最近在温习 Tensorflow,写了一篇笔记,记录了使用 Tensorflow 训练一个猫狗图像分类器的模型并在安卓应用上使用的全过程。
一、数据集准备
1.1 数据集来源
我采用的是微软的猫狗数据集,链接:Download Kaggle Cats and Dogs Dataset from Official Microsoft Download Center Download Kaggle Cats and Dogs Dataset from Official Microsoft Download Center
Download Kaggle Cats and Dogs Dataset from Official Microsoft Download Center
1.2 数据集查看
下载数据集后,解压如下:
Cat 数据如下:

Dog数据集如下:

1.3 删除脏数据
这个数据集有一些文件是有问题的,需要删除掉:
import os
from PIL import Image
# Set the directory to search for corrupted files
directory = 'path/to/directory'
# Loop through all files in the directory
for filename in os.listdir(directory):
# Check if file is an image
if filename.endswith('.jpg') or filename.endswith('.png'):
# Attempt to open image with PIL
try:
img = Image.open(os.path.join(directory, filename))
img.verify()
img.close()
except (IOError, SyntaxError) as e:
print(f"Deleting {filename} due to error: {e}")
os.remove(os.path.join(directory, filename))说明:上面的python代码会把目录下的文件给删除掉
二、训练模型
下面是完整代码,包括数据集划分、数据增强、模型训练、模型评估、模型保存等。
2.1 数据准备
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# 定义数据集路径
dataset_dir = 'I:/数据集/kagglecatsanddogs_5340/PetImages'
img_height, img_width = 224, 224
batch_size = 322.2 数据集划分
将数据集划分为训练集、测试集、验证集:
# 将数据集分为训练集、测试集、验证集
import os
import shutil
import numpy as np
train_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(dataset_dir), 'PetImages_train')
val_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(dataset_dir), 'PetImages_validation')
test_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(dataset_dir), 'PetImages_test')
if not os.path.exists(train_dir):
train_ratio = 0.7 # 训练集比例
val_ratio = 0.15 # 验证集比例
test_ratio = 0.15 # 测试集比例
classfiers = ['Cat', 'Dog']
for cls in classfiers:
# 获取数据集中所有文件名
filenames = os.listdir(os.path.join(dataset_dir, cls))
# 计算拆分后的数据集大小
num_samples = len(filenames)
num_train = int(num_samples * train_ratio)
num_val = int(num_samples * val_ratio)
num_test = num_samples - num_train - num_val
# 将文件名打乱顺序
shuffle_indices = np.random.permutation(num_samples)
filenames = [filenames[i] for i in shuffle_indices]
os.makedirs(os.path.join(train_dir, cls), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(val_dir, cls), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(test_dir, cls), exist_ok=True)
# 拆分数据集并复制文件到相应目录
for i in range(num_train):
src_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, cls, filenames[i])
dst_path = os.path.join(train_dir, cls, filenames[i])
shutil.copy(src_path, dst_path)
for i in range(num_train, num_train+num_val):
src_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, cls, filenames[i])
dst_path = os.path.join(val_dir, cls, filenames[i])
shutil.copy(src_path, dst_path)
for i in range(num_train+num_val, num_samples):
src_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, cls, filenames[i])
dst_path = os.path.join(test_dir, cls, filenames[i])
shutil.copy(src_path, dst_path)
2.3 数据加载和增强处理
# 数据增强处理
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True)
# 加载数据集
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(train_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size,
class_mode='binary')这段代码是用于图像分类模型训练的数据预处理部分。其中,ImageDataGenerator类是Keras中用于数据增强的工具,可以对图像进行一系列随机变换来扩充训练集,以提高模型泛化能力。
在这里,train_datagen对象将使用以下三个参数进行数据增强处理:
- rescale:将图像像素值缩放到0-1之间,加速模型收敛;
- shear_range:随机剪切变换范围;
- zoom_range:随机缩放变换范围;
- horizontal_flip:随机水平翻转。
然后通过调用 flow_from_directory 方法来生成一个 train_generator 对象,它会从指定的 train_dir 文件夹中动态生成包含批次大小为 batch_size 的训练数据样本,并将其转成二进制标签格式(class_mode='binary')。同时,所有图像都将被调整为指定的 img_height 和 img_width 大小,以保证输入神经网络的数据形状相同。
代码输出:Found 17498 images belonging to 2 classes.
2.4 模型定义
# 定义模型结构
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3,3), activation='relu', input_shape=(img_height, img_width, 3)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
这段代码是用于构建卷积神经网络模型的部分,使用了Keras中的Sequential模型,该模型按照一定顺序堆叠不同类型的层。
具体而言,这个模型包含了如下一系列层:
- Conv2D层:使用32个3x3的滤波器进行二维卷积,激活函数为ReLU;
- MaxPooling2D层:使用大小为2x2的窗口进行最大池化操作;
- 再次添加一个 Conv2D 层:使用64个3x3的滤波器进行卷积,激活函数为ReLU;
- 再次添加一个 MaxPooling2D 层;
- 再次添加一个 Conv2D 层:使用128个3x3的滤波器进行卷积,激活函数为ReLU;
- 再次添加一个 MaxPooling2D 层;
- Flatten 层:将卷积部分输出的特征图展平成一维向量,以便后续连接全连接层;
- 全连接 Dense 层:包含128个神经元,激活函数为ReLU;
- 输出层 Dense:只有一个神经元,用Sigmoid激活函数输出二分类结果。
这个模型的输入形状是(img_height, img_width, 3),其中3表示RGB图像的三个通道。第一层 Conv2D 和池化层之后,每个卷积层和池化层都会减小特征图的空间大小,并增加滤波器数量来提取更高层次的特征。最后使用全连接层对特征进行分类。输出层仅有一个神经元,用于二分类任务的概率输出。
2.4 编译模型与训练
编译模型:
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])在这里,使用了Adam优化器(optimizer='adam'),它是一种自适应学习率的优化方法,能够有效解决梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题,加快收敛速度。同时,使用了二元交叉熵作为损失函数(loss='binary_crossentropy'),也是常见的用于二分类问题的损失函数。最后,使用准确率(accuracy)作为评价指标(metrics=['accuracy']),用于评估模型预测的准确性。
训练模型:
# 训练模型
model.fit(train_generator,
epochs=15)我电脑用的是魔改版 2080Ti 22GB,训练的时候显存占用为 21GB,每一个 epoch 约 2分钟,全部跑完大约30分钟。
代码输出:
Epoch 1/15
547/547 [================] - 121s 220ms/step - loss: 0.6190 - accuracy: 0.6480
Epoch 2/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 220ms/step - loss: 0.5057 - accuracy: 0.7540
Epoch 3/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 220ms/step - loss: 0.4398 - accuracy: 0.7949
Epoch 4/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 220ms/step - loss: 0.4021 - accuracy: 0.8180
Epoch 5/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 219ms/step - loss: 0.3753 - accuracy: 0.8302
Epoch 6/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 220ms/step - loss: 0.3512 - accuracy: 0.8435
Epoch 7/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 220ms/step - loss: 0.3256 - accuracy: 0.8580
Epoch 8/15
547/547 [================] - 155s 283ms/step - loss: 0.3046 - accuracy: 0.8677
Epoch 9/15
547/547 [================] - 127s 233ms/step - loss: 0.2897 - accuracy: 0.8764
Epoch 10/15
547/547 [================] - 122s 224ms/step - loss: 0.2705 - accuracy: 0.8861
Epoch 11/15
547/547 [================] - 120s 220ms/step - loss: 0.2519 - accuracy: 0.8930
Epoch 12/15
547/547 [================] - 122s 223ms/step - loss: 0.2363 - accuracy: 0.9011
Epoch 13/15
...
Epoch 14/15
547/547 [================] - 121s 221ms/step - loss: 0.2154 - accuracy: 0.9144
Epoch 15/15
547/547 [================] - 121s 221ms/step - loss: 0.1986 - accuracy: 0.9200
2.5 模型准确率测试
# 测试模型准确率
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(test_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size,
class_mode='binary')
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_generator)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)代码输出:
Found 3752 images belonging to 2 classes.
40/118 [=========>....................] - ETA: 3s - loss: 0.3541 - accuracy: 0.8672
118/118 [==============================] - 6s 47ms/step - loss: 0.3433 - accuracy: 0.8681 Test accuracy: 0.8680703639984131
2.6 模型验证
# 验证模型准确率、损失
val_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
val_generator = val_datagen.flow_from_directory(val_dir,
target_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size,
class_mode='binary')
val_loss, val_acc = model.evaluate(val_generator)
print('Validation accuracy:', val_acc)
print('Validation loss:', val_loss)代码输出:
Found 3748 images belonging to 2 classes. 118/118 [==============================] - 6s 46ms/step - loss: 0.3384 - accuracy: 0.8714 Validation accuracy: 0.8713980913162231 Validation loss: 0.338356614112854
2.6 模型保存
2.6.1 保存为 tf 格式
# save model
model.save('cat_dog_classfier_v1.tf', overwrite=True, include_optimizer=True)tf格式是一个文件夹,该文件夹里面包含了计算图结构、模型元数据信息、模型参数等。
2.6.2 保存为 tflite 格式
这种格式可以在移动端上运行:
# 导出TensorFlow Lite模型
covertor = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
covertor.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
tflife_model = covertor.convert()
with open('cat_dog_classfier_v1.tflite', 'wb') as f:
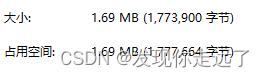
f.write(tflife_model)tflite 格式大小约为 10.6MB;
三、将tflite模型应用在安卓App上
启动 Android Studio,打开一个工程。
然后右击 app 模块,在弹出的右键菜单中选择 “New” - “Other” - "TensorFlow Lite Model",如下图所示:

接着,选中模型:

导入之后,如下图所示:
Android Studio 会自动生成调用该模型的相关代码了。
接下来我们就调用就可以了。
先准备一些猫狗图片,

放到 drawable-nodpi 目录下:
接着开始写代码,以下代码写在 MainActivity 中:
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val map = mapOf(
R.drawable.cat_0 to "R.drawable.cat_0",
R.drawable.cat_1 to "R.drawable.cat_1",
R.drawable.cat_2 to "R.drawable.cat_2",
R.drawable.cat_3 to "R.drawable.cat_3",
R.drawable.cat_4 to "R.drawable.cat_4",
R.drawable.cat_5 to "R.drawable.cat_5",
R.drawable.dog_0 to "R.drawable.dog_0",
R.drawable.dog_1 to "R.drawable.dog_1",
R.drawable.dog_2 to "R.drawable.dog_2",
R.drawable.dog_3 to "R.drawable.dog_3",
R.drawable.dog_4 to "R.drawable.dog_4",
R.drawable.dog_5 to "R.drawable.dog_5"
)
val model = CatDogClassfierV1.newInstance(this)
map.forEach {
doit(model, it.key, it.value)
}
model.close()
}
private fun doit(model: CatDogClassfierV1, id: Int, name: String) {
// Load the input image from resources
val bmp = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, id)
// Resize the input image to 224x224
val resizedBmp = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(bmp, 224, 224, true)
// Convert the resized bitmap to a ByteBuffer
val byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(4 * resizedBmp.width * resizedBmp.height * 3)
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
val pixels = IntArray(resizedBmp.width * resizedBmp.height)
resizedBmp.getPixels(pixels, 0, resizedBmp.width, 0, 0, resizedBmp.width, resizedBmp.height)
var pixel = 0
for (i in 0 until 224) {
for (j in 0 until 224) {
val pixelValue = pixels[pixel++]
byteBuffer.putFloat(((pixelValue shr 16) and 0xFF) / 255.0f)
byteBuffer.putFloat(((pixelValue shr 8) and 0xFF) / 255.0f)
byteBuffer.putFloat((pixelValue and 0xFF) / 255.0f)
}
}
// Creates inputs for reference.
val inputFeature0 = TensorBuffer.createFixedSize(intArrayOf(1, 224, 224, 3), DataType.FLOAT32)
inputFeature0.loadBuffer(byteBuffer)
// Runs model inference and gets result.
val outputs = model.process(inputFeature0)
val outputFeature0 = outputs.outputFeature0AsTensorBuffer
// Get the index of the predicted class
val probabilities = outputFeature0.floatArray
val predictedClassIndex = probabilities.indices.maxByOrNull { probabilities[it] } ?: -1
// Map the predicted class index to "Cat" or "Dog"
val predictedClass = if (predictedClassIndex == 0) "Cat" else if (predictedClassIndex == 1) "Dog" else "Unknown"
Log.i("MainActivity", "$name, probabilities=${probabilities.joinToString()}")
Log.i("MainActivity", "$name, ${if(probabilities[0] < 0.5) '猫' else '狗'}")
// Releases model resources if no longer used.
}运行起来看日志输出:

四、总结
以上是如何使用 tensorflow 训练一个猫狗分类器、并在移动端上部署的完整过程。
tensorflow 已经很完备了。在项目上可以多思考一下怎么应用。