AlphaFold2源码解析(4)–模型架构
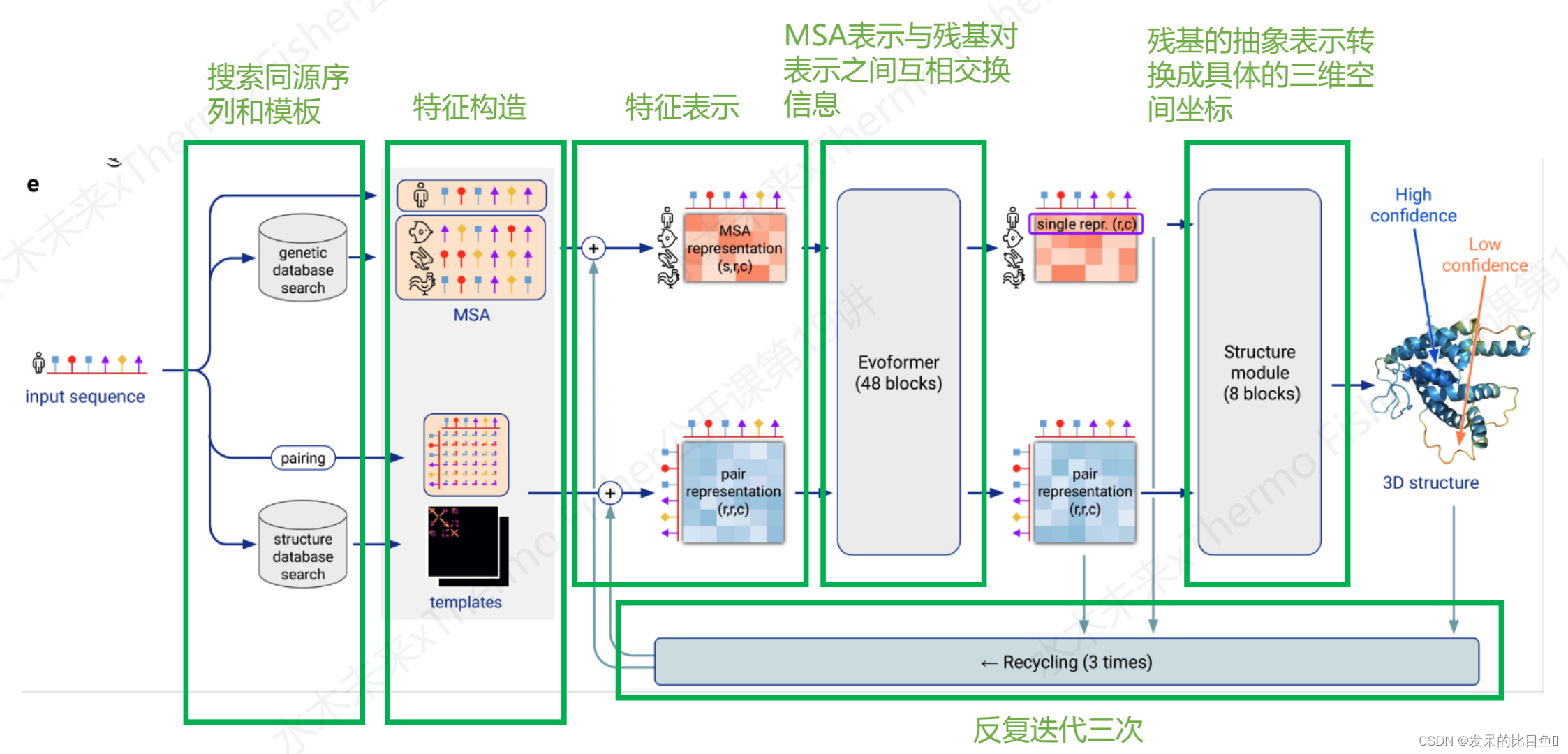
我们将Alphafold的流程分为一下几个部分:
- 搜索同源序列和模板
- 特征构造
- 特征表示
- MSA表示与残基对表示之间互相交换信息
- 残基的抽象表示转换成具体的三维空间坐标
模型参数
AlphaFold有多个不同类型的参数(单体,多聚体, ptm, CASP格式),alphafold.model.config配置了不同参数:
MODEL_PRESETS = {
'monomer': (
'model_1',
'model_2',
'model_3',
'model_4',
'model_5',
),
'monomer_ptm': (
'model_1_ptm',
'model_2_ptm',
'model_3_ptm',
'model_4_ptm',
'model_5_ptm',
),
'multimer': (
'model_1_multimer_v2',
'model_2_multimer_v2',
'model_3_multimer_v2',
'model_4_multimer_v2',
'model_5_multimer_v2',
),
}
MODEL_PRESETS['monomer_casp14'] = MODEL_PRESETS['monomer']
。。。。。
CONFIG_DIFFS = {
'model_1': {
# Jumper et al. (2021) Suppl. Table 5, Model 1.1.1
'data.common.max_extra_msa': 5120,
'data.common.reduce_msa_clusters_by_max_templates': True,
'data.common.use_templates': True,
'model.embeddings_and_evoformer.template.embed_torsion_angles': True,
'model.embeddings_and_evoformer.template.enabled': True
},
'model_2': {
# Jumper et al. (2021) Suppl. Table 5, Model 1.1.2
'data.common.reduce_msa_clusters_by_max_templates': True,
'data.common.use_templates': True,
'model.embeddings_and_evoformer.template.embed_torsion_angles': True,
'model.embeddings_and_evoformer.template.enabled': True
},
'model_3': {
# Jumper et al. (2021) Suppl. Table 5, Model 1.2.1
'data.common.max_extra_msa': 5120,
},
有一些模型并不使用template特征,下面代码可以体现
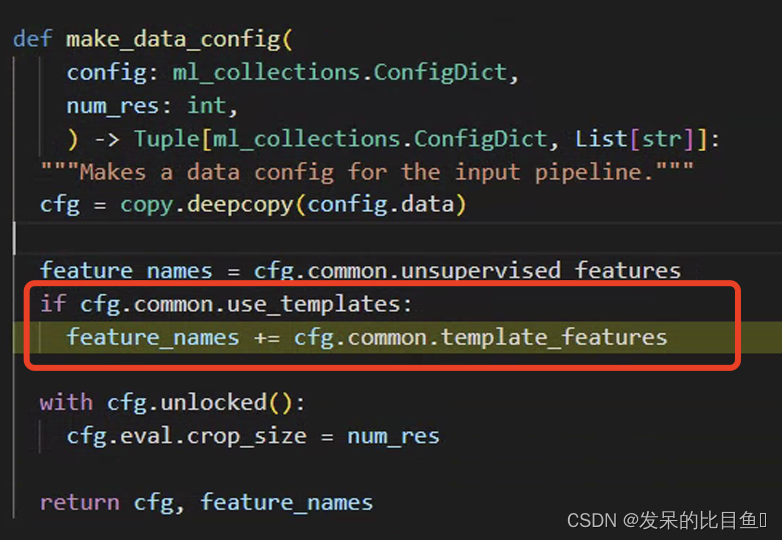
输入模型的数据预处理
按照流程图来说,这个是特征构造的流程。
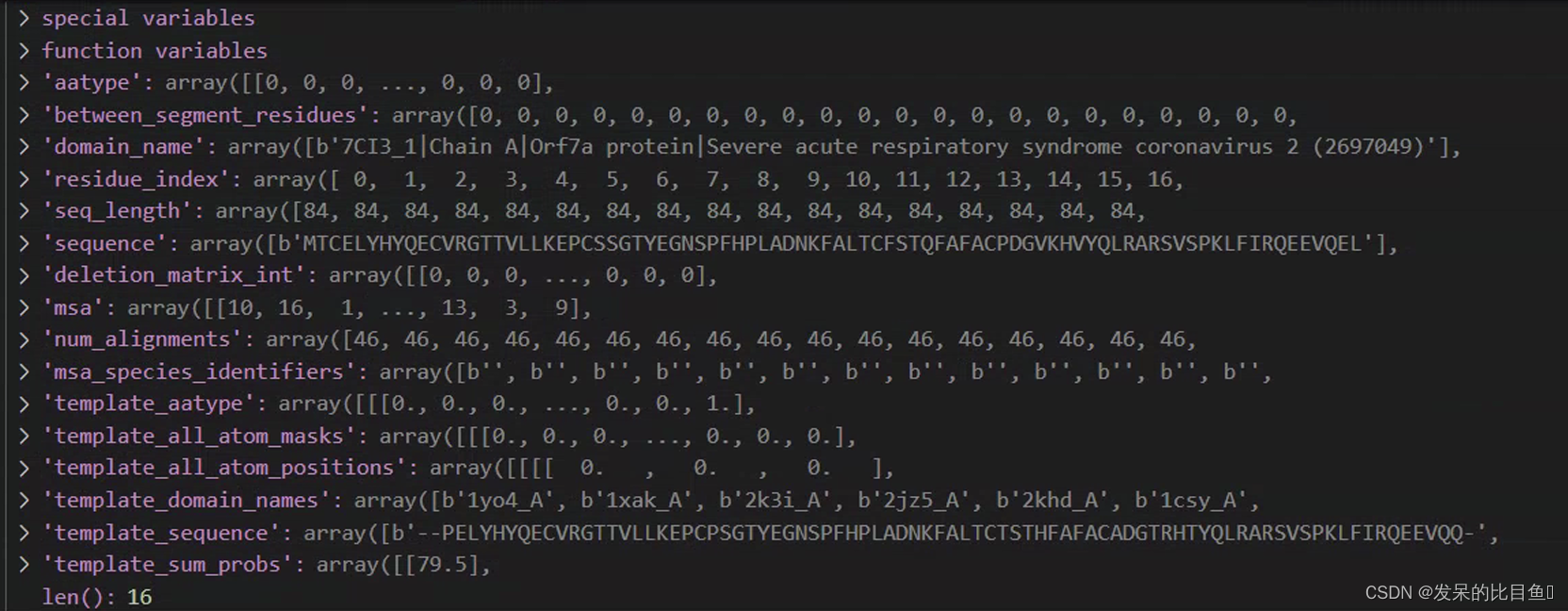
上图是数据预处理得到的输入特征(具体前处理可以参考),现在要把该特征转换成模型需要的tensor格式:
def np_example_to_features(np_example: FeatureDict,
config: ml_collections.ConfigDict,
random_seed: int = 0) -> FeatureDict:
"""Preprocesses NumPy feature dict using TF pipeline.使用TF管道预处理NumPy特征字典"""
。。。。。。
tensor_dict = proteins_dataset.np_to_tensor_dict(
np_example=np_example, features=feature_names)
processed_batch = input_pipeline.process_tensors_from_config(
tensor_dict, cfg) # “根据配置将筛选器和映射应用于现有数据集。
tf_graph.finalize()
。。。。。。
return {k: v for k, v in features.items() if v.dtype != 'O'}
最终结果:

aatype: shape = (E x L),并不是原文中所述的one-hot representation,而是字母表list表示形式,这里限定为input sequence的序列。residue_index: shape = (E x L),input的序列编号,1维数据seq_length: shape = (E, ) input的序列长度,1维数据template_aatype: shape = (E x N x L) 。代表的是模板的residue_id list。N = top template number (default = 4). E = Number of ensemble+recycling. L = sequence lengthtemplate_all_atom_masks:shape=(E x N x L x 37),以37维表示所有的原子占位符。表示L长度的序列,每个残基上都有哪些原子组成。atom_types可以在alphafold.commom.residue_constraint中找到。
atom14字母表顺序:

template_all_atom_positions:shape=(E x N x L x 37 x 3),记录每个残基原子的xyz坐标,存在占位符的才有坐标template_sum_probs: .hhr文件match的打分值 (np.float32)is_distillation:蒸馏seq_mask: shape = (E x L), 全是1的矩阵,长度与input的序列长度相关,这里代表序列残基是否存在,存在=1,反之0(占位符)msa_mask: shape = (E x 510 x L). 510可能是max MSA(每次这个数值貌似还会变),没有MSA序列比对的地方全是0,有msa序列的地方都是1. 这里的含义是,标记MSA矩阵中一共有多少条同源序列。(占位符)msa_row_maskshape = (E x 510) 列版本的mask,那些列存在msa即标记为1,反之0。(占位符)random_crop_to_size_seed: shape = (E x 2)template_mask: shape = (E x N), 占位符=1,表示是否存在模板。template_pseudo_betashape = (E x N x L x 3), pseudo_Cbeta的坐标,gap所在区域设置为(0,0,0)template_pseudo_beta_mask:shape = (E x N x L),pseudo_Cbeta的占位符,存在设置为1,反之0.atom14_atom_exists:shape = (E x L x 14/37) ,以atom14或atom37作为原子占位符的表示形式。这里的atom占位符指的是input sequence,而不是template。residx_atom14_to_atom37: shape = (E x L x 14) 这里的含义是具体的原子号转换 ,这里的数值代表atom37的序号。residx_atom37_to_atom14:shape = (E x L x 37) ,反之数值代表atom14的序号atom37_atom_exists:shape = (E x L x 14/37) ,以atom14或atom37作为原子占位符的表示形式。这里的atom占位符指的是input sequence,而不是template。extra_msa: shape = (E, 5210, L)用目标序列获取msa后,其中除了簇中心外的msaextra_msa_mask: shape = (E x 5210 x L) , 记录extra MSA序列是否存在的mask(占位符),注意第一条序列并不是input sequence。extra_msa_row_mask: shape = (E x 5210) , 列版本的extra MSA mask,那些列存在msa即标记为1,反之0。(占位符)bert_mask: shape = (E x 510 x L),代表MSA中哪些位点被随机bert mask,mask的地方设置为1(占位符),反之0。每条序列被mask的地方其实都不一样。true_msa: shape = (E x 510 x L),记录MSA序列的字母表list, 注意第一条序列即input sequence。extra_has_deletion: shape = (E x 5120 x L), 指示extra MSAz中是否存在被随机crop删除的位点(占位符)。extra_deletion_value: shape = (E x 5120 x L), 指示MSA中被删除的氨基酸的占位符,被删除标记为1,反之0msa_feat:由连接“cluster_msa”, “cluster_has_deletion”, “cluster_deletion_value”, “cluster_deletion_mean”, “cluster_profile”组成,cluster_msa: MSA cluster中心序列的one-hot representation, shape=(N x L x 23 ) (20 amino acids + unknown + gap +
masked_msa_token).cluster_has_deletion: cluster中心序列是否存在deletion,shape = (N x L x 1)cluster_deletion_value: shape = (N x L x 1)cluster_deletion_mean: shape = (N x L x 1)cluster_profile: shape = (N x L x 1), cluster序列PSSM profile (one-hot), ,shape = (N x L x 23) (20 amino acids + unknown + gap +
masked_msa_token).
注意看一下例子: 1-23 index代表cluster_msa的one-hot,27-49为PSSM的one-hot。
arget_feat: shape = (E x L x 22) ,与补充材料不符,多了1维通道。代表target sequence的one-hot。
模型类
这部分这篇文章这里简单的了解一下,后面文章详细讲解!!
预测入口: model_runner.predict(processed_feature_dict, random_seed=model_random_seed), 实例化Alphafold类,
class RunModel:
"""Container for JAX model."""
def __init__(self,
config: ml_collections.ConfigDict,
params: Optional[Mapping[str, Mapping[str, np.ndarray]]] = None):
self.config = config
self.params = params
self.multimer_mode = config.model.global_config.multimer_mode
if self.multimer_mode:
def _forward_fn(batch):
model = modules_multimer.AlphaFold(self.config.model)
return model(batch, is_training=False)
else:
def _forward_fn(batch):
model = modules.AlphaFold(self.config.model)
return model(batch, is_training=False, compute_loss=False, ensemble_representations=True)
def predict(self,
feat: features.FeatureDict,
random_seed: int,
) -> Mapping[str, Any]:
self.init_params(feat)
tree.map_structure(lambda x: x.shape, feat))
result = self.apply(self.params, jax.random.PRNGKey(random_seed), feat)
jax.tree_map(lambda x: x.block_until_ready(), result)
result.update(get_confidence_metrics(result, multimer_mode=self.multimer_mode))
return result
下面代码是AlphaFold模型代码,封装了AlphaFold类
class AlphaFold(hk.Module):
"""AlphaFold model with recycling.
Jumper et al. (2021) Suppl. Alg. 2 "Inference"
"""
def __init__(self, config, name='alphafold'):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.config = config
self.global_config = config.global_config
def __call__(
self,
batch,
is_training,
compute_loss=False,
ensemble_representations=False,
return_representations=False):
"""Run the AlphaFold model."""
impl = AlphaFoldIteration(self.config, self.global_config)
batch_size, num_residues = batch['aatype'].shape
。。。。。。。
AlphaFold架构的单一循环迭代。计算所提供功能的集合(平均)表示。然后将这些表示传递给配置文件请求的各个头。每个头还返回一个损失,该损失作为加权和进行组合以产生总损失。对应下图部分:
class AlphaFoldIteration(hk.Module):
def __init__(self, config, global_config, name='alphafold_iteration'):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.config = config
self.global_config = global_config
def __call__(self, ensembled_batch, non_ensembled_batch, is_training, compute_loss=False, ensemble_representations=False, return_representations=False):
。。。。。。。
# Compute representations for each batch element and average.
evoformer_module = EmbeddingsAndEvoformer(
self.config.embeddings_and_evoformer, self.global_config)
。。。。。。。
下面代码是嵌入输入数据并运行Evoformer。 生成MSA、单个和成对表示。
class EmbeddingsAndEvoformer(hk.Module):
def __init__(self, config, global_config, name='evoformer'):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.config = config
self.global_config = global_config
MSA表征
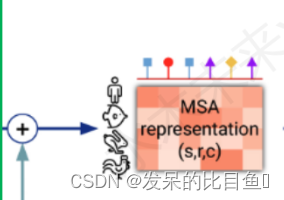
。。。。。
preprocess_msa = common_modules.Linear(
c.msa_channel, name='preprocess_msa')(
batch['msa_feat'])
msa_activations = jnp.expand_dims(preprocess_1d, axis=0) + preprocess_msa
。。。。。。
模版残基对表示
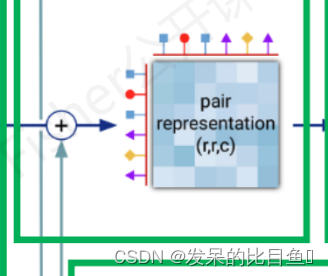
class TemplateEmbedding(hk.Module):
def __init__(self, config, global_config, name='template_embedding'):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.config = config
self.global_config = global_config
Evoformer类, 一共48 层

class EvoformerIteration(hk.Module):
def __init__(self, config, global_config, is_extra_msa,
name='evoformer_iteration'):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.config = config
self.global_config = global_config
self.is_extra_msa = is_extra_msa
def __call__(self, activations, masks, is_training=True, safe_key=None):
。。。。
StructureModule类模型的三维构建

class StructureModule(hk.Module):
def __init__(self, config, global_config, compute_loss=True, name='structure_module'):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.config = config
self.global_config = global_config
self.compute_loss = compute_loss
def __call__(self, representations, batch, is_training,
safe_key=None):
c = self.config
ret = {}
模型输出

dict_keys(['distogram', 'experimentally_resolved', 'masked_msa', 'predicted_lddt', 'structure_module', 'plddt', 'ranking_confidence'])
其中:
distogram: 包含:bin_edges,logitsbin_edges: shape(N_bin-1)将contact map距离分为了64个bin,每个bin含有的是分布概率。logits: logits: NumPy array of shape [N_res, N_res, N_bins]. N_bins = 64。
ranking_confidence: 模型的打分排名,用于最后模型排序:
# result["ranking_confidence"]
84.43703522756158
Structure Embeddings: 模型输出的结构信息可以在此找到,与raw feature特征直接相关:
result["structure_module"]
{'final_atom_mask': DeviceArray([[1., 1....e=float32), 'final_atom_positions': DeviceArray([[[ 1.24...e=float32)}
- `final_atom_mask`和`final_atom_positions`: 原子坐标 37维,对应不同元素的xyz坐标
将上述转化PDB: 将embeddings转换为pdb 人类可读的3D坐标信息:
from alphafold.common import protein
from alphafold.common import residue_constants
# output as PDB files:
# Add the predicted LDDT in the b-factor column.
# Note that higher predicted LDDT value means higher model confidence.
plddt = prediction_result['plddt']
plddt_b_factors = np.repeat(plddt[:, None], residue_constants.atom_type_num, axis=-1)
unrelaxed_protein = protein.from_prediction(
features=processed_feature_dict,
result=prediction_result,
b_factors=plddt_b_factors,
remove_leading_feature_dimension=not model_runner.multimer_mode)
pdb_strings = protein.to_pdb(unrelaxed_protein)
predicted_lddt:dict_keys(['logits']) shape(N, 50) 预测LDDT的logits.
plddt: 每个residue残基的pLDDT打分,维度为L,数值范围0-100,越高代表残基结构的置信度越高。
array([56.58770955, 72.25227958, 89.19100079, 94.3461798 , 95.2949876 ,
95.17576698, 94.646028 , 94.33375267, 90.46989599, 92.5155071 ,
90.99732378, 89.97658003, 90.219173 , 88.5486725 , 90.97755045,
92.11373659, 92.5667079 , 92.87788307, 92.15490895, 93.56230404,
93.32283103, 93.11261657, 91.67360123, 88.2759182 , 84.96945758,
89.2958895 , 92.8082249 , 93.2562638 , 93.36529313, 90.7402335 ,
89.08094255, 85.92625689, 86.89237679, 89.25396414, 93.16832439,
91.93393959, 92.89937397, 90.89946722, 90.46164615, 90.53226716,
93.30375663, 92.81365992, 93.78375695, 92.98305812, 92.35394371,
91.12231586, 91.23854376, 92.17139406, 93.27133283, 94.79373232,
94.39907245, 94.88715618, 94.14012072, 94.67543957, 94.25266391,
91.28641786, 90.86592556, 91.22147374, 94.31161481, 94.98413065,
95.67454539, 95.67216584, 95.22253493, 95.32808057, 93.23769795,
93.25207712, 91.92830375, 88.42148377, 82.76287985, 70.4996139 ,
66.63325502, 54.98882484, 56.25744421, 48.29309031, 56.92003332,
58.87518468, 62.1212084 , 54.99418841, 52.27112645, 40.44010436,
54.76080439, 33.18926716, 47.11334018, 40.31735805])
experimentally_resolve:shape(84, 37)实验分辨率, logits
masked_msa:shape(508, L, N)??? logits
下面的输出因该是在PTM模型中才有的数据
predicted_aligned_error: 维度为LxL,数值范围为0-max_predicted_aligned_error。0代表最可信,该指标也可以作为domain packing质量的评估。
ptm: predicted TM-score. 标量,评估全局的superposition metric。这个指标的代表全局结构的packing质量评估。
AmberRelax
这个在流程图上没有,主要是对蛋白三维结构做分子动力学能量优化。
## run_alphafold.py
if amber_relaxer:
# Relax the prediction.
t_0 = time.time()
relaxed_pdb_str, _, _ = amber_relaxer.process(prot=unrelaxed_protein)
class AmberRelaxation(object):
def __init__(self, *, max_iterations: int, tolerance: float, stiffness: float, exclude_residues: Sequence[int],
max_outer_iterations: int, use_gpu: bool):
参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/492381344
![[ECCV2022]Language-Driven Artistic Style Transfer](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4d00cb6417044464b26b3569ad21eca4.png)