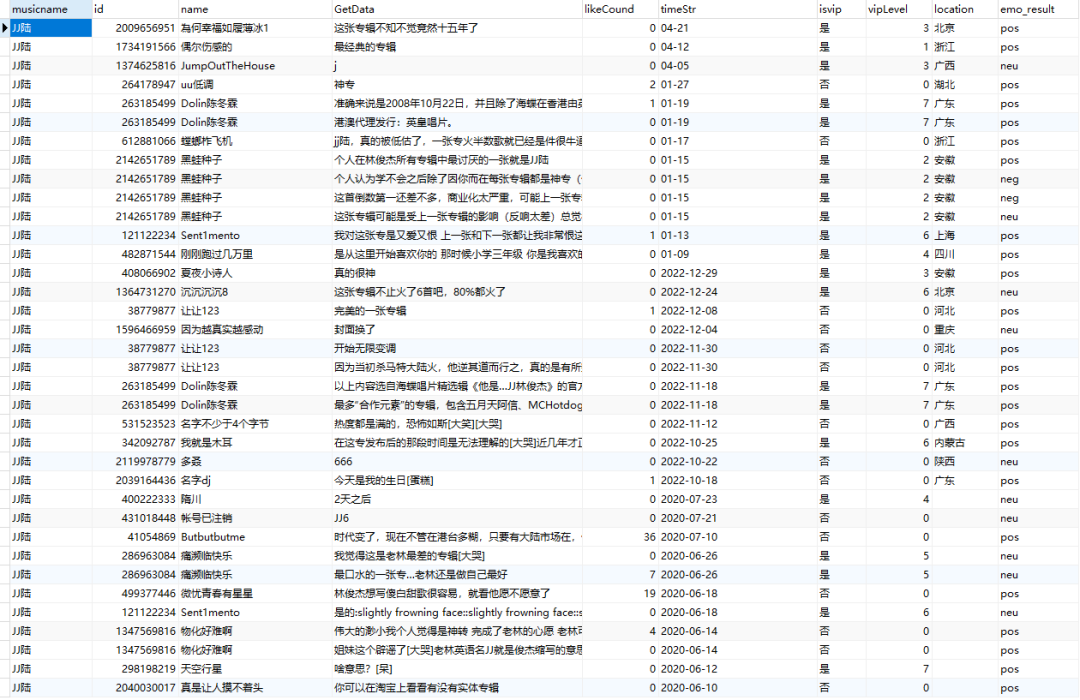
目录
一:SpringMVC注解式开发
1. @RequestMapping定义请求规则
2. 五种数据提交的方式
3. 请求参数中文乱码解决
4. action方法的返回值
5. SpringMVC的四种跳转方式
6. SpringMVC支持的默认参数类型
7. 日期处理
8. 标签的使用
9. 资源在WEB-INF目录下
一:SpringMVC注解式开发
1. @RequestMapping定义请求规则
通过@RequestMapping 注解可以定义处理器对于请求的映射规则(此注解就是来映射服务器访问的路径)。该注解可以注解在方法上,也可以注解在类上,意义是不同的。value 属性值常以“/”开始,当value是其唯一属性时,可以省略属性名;@RequestMapping的value 属性用于定义所匹配请求的 URI,以“/”开始。
(1)此注解可加在方法上,是为此方法注册一个可以访问的名称(路径)
前端请求
<%--发送超链接--%>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo.action">发送请求</a>后端代码:只有方法上有@RequestMapping注解
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class DemoAction {
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public String demo(){
return "main";
}
}
(2)@RequestMapping也可以加在类上,相当于是多了一层路径(虚拟路径),区分不同类中相同的action的名称
前端请求:多一个mvc路径
<%--发送超链接--%>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/mvc/demo.action">发送请求</a>后端代码:在类上和方法上都有@RequestMapping注解
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mvc")
public class DemoAction {
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public String demo(){
return "main";
}
}
(3)此注解可区分get请求和post请求
前端请求:提交一个form表单
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<--发送超链接-->
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/mvc/demo.action" method="get" />
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/mvc/demo.action" method="post" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</body>
</html>
后端代码:使用method属性,指定接收的是get请求还是post请求
使用@RequestMapping注解的method属性method = RequestMethod.GET或.POST!
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mvc")
public class DemoAction {
@RequestMapping(value = "/demo",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String demo(){
System.out.println("发送Get请求");
return "main";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/demo",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String demo1(){
System.out.println("发送Post请求");
return "main";
}
}
(4) 补充:客户端浏览器常用的请求方式,及其提交方式有以下几种
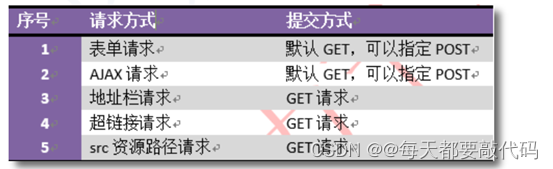
也就是说,只要指定了处理器方法匹配的请求提交方式为 POST请求,则相当于指定了请求发送的方式:要么使用表单请求,要么使用 AJAX 请求,其它请求方式被禁用。当然,若不指定 method 属性,则无论是 GET 还是 POST 提交方式,均可匹配!
接下来我们就来分析一下可优化的内容,也就是下面要讲解的知识点:

2. 五种数据提交的方式
(1)单个提交数据
在后端方法中声明一个和前端表单提交的参数名称相同的参数,由框架按照名称直接注入。
前端代码:
<h1>1.单个数据提交</h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/one.action">
姓名:<input type="text" name="myname"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="myage"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>后端代码:
传的参数必须与前面表中的属性名相同,(myage+10)的目的是为了测试进行了自动类型转换,转换成了int类型。
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class DataSubmitAction {
@RequestMapping("/one")
// 方法中的参数与form表单中name属性的值是相同的---按照名字注入
public String one(String myname,int myage){
System.out.println("myname="+myname+",myage="+(myage+10));
return "main";
}
}
执行结果:

核心:
①表中form中的属性,例如:myname和myage的属性名与action方法参数的名称一致!
②这样就可以完成自动注入值,并且可以自动进行类型的转换!
(2)对象封装提交数据
在方法中声明一个自定义的实体类参数,框架调用实体类中相应的setter方法注入属性值,只要保证实体类中成员变量的名称与提交请求的name属性值一致即可。
定义实体类:
package com.bjpowernode;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
前端代码:
<h1>2.对象封装数据提交</h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/two.action">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>后端代码:
这里传的参数不再是表单中的属性名称,我们借用了实体类User,所以参数就是实体类User
@RequestMapping("/two")
public String two(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "main";
}执行结果:

核心:
①在提交请求中,保证请求参数的名称与实体类中成员变量的名称一致,则可以自动创建对象、可以自动提交数据、自动类型转换、自动封装数据到对象中。
②方法的参数不再是零散的数据,而是我们封装好的实体类User对象。
(3)动态占位符提交(用的少)
仅限于超链接或地址栏提交数据,它是一杠一值(传数据)、一杠一大括号(接收数据),使用注解@PathVariable(路径变量)来解析。
前端代码:
先回忆以前的提交方式,使用?与&的方式,例如:uri/?name=value&name=value的方式
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/three.action?name=张三&age=20" />
现在使用一杠一值的方式,注意位置是在“.action”页面的前面!
<h1>3.动态占位符数据提交</h1>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/three/王五/20.action" />后端代码:
前端使用一杠一值传,后端使用一杠一大括号接收,里面的参数名随意,但是需要@PathVariable注解:若地址栏中大括号里{}的变量与下面方法的变量保持一致,此时路径变量@PathVariable注解中的value属性就可以省略;若变量没有保持一致,就需要使用路径变量@PathVariable的value属性指定上面地址栏大括号里的变量!
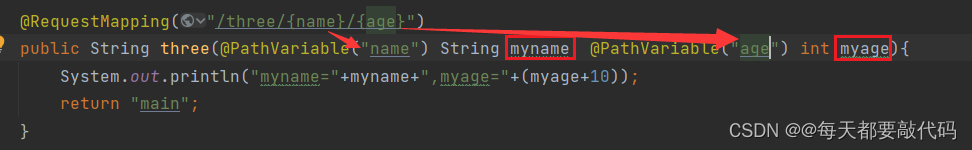
@RequestMapping("/three/{myname}/{myage}")
public String three(@PathVariable String myname, @PathVariable int myage){
System.out.println("myname="+myname+",myage="+(myage+10));
return "main";
}执行结果:

核心:
①前端使用一杠一值的形式提交,后端使用一杠一大括号的形式接收,这里大括号里面的参数随意
②方法中的参数需要使用@PathVariable注解,没有任何属性,这是参数和下面方法中的参数一致
③假如参数不一致,@PathVariable注解就需要带上上面@RequestMapping注解中的参数;例如:
(4)映射名称不一致
form表单中提交请求参数与action方法的形参的名称不一致,使用注解@RequestParam来解析!
前端代码:
前端提交的数据,name属性的值是name和age
<h1>4.映射名称不一致</h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/four.action">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>后端代码:
后端接收数据,方法中的属性名称是myname和myage,名称不一致,如何解决?使用@RequestParam注解
@RequestMapping("/four")
public String four(@RequestParam("name") String myname, @RequestParam("age") int myage){
System.out.println("myname="+myname+",myage="+(myage+10));
return "main";
}执行结果:

核心:
①前端提交数据的表单,属性名我们可能不知道;后端我们编写代码方法中的属性又是根据我们自己的意愿编写,怎么让两者之间建立联系?使用@RequestParam注解即可。
(5)手工提取数据(了解)
使用原始的方式:在方法参数中声明一个HttpServletRequest request对象,使用request的getParameter()获取表单提交的数据,这样得到的数据还要手工进行数据类型的转换。
前端代码:
<h1>5.手工提交</h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/five.action">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>后端代码:
此时方法中的参数是HttpServletRequest对象,可以拿来直接用;然后调用getParameter方法根据key获取对应的value值。
注:从请求中得到的数据都是String类型,要想得到其它类型需要进行手动转换。
@RequestMapping("/five")
public String five(HttpServletRequest request){
// 根据key获取value
String name = request.getParameter("name");
// 需要手动转换为int类型
int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("age"));
System.out.println("name="+name+",age="+(age+10));
return "main";
}
执行结果:

核心:
①方法的参数传一个HttpServletRequest对象,不需要创建直接可以使用,然后调用getParameter方法获取到value;想要其它类型的数据还需要自己手动进行转换。
3. 请求参数中文乱码解决
(1)对于前面所接收的请求参数,若是Post请求,并含有中文,则会出现中文乱码问题。Spring对于请求参数中的中文乱码问题,给出了专门的字符集过滤器:spring-web-5.2.5.RELEASE.jar 的org.springframework.web.filter 包下的 CharacterEncodingFilter 类
(2)在web.xml中配置过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter,建议一开始就放在最前面!
(1)解决方案
在 web.xml配置中注册字符集过滤器,即可解决 Spring 的请求参数的中文乱码问题。不过,最好将该过滤器注册在其它过滤器之前,因为过滤器的执行是按照其注册顺序进行的。
<!--注册过滤器:解决post请求乱码问题-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encode</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!--指定字符集-->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--强制request使用字符集encoding-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--强制response使用字符集encoding-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encode</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
(2)CharaterEncodingFilter源码分析
三个参数:编码方式encoding、forceRequestEncoding和forceResponseEncoding默认值都是false
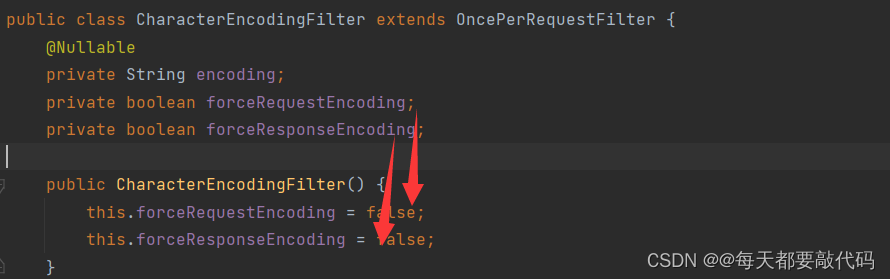
所在在配置中设置encoding值为UTF-8,另外两个参数设置成true后,会走以下代码

4. action方法的返回值
(1)String:客户端资源的地址,自动拼接前缀和后缀,还可以屏蔽自动拼接字符串,可以指定返回的路径。
(2)Object:返回json格式的对象,自动将对象或集合转为json,使用jackson工具进行转换,必须要添加jackson依赖,一般用于ajax请求。
(3)void:无返回值,一般用于ajax请求。
(4)基本数据类型:用于ajax请求。
(5)ModelAndView:返回数据和视图对象,现在用的很少。
完成ajax请求访问服务器,返回学生集合
第一步:增加jackson依赖
<!--添加jackson依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.8</version>
</dependency>第二步:springmvc配置
不需要视图解析器(InternalResourceViewResolver),发送的是ajax请求,哪里来回到哪里去,但是需要添加注解驱动<mvc:annotation-driven/>,这个注解驱动是用来解析@ResponseBody注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!--包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bjpowernode.controller"/>
<!--添加注解驱动,专门处理ajax请求-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
</beans>第三步:web.xml配置
配置解决中文乱码问题和注册springmvc!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--注册过滤器:解决post请求乱码问题-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encode</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!--指定字符集-->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--强制request使用字符集encoding-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--强制response使用字符集encoding-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encode</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--注册springmvc-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>第四步:在webapp目录下新建js目录,添加jQuery函数库,在index.jsp页面上导入函数库
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
<%--引入JQuery库--%>
<script src="js/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<a href="javascript:showStu()">访问服务器返回学生集合</a>
<div id="mydiv">等待服务器返回数据</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 使用JQuery封装的ajax()方法发送请求
$.ajax({
url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/list.action",
type:"get",
dataType:"json",
success:function (stuList){
var s = "";
$.each(stuList,function (i,stu) {
s += stu.name + "---"+stu.age+"<br>";
});
// 回显数据到div
$("#mydiv").html(s);
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Student类:因为上面是要返回学生集合
package com.bjpowernode.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
第五步:服务器端代码
@ResponseBody的作用:其实是将java对象转为json格式的数据,使用<mvc:annotation-driven/>就是专门用来处理@ResponseBody注解的!
注:发送ajax请求一定要使用@ResponseBody注解!
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import com.bjpowernode.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class StudentListAction {
@RequestMapping("/list")
@ResponseBody // 处理ajax一定要加@ResponseBody注解
public List<Student> list(){
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加数据
Student stu1 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student stu2 = new Student("李四", 19);
Student stu3 = new Student("王五", 20);
list.add(stu1);
list.add(stu2);
list.add(stu3);
// 实际上SpringMVC框架会将list集合自动转为json数组
return list;
}
}
第六步:测试
点击超链接前

点击超链接后

5. SpringMVC的四种跳转方式
默认的跳转是请求转发,直接跳转到jsp页面展示,还可以使用框架提供的关键字redirect:,进行一个重定向操作,包括重定向页面和重定向action,使用框架提供的关键字forward:,进行服务器内部转发操作,包括转发页面和转发action。
注:当使用redirect:和forward:关键字时,视图解析器中前缀后缀的拼接就无效了。
首先我们先通过一张图区分一下转发和重定向:
我们也可以通过一个生活中的例子来理解:有三个人你、我、他
转发:你给我打电话问事情,我不知道,我把我的电话给了身边的他;但是本质上还是我的电话,显示的地址就是我的地址:http://localhost:8080/one.action
重定向:你给我打电话问事情,我不知道,把电话挂了;你重新给他打电话进行询问,所以本质是他的电话,显示的地址就是他的地址:http://localhost:8080/main.jsp

(1)请求转发的跳转代码
index.jsp:
两种转发方式,一种是我们前面一直用的,默认的跳转方式;另一种是跳转到其它的action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/one.action">1.请求转发页面(默认)</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/two.action">2.请求转发action</a>
</body>
</html>
Other.action:第二种跳转到其它action,肯定需要定义一个其它的action
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class OtherAction {
@RequestMapping("/other")
public String other(){
System.out.println("这是other的action访问........");
return "main";
}
}
测试:
解释forward:是屏蔽视图解析器中前缀和后缀的拼接;
如果没有forward:,最终展现的结果就是admin/other.action!
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class JumpAction {
@RequestMapping("/one")
public String one(){
// 默认使用视图解析器拼接前缀和后缀进行页面跳转
System.out.println("这是请求转发页面跳转........");
return "main";
}
@RequestMapping("/two")
public String two(){
// 使用forward:可以屏蔽前后缀的拼接
return "forward:/other.action";
}
}
结果1:请求转发页面是从index.jsp--->one.action--->main.jsp,最终地址是one.action的地址

结果2:请求转发页面是从index.jsp--->two.action--->other.action--->main.jsp,最终地址是two.action的地址
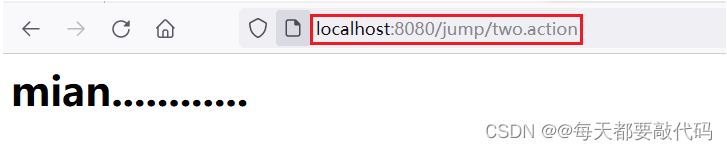
结论:最终的地址都是第一次页面跳转的地址,与前面我们分析的一致!
(2)重定向的跳转代码
index.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/three.action">1.重定向页面</a><br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/four.action">2.重定向action</a><br>
</body>
</html>
测试:
解释redirect:也是屏蔽视图解析器中前缀和后缀的拼接;无论是重定向页面还是重定向其它action,都要使用redirect。
注:在重定向页面时需要写上页面的绝对路径,例如:redirect:/admin/main.jsp,对于重定向其它action和转发相似。
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class JumpAction {
@RequestMapping("/three")
public String three(){
// 屏蔽视图解析器拼接前缀和后缀进行页面跳转
System.out.println("这是重定向页面跳转........");
return "redirect:/admin/main.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("/four")
public String four(){
// 屏蔽视图解析器拼接前缀和后缀进行页面跳转
System.out.println("这是重定向其它action........");
return "redirect:/other.action";
}
}
结果1:从index.jsp--->three.action,发现是重定向到main.jsp,所以是又重新发出请求从index.jsp
--->main.jsp,最终地址是main.jsp的地址

结果2:先从index.jsp--->four.action,发现是是重定向到other.action,
所以是又重新发出请求从index.jsp--->other.action,然后other.action又是转发到main.jsp,最终地址是other.action的地址

结论:最终的地址是最后一次重定向的地址,与前面我们分析的一致!
注:我们也可以利用forword和redirect随便跳转页面,后面跟绝对路径即可;但是转发可以携带数据,重定向不能携带数据(容易数据丢失);并且转发是只能在服务器内部转发,重定向可以访问外部资源!
6. SpringMVC支持的默认参数类型
这些类型不需要创建,只要写在方法参数中就可以使用了(常见的)
(1)HttpServletRequest 对象
(2)HttpServletResponse 对象
(3)HttpSession 对象
(4)Model/ModelMap 对象
(5)Map<String,Object>对象
注意:Map、Model、ModelMap和request一样,都使用请求作用域进行数据传递,所以服务器端的跳转必须是请求转发,这样才能携带数据。
index.jsp页面,也可以携带数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<br><br><br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/data.action?data=李四">访问服务器,进行数据携带跳转</a><br>
</body>
</html>
DataAction类,存入数据
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import com.bjpowernode.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
public class DataAction {
@RequestMapping("/data")
public String data(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
HttpSession session,
Model model,
Map map,
ModelMap modelMap
){
// 创建一个数据
Student stu = new Student("张三", 22);
// 传递数据
request.setAttribute("requestStu",stu);
session.setAttribute("sessionStu",stu);
model.addAttribute("modelStu",stu);
map.put("mapStu",stu);
modelMap.addAttribute("modelMapStu",stu);
return "main";
}
}
跳转到main.jsp取出数据
注:取数据,可以从DataAction类中取出存入的数据;也可以直接从index.jsp中取出携带的数据,但是需要使用 “param.” 的方式!
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--取出数据--%>
requestStu对应数据:${requestStu}<br>
sessionStu对应数据:${sessionStu}<br>
modelStu对应数据:${modelStu}<br>
mapStu对应数据:${mapStu}<br>
modelMapStu对应数据:${modelMapStu}<br>
从index.jsp页面中来的数据:${param.data}
</body>
</html>
测试结果:都能正常取出数据

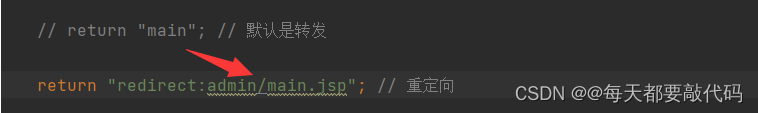
注意:如果使用重定向呢?
如果使用重定向,只有session域的数据还在,其它数据都会丢失!
执行结果:

7. 日期处理
日期类型不能自动注入到方法的参数中,需要单独做转换处理。
(1)日期注入
第一种情况:单个日期注入
使用注解的方式对日期进行格式化:@DateTimeFormat,此注解必须搭配springmvc.xml文件中的<mvc:annotation-driven>标签一起使用!
index.jsp中表单提交日期格式的字符串
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/mydate.action">
日期:<input type="date" name="mydate">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
springmvc.xml中添加注解驱动
<!--添加注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />MyDateAction程序
①@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")是把提交过来的字符串转换为日期格式
②new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd")是为了格式化日期
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Controller
public class MyDateAction {
// 用来格式化日期
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
@RequestMapping("/mydate")
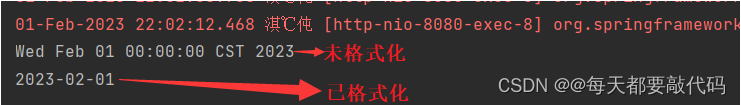
public String MyDate(@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date mydate){
// 未格式化的日期
System.out.println(mydate);
// 格式化的日期
System.out.println(sdf.format(mydate));
return "main";
}
}
执行结果:
第二种情况:类中全局日期处理
注册一个@InitBinder注解,用来解析本类中所有的日期类型,自动转换!
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.CustomDateEditor;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Controller
public class MyDateAction {
// 用来格式化日期
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
// 注册一个全局的日期处理注解
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder){
dataBinder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class,new CustomDateEditor(sdf,true));
}
@RequestMapping("/mydate")
public String MyDate(Date mydate){
System.out.println(sdf.format(mydate));
return "main";
}
}
核心代码解析:
①WebDataBinder参数表示数据绑定,表示所有的数据都可以通过它进行绑定!
②调用registerCustomEditor方法表示自定义一个转换器:
第一个参数是要转换的类型:Date.class
第二个参数是使用什么工具去转?
创建一个CustomDateEditor对象:一个参数是格式化的日期的sdf,另一个参数是boolean类型,true表示日期为空也不报错。
// 注册一个全局的日期处理注解,下面这个方法需要自己编写
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder){
dataBinder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class,new CustomDateEditor(sdf,true));
}补充:如果日期作为成员变量,例如在User类当中有一个属性是Date,那么既可以在属性上使用@DateTimeFormat注解,也可以在对应的set方法setDate上面使用@DateTimeFormat注解

(2)日期显示
第一种情况:单个数据显示
单个日期传递很简单,直接格式化好以后,放到request域当中即可
传数据
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.CustomDateEditor;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Controller
public class MyDateAction {
// 用来格式化日期
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
// 注册一个全局的日期处理注解
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder){
dataBinder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class,new CustomDateEditor(sdf,true));
}
// 存入数据
@RequestMapping("/mydate")
public String MyDate(Date mydate, HttpServletRequest request){
// 格式化以后放到request域当中,传过去的实际上是日期格式的字符串
request.setAttribute("mydate",sdf.format(mydate));
return "showdate";
}
}
取数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
单个日期提交数据:${mydate}
</body>
</html>
第二种情况:实体类对象的成员变量是日期类型
如果是list集合当中的实体类对象的成员变量是日期类型,则必须使用JSTL标签库进行显示,使用JSTL的步骤:
①添加依赖
②在页面上导入标签库
③使用标签遍历显示数据
先创建一个User类
package com.bjpowernode.pojo;
import java.util.Date;
public class User {
private String name;
// 实体类当中含有Date类型
private Date birth;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, Date birth) {
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", birth=" + birth +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
}
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/list.action">显示集合对象的日期成员</a>
</body>
</html>
存入数据
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import com.bjpowernode.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.CustomDateEditor;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class MyDateAction {
// 用来格式化日期
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String list(HttpServletRequest request) throws ParseException {
User u1 = new User("张三", sdf.parse("1999-01-01"));
User u2 = new User("李四", sdf.parse("1999-02-02"));
User u3 = new User("王五", sdf.parse("1999-03-03"));
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(u1);
list.add(u2);
list.add(u3);
// 放到request当中
request.setAttribute("userList",list);
return "showdate";
}
}
获取数据
①添加JSTL依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>②在页面上导入标签库
<%--导入jstl核心标签库--%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--导入jstl格式化标签库--%>
<%@taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>③使用标签格式化和遍历显示数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
<%--导入jstl核心标签库--%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--导入jstl格式化标签库--%>
<%@taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
</head>
<body>
单个日期提交数据:${mydate}
<br><br>
<h2>学生集合</h2>
<table width="50%" border="1px">
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>生日</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${userList}" var="user">
<tr>
<td>${user.name}</td>
<td><fmt:formatDate value="${user.birth}" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd"></fmt:formatDate> </td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
执行结果:

补充:JSON中的日期显示
需要在类中的成员变量的getXXX方法上加@JsonFormat注解

8. <mvc:annotation-driven/>标签的使用
前言:目前我们发送ajax请求和日期转换都使用了这个标签,功能很强大!
<mvc:annotation-driven/>会自动注册两个bean(俩个帮手),分别为DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping和AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter。是springmvc为@controller分发请求所必须的,除了注册了这两个bean,还提供了很多支持。
(1)支持使用ConversionService 实例对表单参数进行类型转换;
(2)支持使用 @NumberFormat 、@DateTimeFormat;
(3)注解完成数据类型的 格式化;
(4)支持使用 @RequestBody 和 @ResponseBody 注解;
(5)静态资源的分流也使用这个标签;
9. 资源在WEB-INF目录下
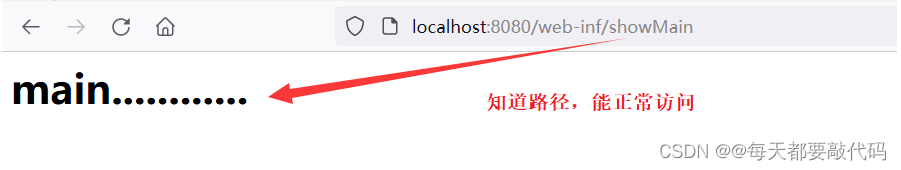
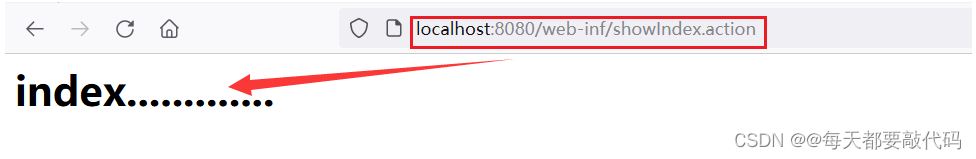
(1)将动态资源放在WEB-INF目录下,这样可以保证资源的安全性;在WEB-INF目录下的动态资源不可以直接访问,必须要通过请求转发的方式进行访问。这样避免了通过地址栏直接对资源的访问,重定向也无法访问动态资源。
第一步:在WEB-INF目录下创建一个jsp目录,在目录下创建index.jsp和main.jsp

开启Tomcat服务器,使用路径直接访问,根本访问不到,更安全了

第二步:只能通过请求转发的方式进行访问
WebInfAction程序
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class WebInfAction {
@RequestMapping("/showIndex")
public String showIndex(){
System.out.println("访问index.jsp页面");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/showMain")
public String showMain(){
System.out.println("访问main.jsp页面");
return "main";
}
}
需要地址的拼接,所以springmvc.xml中也要修改视图解析器的前缀
<!--视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!--<property name="prefix" value="/admin/"></property>-->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>第三步:进行测试,直接输入地址栏,通过转发的方式,可以正常访问
注:这样就相当于把index.jsp和main.jsp保护起来了,不能直接访问,要想访问必须通过WebInfAction才可以
(2)去掉后缀action的访问
修改web.xml,把<url-pattern>标签的路径修改为“/”,表示拦截所有的请求;优先访问的是没有后缀的,然后再去访问带.jsp或.action的
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<!-- <url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>测试:以后访问就可以不需要后缀直接访问
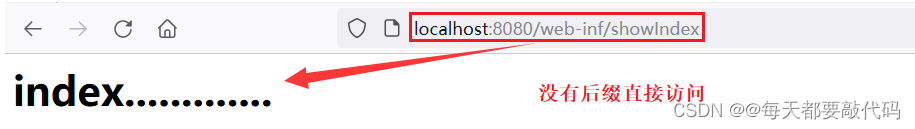
缺点:知道http://localhost:8080/web-inf/showIndex这个地址也能直接访问到,所以就需要增加一个权限验证功能。
(3)登录页面处理:登录成功才让你访问,登录失败打回原始的登录页面
增加login.jsp登录页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
WebInfAction中做登录判断
package com.bjpowernode.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller
public class WebInfAction {
// 首先要跳转到登录页面
@RequestMapping("/showLogin")
public String submit(){
System.out.println("访问login.jsp进行登录");
return "login";
}
// 跳转到login.jsp后,在进行判断
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String name, String pwd, HttpServletRequest request){ // 与前端保持一致,提交的数据自动吸过来
// 进行判断,equalsIgnoreCase忽略大小写
if ("root".equalsIgnoreCase(name) && "123".equalsIgnoreCase(pwd)){
// 登录成功,可以访问main.jsp
return "main";
}else {
// HttpServletRequest是用来提示登录失败的信息
request.setAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码不正确");
// 登录失败,跳转到登录页面login.jsp,在login.jsp中${msg}打印这个提示错误的信息
return "login";
}
}
}
登录失败:会有提示,并且保持原来的登录页面

登录成功:正常跳转访问

存在的问题:还是同样的道理,假如我们知道main.jsp的路径,直接在地址栏上输出进行访问也可以,根本就不需要登录,所以此时的登录页面就是一个摆设;这就需要我们接下来学习拦截器!