此题为世纪难题
题目提供者 洛谷
难度 NOI/NOI+/CTSC


输入输出样例
输入 #1
5 1 6 0 0
1
5 2 2 0 0输出 #1
1
5
5 2 2 1
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~此题非常难,小白就不用想着独自完成了
题解: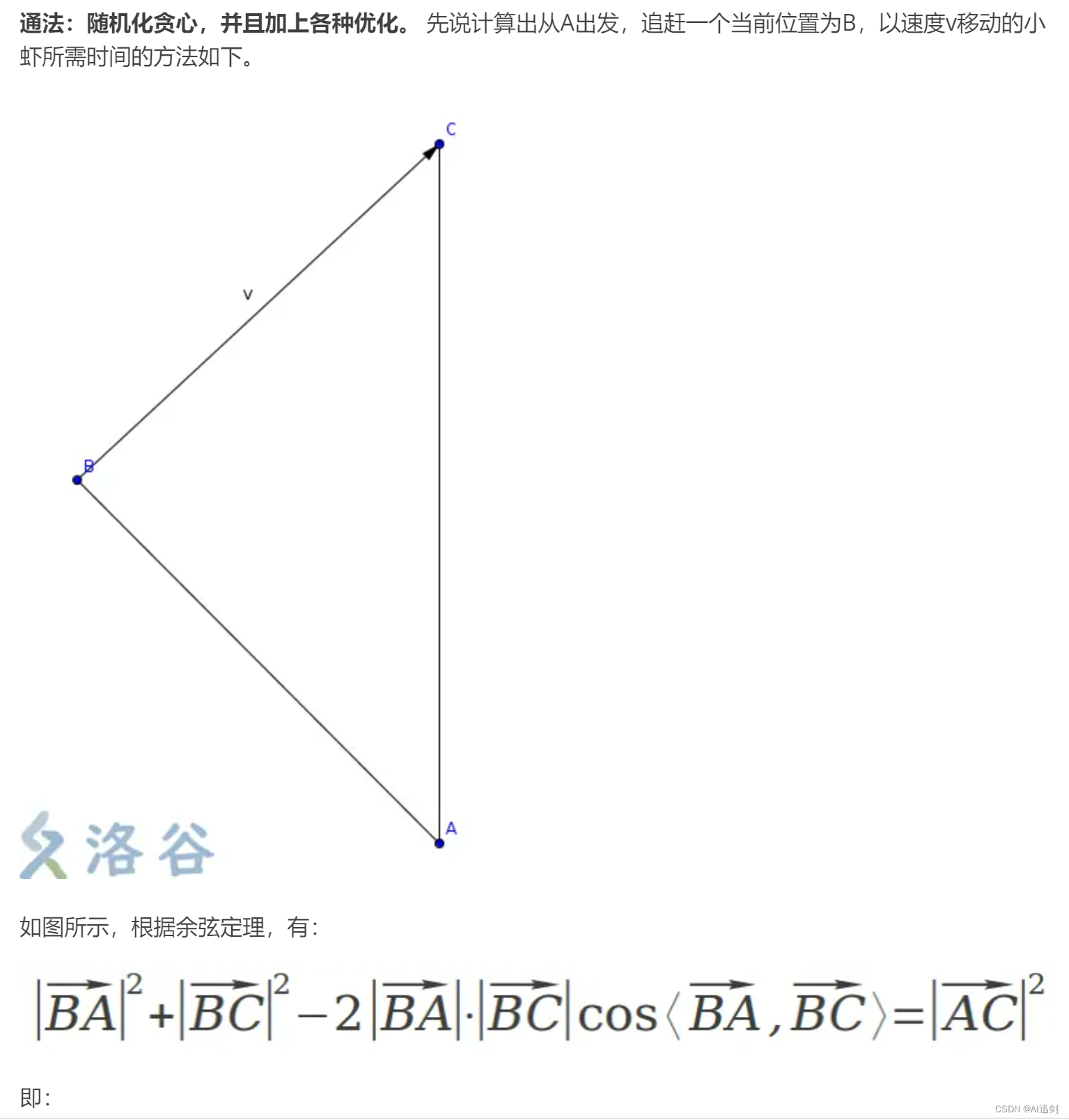

#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <complex>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxN = 10010;
const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198;
struct Res
{
double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {}
Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord):
t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {}
} res[maxN], _res[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN];
complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN];
double w[maxN], V, _deltaw, deltaw, T, tem;
vector <pair <double, int> > ls;
vector <pair <double, int> >::iterator iter;
int ord[maxN], n, cnt, _cnt;
inline bool cmp(const int &a, const int &b)
{return w[a] < w[b];}
inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;}
inline double sqr(complex <double> z)
{return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));}
inline double solve(complex <double> p,
complex <double> v,
complex <double> O)
{
double a = sqr(v) - sqr(V),
b = -2 * (real(v) * real(O - p) + imag(v) * imag(O - p)),
c = sqr(p - O),
delta = sqr(b) - 4 * a * c;
if (delta < -zero) return INF;
if (fabs(a) < zero)
return (b > -zero) ? INF : (-c / b);
double ans = INF,
x1 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a),
x2 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a);
if (x1 > -zero) ans = x1;
if (x2 > -zero && x2 < ans) ans = x2;
return ans;
} //计算出从O出发,追赶一个当前位置为p,以速度v移动的小虾所需时间。
inline double _rand() {return (double)rand() / RAND_MAX;}
inline bool judge()
{
if (++iter == ls.end()) {--iter; return 0;}
if (rand() & 1) {--iter; return 0;}
//先以0.5的概率初步淘汰较差的解。
double nxt = iter -> first;
--iter; double ths = iter -> first;
double delta = (ths - nxt);
if (delta / ths < 3.40e-2) return 1;
//若较差的解比当前解差3.4%以上,直接淘汰。
return _rand() < 1 / exp(delta / tem);
//否则以概率e ^ (-delta / tem)的概率接受更差的解。
}
int main()
{
freopen("nemo10.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("nemo10.out", "w", stdout);
srand(time(NULL));
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n);
complex <double> p0 = p[0]; double w0 = w[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ord[i] = i, ++i)
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag());
sort(ord + 1, ord + n + 1, cmp); //将小虾按体重从小到大的顺序排序。
tem = 1; //初始温度设为1。
for (int k = 0; k < 15; ++k)
{
memset(eaten, 0, sizeof eaten);
_deltaw = 0; _cnt = 0; p[0] = p0; w[0] = w0;
for (double t = 0; t < T;)
{
ls.clear();
for (int i = 1; w[ord[i]] < w[0]; ++i)
if (!eaten[ord[i]])
ls.push_back(make_pair(w[ord[i]] / sqr(solve(p[ord[i]] + t * v[ord[i]], v[ord[i]], p[0])), ord[i]));
sort(ls.begin(), ls.end(), greater <pair <double, int> > ());
iter = ls.begin(); if (iter == ls.end()) break;
while (judge()) ++iter;
int pos = iter -> second;
if (T - (t += solve(p[pos] + t * v[pos], v[pos], p[0])) < -zero) break;
_deltaw += w[pos], w[0] += w[pos]; eaten[pos] = 1;
_res[_cnt++] = Res(t, p[0] = p[pos] + t * v[pos], pos);
}
if (_deltaw > deltaw)
{
deltaw = _deltaw;
for (cnt = 0; cnt < _cnt; ++cnt) res[cnt] = _res[cnt];
} //更新最优解。
tem *= .5;
}
printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i)
printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord);
return 0;
}
对于不同的数据,还可以用特殊方法求解。
第一组数据显然手算,不多说。
第二组数据较小,可以暴力枚举,附程序:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <complex>
using namespace std;
const int maxN = 10010;
const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198;
struct Res
{
double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {}
Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord):
t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {}
} res[maxN], tmp[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN];
complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN];
double w[maxN], V, deltaw, T;
int n, cnt;
inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;}
inline double sqr(complex <double> z)
{return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));}
inline double solve(complex <double> p,
complex <double> v,
complex <double> O)
{
double a = sqr(v) - sqr(V),
b = -2 * (real(v) * real(O - p) + imag(v) * imag(O - p)),
c = sqr(p - O),
delta = sqr(b) - 4 * a * c;
if (delta < -zero) return INF;
if (fabs(a) < zero)
return (b > -zero) ? INF : (-c / b);
double ans = INF,
x1 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a),
x2 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a);
if (x1 > -zero) ans = x1;
if (x2 > -zero && x2 < ans) ans = x2;
return ans;
}
void Dfs(int i, double w0, double t, complex <double> p0)
{
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; ++j)
if (!eaten[j] && w[j] < w0)
{
double ths = solve(p[j] + t * v[j], v[j], p0);
if (t + ths - T > zero) continue;
complex <double> pos = p[j] + (t + ths) * v[j];
eaten[j] = 1;
tmp[i] = Res(t + ths, pos, j);
Dfs(i + 1, w0 + w[j], t + ths, pos);
tmp[i] = Res(0, 0, 0);
eaten[j] = 0;
}
if (w0 - w[0] > deltaw)
{
deltaw = w0 - w[0];
for (cnt = 0; tmp[cnt].t > zero; ++cnt)
res[cnt] = tmp[cnt];
}
return;
}
int main()
{
freopen("nemo2.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("nemo2.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n);
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i)
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag());
Dfs(0, w[0], 0, p[0]);
printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i)
printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord);
return 0;
}第三组数据小虾的体重有规律,按顺序吃就是了,附程序:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <complex>
using namespace std;
const int maxN = 10010;
const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198;
struct Res
{
double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {}
Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord):
t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {}
} res[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN];
complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN];
double w[maxN], V, deltaw, T;
int ord[maxN], n, cnt;
inline bool cmp(const int &a, const int &b)
{return w[a] < w[b];}
inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;}
inline double sqr(complex <double> z)
{return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));}
inline double solve(complex <double> p,
complex <double> v,
complex <double> O)
{
double a = sqr(v) - sqr(V),
b = -2 * (real(v) * real(O - p) + imag(v) * imag(O - p)),
c = sqr(p - O),
delta = sqr(b) - 4 * a * c;
if (delta < -zero) return INF;
if (fabs(a) < zero)
return (b > -zero) ? INF : (-c / b);
double ans = INF,
x1 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a),
x2 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a);
if (x1 > -zero) ans = x1;
if (x2 > -zero && x2 < ans) ans = x2;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
freopen("nemo3.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("nemo3.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n);
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ord[i] = i, ++i)
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag());
sort(ord + 1, ord + n + 1, cmp);
for (double t = 0; T - t > zero;)
{
static int i = 0; ++i; if (i > n) break;
double Min = solve(p[ord[i]] + t * v[ord[i]], v[ord[i]], p[0]);
int pos = ord[i];
if (fabs(Min - INF) < zero) break;
if (T - (t += Min) < -zero) break;
w[0] += w[pos]; deltaw += w[pos]; eaten[pos] = 1;
res[cnt++] = Res(t, p[0] = p[pos] + t * v[pos], pos);
}
printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i)
printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord);
return 0;
}
第四组数据中所有小虾静止不动且在一条直线上,据说是区间动态规划,方法至今未知。
第五、六组数据中所有小虾都在高速向下掉,而Nemo的移动速度很小,可以近似看作Nemo在只能水平移动的情况下去接住小虾来吃。
先将小虾按竖直方向排序,然后进行一下操作。
设f[i]表示前i个小虾中恰好第i个被吃所能得到的最大收益,只需要一个n^2的动态规划即可求解。
附程序:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <complex>
using namespace std;
const int maxN = 10010;
const double zero = 1e-12, INF = 1e198;
struct Res
{
double t; complex <double> p; int ord; Res() {}
Res(double t, complex <double> p, int ord):
t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {}
} res[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN];
complex <double> p[maxN], v[maxN];
double f[maxN], w[maxN], V, deltaw, T;
int ord[maxN], g[maxN], n, cnt;
inline bool cmp(const int &a, const int &b)
{return imag(p[a]) < imag(p[b]);}
void calc(int i)
{
if (g[i]) calc(g[i]);
res[cnt++] = Res(imag(p[i]) / 1000, p[i], i);
deltaw += w[i];
return;
}
int main()
{
freopen("nemo5.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("nemo5.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n);
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ord[i] = i, ++i)
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag());
sort(ord + 1, ord + n + 1, cmp);
int st = 1;
while (imag(p[ord[st]]) / 1000 - real(p[ord[st]]) / V < -zero) ++st;
f[ord[st]] = w[ord[st]];
for (int i = 1; i < st; ++i) f[ord[i]] = -INF;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (f[ord[i]] > -INF)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n + 1; ++j)
{
if (imag(p[ord[j]] - p[ord[i]]) / 1000 - fabs(real(p[ord[i]] - p[ord[j]])) / V > -zero)
if (f[ord[i]] + w[ord[j]] > f[ord[j]])
f[ord[j]] = f[ord[i]] + w[ord[j]],
g[ord[j]] = ord[i];
}
int pos = ord[n];
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i) if (f[i] > f[pos]) pos = i;
calc(pos);
printf("%d\n%.9lf\n", cnt, deltaw);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i)
printf("%.9lf %.9lf %.9lf %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), 0., res[i].ord);
return 0;
}
第七、八组数据中可以发现小虾的位置呈现数字三角形的形状,只需要按数字三角形的方法进行动态规划即可。
附程序:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <complex>
using namespace std;
const int maxN = 2010, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double zero = 1e-12;
struct Res
{
double t; complex <int> p; int ord; Res() {}
Res(double t, complex <int> p, int ord):
t(t), p(p), ord(ord) {}
} res[maxN], tmp[maxN]; bool eaten[maxN];
complex <int> p[maxN], v[maxN];
double w[maxN], deltaw, V, T, f[maxN][maxN];
int ord[maxN][maxN], g[maxN], n, cnt;
inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;}
inline double sqr(complex <double> z)
{return sqr(real(z)) + sqr(imag(z));}
int main()
{
freopen("nemo8.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("nemo8.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%d%d%d", w + 0, &V, &T, &p[0].real(), &p[0].imag(), &n);
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i)
scanf("%lf%d%d%d%d", w + i, &p[i].real(), &p[i].imag(), &v[i].real(), &v[i].imag());
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i)
ord[real(p[i])][imag(p[i])] = i;
int i = n;
for (; i; --i)
{
f[real(p[i])][imag(p[i])] = w[i];
if (imag(p[i - 1]) < imag(p[i])) break;
}
while (--i)
{
int x = real(p[i]), y = imag(p[i]), ths = ord[x][y];
if (f[x - 1][y + 1] > f[x + 1][y + 1])
{
f[x][y] = w[i] + f[x - 1][y + 1];
g[ths] = ord[x - 1][y + 1];
}
else
{
f[x][y] = w[i] + f[x + 1][y + 1];
g[ths] = ord[x + 1][y + 1];
}
}
double t = 0;
res[cnt++] = Res(t = abs(p[1] - p[0]) / V, p[1], 1);
for (int ths = 1; g[ths]; ths = g[ths])
res[cnt++] = Res(t += abs(complex <double> (real(p[g[ths]] - p[ths]), imag(p[g[ths]] - p[ths]))) / V, p[g[ths]], g[ths]);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) deltaw += w[res[i].ord];
printf("%d\n%lf\n", cnt, deltaw);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i)
printf("%.9lf %d %d %d\n", res[i].t, res[i].p.real(), res[i].p.imag(), res[i].ord);
return 0;
}
第九组数据中所有小虾都静止不动,简单的贪心就可以过。
第十组数据可能就只有随机化贪心能够解决了……