“本文基于Android13源码,分析Input系统中,事件分发的实现原理“
整个事件分发到事件的确认过程很长,如果读者只是想大概了解一下,可以直接看末尾总结部分的流程图。
1. 前言
在文章之前,有必要提一下InputReader。其在启动的时候,会创建一个InputReader线程,用于从/dev/input节点获取事件,转换成EventEntry事件加入到InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue。详情见 Input系统—InputReader线程
Inputdispatcher 则负责消费mInboundQueue中的事件,并将事件转化后发送给app端,他们的关系如下:

1.1 InputDispatcher
Inputdispatcher中,在线程里面调用到dispatchOnce方法,该方法中主要做:
- 通过dispatchOnceInnerLocked(),取出mInboundQueue 里面的 EventEntry事件
- 通过enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(),生成事件DispatchEntry并加入connection的
outbound队列。 - 通过startDispatchCycleLocked(),从outboundQueue中取出事件DispatchEntry, 重新放入connection的
waitQueue队列。 - 通过runCommandsLockedInterruptable(),遍历mCommandQueue队列,依次处理所有命令。
- 通过processAnrsLocked(),判断是否需要触发ANR。
- 在startDispatchCycleLocked()里面,通过inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent() 方法将按键事件分发给java层。publishKeyEvent的实现是在InputTransport.cpp 中
通过上面的概括,可以知道按键事件主要存储在3个queue中:
- InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue:存储的是从InputReader 送来的输入事件。
- Connection的outboundQueue:该队列是存储即将要发送给应用的输入事件。
- Connection的waitQueue:队列存储的是已经发给应用的事件,但是应用还未处理完成的。
1.2 InputEventInjectionResult
在处理按键分发过程中,经常会遇到该枚举,对应含义如下
enum InputEventInjectionResult {
/* (仅限内部使用)指定注入挂起且其结果未知 */
PENDING = -1,
/* 事件注射成功. */
SUCCEEDED = 0,
/* 注入失败,因为注入的事件未针对相应的窗口 */
TARGET_MISMATCH = 1,
/* 注入失败,因为没有可用的输入目标。*/
FAILED = 2,
/* Injection failed due to a timeout. */
TIMED_OUT = 3,
}
2. 事件分发
InputDispatcher 在start() 方法中会启动一个线程,在被唤醒后会调用到dispatchOnce 方法,在该方法中,通过调用dispatchOnceInnerLocked来分发事件
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{
...
// 如果没有挂起的命令,则运行调度循环。调度循环可能会将命令排入队列,以便稍后运行。
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
....
}
// 等待回调、超时或唤醒。
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
2.1 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
dispatchOnceInnerLocked主要是:
-
从mInboundQueue 中取出mPendingEvent
-
通过mPendingEvent的type决定事件类型和分发方式。
-
最后如果处理了事件,就处理相关的回收。
主要代码如下:
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
...
// 优化应用切换的延迟。本质上,当按下应用程序切换键(HOME)时,我们会开始一个短暂的超时。
// 当它过期时,我们会抢占调度并删除所有其他挂起的事件。
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime; // mAppSwitchDueTime是应用切换到期时间
if (mAppSwitchDueTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mAppSwitchDueTime; // 更新下一次唤醒的时间
}
// 当前没有PendingEvent(即EventEntry),则取一个
if (!mPendingEvent) {
// 1、mInboundQueue 为空
if (mInboundQueue.empty()) {
// 如果合适就合成一个重复按键。
if (mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry) {
if (currentTime >= mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime) {
// 用于创建一个新的repeat按键
mPendingEvent = synthesizeKeyRepeatLocked(currentTime);
} else {
if (mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime;
}
}
}
// 如果没有PendingEvent,就直接返回
if (!mPendingEvent) {
return;
}
} else {
// 2、mInboundQueue不为空,就从队列前面取一个PendingEvent
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.front();
mInboundQueue.pop_front();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
}
if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
// 根据当前的event 类型,post 一个 command 到 mCommandQueue
// 最后是调用到Java层的PowerManagerService#userActivityFromNative()
pokeUserActivityLocked(*mPendingEvent);
}
}
// 现在我们有一个事件要发送。所有事件最终都会以这种方式取消排队和处理,即使我们打算删除它们。
...
bool done = false;
DropReason dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED;
...
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
...
case EventEntry::Type::KEY: {
...
// 最后会调用到dispatchEventLocked
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, keyEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
...
// 最后会调用到dispatchEventLocked
done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, motionEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
}
if (done) {
if (dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
// 事件没有被丢弃。找到对应的原因并通知
dropInboundEventLocked(*mPendingEvent, dropReason);
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
// 将mPendingEvent 置为 Null,方便下次重新获取
releasePendingEventLocked();
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // force next poll to wake up immediately
}
}
2.1.1 dispatchKeyLocked
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchKeyLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, std::shared_ptr<KeyEntry> entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
//预处理:主要处理按键重复问题
if (!entry->dispatchInProgress) {
...
if (mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry &&
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->keyCode == entry->keyCode &&
// 我们已经看到连续两个相同的按键,这表明设备驱动程序正在自动生成键重复。
// 我们在这里记下重复,但我们禁用了自己的下一个键重复计时器,因为很明显我们不需要自己合成键重复。
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->deviceId == entry->deviceId) {
// 确保我们不会从其他设备获取密钥。如果按下了相同的设备 ID,则新的设备 ID 将替换当前设备 ID 以按住重复键并重置重复计数。
// 将来,当设备ID上出现KEY_UP时,请将其删除,并且不要停止当前设备上的密钥重复。
entry->repeatCount = mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->repeatCount + 1;
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime = LONG_LONG_MAX; // 不要自己生成重复
} else {
//不是重复。保存按键down状态,以防我们稍后遇到重复。
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime = entry->eventTime + mConfig.keyRepeatTimeout;
}
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = entry;
...
}
// 处理policy 上次要求我们重试的情况
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_TRY_AGAIN_LATER) {
// 当前时间 < 唤醒时间,则进入等待状态
if (currentTime < entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime) {
if (entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime;
}
return false; // 等到下次醒来
}
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_UNKNOWN;
entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime = 0;
}
// 给policy提供拦截key的机会。
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_UNKNOWN) {
if (entry->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
sp<IBinder> focusedWindowToken =
mFocusResolver.getFocusedWindowToken(getTargetDisplayId(*entry));
auto command = [this, focusedWindowToken, entry]() REQUIRES(mLock) {
doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingCommand(focusedWindowToken, *entry);
};
postCommandLocked(std::move(command));
return false; // wait for the command to run
} else {
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_CONTINUE;
}
} else if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_SKIP) {
if (*dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
*dropReason = DropReason::POLICY;
}
}
// 如果删除事件,则清理。
if (*dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
setInjectionResult(*entry,
*dropReason == DropReason::POLICY ? InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED
: InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED);
mReporter->reportDroppedKey(entry->id);
return true;
}
// 寻找输入目标
std::vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult =
findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING) {
return false;
}
setInjectionResult(*entry, injectionResult);
if (injectionResult != InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED) {
return true;
}
// 从事件或焦点显示添加监视器通道。
addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, getTargetDisplayId(*entry));
// 分发按键
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
2.1.2 dispatchMotionLocked
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, std::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> entry,DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
...
// 是否是指针事件
const bool isPointerEvent = isFromSource(entry->source, AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER);
// Identify targets.
std::vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
bool conflictingPointerActions = false;
InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult;
if (isPointerEvent) { // 指针事件。(例如触摸屏)
// 查找已锁定的触摸窗口目标,主要根据读取到的触控事件所属的屏幕displayid、x、y坐标位置等属性来确认目标窗口
// 这里不是我们的重点
injectionResult =
findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime, &conflictingPointerActions);
} else { // 非触摸事件。(例如轨迹球)
injectionResult =
findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
}
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING) {
// 如果是pending就直接返回
return false;
}
....
// 从事件或焦点显示添加监视器通道。
addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, getTargetDisplayId(*entry));
// 分发事件
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
2.2 dispatchEventLocked
dispatchEventLocked 主要是遍历inputTargets,通过prepareDispatchCycleLocked分发事件。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
...
for (const InputTarget& inputTarget : inputTargets) {
sp<Connection> connection =
getConnectionLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
if (connection != nullptr) {
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
}
}
2.3 prepareDispatchCycleLocked
prepareDispatchCycleLocked内部又会调用enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked方法。
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
// 不分裂。按原样将事件的调度条目排队。
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
2.4 enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked
主要做两个事情:
- 1)将请求模式的调度条目排队。
- 2)启动调度周期。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.empty();
// 将请求模式的调度条目排队。
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT);
...
// 如果出站队列以前为空,请开始调度周期。
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
}
}
2.4.1 enqueueDispatchEntryLocked
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked 会创建一个新的DispatchEntry,然后将DispatchEntry 加入到connection的outboundQueue中
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget,
int32_t dispatchMode) {
// 这是一个新事件。将新的调度条目排队到此连接的出站队列中。
std::unique_ptr<DispatchEntry> dispatchEntry =
createDispatchEntry(inputTarget, eventEntry, inputTargetFlags);
...
// 将生成的 dispatchEntry 加入到 connection的outboundQueue 中
connection->outboundQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry.release());
traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
}
2.4.2 startDispatchCycleLocked
该方法主要通过connection 发布最终的事件,至此,InputDispatcher完成事件的发布,并且将发布的事件保存在connection的waitQueue中。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
while (connection->status == Connection::Status::NORMAL && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {
// 从outboundQueue 队列中取出 DispatchEntry
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.front();
// 发布事件
status_t status;
const EventEntry& eventEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
switch (eventEntry.type) {
case EventEntry::Type::KEY: {
...
// 发布按键事件
status = connection->inputPublisher
.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq ...);
break;
}
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
...
// 发布运动事件。
status = connection->inputPublisher
.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq ...);
break;
}
....
}
// 如果status 已赋值
if (status) {
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
if (connection->waitQueue.empty()) {
// pip 管道满了导致无法发布事件。
// 该问题是出乎意料的,因为等待队列是空的,所以管道应该是空的
// 将outboundQueue,waitQueue 队列清空,并释放队列中的DispatchEntry 对象
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
} else {
// 管道已满,并且waitQueue 不为空,我们正在等待应用程序完成处理一些事件,然后再向其发送更多事件。
}
} else {
// 将outboundQueue,waitQueue 队列清空,并释放队列中的DispatchEntry 对象
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
}
return;
}
// 将事件从outboundQueue中移除
connection->outboundQueue.erase(std::remove(connection->outboundQueue.begin(),
connection->outboundQueue.end(),
dispatchEntry));
// 在waitQueue 尾部重新插入
connection->waitQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry);
}
}
2.5 publishMotionEvent
查看connection的头文件,可以知道connection->inputPublisher 是InputPublisher类
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/Connection.h
class Connection : public RefBase {
public:
InputPublisher inputPublisher;
}
InputPublisher class的定义如下,负责将输入事件发布到输入通道。
> frameworks/native/include/input/InputTransport.h
// 负责将输入事件发布到输入通道。
class InputPublisher {
....
private:
std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> mChannel;
}
class InputChannel : public Parcelable {
}
publishMotionEvent 对应的实现如下
> frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent(
uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, int32_t deviceId, int32_t source, int32_t displayId ..) {
....
InputMessage msg;
// 设置event的参数
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::MOTION;
msg.body.motion.action = action;
....
// 调用InputChannel的sendMessage方法
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
mChannel即 InputChannel
> frameworks/native/include/input/InputTransport.h
private:
std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> mChannel;
2.6 runCommandsLockedInterruptable
dispatchOnceInnerLocked已经分析完,我们再次回到dispatchOnce,分析runCommandsLockedInterruptable方法
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{
...
// 运行所有挂起的命令(如果有)。如果运行了任何命令,则强制下一次轮询立即唤醒。
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
...
}
}
该方法很简单,就是遍历mCommandQueue 执行对应的command。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptable() {
do {
auto command = std::move(mCommandQueue.front());
mCommandQueue.pop_front();
// Commands are run with the lock held, but may release and re-acquire the lock from within.
// 命令在锁保持的情况下运行,但可能会从内部释放并重新获取锁。
command();
} while (!mCommandQueue.empty());
return true;
}
通过postCommandLocked 方法将command添加到队列中
void InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command&& command) {
mCommandQueue.push_back(command);
}
2.7 调用栈
native层的事件分发调用栈如下
libs/input/InputTransport.cpp : InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::dispatchKeyLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::start()
3. InputChannel
InputChannel负责将消息发送给到app端,那它是如何做到的呢?
3.1 sendMessage
InputChannel的sendMessage 方法定义如下,
> frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
....
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
nWrite = ::send(getFd(), &cleanMsg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
....
return OK;
}
其中fd很关键,当fd 写入消息的时候,会唤醒处于epoll_wait 状态的线程(原理跟handler一样)
那他是如何跟app端的fd绑定的呢?
3.2 客户端创建FD
在ViewRootImpl的setView方法中,
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mWinFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel); // 将mInputChannel 注册到WMS中
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
// 创建app端监听,即WindowInputEventReceiver 作为事件的接收端
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
}
mWindowSession.addToDisplay 对应AIDL实现为
> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java
class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
@Override
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window .... DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
// mService 即 WindowManagerService
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outFrame,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outDisplayCutout, outInputChannel);
}
}
WindowManagerService实现如下
> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow,
appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid,
session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
final boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null
&& (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0);
if (openInputChannels) {
// 通过WindowState 打开对应的inputChannel
win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel);
}
}
WindowState实现如下
> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java
// 输入调度程序使用的输入通道和输入窗口句柄。
final InputWindowHandle mInputWindowHandle;
void openInputChannel(InputChannel outInputChannel) {
String name = getName();
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);
mInputChannel = inputChannels[0];
mClientChannel = inputChannels[1];
mInputWindowHandle.inputChannel = inputChannels[0];
if (outInputChannel != null) {
mClientChannel.transferTo(outInputChannel);
mClientChannel.dispose();
mClientChannel = null;
} else {
mDeadWindowEventReceiver = new DeadWindowEventReceiver(mClientChannel);
}
// 将inputChannel注册到InputManagerService中
mService.mInputManager.registerInputChannel(mInputChannel, mInputWindowHandle);
}
InputManagerService 如下,最后注册到native中
> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
// 注册输入通道,以便将其用作输入事件目标。
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel,
InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle) {
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, false);
}
3.3 native层注册
nativeRegisterInputChannel 实现如下
> frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj, jobject inputWindowHandleObj, jboolean monitor) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
if (inputChannel == NULL) {
throwInputChannelNotInitialized(env);
return;
}
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle =
android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle(env, inputWindowHandleObj);
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(
env, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
if (status) {
std::string message;
message += StringPrintf("Failed to register input channel. status=%d", status);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.c_str());
return;
}
if (! monitor) {
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
}
}
3.4 接收端
3.4.1 初始化
WindowInputEventReceiver对应构造函数如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper);
}
}
其父类实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
public InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
mInputChannel = inputChannel;
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue(); // UI线程的looper
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),
inputChannel, mMessageQueue); // 通过nativeInit 与inputChannel绑定
mCloseGuard.open("dispose");
}
3.4.2 nativeInit
> frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,
jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
// 获取主线程的消息队列
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
// 创建一个NativeInputEventReceiver对象
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,
receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue);
status_t status = receiver->initialize();
.....
receiver->incStrong(gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz); // retain a reference for the object
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(receiver.get());
}
3.4.3 NativeInputEventReceiver
initialize 实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
class NativeInputEventReceiver : public LooperCallback {
.....
}
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() {
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT);
return OK;
}
setFdEvents 如下
> frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
if (mFdEvents != events) {
mFdEvents = events;
int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();
if (events) {
//将FD添加到消息池中
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, NULL);
} else {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);
}
}
}
当事件分发的时候,looper会调用到NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent 方法
> system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
....
int callbackResult = response.request.callback->handleEvent(fd, events, data);
if (callbackResult == 0) {
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
removeSequenceNumberLocked(response.seq);
}
....
}
NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent 对应实现如下:
> frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
int NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent(int receiveFd, int events, void* data) {
....
if (events & ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT) {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
// 调用consumeEvents 来消费事件
status_t status = consumeEvents(env, false /*consumeBatches*/, -1, NULL);
mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "handleReceiveCallback");
return status == OK || status == NO_MEMORY ? 1 : 0;
}
}
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
.....
if (inputEventObj) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dispatching input event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
// 调用java层的InputEventReceiver#dispatchInputEvent方法
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj,
displayId);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
ALOGE("Exception dispatching input event.");
skipCallbacks = true;
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputEventObj);
}
}
4. Activity事件接收
4.1 WindowInputEventReceiver
从上面得知,事件会分发到InputEventReceiver#dispatchInputEvent方法中
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event, int displayId) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
onInputEvent(event, displayId);
}
WindowInputEventReceiver 重写了onInputEvent 方法
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
@Override
public void onInputEvent(InputEvent event, int displayId) {
enqueueInputEvent(event, this, 0, true);
}
...
}
4.2 ViewRooImpl
4.2.1 enqueueInputEvent
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
void enqueueInputEvent(InputEvent event,
InputEventReceiver receiver, int flags, boolean processImmediately) {
adjustInputEventForCompatibility(event);
QueuedInputEvent q = obtainQueuedInputEvent(event, receiver, flags);
// 始终按顺序对输入事件进行排队,而不考虑其时间戳。我们这样做是因为应用程序或 IME 可能会注入密钥事件以响应触摸事件,
// 我们希望确保按接收顺序处理注入的密钥,并且我们不能相信注入事件的时间戳是单调的。
QueuedInputEvent last = mPendingInputEventTail;
if (last == null) {
mPendingInputEventHead = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
} else {
last.mNext = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
}
mPendingInputEventCount += 1;
if (processImmediately) {
doProcessInputEvents(); // 分发输入事件
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
}
4.2.2 doProcessInputEvents
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
void doProcessInputEvents() {
// 传递队列中所有pending 输入事件。
while (mPendingInputEventHead != null) {
QueuedInputEvent q = mPendingInputEventHead; // QueuedInputEvent 封装了KeyEvent的信息
mPendingInputEventHead = q.mNext;
if (mPendingInputEventHead == null) {
mPendingInputEventTail = null;
}
q.mNext = null;
mPendingInputEventCount -= 1;
long eventTime = q.mEvent.getEventTimeNano();
long oldestEventTime = eventTime;
if (q.mEvent instanceof MotionEvent) {
MotionEvent me = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
if (me.getHistorySize() > 0) {
oldestEventTime = me.getHistoricalEventTimeNano(0);
}
}
// 更新输入事件时间
mChoreographer.mFrameInfo.updateInputEventTime(eventTime, oldestEventTime);
deliverInputEvent(q);// 给应用提供输入事件
}
}
4.2.3 deliverInputEvent
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private void deliverInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onInputEvent(q.mEvent, 0);
}
InputStage stage;
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
// shouldSkipIme 用于判断是否跳过输入法,默认是跳过
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
mUnhandledKeyManager.preDispatch((KeyEvent) q.mEvent);
}
if (stage != null) {
handleWindowFocusChanged();
stage.deliver(q); // 通过InputStage分发事件
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
}
我们先考虑跳过输入法的场景,故这里的stage是mFirstPostImeInputStage,mFirstPostImeInputStage在setView中赋值,对应是EarlyPostImeInputStage
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
....
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage,
"aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage);
InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage,"aq:ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage);
InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage,"aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix);
mFirstInputStage = nativePreImeStage;
mFirstPostImeInputStage = earlyPostImeStage;
....
}
4.5 InputStage
InputStage 是一个链表结构,其内部存储下一个InputStage,采用拦截器模式来分发事件。
4.5.1 deliver
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
abstract class InputStage {
private final InputStage mNext;
public final void deliver(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if ((q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED) != 0) {
forward(q);
} else if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
finish(q, false);
} else {
apply(q, onProcess(q)); // 调用到子类的onProcess来决定是否需要拦截该事件
}
}
}
4.6 EarlyPostImeInputStage
EarlyPostImeInputStage 的实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class EarlyPostImeInputStage extends InputStage {
public EarlyPostImeInputStage(InputStage next) {
super(next);
}
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
return processKeyEvent(q);
} else {
final int source = q.mEvent.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
return processPointerEvent(q);
}
}
return FORWARD; // 由于是触摸事件,这里会转发给下一个拦截器
}
.....
}
EarlyPostImeInputStage没有对触摸事件做拦截,故会分发给NativePostImeInputStage
4.7 NativePostImeInputStage
定义如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class NativePostImeInputStage extends AsyncInputStage
implements InputQueue.FinishedInputEventCallback {
public NativePostImeInputStage(InputStage next, String traceCounter) {
super(next, traceCounter);
}
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (mInputQueue != null) {
mInputQueue.sendInputEvent(q.mEvent, q, false, this);
return DEFER;
}
return FORWARD;
}
}
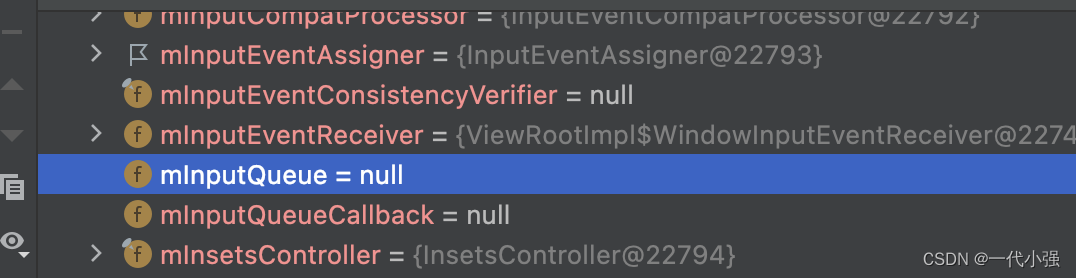
mInputQueue 是ViewRootImpl的变量,通过debug发现mInputQueue为null,故会继续转发给ViewPostImeInputStage。
4.8 ViewPostImeInputStage
实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class ViewPostImeInputStage extends InputStage {
public ViewPostImeInputStage(InputStage next) {
super(next);
}
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
return processKeyEvent(q);
} else {
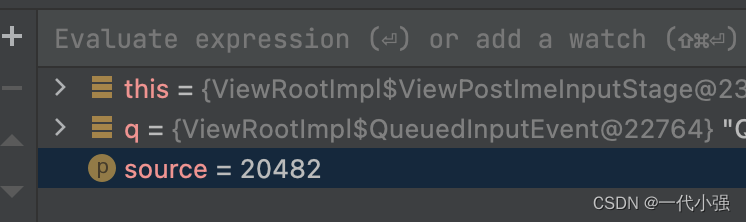
final int source = q.mEvent.getSource(); //source值是20482
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
return processPointerEvent(q);
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_TRACKBALL) != 0) {
return processTrackballEvent(q);
} else {
return processGenericMotionEvent(q);
}
}
}
}
通过计算得知source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER != 0,故会调用到processPointerEvent 方法
4.8.1 processPointerEvent
实现如下:
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class ViewPostImeInputStage extends InputStage {
....
private int processPointerEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final MotionEvent event = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
mAttachInfo.mUnbufferedDispatchRequested = false;
mAttachInfo.mHandlingPointerEvent = true;
boolean handled = mView.dispatchPointerEvent(event); // 即调用到DecorView的dispatchPointerEvent方法
....
return handled ? FINISH_HANDLED : FORWARD; // 如果已经消费事件,就拦截事件,返回finish。
}
}
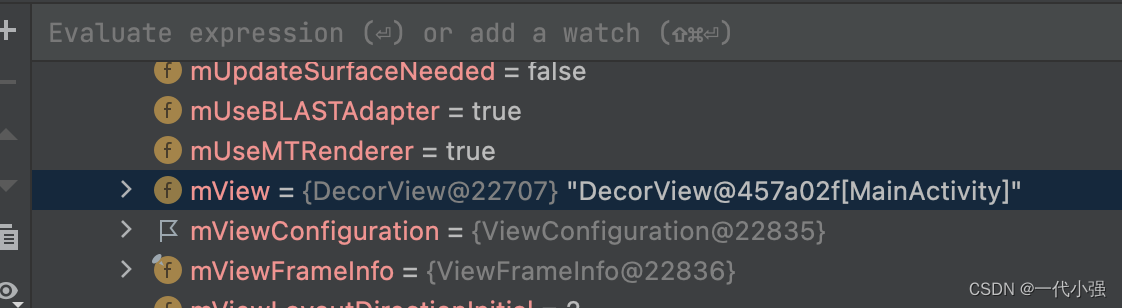
其中mView即为ViewRootImpl中的DecorView
4.9 DecorView
4.9.1 dispatchPointerEvent
dispatchPointerEvent实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public final boolean dispatchPointerEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.isTouchEvent()) {
return dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
return dispatchGenericMotionEvent(event);
}
}
这里是触摸事件,故会分发给dispatchTouchEvent
4.9.2 dispatchTouchEvent
DecorView 重写了dispatchTouchEvent 方法,内部通过window.callback来决定事件分发。
> frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/DecorView.java
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final Window.Callback cb = mWindow.getCallback(); // 通过phineWindow获取callBack
return cb != null && !mWindow.isDestroyed() && mFeatureId < 0
? cb.dispatchTouchEvent(ev) : super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
Activity 在attach的时候,会通过phonewindow注册监听
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
....
}
故最终分发到Activity的dispatchTouchEvent 中
4.10 调用栈
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java : Activity.dispatchTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/DecorView.java : DecorView.dispatchTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java : View.dispatchPointerEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : ViewPostImeInputStage.processPointerEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : ViewPostImeInputStage.onProcess()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : NativePostImeInputStage.onProcess()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : EarlyPostImeInputStage.onProcess()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : ViewRootImpl.deliverInputEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : ViewRootImpl.enqueueInputEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java : InputEventReceiver.onInputEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java : InputEventReceiver.dispatchInputEvent()
5. View 事件分发
5.1 Activity
dispatchTouchEvent 实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
onUserInteraction();
}
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {
return true;
}
return onTouchEvent(ev); // 如果window没有消费,就默认传给activity的onTouchEvent方法。
}
// 该方法默认不消费
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (mWindow.shouldCloseOnTouch(this, event)) {
finish();
return true;
}
return false;
}
5.2 PhoneWindow
superDispatchTouchEvent的实现如下,只是调用DecorView的superDispatchTouchEvent
> frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/PhoneWindow.java
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
superDispatchTouchEvent 实现也很简单,直接调用ViewGroup 的 dispatchTouchEvent
> frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/DecorView.java
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
5.3 ViewGroup
5.3.1 dispatchTouchEvent
view层的事件,最终是由ViewGroup去分发的,在分发的时候,会优先分发给子view
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// 1、检查是否拦截
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) { // 有触摸目标或者action为down
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); // 判断是否拦截,默认false
ev.setAction(action);
}
} else {
// 没有触摸目标,此操作不是初始关闭,因此此视图组继续拦截触摸。
intercepted = true;
}
// 2、检查是否取消
final boolean canceled = resetCancelNextUpFlag(this)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL;
// 没有取消,也没有被拦截
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
// 找一个可以接收事件的孩子。从前到后扫描mChildren。
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// childView想在边界内接受触摸。
}
}
}
// 分发给触摸目标。
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// 没有触摸目标,因此请将其视为普通视图
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
}
....
}
5.3.2 onInterceptTouchEvent
默认不做拦截
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.isFromSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE)
&& ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& ev.isButtonPressed(MotionEvent.BUTTON_PRIMARY)
&& isOnScrollbarThumb(ev.getX(), ev.getY())) {
// 事件在滚动条上
return true;
}
return false;
}
5.3.3 dispatchTransformedTouchEvent
该方法负责将运动事件转换为特定子视图的坐标空间,如果子项为空,则假定 MotionEvent 将改为发送到此视图组。
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
....
// 执行任何必要的转换和调度。
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent); // 调用View的dispatchTouchEvent
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());
}
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent); // 调用子View的dispatchTouchEvent
}
return handled;
}
最后都是调用到view的dispatchTouchEvent方法
5.4 View
5.4.1 dispatchTouchEvent
实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
.....
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
// 1、如果有设置OnTouchListener,就先交给mOnTouchListener 处理
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
//2、如果没有处理,交给onTouchEvent方法
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
....
}
5.4.2 onTouchEvent
在action down的时候,会延迟检查是否发生长按事件
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// 1、如果设置了mTouchDelegate,就直接交给它处理
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
// 如果可以点击或者支持在悬停或长按时显示工具提示。
if (clickable || (viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
....
// 仅当我们处于按下状态时才执行单击操作
if (!focusTaken) {
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClickInternal();
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// 对于滚动容器内的视图,请将按下的反馈延迟一小段时间,以防这是滚动。
if (isInScrollingContainer) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;
if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
}
mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();
mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
} else {
// 不在滚动容器内,因此请立即显示反馈
setPressed(true, x, y);
// 检查是否长按
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
}
break;
}
return false;
}
5.4.3 LongClick
checkForLongClick用于发送延时消息,触发长按
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
private void checkForLongClick(int delayOffset, float x, float y) {
if ((mViewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE || (mViewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
if (mPendingCheckForLongPress == null) {
mPendingCheckForLongPress = new CheckForLongPress();
}
mPendingCheckForLongPress.setAnchor(x, y);
mPendingCheckForLongPress.rememberWindowAttachCount();
mPendingCheckForLongPress.rememberPressedState();
// 延迟消息触发长按事件
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForLongPress,
ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout() - delayOffset);
}
}
private final class CheckForLongPress implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
if ((mOriginalPressedState == isPressed()) && (mParent != null)
&& mOriginalWindowAttachCount == mWindowAttachCount) {
// 触发长按
if (performLongClick(mX, mY)) {
mHasPerformedLongPress = true;
}
}
}
....
}
5.4.4 onClick
在action up的时候,会post一个PerformClick
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
private final class PerformClick implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
performClickInternal();
}
}
private boolean performClickInternal() {
// Must notify autofill manager before performing the click actions to avoid scenarios where
// the app has a click listener that changes the state of views the autofill service might
// be interested on.
notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
return performClick();
}
最后调用到performClick()
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public boolean performClick() {
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this); // 如果设置点击事件就调用onClick回调。
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
return result;
}
5.5 调用栈
View 的点击事件调用栈如下
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java : View.performClick()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java : View.performClickInternal()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java : PerformClick.run()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java : View.onTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java : View.dispatchTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java : ViewGroup.dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java : ViewGroup.dispatchTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/DecorView.java : DecorView.superDispatchTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/PhoneWindow.java : PhoneWindow.superDispatchTouchEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java : Activity.dispatchTouchEvent()
6. 事件确认
6.1 ViewPostImeInputStage
在ViewPostImeInputStage 中,如果我们的view处理了对应的事件,就会调用到finish方法,接着调用下一个处理器
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
protected void apply(QueuedInputEvent q, int result) {
if (result == FORWARD) {
forward(q);
} else if (result == FINISH_HANDLED) {
finish(q, true);
} else if (result == FINISH_NOT_HANDLED) {
finish(q, false);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid result: " + result);
}
}
protected void finish(QueuedInputEvent q, boolean handled) {
q.mFlags |= QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED;
if (handled) {
q.mFlags |= QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED_HANDLED;
}
forward(q);
}
// 调用下一个处理器
protected void forward(QueuedInputEvent q) {
onDeliverToNext(q);
}
由初始化得知下一个处理器是SyntheticInputStage
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage();
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
}
6.2 SyntheticInputStage
6.2.1 onProcess
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class SyntheticInputStage extends InputStage {
public SyntheticInputStage() {
super(null);
}
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
q.mFlags |= QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_RESYNTHESIZED;
if (q.mEvent instanceof MotionEvent) {
final MotionEvent event = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
final int source = event.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_TRACKBALL) != 0) { // 是轨迹球
mTrackball.process(event);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_JOYSTICK) != 0) { // 是操纵杆
mJoystick.process(event);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCH_NAVIGATION)
== InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCH_NAVIGATION) { // 是摸导航
mTouchNavigation.process(event);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
} else if ((q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_UNHANDLED) != 0) {
mKeyboard.process((KeyEvent)q.mEvent);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
return FORWARD;
}
}
onProcess 返回值是FORWARD,会继续调用onDeliverToNext
forward 方法中直接调用onDeliverToNext
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
abstract class InputStage {
protected void forward(QueuedInputEvent q) {
onDeliverToNext(q);
}
}
6.2.2 onDeliverToNext
onProcess 返回值是FORWARD,在调用onDeliverToNext 的时候,由于next为null就会调用finish方法
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
abstract class InputStage {
protected void onDeliverToNext(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (mNext != null) {
mNext.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
}
}
6.2.3 finishInputEvent
这里的mReceiver 是WindowInputEventReceiver
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private void finishInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mReceiver != null) {
boolean handled = (q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED_HANDLED) != 0;
q.mReceiver.finishInputEvent(q.mEvent, handled);
} else {
q.mEvent.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();
}
// 回收队列中的输入事件
recycleQueuedInputEvent(q);
}
6.3 WindowInputEventReceiver
finishInputEvent 的实现如下
> frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
public final void finishInputEvent(InputEvent event, boolean handled) {
....
int index = mSeqMap.indexOfKey(event.getSequenceNumber());
if (index < 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event that is not in progress.");
} else {
int seq = mSeqMap.valueAt(index);
mSeqMap.removeAt(index);
// 调用naive接口通知事件是否已经消费
nativeFinishInputEvent(mReceiverPtr, seq, handled);
}
event.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();
}
6.4 android_view_InputEventReceiver
来到native层,nativeFinishInputEvent 实现如下
> frameworks/native/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
static void nativeFinishInputEvent(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong receiverPtr,
jint seq, jboolean handled) {
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputEventReceiver*>(receiverPtr);
status_t status = receiver->finishInputEvent(seq, handled);
.....
}
6.5 NativeInputEventReceiver
NativeInputEventReceiver::finishInputEvent 方法实现
> frameworks/native/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::finishInputEvent(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
....
Finish finish{
.seq = seq,
.handled = handled,
};
mOutboundQueue.push_back(finish);// 将finish事件添加到集合的最后
return processOutboundEvents();
}
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::processOutboundEvents() {
while (!mOutboundQueue.empty()) {
OutboundEvent& outbound = *mOutboundQueue.begin();
status_t status;
if (std::holds_alternative<Finish>(outbound)) {
const Finish& finish = std::get<Finish>(outbound);
// mInputConsumer是InputConsumer的实例
status = mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal(finish.seq, finish.handled);
} else if (std::holds_alternative<Timeline>(outbound)) {
const Timeline& timeline = std::get<Timeline>(outbound);
status = mInputConsumer.sendTimeline(timeline.inputEventId, timeline.timeline);
}
....
return status;
}
return OK;
}
mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal() 实现是在InputTransport.cpp 中
6.6 InputTransport
sendFinishedSignal 实现如下
> frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputConsumer::sendFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
if (seqChainCount) {
....
while (!status && chainIndex > 0) {
chainIndex--;
status = sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(chainSeqs[chainIndex], handled);
}
....
}
// 为批次中的最后一条消息发送完成信号。
return sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(seq, handled);
}
主要在sendUnchainedFinishedSignal中,通过InputChannel 发送完成信号
> frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputConsumer::sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::FINISHED;
msg.header.seq = seq;
msg.body.finished.handled = handled;
msg.body.finished.consumeTime = getConsumeTime(seq);
status_t result = mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
return result;
}
那这个message是在哪里接收到呢?
6.7 InputManagerService
createInputChannel 的实现如下
> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
// 创建一个输入通道以用作输入事件目标。
public InputChannel createInputChannel(String name) {
// mNative是NativeInputManagerService 接口的实例,NativeImpl 实现了该接口,所以实现在NativeImpl 中
return mNative.createInputChannel(name);
}
createInputChannel 是一个native方法
> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/NativeInputManagerService.java
class NativeImpl implements NativeInputManagerService {
....
public native InputChannel createInputChannel(String name);
}
createInputChannel() 在 native层对应的方法是nativeCreateInputChannel
> frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
// Java层的createInputChannel 方法映射到native的nativeCreateInputChannel 方法
static const JNINativeMethod gInputManagerMethods[] = {
...
{"createInputChannel", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Landroid/view/InputChannel;",
(void*)nativeCreateInputChannel},
}
int register_android_server_InputManager(JNIEnv* env) {
// 注册native层的方法,与Java层的NativeInputManagerService$NativeImpl绑定
int res = jniRegisterNativeMethods(env,
"com/android/server/input/"
"NativeInputManagerService$NativeImpl",
gInputManagerMethods, NELEM(gInputManagerMethods));
}
static jobject nativeCreateInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject nativeImplObj, jstring nameObj) {
NativeInputManager* im = getNativeInputManager(env, nativeImplObj);
....
base::Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> inputChannel = im->createInputChannel(name);
...
jobject inputChannelObj =
android_view_InputChannel_createJavaObject(env, std::move(*inputChannel));
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
return inputChannelObj;
}
// NativeInputManager的createInputChannel 方法定义
base::Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> NativeInputManager::createInputChannel(
const std::string& name) {
// mInputManager 是 InputManager 的实例
return mInputManager->getDispatcher().createInputChannel(name);
}
getDispatcher() 方法返回InputDispatcher实例
6.8 InputDispatcher
createInputChannel实现如下
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> InputDispatcher::createInputChannel(const std::string& name) {
std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> serverChannel;
std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> clientChannel;
// 将serverChannel(接收端) 与 clientChannel(发送端) 绑定
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
const sp<IBinder>& token = serverChannel->getConnectionToken();
int fd = serverChannel->getFd();
sp<Connection> connection =
new Connection(std::move(serverChannel), false /*monitor*/, mIdGenerator);
mConnectionsByToken.emplace(token, connection);
// 注册回调 handleReceiveCallback 方法
std::function<int(int events)> callback = std::bind(&InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback,
this, std::placeholders::_1, token);
// 将callback 与 FD(即serverChannel) 关联起来
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, new LooperEventCallback(callback), nullptr);
} // release lock
mLooper->wake();
return clientChannel;
}
所以应用层发送的finish事件最终来到了InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback 方法
handleReceiveCallback实现如下
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
int InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback(int events, sp<IBinder> connectionToken) {
sp<Connection> connection = getConnectionLocked(connectionToken);
bool notify;
if (!(events & (ALOOPER_EVENT_ERROR | ALOOPER_EVENT_HANGUP))) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
bool gotOne = false;
status_t status = OK;
for (;;) {
Result<InputPublisher::ConsumerResponse> result =
connection->inputPublisher.receiveConsumerResponse();
if (!result.ok()) {
status = result.error().code();
break;
}
// 如果分发结束
if (std::holds_alternative<InputPublisher::Finished>(*result)) {
const InputPublisher::Finished& finish =
std::get<InputPublisher::Finished>(*result);
// 执行事件分发结束的回收处理
finishDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, finish.seq, finish.handled,
finish.consumeTime);
} else if (std::holds_alternative<InputPublisher::Timeline>(*result)) {
if (shouldReportMetricsForConnection(*connection)) {
const InputPublisher::Timeline& timeline =
std::get<InputPublisher::Timeline>(*result);
mLatencyTracker
.trackGraphicsLatency(timeline.inputEventId,
connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken(),
std::move(timeline.graphicsTimeline));
}
}
gotOne = true;
}
}
....
return 0; // remove the callback
}
finishDispatchCycleLocked实现如下
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::finishDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq,
bool handled, nsecs_t consumeTime) {
// 通知其他系统组件并准备开始下一个调度周期。
auto command = [this, currentTime, connection, seq, handled, consumeTime]() REQUIRES(mLock) {
doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand(currentTime, connection, seq, handled, consumeTime);
};
postCommandLocked(std::move(command));
}
doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand 该方法主要处理执行完成后的回收动作,包括将对应的事件从waitQueue 队列中移除。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand(... uint32_t seq ..) {
std::deque<DispatchEntry*>::iterator dispatchEntryIt = connection->findWaitQueueEntry(seq);
// 将事件出列并开始下一个循环。因为锁可能已经被释放,等待队列的内容可能已经被清空,所以我们需要仔细检查一些事情。
if (dispatchEntryIt != connection->waitQueue.end()) {
dispatchEntry = *dispatchEntryIt;
// 将对应的事件从waitQueue移除
connection->waitQueue.erase(dispatchEntryIt);
const sp<IBinder>& connectionToken = connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken();
// 将事件对应的anr超时移除
mAnrTracker.erase(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime, connectionToken);
// 如果连接没有响应
if (!connection->responsive) {
connection->responsive = isConnectionResponsive(*connection);
if (connection->responsive) {
// 连接之前没有响应,现在有响应了。
processConnectionResponsiveLocked(*connection);
}
}
....
}
}
6.9 调用栈
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand()
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::finishDispatchCycleLocked()
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback()
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp : InputConsumer::sendUnchainedFinishedSignal()
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp : InputConsumer::sendFinishedSignal()
frameworks/native/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp : NativeInputEventReceiver::processOutboundEvents()
frameworks/native/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp : NativeInputEventReceiver::finishInputEvent()
frameworks/native/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp : nativeFinishInputEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java : InputEventReceiver.finishInputEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : ViewRootImpl.finishInputEvent()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : InputStage.forward()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : InputStage.onDeliverToNext()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : SyntheticInputStage.apply()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java : ViewPostImeInputStage.apply()
总结
事件分发流程图
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FoEWGzHh-1682737256424)(/img/blog_activity_dispatch_input_event/5.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dc6b95230a9143d7b98ff7e37e12ede3.png)
参考文章:
- Input系统—事件处理全过程