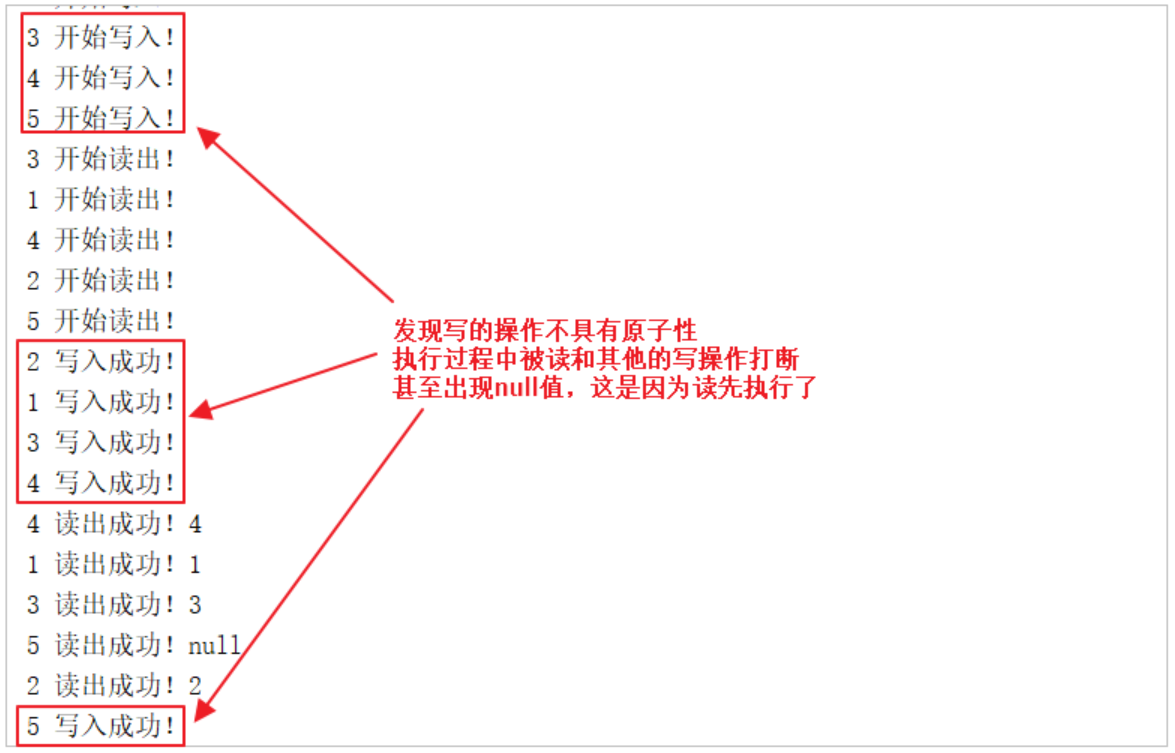
二叉搜索树是一种二叉树,但它对树中元素的顺序作了限制。在二叉搜索树中,对于任意一个结点,它的左子树(如果有)中的所有元素值都小于它,它的右子树中的所有元素值都大于它。那么基于这个性质,对于二叉搜索树的插入删除或是查找等操作的逻辑就非常清楚了。下面给出C语言实现的二叉搜索树代码,对于每一种操作,都有递归写法和迭代写法两种实现方法:
如果插入的数据分布比较随机,那么二叉树的树高的量级就为,N为结点的数量。插入时需要找到插入位置,也就是最底层为NULL的结点,一次插入的时间复杂度就为
。 相似的,删除、查找或是修改等操作都需要在树中找到相应的结点,它们的时间复杂度也就为
。但这都是建立在输入数据随机的情况下,如果输入数据比较有序,那么建立的树高就不会是
,一次操作需要的时间就多多了。
搜索二叉树结构定义:
//二叉搜索树,假设关键字为整型,且不存在重复的关键字
//在二叉搜索树中,每个结点的左子树(如果有)中的关键字都小于它
//每个结点右子树(如果有)中的关键字都大于它
//二叉搜索树结点定义
typedef struct BstNode {
int val;//关键字
struct BstNode* left;//左孩子
struct BstNode* right;//右孩子
}BstNode;插入:
//向二叉树中插入一个结点
//插入结点的逻辑与查找是相似的,假设要插入的结点就在树中,那么我们现在要找到该结点
//就需要使用查找,最后找到该结点应该在的位置,那么如果这个结点不存在,最后找到的位置就为空
//但这个位置刚好也是新节点要插入的位置。并且插入函数返回树或子树的根节点
BstNode* Insert(BstNode* root, int k) {
//插入的递归写法
//如果root为空,那么root就是要插入的位置
if (root == NULL) {
//建立新结点
BstNode* p = (BstNode*)malloc(sizeof(BstNode));
if (p == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
p->left = p->right = NULL;
p->val = k;
return p;
}
else {
//如果根节点不为空,那么就需要判断在其左子树还是右子树中插入
if (root->val > k)
//使用这样的逻辑,当root的左子树为空,那么建立的新节点就会连接在其左子树
root->left = Insert(root->left, k);
else
root->right = Insert(root->right, k);
return root;
}
插入的迭代写法
需要找到要插入位置的父节点
//BstNode* father = NULL;
//BstNode* child = root;
//if (child == NULL) {
// //建立新结点
// child = (BstNode*)malloc(sizeof(BstNode));
// if (child == NULL) {
// perror("malloc");
// return NULL;
// }
// child->left = child->right = NULL;
// child->val = k;
// return child;
//}
//else {
// while (child) {
// if (child->val > k) {
// father = child;
// child = child->left;
// }
// else {
// father = child;
// child = child->right;
// }
// }
// child = (BstNode*)malloc(sizeof(BstNode));
// if (child == NULL) {
// perror("malloc");
// return NULL;
// }
// child->left = child->right = NULL;
// child->val = k;
// if (father->val > k)
// father->left = child;
// else
// father->right = child;
// return root;
//}
}删除:
//找到某一个有两个孩子的结点的中序前驱结点
BstNode* FindPre(BstNode* root) {
BstNode* pre = root->left;
while (pre->right)
pre = pre->right;
return pre;
}
//找到某一个有两个孩子的结点的中序后继
BstNode* FindNext(BstNode* root) {
BstNode* next = root->right;
while (next->left)
next = next->left;
return next;
}
//删除bst中的结点,总共分为三种情况
//1.删除的结点为叶节点,那么可以直接删除,因为删除叶节点不会影响其他结点
//2.删除的结点有一个孩子,那么只需要将这个孩子代替删除结点的位置即可
//3.删除的结点有两个孩子,那么在删除时就需要对这个两个孩子的位置进行处理
//首先找到要删除结点的前驱或是后继,然后删除前驱或后继结点,再将前驱或后继
//的关键字赋给要删除结点,也就是说,用它的前驱或后继来替换它的位置
//因为这样可以保证满足bst的结构要求,函数返回删除结点之后的根节点
BstNode* Delete(BstNode* root, int k) {
递归写法
删除首先还是找到查找到要删除的结点
//if (root == NULL) {
// //root为空时,说明要删除的结点不存在
// return NULL;
//}
//else {
// if (root->val == k) {
// //要删除结点就为root
// if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
// //叶节点的情况
// free(root);
// root = NULL;
// }
// else if (root->left == NULL || root->right == NULL) {
// //只有一个孩子的情况
// BstNode* tmp = root->left ? root->left : root->right;
// free(root);
// root = tmp;
// }
// else {
// //有两个孩子的情况
// //找到k的中序遍历前驱
// BstNode* pre = FindPre(root);
// root->val = pre->val;
// //然后在其左子树中删除其前驱
// root->left = Delete(root->left, root->val);
// }
// }
// else if (root->val > k)
// root->left = Delete(root->left, k);
// else
// root->right = Delete(root->right, k);
// return root;
//}
//迭代写法
//首先需要找到被删除结点及其父节点
BstNode* father = NULL;
BstNode* child = root;
if (child == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
else {
//首先处理删除根节点的情况
if (root->val == k) {
//没有孩子
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
free(root);
return NULL;
}
else if (root->left == NULL || root->right == NULL) {
BstNode* ret = root->left ? root->left : root->right;
free(root);
return ret;
}
else {
//首先找到前驱和前驱的父节点
BstNode* prefather = root;
BstNode* pre = root->left;
while (pre->right) {
prefather = pre;
pre = pre->right;
}
int val = pre->val;
//前驱一定没有右子树
if (prefather == root) {
//如果前驱的父节点是root,那么需要将前驱的左子树连接在root的左子树
prefather->left = pre->left;
free(pre);
}
else {
//否则将前驱的左子树连接在父节点的右子树
prefather->right = pre->left;
free(pre);
}
//将root的val修改
root->val = val;
return root;
}
}
else {
//删除的不是根节点,那么先找到删除结点和它的父节点
while (child->val != k) {
if (child->val > k) {
father = child;
child = child->left;
}
else {
father = child;
child = child->right;
}
}
//删除结点分为三种情况
//没有孩子
if (child->left == NULL && child->right == NULL) {
if (child->val < father->val)
father->left = NULL;
else
father->right = NULL;
free(child);
child = NULL;
}
else if (child->left == NULL || child->right == NULL) {
BstNode* ret = child->left ? child->left : child->right;
if (child->val < father->val)
father->left = ret;
else
father->right = ret;
free(child);
child = NULL;
}
else {
//首先找到前驱和前驱的父节点
BstNode* prefather = child;
BstNode* pre = child->left;
while (pre->right) {
prefather = pre;
pre = pre->right;
}
int val = pre->val;
//前驱一定没有右子树
if (prefather->val > pre->val)
prefather->left = pre->left;
else {
prefather->right = pre->left;
}
free(pre);
pre = NULL;
//将root的val修改
child->val = val;
}
return root;
}
}
}
//修改某个元素的值
BstNode* ChangeNodeVal(BstNode* root, int k, int target) {
BstNode* tmp = FindKeyNode(root, k);
if (tmp == NULL)
return NULL;
tmp->val = target;
return tmp;
}查找:
//在bst中查找一个值为k的结点
//由bst的定义可知,对于当前子树,如果根节点的值等于k,那么直接返回根节点
//如果根节点的值大于k,那么k一定位于它的左子树,否则位于右子树
//对于每个子树都是同样的处理过程,所以可以使用递归来实现
//当发现当前子树为空时,就说明没有找到目标值
BstNode* FindKeyNode(BstNode* root, int k) {
//递归实现
//root为空,则查找失败
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//root不为空,分为三个逻辑
if (root->val == k)
return root;
else if (root->val > k)
return FindKeyNode(root->left, k);
else
return FindKeyNode(root->right, k);
迭代实现
//BstNode* curnode = root;//当前判断的结点
如果它为空,则查找失败
//while (curnode) {
// if (curnode->val == k)
// return curnode;
// else if (curnode->val > k)
// curnode = curnode->left;
// else
// curnode = curnode->right;
//}
//return curnode;
}修改:
//修改某个元素的值
BstNode* ChangeNodeVal(BstNode* root, int k, int target) {
BstNode* tmp = FindKeyNode(root, k);
if (tmp == NULL)
return NULL;
tmp->val = target;
return tmp;
}测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
//建立二叉树
printf("请输入初始元素的个数:");
int num;
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("请输入这%d个元素的值:\n", num);
BstNode* root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
int key;
scanf("%d", &key);
root = Insert(root, key);
}
printf("\n----------------------------\n");
InOrderPrint(root);
printf("\n----------------------------\n");
root = Delete(root, 44);
printf("删除后的序列是:\n");
InOrderPrint(root);
printf("\n-------------------------\n");
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
BstNode* tmp = FindKeyNode(root, i);
if (tmp == NULL) {
printf("元素%d不存在\n", i);
}
else {
printf("查找%d,找到的元素是%d\n", i, tmp->val);
root = Delete(root, tmp->val);
printf("删除后的序列是:\n");
InOrderPrint(root);
printf("\n-------------------------\n");
}
}
return 0;
}![[计算机图形学]蒙特卡洛积分与路径追踪(前瞻预习/复习回顾)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/432c9ab4117f46b786ce3097a17b4fb7.png)