1.enumerate() 函数用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在 for 循环当中。
enumerate(sequence, [start=0])
>>>seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
>>> list(enumerate(seasons))
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
>>> list(enumerate(seasons, start=1)) # 下标从 1 开始
[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]
>>> tuple(enumerate(seasons, start=1))
((1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter'))
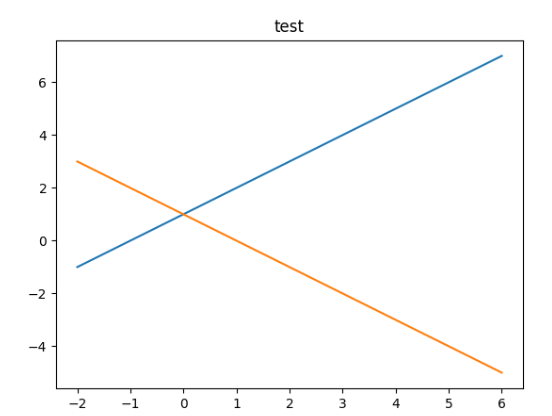
2.绘图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(-2, 6, 50)
y1 = x + 3 # 曲线 y1
y2 = 3 - x # 曲线 y2
plt.figure() # 定义一个图像窗口
plt.plot(x, y1) # 绘制曲线 y1
plt.plot(x, y2) # 绘制曲线 y2
plt.title("test")
plt.show()
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("test")
plt.show()

3.json.dumps的功能是将字典类型转换为json格式的字符串类型
参数: (1)sort_keys是告诉编码器按照字典key排序(a到z)输出。
(2)indent参数根据数据格式缩进显示,读起来更加清晰, indent的值,代表缩进空格
(3) 要正确输出中文可以指定ensure_ascii=False:
#将label写进json
def write_json(cla_dict,json_path):#要写入的label,json路径
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4) # 编码成json格式
with open(json_path, 'w') as json_file: # 写进去
json_file.write(json_str)
#从json读出label
def read_json(json_path): #json路径
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
with open(json_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
return class_indict
实例:
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx # ----大概是已经通过数据集已经分类好的文件名确定的图片类别
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items()) # 将key,value值反过来,已达到通过索引找到分类的目的
# label信息写入json
json_path = './class_indices.json'
write_json(cla_dict,json_path)
class_indices.json
{
"0": "daisy",
"1": "dandelion",
"2": "roses",
"3": "sunflowers",
"4": "tulips"
}
4.cv2.resize函数
resize是opencv库中的一个函数,主要起到对图片进行缩放的作用。
example: 以下代码就可以将原图片转化为宽和长分别为300,300的图片。width和height可以自己任意指定,不论大小。
interpolation(插值):这个是指定插值的方式,图像缩放之后,肯定像素要进行重新计算的,就靠这个参数来指定重新计算像素的方式,有以下几种:
INTER_NEAREST - 最邻近插值
INTER_LINEAR - 双线性插值,如果最后一个参数你不指定,默认使用这种方法
INTER_CUBIC - 4x4像素邻域内的双立方插值
INTER_LANCZOS4 - 8x8像素邻域内的Lanczos插值
放大缩小都使用的以上插值方法。具体插值方法见图像处理: 五种 插值法
实例:
import cv2 as cv
width = 300
height = 300
img = cv.imread('E:\\both.png')# 原图224*224
img = cv.resize(img, (width, height))# 默认使用双线性插值法
cv.imshow("img", img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
这么说resize岂不是和上采样和下采样功能方法几乎一致????
5.baseline
baseline 就只是「参照物」的意思,至于 baseline 系统是怎么来的、性能如何,并没有一定的标准。