2005 NIPS
文章目录
- 特征提取
- 卷积核的使用
- Multiscale 多尺度提取特征
- 特征的相对深度
- 模型
- 结论
- 特征提取
- 数据集导致的error
文章使用了Markov 随机场(Markov Random Fields, MRF) 从单图像上直接估计出图像的深度信息。
与RGBD输入数据不同的是,文章中采用了YCbCr数据+depth数据。
使用MRF是为了在一张图上融合局部和整体的信息。
特征提取
卷积核的使用
作者为了提取出文本信息,使用了15种卷积和应用在YCbCr的Y通道(intensity channel)上,并用第一个Laws’s mask 卷积核(计算平均)在两个颜色通道上,所以一共是17个特征向量。同时采用absolute energy和sum squared energy进行计算,所以一共是34个特征向量。
在15个卷积核中,分为9个Laws’ masks和6个边界检测。

Multiscale 多尺度提取特征
作者为了融合全局特征,使用了三个scale。其中,scale1x为高分辨率特征,scale9x为低分辨率特征。同时考虑每一个patch周围的四个邻居。同时考虑到树木之类的景观具有垂直特征,因此将patch所在的一列分为四个垂直patch。对于每一个patch(C0)来说,一共是3*5+4=19个patch的特征进行融合。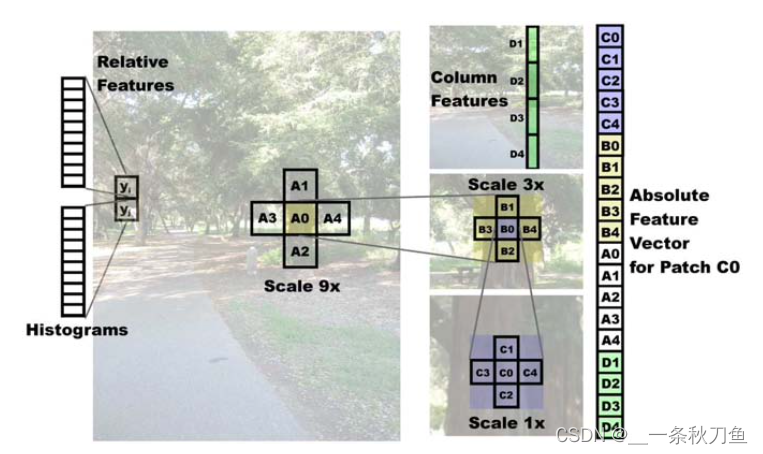
考虑到34个特征向量,对于每一个patch一共要算19*34。
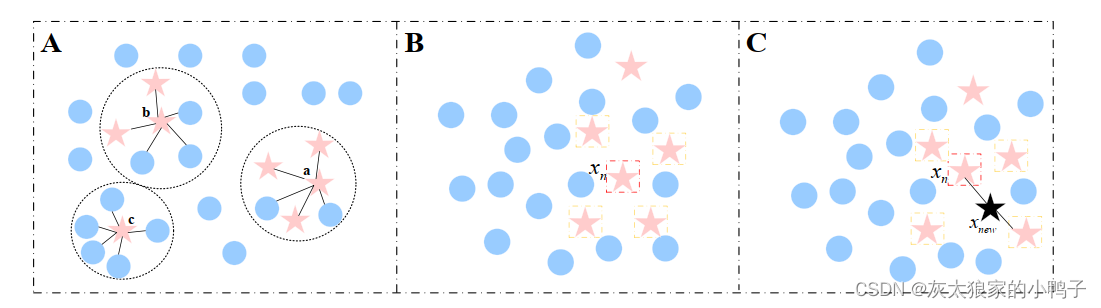
特征的相对深度
上述图像中考虑x和y两块相邻patch,计算他们是否属于同一物体,或者是不同的物体。对于17个filter的output(absolute),采用10个bins的直方图量化。从170个bins中判断是否属于同一物体。
模型
作者使用了Gaussian MRF(1)和 Laplacians MRF(2)两种模型。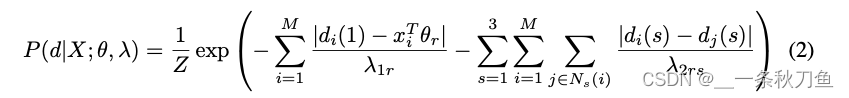
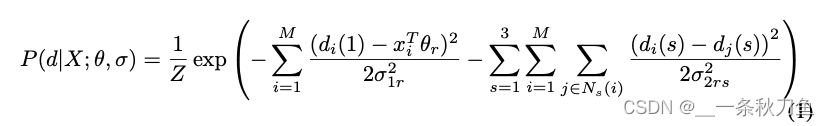
相比较Gaussian Distribution, Laplacians Distribution
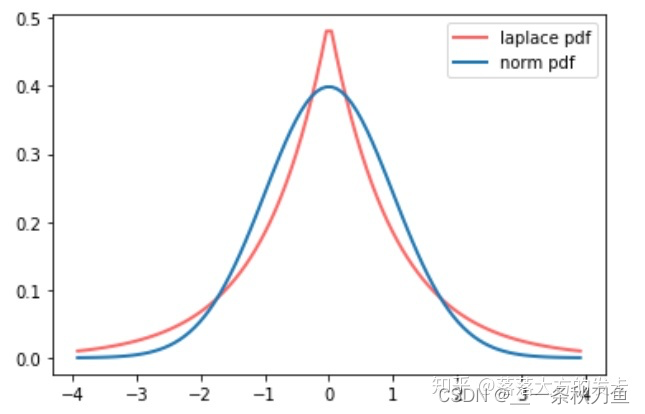
- 特征相对深度的直方图是天然的Laplacians分布。
- 具有更宽的尾部,因此对于深度估计中的离群值和异常值有更好的鲁棒性。
- 结果也证明使用Laplacians model估计出的深度具有更清晰的边缘。
结论
特征提取
- using multiscale and column features significantly improves the algorithm’s performance.
数据集导致的error
- Some of the errors can be attributed to errors or limitations of the training set. For example, the training set images and depthmaps are slightly misaligned, and therefore the edges in the learned depthmap are not very sharp.
- Further, the maximum value of the depths in the training set is 81m; therefore, far-away objects are all mapped to the one distance of 81m.