STL
1. STL初识
1.1 迭代器
1.1.1 原生指针也是迭代器
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void test01() {
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int* p = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
cout << *(p+i) << endl;
}
};
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.1.2 循环迭代
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int i) {
cout <<i << endl;
}
void test02() {
vector<int >v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
vector<int>::iterator itbegin = v.begin();
vector<int>::iterator itend = v.end();
while (itbegin != itend) {
cout << *itbegin << endl;
itbegin++;
}
for (vector<int>::iterator i = itbegin; i!=v.end();i++) {
cout << *i << endl;
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print);
}
int main() {
test02();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.1.3 自定义数据结构
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person(string name,int age) {
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
string name;
int age;
};
void test03() {
vector<Person> v;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
Person p5("eee", 50);
Person p6("fff", 60);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
v.push_back(p6);
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it!=v.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it).name<< endl;
}
}
int main() {
test03();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2 string容器
1.2.1 string初始化
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test01() {
string str;// 初始化对象
string str2(str); // 用另外一个对象初始化
string str3 = "abc"; // 把值赋值给当前字符串
string str4(10, 'q'); // 用n个字符赋值给当前字符串
cout << "str3= " << str3 << endl;
cout << "str4= " << str4 << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.2 字符串赋值
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test02() {
string str;
str = "abc";
str.assign("abcde", 3);
cout << str << endl;
string str2;
str2.assign(str); //字符串赋值
cout << str2 << endl;
str2.assign(str, 0, 2); // 将s从start开始n个字符赋值给字符串
cout << str2 << endl;
}
int main() {
test02();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.3 at 查值
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test03() {
string str="hello world!";
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
cout << str[i] << endl;
}
// [] 和at 区别,[] 访问越界直接挂掉,at访问越界,抛出out_of_range 异常
try {
cout << str.at(100) << endl;
}
catch (out_of_range& e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
catch (...) {
cout << "异常捕获"<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
test03();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.4 增删改查
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test04() {
// 字符串拼接
string str1 = "我";
string str2 = "爱天安门";
cout <<"1:" << str1 + str2 << endl;
cout <<"2:" << str1.append(str2) << endl;
string str = "abcdefgde";
int pos = str.find("de");
if (pos == -1) {
cout << "未找到字符串" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了字符串,位置为:" << pos << endl;
}
str.replace(1, 3, "11111");// 替换从pos开始n个字符的字符串为str
cout << str << endl;
}
int main() {
test04();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.5 字符串比较
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test05() {
string str1 = "abcde";
string str2 = "abcdef";
if (str1.compare(str2) == 0) {
cout << "str1==str2" << endl;
}
else if (str1.compare(str2) > 0) {
cout << "str1>str2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "str1<str2" << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test05();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.6 字符串索引
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test06() {
string email = "zhangtoa@sina.com";
int pos = email.find("@");
// [start:end]
string userName = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << userName << endl;
}
int main() {
test06();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.7 解析字符串
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test07() {
string str = "www.baidu.com";
vector<string> v;
int start = 0;
int pos = -1;
while (true) {
pos = str.find(".", start);
if (pos == -1) {
string tempStr = str.substr(start, str.size() - start);
v.push_back(tempStr);
break;
}
string tempStr = str.substr(start, pos - start);
v.push_back(tempStr);
start = pos + 1;
}
for (vector<string>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test07();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.8 插入和删除
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test08() {
string str = "hello";
str.insert(1, "111");
cout << str << endl;
str.erase(1, 3);// 从pos开始的n个字符
cout << str << endl;
}
int main() {
test08();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.9 char 与字符串互相转换
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test09() {
const char* str = "abcd";
// 转str
string s(str);
//str 转const
const char* str2 = s.c_str();
// const char* 可以隐式转换string,反之不可
}
int main() {
test09();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.10 字符串转换
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test10() {
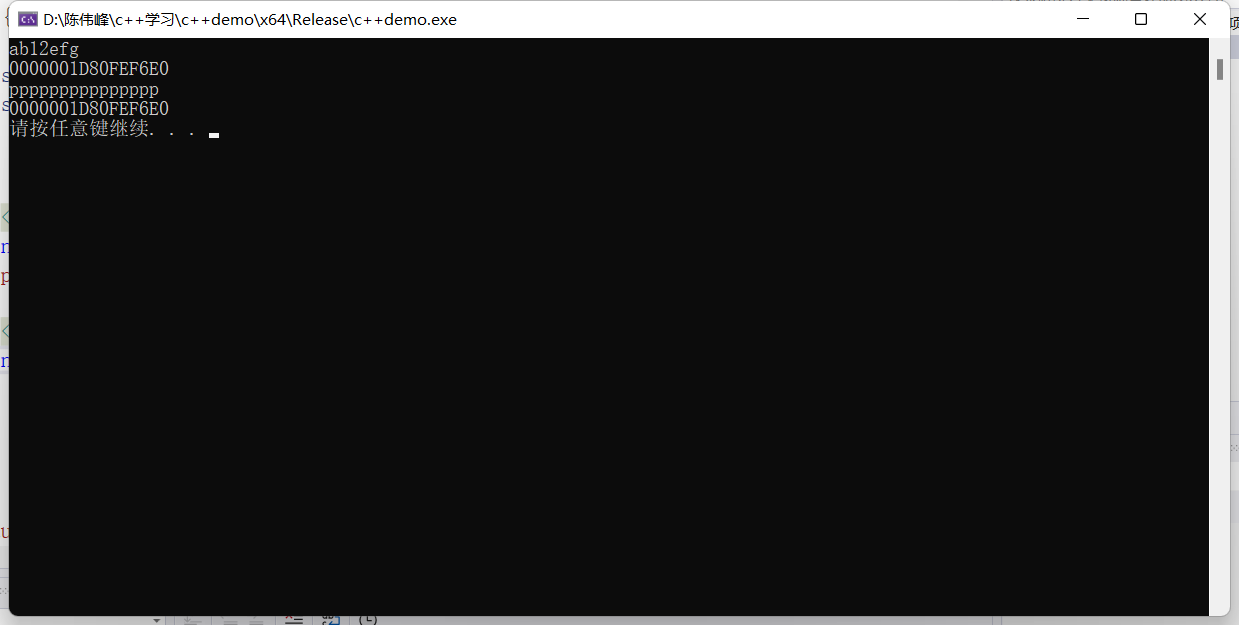
string s = "abcdefg";
char& a = s[2];
char& b = s[3];
a = '1';
b = '2';
cout << s << endl;
cout << (int*)s.c_str() <<endl;
s = "ppppppppppppppp";
cout << s << endl;
cout << (int*)s.c_str() << endl;
}
int main() {
test10();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.3. vector容器
1.3.1 capacity
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test01() {
vector<int> v;
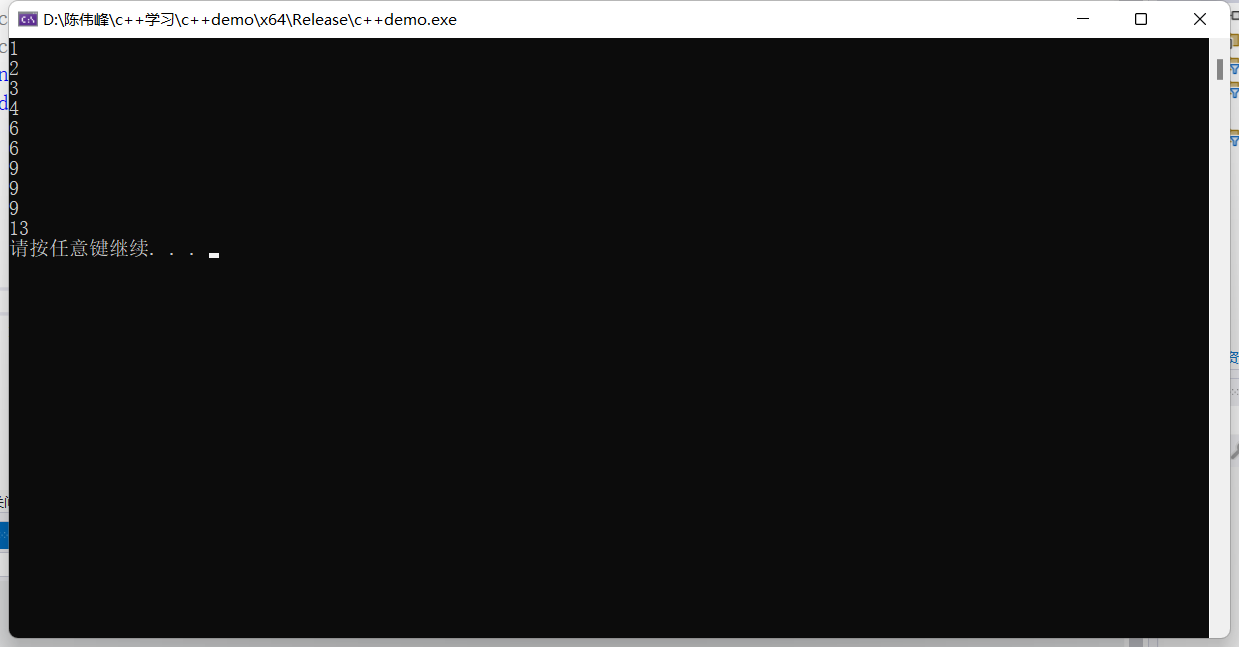
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
v.push_back(i);
cout << v.capacity() << endl; // v.capacity()容器的容量
}
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.3.2 赋值
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test02() {
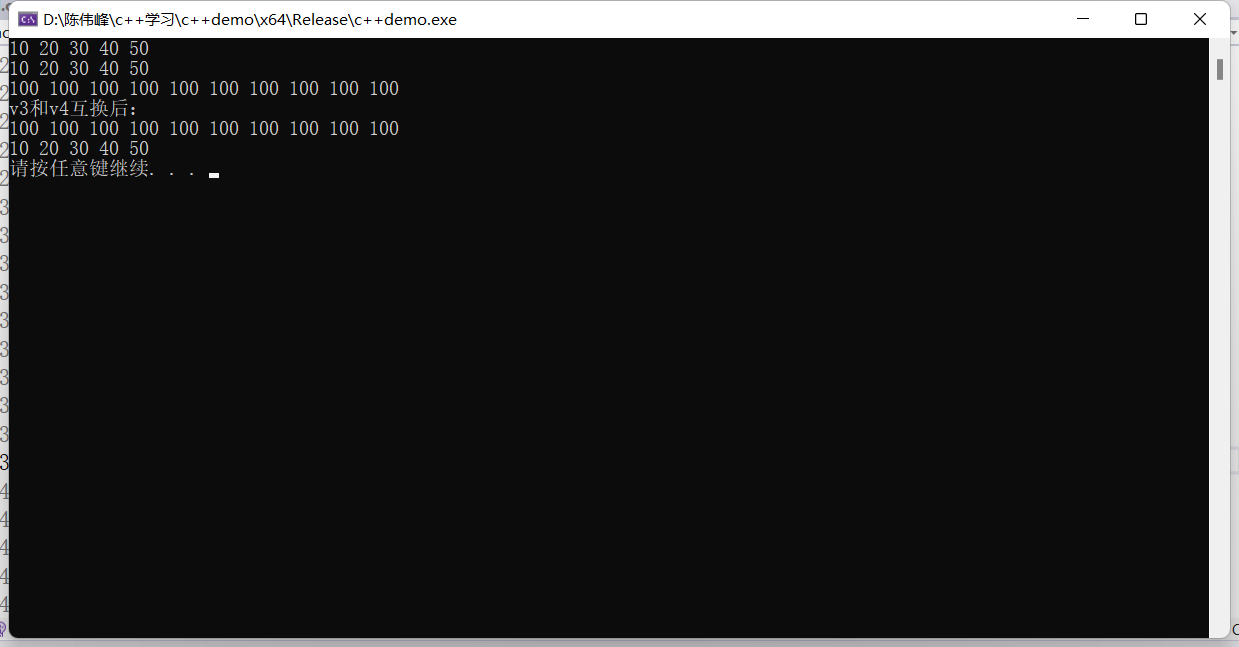
vector<int>v1;
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(30);
v1.push_back(40);
v1.push_back(50);
//vector& operator=(const vector & vec);//重载等号操作符
//assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
//assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
//vector& operator=(const vector & vec);//重载等号操作符
vector<int>v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v2);
vector<int>v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v3);
vector<int>v4(10, 100);
printVector(v4);
cout << "v3和v4互换后:" << endl;
v3.swap(v4);
printVector(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main() {
test02();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.3.3 状态判断与操作
- size();//返回容器中元素的个数
- empty();//判断容器是否为空
- resize(int num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长>度的元素被删除。
- capacity();//容器的容量
- reserve(int len);//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。
- at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据,如果idx越界,抛出out_of_range异常。
- operator[];//返回索引idx所指的数据,越界时,运行直接报错
- front();//返回容器中第一个数据元素
- back();//返回容器中最后一个数据元素
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test03()
{
vector<int>v1;
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(30);
v1.push_back(40);
v1.push_back(50);
if (v1.empty())
{
cout << "v1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1不为空 ,大小为: " << v1.size() << endl;
}
v1.resize(10, 100); //第二个参数代表默认填充值
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(3);
printVector(v1);
cout << "v1的front = " << v1.front() << endl;
cout << "v1的back = " << v1.back() << endl;
}
int main() {
test03();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}

1.3.4 插入与删除
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test04()
{
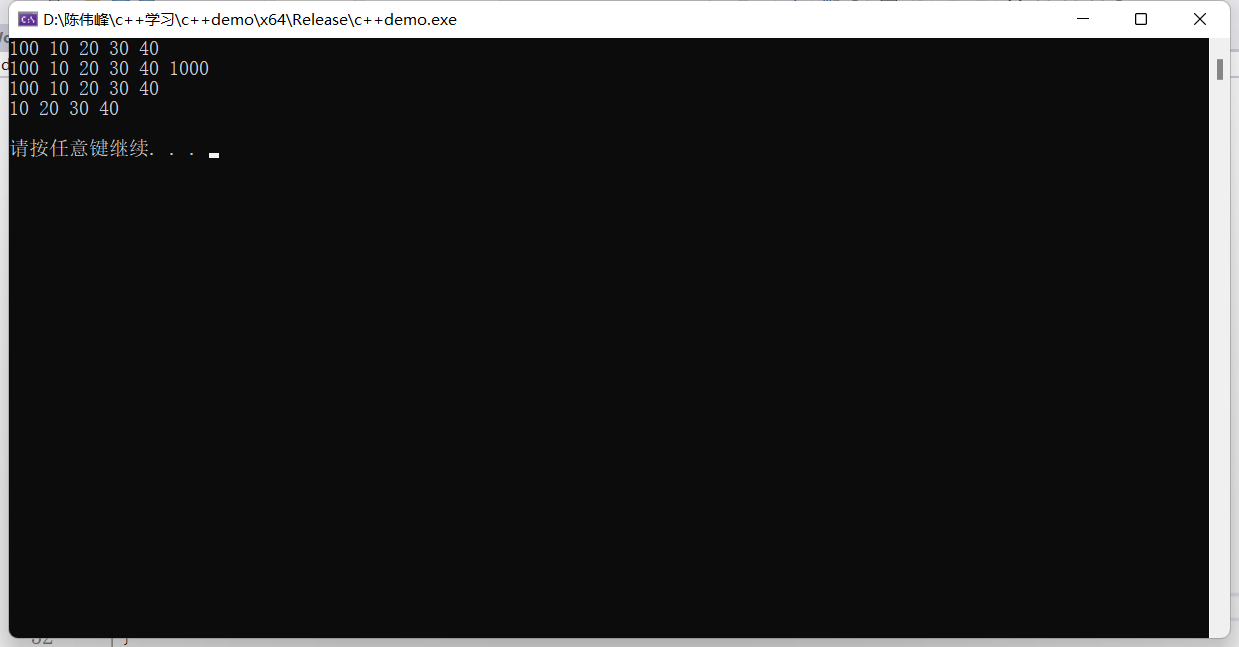
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.insert(v.begin(), 100);
printVector(v);
v.push_back(1000);
printVector(v);
v.pop_back();
printVector(v);
v.erase(v.begin());
printVector(v);
//v.erase(v.begin(), v.end()); 等价于 v.clear();
v.clear();
//v.erase(v.begin(), v.end());
printVector(v);
}
int main() {
test04();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.4 deque
1.4.1 构造函数
- deque deqT;//默认构造形式
- deque(beg, end);//构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
- deque(n, elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
- deque(const deque &deq);//拷贝构造函数。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
//iterator普通迭代器
//reverse_iterator 反转迭代器
//const_iterator 只读迭代器
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
//*it = 1000;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(40);
deque<int>d2;
d2 = d;
printDeque(d2);
if (d2.empty())
{
cout << "d2为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "d2不为空 size = " << d2.size() << endl;
}
}
void test02() {
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(100);
d.push_back(200);
d.push_back(300);
printDeque(d);
d.pop_back(); // 尾删
d.pop_front(); // 头删
printDeque(d);
cout << "第一个元素为:" << d.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << d.back() << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.4.2 赋值操作
- assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
- assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
- deque& operator=(const deque &deq); //重载等号操作符
- swap(deq);// 将deq与本身的元素互换
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
//iterator普通迭代器
//reverse_iterator 反转迭代器
//const_iterator 只读迭代器
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
//*it = 1000;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(40);
deque<int>d2;
d2 = d;
printDeque(d2);
if (d2.empty())
{
cout << "d2为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "d2不为空 size = " << d2.size() << endl;
}
}
void test02() {
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(100);
d.push_back(200);
d.push_back(300);
printDeque(d);
d.pop_back(); // 尾删
d.pop_front(); // 头删
printDeque(d);
cout << "第一个元素为:" << d.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << d.back() << endl;
}
void test03(){
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(100);
d.push_back(200);
d.push_back(300);
d.insert(++d.begin(), 2, 1000);
printDeque(d);
d.erase(++d.begin());
d.erase(++d.begin());
deque<int>::iterator it1 = d.begin();
it1 = it1 + 1;
deque<int>::iterator it2 = d.begin();
it2 = it2 + 3;
d.erase(it1, it2);
printDeque(d);
d.clear();
printDeque(d);
}
bool myComare(int v1, int v2) {
return v1 < v2;
}
int main() {
// test01();
// test02();
test03();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.4.3 大小操作
- deque.size();//返回容器中元素的个数
- deque.empty();//判断容器是否为空
- deque.resize(num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- deque.resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
//iterator普通迭代器
//reverse_iterator 反转迭代器
//const_iterator 只读迭代器
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
//*it = 1000;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(40);
deque<int>d2;
d2 = d;
printDeque(d2);
if (d2.empty())
{
cout << "d2为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "d2不为空 size = " << d2.size() << endl;
}
}
void test02() {
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(100);
d.push_back(200);
d.push_back(300);
printDeque(d);
d.pop_back(); // 尾删
d.pop_front(); // 头删
printDeque(d);
cout << "第一个元素为:" << d.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << d.back() << endl;
}
void test03(){
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_back(100);
d.push_back(200);
d.push_back(300);
d.insert(++d.begin(), 2, 1000);
printDeque(d);
d.erase(++d.begin());
d.erase(++d.begin());
deque<int>::iterator it1 = d.begin();
it1 = it1 + 1;
deque<int>::iterator it2 = d.begin();
it2 = it2 + 3;
d.erase(it1, it2);
printDeque(d);
d.clear();
printDeque(d);
}
bool myComare(int v1, int v2) {
return v1 < v2;
}
void test04() {
deque<int>d;
d.push_back(10);
d.push_back(20);
d.push_back(30);
d.push_front(100);
d.push_front(200);
d.push_front(300);
// 默认排序从小到大
//sort(d.begin(), d.end());
sort(d.begin(), d.end(), myComare);
printDeque(d);
}
int main() {
// test01();
// test02();
// test03();
test04();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Player
{
public:
Player(string name, int score) {
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Score = score;
};
string m_Name; // 姓名
int m_Score; // 平均分
};
void createPlayer(vector<Player>& v) {
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
string name = "选手";
name += nameSeed[i];
int score = 0;
Player player(name, score);
v.push_back(player);
}
};
void setScore(vector<Player>& v) {
for (vector<Player>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
deque<int> d;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int score = rand() % 41 + 60;
d.push_back(score);
}
sort(d.begin(), d.end());
d.pop_back();
d.pop_front();
int sum = 0;
for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) {
sum += *dit;
}
int avg = sum / d.size();
it->m_Score = avg;
}
}
void showScore(vector<Player>&v){
for (vector<Player>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << "平均分数:" << it->m_Score << endl;
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<Player> v;
createPlayer(v);
setScore(v);
showScore(v);
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.5 Stack容器
- stack& operator=(const stack &stk);//重载等号操作符
- push(elem);//向栈顶添加元素
- pop();//从栈顶移除第一个元素
- top();//返回栈顶元素
- empty();//判断堆栈是否为空
- size();//返回堆栈的大小
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stack>
void test01()
{
stack<int>S;
//入栈
S.push(10);
S.push(20);
S.push(30);
S.push(40);
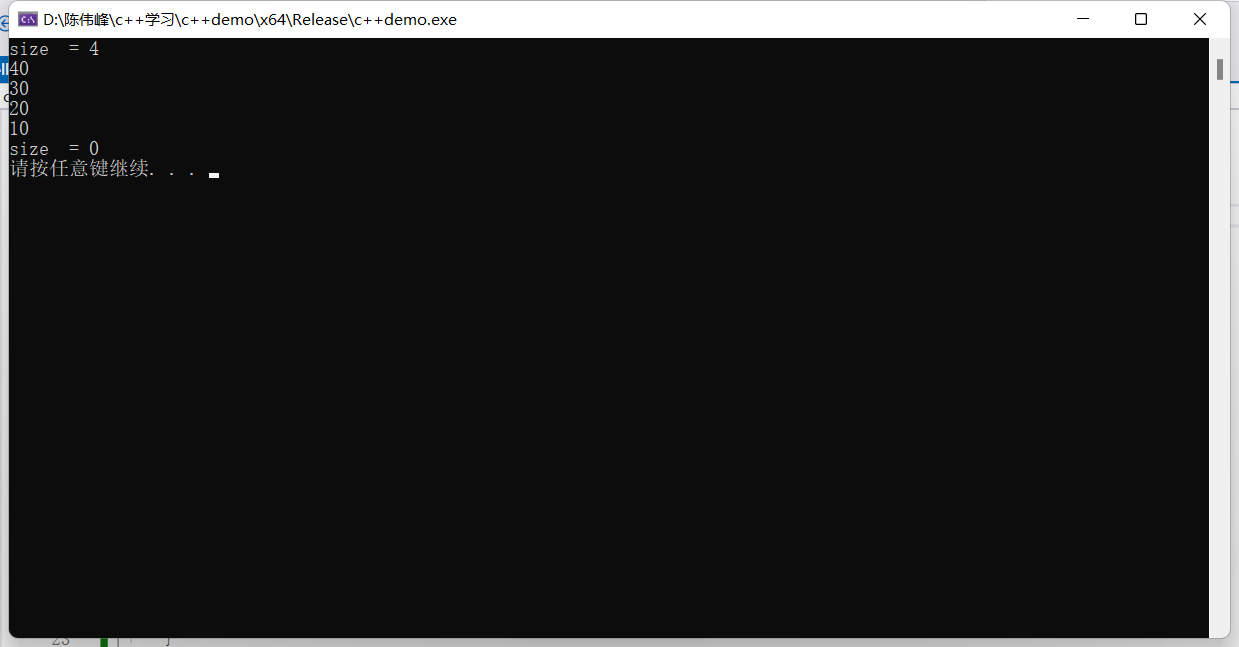
cout << "size = " << S.size() << endl;
while (!S.empty())
{
//访问栈顶元素
cout << S.top() << endl;
//出栈
S.pop();
}
cout << "size = " << S.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.6 队列queue
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <queue>
#include <string>
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
queue<Person> Q; //队列容器
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
//入队
Q.push(p1);
Q.push(p2);
Q.push(p3);
Q.push(p4);
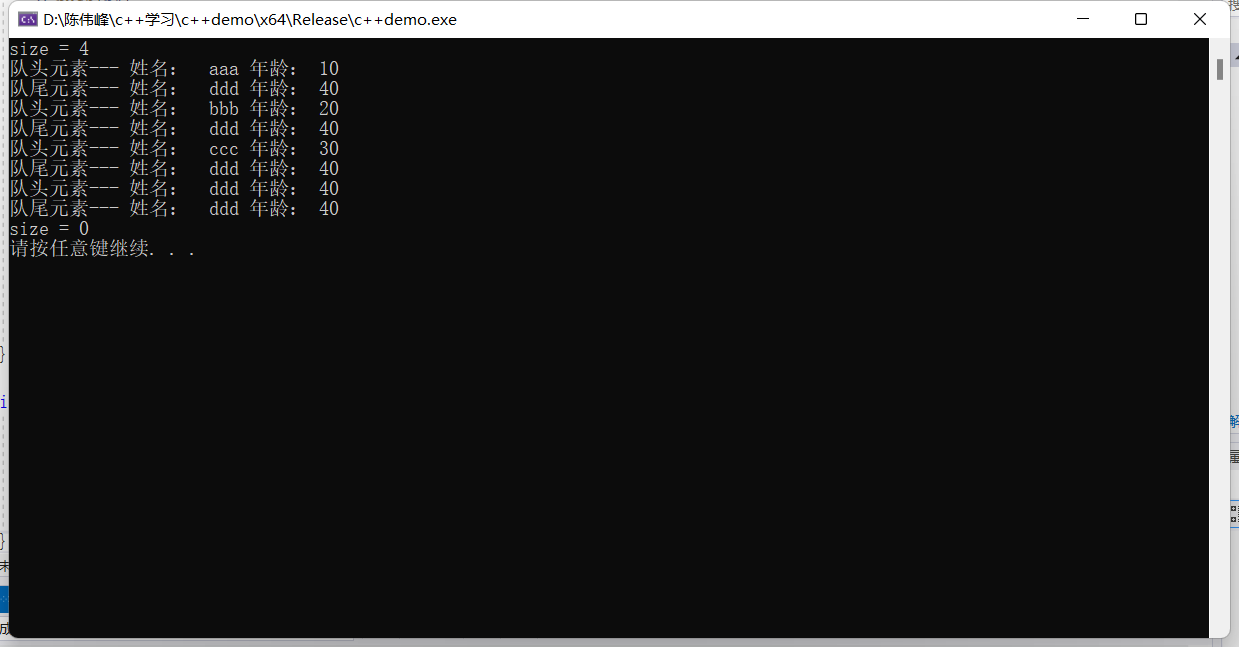
cout << "size = " << Q.size() << endl;
while ( !Q.empty())
{
cout << "队头元素--- 姓名: " << Q.front().m_Name << " 年龄: " << Q.front().m_Age << endl;
cout << "队尾元素--- 姓名: " << Q.back().m_Name << " 年龄: " << Q.back().m_Age << endl;
//出队
Q.pop();
}
cout << "size = " << Q.size() << endl;
}
int main(){
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
1.7 list容器
1.7.1 构造函数
- list lstT;//list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:
- list(beg,end);//构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
- list(n,elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
- list(const list &lst);//拷贝构造函数。
- push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素
- push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素
- pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素
- insert(pos,elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
- insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
- insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
- clear();//移除容器的所有数据
- erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
list<T> lstT;//list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:
list(beg,end);//构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
list(n,elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
list(const list &lst);//拷贝构造函数。
1.7.2 数据元素插入和删除操作
push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素
pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素
push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素
pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素
insert(pos,elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
clear();//移除容器的所有数据
erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
1.7.3 list大小操作
size();//返回容器中元素的个数
empty();//判断容器是否为空
resize(num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,
若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。
如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
resize(num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,
若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。
如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
1.7.4 list数据的存取
front();//返回第一个元素。
back();//返回最后一个元素。
1.7.5 list反转排序
reverse();//反转链表,比如lst包含1,3,5元素,运行此方法后,lst就包含5,3,1元素。
sort(); //list排序
1.8 set/multiset
- Set的特性是。所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动被排序。Set的元素不像map那样可以同时拥有实值和键值,set的元素即是键值又是实值。Set不允许两个元素有相同的键值。
- multiset特性及用法和set完全相同,唯一的差别在于它允许键值重复。set和multiset的底层实现是红黑树,红黑树为平衡二叉树的一种。
1.8.1 构造函数
set<T> st;//set默认构造函数:
mulitset<T> mst; //multiset默认构造函数:
set(const set &st);//拷贝构造函数
1.8.2 赋值操作
set& operator=(const set &st);//重载等号操作符
swap(st);//交换两个集合容器
1.8.3 set大小操作
size();//返回容器中元素的数目
empty();//判断容器是否为空
1.8.4 插入和删除操作
insert(elem);//在容器中插入元素。
clear();//清除所有元素
erase(pos);//删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(beg, end);//删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(elem);//删除容器中值为elem的元素。
1.8.5 查找操作
find(key);//查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();
count(key);//查找键key的元素个数
lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。
1.9 map/multimap容器
1.9.1 map/multimap基本概念
Map的特性是,所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序。Map所有的元素都是pair,同时拥有实值和键值,pair的第一元素被视为键值,第二元素被视为实值,map不允许两个元素有相同的键值。
map的键值关系到map元素的排列规则,任意改变map键值将会严重破坏map组织。如果想要修改元素的实值,那么是可以的。
Map和list拥有相同的某些性质,当对它的容器元素进行新增操作或者删除操作时,操作之前的所有迭代器,在操作完成之后依然有效,当然被删除的那个元素的迭代器必然是个例外。
Multimap和map的操作类似,唯一区别multimap键值可重复。
Map和multimap都是以红黑树为底层实现机制。
1.9.2 构造函数
map<T1, T2> mapTT;//map默认构造函数:
map(const map &mp);//拷贝构造函数
1.9.3 赋值
map& operator=(const map &mp);//重载等号操作符
swap(mp);//交换两个集合容器
1.9.4 map大小操作
size();//返回容器中元素的数目
empty();//判断容器是否为空
1.9.5 插入元素操作
map.insert(...); //往容器插入元素,返回pair<iterator,bool>
map<int, string> mapStu;
// 第一种 通过pair的方式插入对象
mapStu.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "小张"));
// 第二种 通过pair的方式插入对象
mapStu.inset(make_pair(-1, "校长"));
// 第三种 通过value_type的方式插入对象
mapStu.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(1, "小李"));
// 第四种 通过数组的方式插入值
mapStu[3] = "小刘";
mapStu[5] = "小王";
1.9.6 map 删除操作
clear();//删除所有元素
erase(pos);//删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(beg,end);//删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(keyElem);//删除容器中key为keyElem的对组。
1.9.7 map查找操作
find(key);//查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;/若不存在,返回map.end();
count(keyElem);//返回容器中key为keyElem的对组个数。对map来说,要么是0,要么是1。对multimap来说,值可能大于1。
lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。