文章目录
- FID
- LPIPS
- NIQE
FID
FID的全称是Fréchet Inception Distance,用于衡量两个多元正态分布的距离,数值越小越好。具体的,FID使用Inception Net-V3全连接前的2048维向量作为图片的特征向量,再计算两张图像特征之间的距离。
F
I
D
=
∣
∣
μ
r
−
μ
g
∣
∣
2
+
T
r
(
Σ
r
+
Σ
g
−
2
(
Σ
r
Σ
g
)
1
/
2
)
FID = || \mu_r - \mu_g ||^2 + Tr(\Sigma_r + \Sigma_g -2(\Sigma_r \Sigma_g)^{1/2})
FID=∣∣μr−μg∣∣2+Tr(Σr+Σg−2(ΣrΣg)1/2)
μ
r
\mu_r
μr: 真实图像的特征均值
μ
g
\mu_g
μg: 生成图像的特征均值
Σ
r
\Sigma_r
Σr: 真实图像的协方差矩阵
Σ
g
\Sigma_g
Σg: 生成图像的协方差矩阵
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""Calculates the Frechet Inception Distance (FID) to evalulate GANs
The FID metric calculates the distance between two distributions of images.
Typically, we have summary statistics (mean & covariance matrix) of one
of these distributions, while the 2nd distribution is given by a GAN.
When run as a stand-alone program, it compares the distribution of
images that are stored as PNG/JPEG at a specified location with a
distribution given by summary statistics (in pickle format).
The FID is calculated by assuming that X_1 and X_2 are the activations of
the pool_3 layer of the inception net for generated samples and real world
samples respectivly.
See --help to see further details.
Code apapted from https://github.com/bioinf-jku/TTUR to use PyTorch instead
of Tensorflow
Copyright 2018 Institute of Bioinformatics, JKU Linz
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
"""
import os
import pathlib
from argparse import ArgumentParser, ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
import torch
import numpy as np
# from scipy.misc import imread
from skimage import io
from scipy import linalg
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torch.nn.functional import adaptive_avg_pool2d
from inception import InceptionV3
def get_activations(images, model, batch_size=64, dims=2048,
cuda=False, verbose=False):
"""Calculates the activations of the pool_3 layer for all images.
Params:
-- images : Numpy array of dimension (n_images, 3, hi, wi). The values
must lie between 0 and 1.
-- model : Instance of inception model
-- batch_size : the images numpy array is split into batches with
batch size batch_size. A reasonable batch size depends
on the hardware.
-- dims : Dimensionality of features returned by Inception
-- cuda : If set to True, use GPU
-- verbose : If set to True and parameter out_step is given, the number
of calculated batches is reported.
Returns:
-- A numpy array of dimension (num images, dims) that contains the
activations of the given tensor when feeding inception with the
query tensor.
"""
model.eval()
d0 = images.shape[0]
if batch_size > d0:
print(('Warning: batch size is bigger than the data size. '
'Setting batch size to data size'))
batch_size = d0
n_batches = d0 // batch_size
n_used_imgs = n_batches * batch_size
pred_arr = np.empty((n_used_imgs, dims))
for i in range(n_batches):
if verbose:
print('\rPropagating batch %d/%d' % (i + 1, n_batches),
end='', flush=True)
start = i * batch_size
end = start + batch_size
batch = torch.from_numpy(images[start:end]).type(torch.FloatTensor)
batch = Variable(batch, volatile=True)
if cuda:
batch = batch.cuda()
pred = model(batch)[0]
# If model output is not scalar, apply global spatial average pooling.
# This happens if you choose a dimensionality not equal 2048.
if pred.shape[2] != 1 or pred.shape[3] != 1:
pred = adaptive_avg_pool2d(pred, output_size=(1, 1))
pred_arr[start:end] = pred.cpu().data.numpy().reshape(batch_size, -1)
if verbose:
print(' done')
return pred_arr
def calculate_frechet_distance(mu1, sigma1, mu2, sigma2, eps=1e-6):
"""Numpy implementation of the Frechet Distance.
The Frechet distance between two multivariate Gaussians X_1 ~ N(mu_1, C_1)
and X_2 ~ N(mu_2, C_2) is
d^2 = ||mu_1 - mu_2||^2 + Tr(C_1 + C_2 - 2*sqrt(C_1*C_2)).
Stable version by Dougal J. Sutherland.
Params:
-- mu1 : Numpy array containing the activations of a layer of the
inception net (like returned by the function 'get_predictions')
for generated samples.
-- mu2 : The sample mean over activations, precalculated on an
representive data set.
-- sigma1: The covariance matrix over activations for generated samples.
-- sigma2: The covariance matrix over activations, precalculated on an
representive data set.
Returns:
-- : The Frechet Distance.
"""
mu1 = np.atleast_1d(mu1)
mu2 = np.atleast_1d(mu2)
sigma1 = np.atleast_2d(sigma1)
sigma2 = np.atleast_2d(sigma2)
assert mu1.shape == mu2.shape, \
'Training and test mean vectors have different lengths'
assert sigma1.shape == sigma2.shape, \
'Training and test covariances have different dimensions'
diff = mu1 - mu2
# Product might be almost singular
covmean, _ = linalg.sqrtm(sigma1.dot(sigma2), disp=False)
if not np.isfinite(covmean).all():
msg = ('fid calculation produces singular product; '
'adding %s to diagonal of cov estimates') % eps
print(msg)
offset = np.eye(sigma1.shape[0]) * eps
covmean = linalg.sqrtm((sigma1 + offset).dot(sigma2 + offset))
# Numerical error might give slight imaginary component
if np.iscomplexobj(covmean):
if not np.allclose(np.diagonal(covmean).imag, 0, atol=1e-3):
m = np.max(np.abs(covmean.imag))
raise ValueError('Imaginary component {}'.format(m))
covmean = covmean.real
tr_covmean = np.trace(covmean)
return (diff.dot(diff) + np.trace(sigma1) +
np.trace(sigma2) - 2 * tr_covmean)
def calculate_activation_statistics(images, model, batch_size=64,
dims=2048, cuda=False, verbose=False):
"""Calculation of the statistics used by the FID.
Params:
-- images : Numpy array of dimension (n_images, 3, hi, wi). The values
must lie between 0 and 1.
-- model : Instance of inception model
-- batch_size : The images numpy array is split into batches with
batch size batch_size. A reasonable batch size
depends on the hardware.
-- dims : Dimensionality of features returned by Inception
-- cuda : If set to True, use GPU
-- verbose : If set to True and parameter out_step is given, the
number of calculated batches is reported.
Returns:
-- mu : The mean over samples of the activations of the pool_3 layer of
the inception model.
-- sigma : The covariance matrix of the activations of the pool_3 layer of
the inception model.
"""
act = get_activations(images, model, batch_size, dims, cuda, verbose)
mu = np.mean(act, axis=0)
sigma = np.cov(act, rowvar=False)
return mu, sigma
def _compute_statistics_of_path(path, model, batch_size, dims, cuda):
if path.endswith('.npz'):
f = np.load(path)
m, s = f['mu'][:], f['sigma'][:]
f.close()
else:
path = pathlib.Path(path)
files = list(path.glob('*.jpg')) + list(path.glob('*.png'))
imgs = np.array([io.imread(str(fn)).astype(np.float32) for fn in files])
# for gray images, expand image dims
if imgs.ndim==3 and not 1 in imgs.shape:
imgs = imgs[:,:,:,np.newaxis]
imgs = np.repeat(imgs, repeats=3, axis=3)
# Bring images to shape (B, 3, H, W)
imgs = imgs.transpose((0, 3, 1, 2))
# Rescale images to be between 0 and 1
imgs /= 255
m, s = calculate_activation_statistics(imgs, model, batch_size,
dims, cuda)
return m, s
def calculate_fid_given_paths(path1, path2, batch_size, cuda, dims):
"""Calculates the FID of two paths"""
if not os.path.exists(path1):
raise RuntimeError('Invalid path: %s' % path1)
if not os.path.exists(path2):
raise RuntimeError('Invalid path: %s' % path2)
block_idx = InceptionV3.BLOCK_INDEX_BY_DIM[dims]
model = InceptionV3([block_idx])
if cuda:
model.cuda()
m1, s1 = _compute_statistics_of_path(path1, model, batch_size,
dims, cuda)
m2, s2 = _compute_statistics_of_path(path2, model, batch_size,
dims, cuda)
fid_value = calculate_frechet_distance(m1, s1, m2, s2)
return fid_value
if __name__ == '__main__':
from skimage import io
clean = 'clean_patch/'
noisy = 'noisy_patch/'
# parser = ArgumentParser(formatter_class=ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
parser = ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--path1', type=str, default=clean,
help='Path to the generated images or to .npz statistic files')
parser.add_argument('--path2', type=str, default=noisy,
help='Path to the generated images or to .npz statistic files')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64,
help='Batch size to use')
parser.add_argument('--dims', type=int, default=2048,
choices=list(InceptionV3.BLOCK_INDEX_BY_DIM),
help=('Dimensionality of Inception features to use. '
'By default, uses pool3 features'))
parser.add_argument('-c', '--gpu', default='0', type=str,
help='GPU to use (leave blank for CPU only)')
args = parser.parse_args()
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = args.gpu
fid_value = calculate_fid_given_paths(args.path1,
args.path2,
args.batch_size,
args.gpu != '',
args.dims)
print('FID: ', fid_value)
使用时,只需要修改path1, path2的路径即可(分别代表reference 图像和生成图像的路径)。
其中 inception.py的代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import models
try:
from torchvision.models.utils import load_state_dict_from_url
except ImportError:
from torch.utils.model_zoo import load_url as load_state_dict_from_url
# Inception weights ported to Pytorch from
# http://download.tensorflow.org/models/image/imagenet/inception-2015-12-05.tgz
FID_WEIGHTS_URL = 'https://github.com/mseitzer/pytorch-fid/releases/download/fid_weights/pt_inception-2015-12-05-6726825d.pth'
class InceptionV3(nn.Module):
"""Pretrained InceptionV3 network returning feature maps"""
# Index of default block of inception to return,
# corresponds to output of final average pooling
DEFAULT_BLOCK_INDEX = 3
# Maps feature dimensionality to their output blocks indices
BLOCK_INDEX_BY_DIM = {
64: 0, # First max pooling features
192: 1, # Second max pooling featurs
768: 2, # Pre-aux classifier features
2048: 3 # Final average pooling features
}
def __init__(self,
output_blocks=[DEFAULT_BLOCK_INDEX],
resize_input=True,
normalize_input=True,
requires_grad=False,
use_fid_inception=True):
"""Build pretrained InceptionV3
Parameters
----------
output_blocks : list of int
Indices of blocks to return features of. Possible values are:
- 0: corresponds to output of first max pooling
- 1: corresponds to output of second max pooling
- 2: corresponds to output which is fed to aux classifier
- 3: corresponds to output of final average pooling
resize_input : bool
If true, bilinearly resizes input to width and height 299 before
feeding input to model. As the network without fully connected
layers is fully convolutional, it should be able to handle inputs
of arbitrary size, so resizing might not be strictly needed
normalize_input : bool
If true, scales the input from range (0, 1) to the range the
pretrained Inception network expects, namely (-1, 1)
requires_grad : bool
If true, parameters of the model require gradients. Possibly useful
for finetuning the network
use_fid_inception : bool
If true, uses the pretrained Inception model used in Tensorflow's
FID implementation. If false, uses the pretrained Inception model
available in torchvision. The FID Inception model has different
weights and a slightly different structure from torchvision's
Inception model. If you want to compute FID scores, you are
strongly advised to set this parameter to true to get comparable
results.
"""
super(InceptionV3, self).__init__()
self.resize_input = resize_input
self.normalize_input = normalize_input
self.output_blocks = sorted(output_blocks)
self.last_needed_block = max(output_blocks)
assert self.last_needed_block <= 3, \
'Last possible output block index is 3'
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList()
if use_fid_inception:
inception = fid_inception_v3()
else:
inception = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
# Block 0: input to maxpool1
block0 = [
inception.Conv2d_1a_3x3,
inception.Conv2d_2a_3x3,
inception.Conv2d_2b_3x3,
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
]
self.blocks.append(nn.Sequential(*block0))
# Block 1: maxpool1 to maxpool2
if self.last_needed_block >= 1:
block1 = [
inception.Conv2d_3b_1x1,
inception.Conv2d_4a_3x3,
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2)
]
self.blocks.append(nn.Sequential(*block1))
# Block 2: maxpool2 to aux classifier
if self.last_needed_block >= 2:
block2 = [
inception.Mixed_5b,
inception.Mixed_5c,
inception.Mixed_5d,
inception.Mixed_6a,
inception.Mixed_6b,
inception.Mixed_6c,
inception.Mixed_6d,
inception.Mixed_6e,
]
self.blocks.append(nn.Sequential(*block2))
# Block 3: aux classifier to final avgpool
if self.last_needed_block >= 3:
block3 = [
inception.Mixed_7a,
inception.Mixed_7b,
inception.Mixed_7c,
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(1, 1))
]
self.blocks.append(nn.Sequential(*block3))
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = requires_grad
def forward(self, inp):
"""Get Inception feature maps
Parameters
----------
inp : torch.autograd.Variable
Input tensor of shape Bx3xHxW. Values are expected to be in
range (0, 1)
Returns
-------
List of torch.autograd.Variable, corresponding to the selected output
block, sorted ascending by index
"""
outp = []
x = inp
if self.resize_input:
x = F.interpolate(x,
size=(299, 299),
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=False)
if self.normalize_input:
x = 2 * x - 1 # Scale from range (0, 1) to range (-1, 1)
for idx, block in enumerate(self.blocks):
x = block(x)
if idx in self.output_blocks:
outp.append(x)
if idx == self.last_needed_block:
break
return outp
def fid_inception_v3():
"""Build pretrained Inception model for FID computation
The Inception model for FID computation uses a different set of weights
and has a slightly different structure than torchvision's Inception.
This method first constructs torchvision's Inception and then patches the
necessary parts that are different in the FID Inception model.
"""
inception = models.inception_v3(num_classes=1008,
aux_logits=False,
pretrained=False)
inception.Mixed_5b = FIDInceptionA(192, pool_features=32)
inception.Mixed_5c = FIDInceptionA(256, pool_features=64)
inception.Mixed_5d = FIDInceptionA(288, pool_features=64)
inception.Mixed_6b = FIDInceptionC(768, channels_7x7=128)
inception.Mixed_6c = FIDInceptionC(768, channels_7x7=160)
inception.Mixed_6d = FIDInceptionC(768, channels_7x7=160)
inception.Mixed_6e = FIDInceptionC(768, channels_7x7=192)
inception.Mixed_7b = FIDInceptionE_1(1280)
inception.Mixed_7c = FIDInceptionE_2(2048)
# state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(FID_WEIGHTS_URL, progress=True)
checkpoint = torch.load('fid/pt_inception-2015-12-05-6726825d.pth')
state_dict = checkpoint
inception.load_state_dict(state_dict)
return inception
class FIDInceptionA(models.inception.InceptionA):
"""InceptionA block patched for FID computation"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, pool_features):
super(FIDInceptionA, self).__init__(in_channels, pool_features)
def forward(self, x):
branch1x1 = self.branch1x1(x)
branch5x5 = self.branch5x5_1(x)
branch5x5 = self.branch5x5_2(branch5x5)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_1(x)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_2(branch3x3dbl)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_3(branch3x3dbl)
# Patch: Tensorflow's average pool does not use the padded zero's in
# its average calculation
branch_pool = F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
count_include_pad=False)
branch_pool = self.branch_pool(branch_pool)
outputs = [branch1x1, branch5x5, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
class FIDInceptionC(models.inception.InceptionC):
"""InceptionC block patched for FID computation"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, channels_7x7):
super(FIDInceptionC, self).__init__(in_channels, channels_7x7)
def forward(self, x):
branch1x1 = self.branch1x1(x)
branch7x7 = self.branch7x7_1(x)
branch7x7 = self.branch7x7_2(branch7x7)
branch7x7 = self.branch7x7_3(branch7x7)
branch7x7dbl = self.branch7x7dbl_1(x)
branch7x7dbl = self.branch7x7dbl_2(branch7x7dbl)
branch7x7dbl = self.branch7x7dbl_3(branch7x7dbl)
branch7x7dbl = self.branch7x7dbl_4(branch7x7dbl)
branch7x7dbl = self.branch7x7dbl_5(branch7x7dbl)
# Patch: Tensorflow's average pool does not use the padded zero's in
# its average calculation
branch_pool = F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
count_include_pad=False)
branch_pool = self.branch_pool(branch_pool)
outputs = [branch1x1, branch7x7, branch7x7dbl, branch_pool]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
class FIDInceptionE_1(models.inception.InceptionE):
"""First InceptionE block patched for FID computation"""
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super(FIDInceptionE_1, self).__init__(in_channels)
def forward(self, x):
branch1x1 = self.branch1x1(x)
branch3x3 = self.branch3x3_1(x)
branch3x3 = [
self.branch3x3_2a(branch3x3),
self.branch3x3_2b(branch3x3),
]
branch3x3 = torch.cat(branch3x3, 1)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_1(x)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_2(branch3x3dbl)
branch3x3dbl = [
self.branch3x3dbl_3a(branch3x3dbl),
self.branch3x3dbl_3b(branch3x3dbl),
]
branch3x3dbl = torch.cat(branch3x3dbl, 1)
# Patch: Tensorflow's average pool does not use the padded zero's in
# its average calculation
branch_pool = F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
count_include_pad=False)
branch_pool = self.branch_pool(branch_pool)
outputs = [branch1x1, branch3x3, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
class FIDInceptionE_2(models.inception.InceptionE):
"""Second InceptionE block patched for FID computation"""
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super(FIDInceptionE_2, self).__init__(in_channels)
def forward(self, x):
branch1x1 = self.branch1x1(x)
branch3x3 = self.branch3x3_1(x)
branch3x3 = [
self.branch3x3_2a(branch3x3),
self.branch3x3_2b(branch3x3),
]
branch3x3 = torch.cat(branch3x3, 1)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_1(x)
branch3x3dbl = self.branch3x3dbl_2(branch3x3dbl)
branch3x3dbl = [
self.branch3x3dbl_3a(branch3x3dbl),
self.branch3x3dbl_3b(branch3x3dbl),
]
branch3x3dbl = torch.cat(branch3x3dbl, 1)
# Patch: The FID Inception model uses max pooling instead of average
# pooling. This is likely an error in this specific Inception
# implementation, as other Inception models use average pooling here
# (which matches the description in the paper).
branch_pool = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
branch_pool = self.branch_pool(branch_pool)
outputs = [branch1x1, branch3x3, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
注:考虑到模型下载缓慢,可以提前从 inception模型 把模型下载好,并修改inception.py的 184 行的路径:
checkpoint = torch.load('fid/pt_inception-2015-12-05-6726825d.pth')
LPIPS
主页:https://github.com/richzhang/PerceptualSimilarity
来自论文:
@inproceedings{zhang2018perceptual,
title={The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric},
author={Zhang, Richard and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A and Shechtman, Eli and Wang, Oliver},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2018}
}
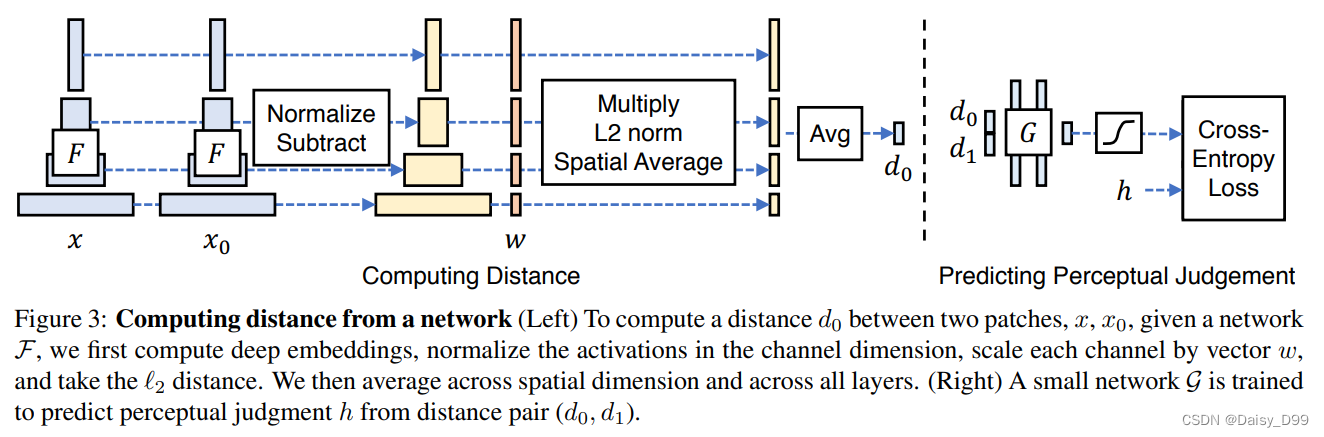
数值越小代表两张图像越相似。将两个输入送入神经网络F(可以为VGG、Alexnet、Squeezenet)中进行特征提取,对每个层的输出进行激活后归一化处理,然后经过w层权重点乘后计算L2距离。
d ( x , x 0 ) = ∑ l 1 H l W l ∑ h , w ∣ ∣ w l ⊙ ( y ^ h w l − y ^ 0 h w l ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 d(x, x_0) = \sum_l \frac{1}{H_l W_l} \sum_{h,w} || w_l \odot (\hat{y}_{hw}^l - \hat{y}_{0hw}^l) ||_2^2 d(x,x0)=l∑HlWl1h,w∑∣∣wl⊙(y^hwl−y^0hwl)∣∣22
需要先pip install lpips
下面给出灰度图的使用示例:
import lpips
from skimage import io
def img2tensor(img):
img = (img / 255.).astype('float32')
if img.ndim ==2:
img = np.expand_dims(np.expand_dims(img, axis = 0),axis=0)
else:
img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1)) # C, H, W
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img, dtype=np.float32)
tensor = torch.from_numpy(img)
return tensor
loss_fn_alex = lpips.LPIPS(net='alex') # best forward scores
loss_fn_vgg = lpips.LPIPS(net='vgg') # closer to "traditional" perceptual loss, when used for optimization
clean = io.imread('clean/2762.png')
noisy = io.imread('noisy/2762.png')
print(loss_fn_alex(img2tensor(clean), img2tensor(noisy)))
print(loss_fn_vgg(img2tensor(clean), img2tensor(noisy)))
输出:
tensor([[[[0.6622]]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
tensor([[[[0.6338]]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
NIQE
NIQE是无参图像质量评价指标。
依赖的函数:reorder_image, to_y_channel,imresize
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
import os
from scipy.ndimage import convolve
from scipy.special import gamma
from utils import reorder_image, to_y_channel,imresize
def estimate_aggd_param(block):
"""Estimate AGGD (Asymmetric Generalized Gaussian Distribution) parameters.
Args:
block (ndarray): 2D Image block.
Returns:
tuple: alpha (float), beta_l (float) and beta_r (float) for the AGGD
distribution (Estimating the parames in Equation 7 in the paper).
"""
block = block.flatten()
gam = np.arange(0.2, 10.001, 0.001) # len = 9801
gam_reciprocal = np.reciprocal(gam)
r_gam = np.square(gamma(gam_reciprocal * 2)) / (gamma(gam_reciprocal) * gamma(gam_reciprocal * 3))
left_std = np.sqrt(np.mean(block[block < 0]**2))
right_std = np.sqrt(np.mean(block[block > 0]**2))
gammahat = left_std / right_std
rhat = (np.mean(np.abs(block)))**2 / np.mean(block**2)
rhatnorm = (rhat * (gammahat**3 + 1) * (gammahat + 1)) / ((gammahat**2 + 1)**2)
array_position = np.argmin((r_gam - rhatnorm)**2)
alpha = gam[array_position]
beta_l = left_std * np.sqrt(gamma(1 / alpha) / gamma(3 / alpha))
beta_r = right_std * np.sqrt(gamma(1 / alpha) / gamma(3 / alpha))
return (alpha, beta_l, beta_r)
def compute_feature(block):
"""Compute features.
Args:
block (ndarray): 2D Image block.
Returns:
list: Features with length of 18.
"""
feat = []
alpha, beta_l, beta_r = estimate_aggd_param(block)
feat.extend([alpha, (beta_l + beta_r) / 2])
# distortions disturb the fairly regular structure of natural images.
# This deviation can be captured by analyzing the sample distribution of
# the products of pairs of adjacent coefficients computed along
# horizontal, vertical and diagonal orientations.
shifts = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1], [1, -1]]
for i in range(len(shifts)):
shifted_block = np.roll(block, shifts[i], axis=(0, 1))
alpha, beta_l, beta_r = estimate_aggd_param(block * shifted_block)
# Eq. 8
mean = (beta_r - beta_l) * (gamma(2 / alpha) / gamma(1 / alpha))
feat.extend([alpha, mean, beta_l, beta_r])
return feat
def niqe(img, mu_pris_param, cov_pris_param, gaussian_window, block_size_h=96, block_size_w=96):
"""Calculate NIQE (Natural Image Quality Evaluator) metric.
``Paper: Making a "Completely Blind" Image Quality Analyzer``
This implementation could produce almost the same results as the official
MATLAB codes: http://live.ece.utexas.edu/research/quality/niqe_release.zip
Note that we do not include block overlap height and width, since they are
always 0 in the official implementation.
For good performance, it is advisable by the official implementation to
divide the distorted image in to the same size patched as used for the
construction of multivariate Gaussian model.
Args:
img (ndarray): Input image whose quality needs to be computed. The
image must be a gray or Y (of YCbCr) image with shape (h, w).
Range [0, 255] with float type.
mu_pris_param (ndarray): Mean of a pre-defined multivariate Gaussian
model calculated on the pristine dataset.
cov_pris_param (ndarray): Covariance of a pre-defined multivariate
Gaussian model calculated on the pristine dataset.
gaussian_window (ndarray): A 7x7 Gaussian window used for smoothing the
image.
block_size_h (int): Height of the blocks in to which image is divided.
Default: 96 (the official recommended value).
block_size_w (int): Width of the blocks in to which image is divided.
Default: 96 (the official recommended value).
"""
assert img.ndim == 2, ('Input image must be a gray or Y (of YCbCr) image with shape (h, w).')
# crop image
h, w = img.shape
num_block_h = math.floor(h / block_size_h)
num_block_w = math.floor(w / block_size_w)
img = img[0:num_block_h * block_size_h, 0:num_block_w * block_size_w]
distparam = [] # dist param is actually the multiscale features
for scale in (1, 2): # perform on two scales (1, 2)
mu = convolve(img, gaussian_window, mode='nearest')
sigma = np.sqrt(np.abs(convolve(np.square(img), gaussian_window, mode='nearest') - np.square(mu)))
# normalize, as in Eq. 1 in the paper
img_nomalized = (img - mu) / (sigma + 1)
feat = []
for idx_w in range(num_block_w):
for idx_h in range(num_block_h):
# process ecah block
block = img_nomalized[idx_h * block_size_h // scale:(idx_h + 1) * block_size_h // scale,
idx_w * block_size_w // scale:(idx_w + 1) * block_size_w // scale]
feat.append(compute_feature(block))
distparam.append(np.array(feat))
if scale == 1:
img = imresize(img / 255., scale=0.5, antialiasing=True)
img = img * 255.
distparam = np.concatenate(distparam, axis=1)
# fit a MVG (multivariate Gaussian) model to distorted patch features
mu_distparam = np.nanmean(distparam, axis=0)
# use nancov. ref: https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/stats/nancov.html
distparam_no_nan = distparam[~np.isnan(distparam).any(axis=1)]
cov_distparam = np.cov(distparam_no_nan, rowvar=False)
# compute niqe quality, Eq. 10 in the paper
invcov_param = np.linalg.pinv((cov_pris_param + cov_distparam) / 2)
quality = np.matmul(
np.matmul((mu_pris_param - mu_distparam), invcov_param), np.transpose((mu_pris_param - mu_distparam)))
quality = np.sqrt(quality)
quality = float(np.squeeze(quality))
return quality
def calculate_niqe(img, crop_border, params_path, input_order='HWC', convert_to='y', **kwargs):
"""Calculate NIQE (Natural Image Quality Evaluator) metric.
``Paper: Making a "Completely Blind" Image Quality Analyzer``
This implementation could produce almost the same results as the official
MATLAB codes: http://live.ece.utexas.edu/research/quality/niqe_release.zip
> MATLAB R2021a result for tests/data/baboon.png: 5.72957338 (5.7296)
> Our re-implementation result for tests/data/baboon.png: 5.7295763 (5.7296)
We use the official params estimated from the pristine dataset.
We use the recommended block size (96, 96) without overlaps.
Args:
img (ndarray): Input image whose quality needs to be computed.
The input image must be in range [0, 255] with float/int type.
The input_order of image can be 'HW' or 'HWC' or 'CHW'. (BGR order)
If the input order is 'HWC' or 'CHW', it will be converted to gray
or Y (of YCbCr) image according to the ``convert_to`` argument.
crop_border (int): Cropped pixels in each edge of an image. These
pixels are not involved in the metric calculation.
input_order (str): Whether the input order is 'HW', 'HWC' or 'CHW'.
Default: 'HWC'.
convert_to (str): Whether converted to 'y' (of MATLAB YCbCr) or 'gray'.
Default: 'y'.
Returns:
float: NIQE result.
"""
# ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
# we use the official params estimated from the pristine dataset.
niqe_pris_params = np.load(os.path.join(params_path, 'niqe_pris_params.npz'))
mu_pris_param = niqe_pris_params['mu_pris_param']
cov_pris_param = niqe_pris_params['cov_pris_param']
gaussian_window = niqe_pris_params['gaussian_window']
img = img.astype(np.float32)
if input_order != 'HW':
img = reorder_image(img, input_order=input_order)
if convert_to == 'y':
img = to_y_channel(img)
elif convert_to == 'gray':
img = cv2.cvtColor(img / 255., cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) * 255.
img = np.squeeze(img)
if crop_border != 0:
img = img[crop_border:-crop_border, crop_border:-crop_border]
# round is necessary for being consistent with MATLAB's result
img = img.round()
niqe_result = niqe(img, mu_pris_param, cov_pris_param, gaussian_window)
return niqe_result
if __name__ =='__main__':
from skimage import io
clean = io.imread('clean/2762.png')
noisy = io.imread('noisy/2762.png')
params_path = 'pre-train-models/'
'''
NIQE值越小,图像质量越好。
'''
print(calculate_niqe(clean, crop_border=0, params_path=params_path))
print(calculate_niqe(noisy, crop_border=0, params_path=params_path))