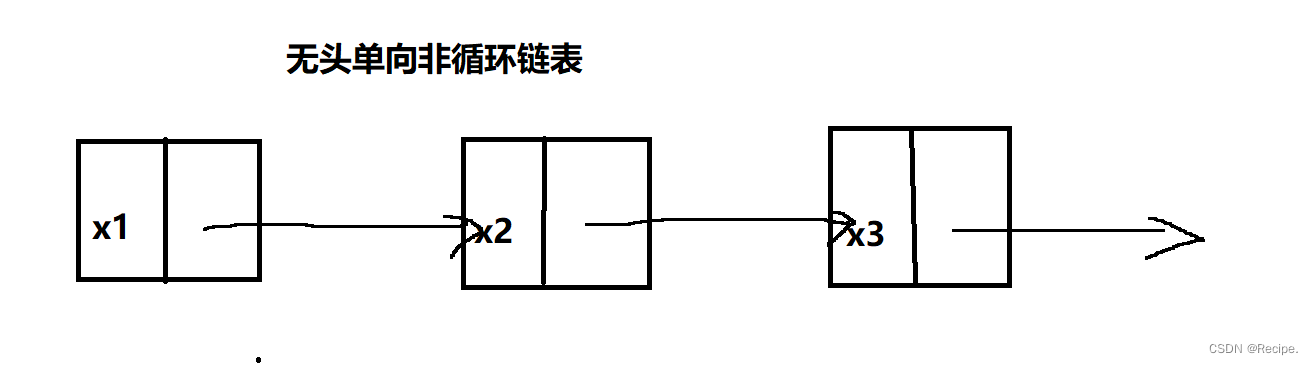
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结
构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
今天我们重点来实现无头单向非循环链表的实现俗称单链表。
单链表上的操作
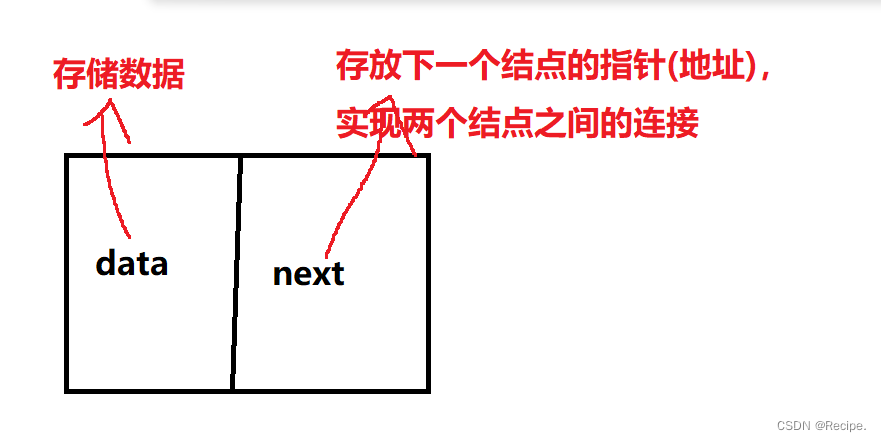
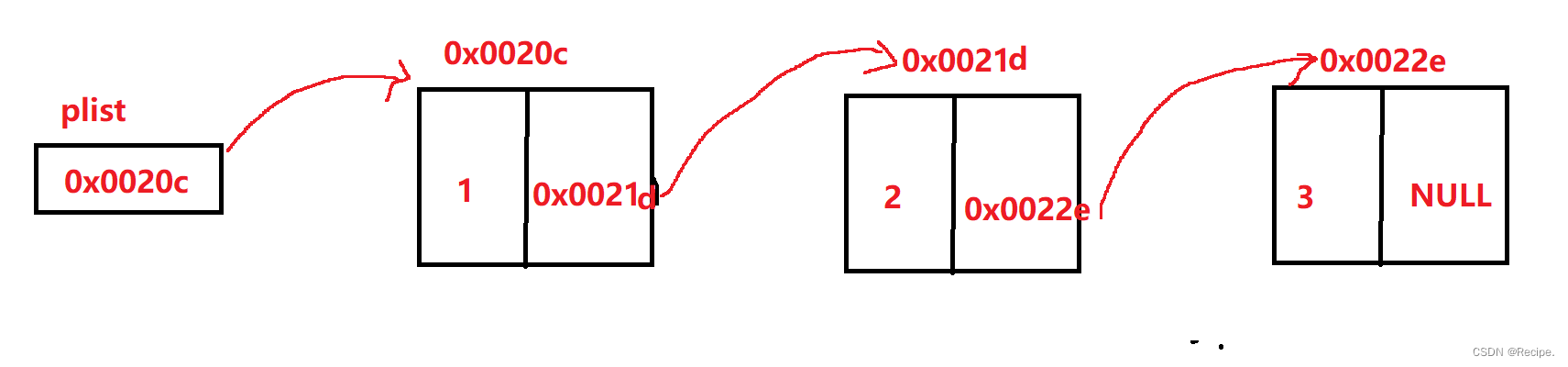
1.从上图可以看出,链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理上不一定是连续的。
2.现实中的结点一般都是在堆上malloc申请出来的。
3.从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策略来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续。
4.如果最后一个结点后面没有要存储的值,要把最后一个结点的指针设成NULL,方便下一次的插入新存储的值。
建立单链表
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SedListdatatype;
typedef struct SedList
{
SedListdatatype data;
struct SedList* next;
}SLNode;因为我们不知道单链表存储的数据是什么类型的,所以我们把int重定义成 SedListdatatype,如果我们要改其他数据类型,只需要在上面改一下即可。
我们再把结构体的名字也重定义方便实现单链表的功能实现。
单链表不需要初始化,因为我们都是从堆上malloc申请出的空间结点。
数据结构无非是对数据进行管理,要实现数据的增删查改,因此链表的基本功能也都是围绕着数据的增删查改展开。
单链表的打印
void SLprint(SLNode* phead)
{
SLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL");
printf("\n");
}单链表传过来的指针为空,就打印NULL。因为单链表传过来的指针也可能为空,所以不用断言。
这里while的条件为什么是cur!=NULL?因为这样才能打印单链表的所有存储的值,如果写出cur->next,单链表最后一个元素存储的值就不能打印出来,因为单链表最后一个结点指针为NULL。
所以当cur为NULL就可以停止打印。
创建malloc出新结点
SLNode* buynode(SedListdatatype x)
{
SLNode* newnode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}我们要在单链表中实现尾插和头插等等功能,这个结点包括存储的数据和指针(地址),为了方便和减少代码的重复度,我们另写一个函数用来专门创建新结点。
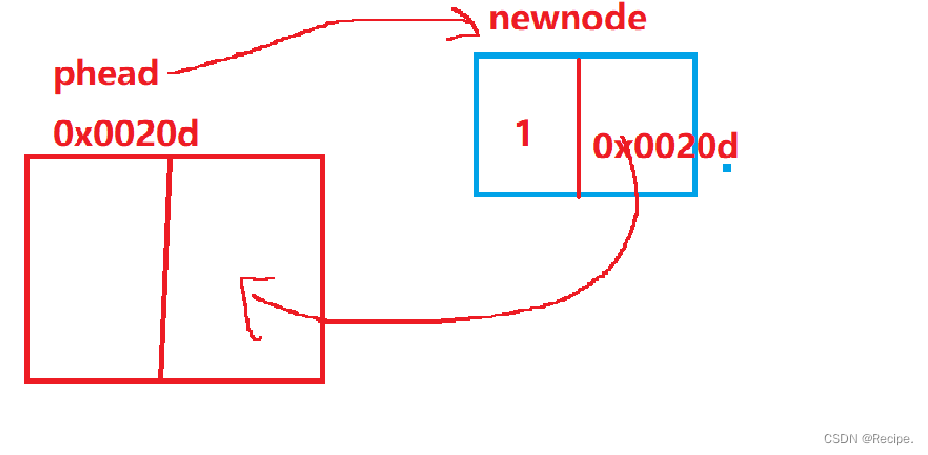
单链表的头插
void SLPushFront(SLNode** phead, SedListdatatype x)
{
assert(phead);即使链表为空,phead也不为空,因为指向的是链表头指针plist的地址
SLNode* newnode = buynode(x);
newnode->next = *phead;
*phead = newnode;
}
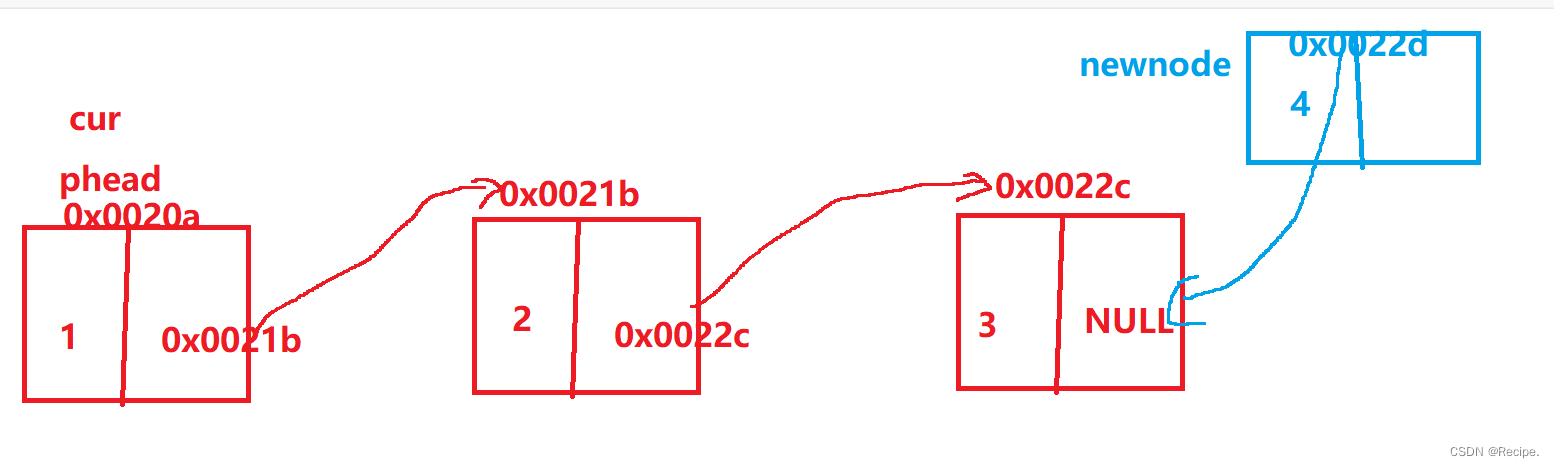
单链表的尾插
void SLPushBack(SLNode** phead, SedListdatatype x)
{
assert(phead);即使链表为空,phead也不为空,因为指向的是链表头指针plist的地址
SLNode* newnode = buynode(x);
链表为空
if (*phead == NULL)
{
*phead = newnode;
不用让newnode->next=NULL,因为我们在开堆上申请新结点的时候已经完成了这步操作
}
多个结点
SLNode* cur = *phead;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newnode;
}
当我们遍历单链表的时候,最好给一个另外的变量赋值去遍历,因为我们有时候会需要找到头的地址,为了不丢失头指针的地址,所以我们不用头指针phead自己遍历单链表。
另外大家已经注意到为什么头插和尾插使用的是二级指针?因为结构体里面的next本身就是一个一级指针,尾插和头插,都会改变结构体里面存储的数据,而修改一级指针的内容就需要去二级指针来存储一级指针的地址,并传址才能改变单链表的内容,如果使用一级指针来存储一级指针的地址出了循环以后就会销毁,并不会影响单链表的内容也不能增删查改和管理存储数据。相当于形参与实参的差别。形参不会影响实参的改变,只是实参的临时的一份拷贝。所以要用二级指针。
当尾插时链表为空,就相当于头插。不为空时,就找尾再插入即可。
单链表的头删
void SLPopFront(SLNode** phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(*phead);//第一种方法
//第二种方法 温柔的检查 选一种即可
if (*phead == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!不能删除!");
return;
}
//只有一个结点
if ((*phead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
}
//多个结点
else
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
*phead = (*phead)->next;
free(cur);
}
}单链表的尾删
void SLPopBack(SLNode** phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(*phead);//第一种方法
//第二种方法 温柔的检查 选一种即可
if (*phead == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!不能删除!");
return;
}
//只有一个结点
if ((*phead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
}
//多个结点
else
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
SLNode* pre = NULL;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
pre = cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
free(cur);
pre->next = NULL;
}
}用一个新指针指向cur指向的上一个结点next,等cur找到最后一个NULL就free,然后再把pre的next设为NULL即可。
单链表的遍历和查找数据
SLNode* Find(SLNode* phead, SedListdatatype x)
{
SLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}函数的返回值不再是void,而是一个指针变量,因为我们要把找到的结点地址返回回去,这个函数可以配合修改返回当前结点的值。所以这个函数既能查找又修改单链表结点。
单链表的插入分为pos之前插入和pos之后插入
单链表的pos之后插入
void SLInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SedListdatatype x)
{
SLNode* newnode = buynode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}单链表的删除分为pos之前删除和pos之后删除
单链表的pos之后删除
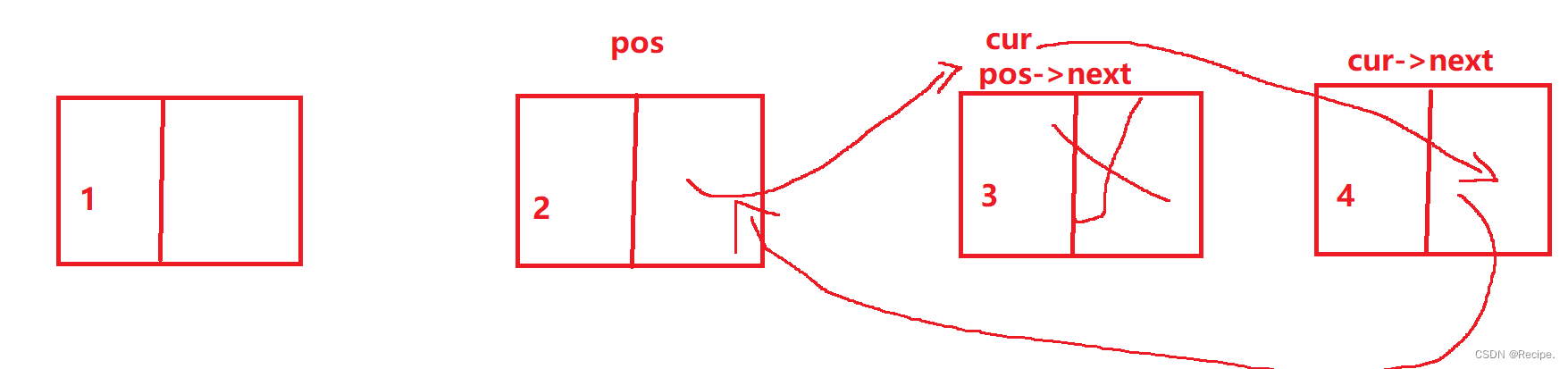
void SLEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
SLNode* cur = pos->next;
pos->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
}
单链表的销毁
void SLDestory(SLNode** phead)
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
SLNode* pre = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = pre;
}
*phead = NULL;
}在销毁链表的时候不能直接free,因为单链表在物理结构上是不连续存储的,必须要一个一个结点的销毁,再把phead设为NULL。
总代码展示
SedList.h
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SedListdatatype;
typedef struct SedList
{
SedListdatatype data;
struct SedList* next;
}SLNode;
void SLprint(SLNode* phead);//打印
void SLPushFront(SLNode** phead, SedListdatatype x);//头插
void SLPushBack(SLNode** phead, SedListdatatype x);//尾插
void SLPopFront(SLNode** phead);//头删
void SLPopBack(SLNode** phead);//尾删
SLNode* Find(SLNode* phead,SedListdatatype x);//查找和遍历
void SLInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SedListdatatype x);//在pos之后插入
void SLEraseAfter(SLNode* pos);//在pos之后删除
void SLDestory(SLNode** phead);//销毁SedList.c
#include"SedList.h"
void SLprint(SLNode* phead)
{
SLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL");
printf("\n");
}
SLNode* buynode(SedListdatatype x)
{
SLNode* newnode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void SLPushFront(SLNode** phead, SedListdatatype x)
{
assert(phead);//即使链表为空,phead也不为空,因为指向的是链表头指针plist的地址
SLNode* newnode = buynode(x);
newnode->next = *phead;
*phead = newnode;
}
void SLPushBack(SLNode** phead, SedListdatatype x)
{
assert(phead);
SLNode* newnode = buynode(x);
//链表为空
if (*phead == NULL)
{
*phead = newnode;
}
//多个结点
else
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newnode;
}
}
void SLPopFront(SLNode** phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(*phead);//第一种方法
//第二种方法 温柔的检查
if (*phead == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!不能删除!");
return;
}
//只有一个结点
if ((*phead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
}
//多个结点
else
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
*phead = (*phead)->next;
free(cur);
}
}
void SLPopBack(SLNode** phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(*phead);//第一种方法
//第二种方法 温柔的检查
if (*phead == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!不能删除!");
return;
}
//只有一个结点
if ((*phead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
}
//多个结点
else
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
SLNode* pre = NULL;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
pre = cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
free(cur);
pre->next = NULL;
}
}
SLNode* Find(SLNode* phead, SedListdatatype x)
{
SLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void SLInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SedListdatatype x)
{
assert(pos);
SLNode* newnode = buynode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
void SLEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
SLNode* cur = pos->next;
pos->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
}
void SLDestory(SLNode** phead)
{
SLNode* cur = *phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
SLNode* pre = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = pre;
}
*phead = NULL;
}test.c
#include"SedList.h"
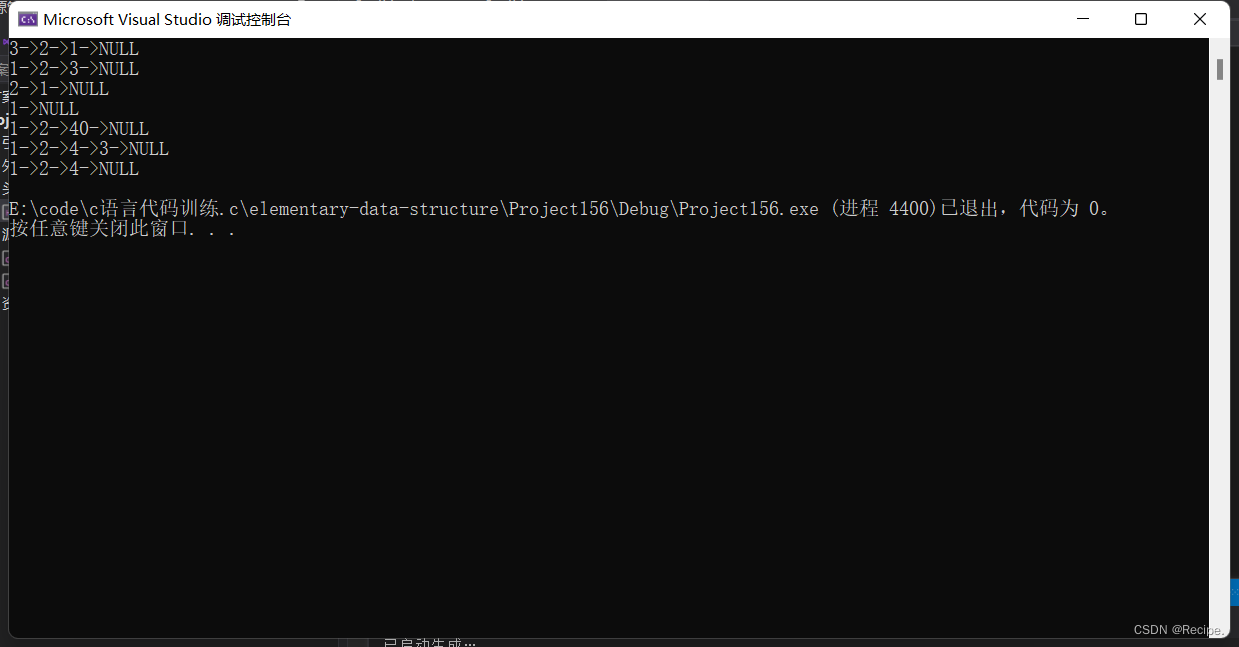
void test1()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushFront(&plist, 1);
SLPushFront(&plist, 2);
SLPushFront(&plist, 3);
SLprint(plist);
}
void test2()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLprint(plist);
}
void test3()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushFront(&plist, 1);
SLPushFront(&plist, 2);
SLPushFront(&plist, 3);
SLPopFront(&plist);
SLprint(plist);
}
void test4()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLPopBack(&plist);
SLPopBack(&plist);
SLprint(plist);
}
void test5()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLNode* pos = Find(plist, 3);
pos->data = 40;
SLprint(plist);
}
void test6()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLNode* pos = Find(plist, 2);
if (pos)
{
SLInsertAfter(pos, 4);
}
SLprint(plist);
}
void test7()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLPushBack(&plist, 4);
SLNode* pos = Find(plist, 2);
if (pos)
{
SLEraseAfter(pos);
}
SLprint(plist);
}
int main()
{
test1();
test2();
test3();
test4();
test5();
test6();
test7();
return 0;
}