文章目录
- 说明
- day38
- 1.Dijkstra 算法思路分析
- 2.Prim 算法思路分析
- 3.对比
- 4.代码
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
day38
1.Dijkstra 算法思路分析
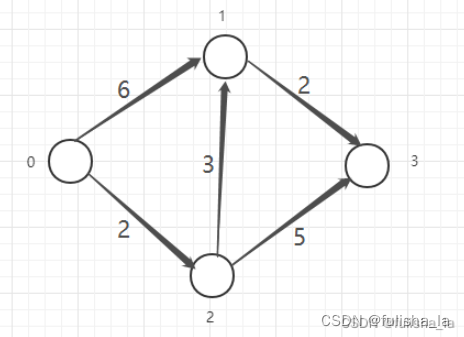
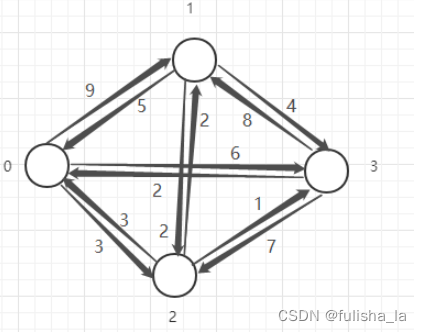
假设以顶点0出发
(1)0到各个顶点距离为:<0,1> 6;<0,2> 2 ;<0,3> ∞;选取最小距离<0,2> 2
(2)加入<0,2>一条边,看0到剩余顶点距离:
<0,1>: 原<0,1> 6,在加入<0,2>,则可以借助<0,2>,<0,2><2,1> 5;选取最小距离5
<0,3>:原<0,3> ∞,在加入<0,2>,<0,2><2,3> 7;选取最小距离7
比较5和7选取最小的距离5 0->1: 5
(3)加入<0,2><2,1>边,看0到剩余顶点的距离
<0,3>:原<0,2><2,3> 7,在加入<2,1>,<0,2><2,1><1,3>7; 选取最小距离<0,2><2,3> 7
节点遍历完,找到0到各点最短距离 0->3: 7
在这个过程中进一步思考:
在实现这个过程中需要借助一些数组来存储数据:
开始顶点到每一个顶点的最短距离需要有一个数组来存储,并且在每循环一次都需要检查这个数组是否需要更新
开始顶点到某个顶点不一定是直连路径,则需要存储开始顶点到某个顶点的路径,则也需要一个数组来存储路径。
顶点是否已经确定为最短路径结点,需要一个数组来做一个标志。
2.Prim 算法思路分析
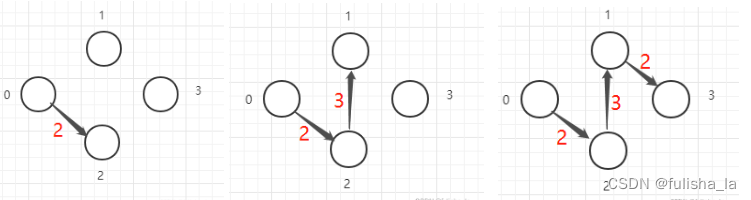
prim算法为最小生成树,过程:任意选一个顶点(如选0顶点)
从0顶点到与之相连的结点之间距离最短的顶点,图中为2
在0,2结点中选择距离最短的结点,则为 1 节点
在0,1,2结点中选择距离最短的结点,则为3节点
当结点树n = 边树n-1即构建成功
3.对比
Dijkstra 算法是求单源最短路径,可以算出开始顶点到其他顶点的最短路径,但是如果权重有负数,则dijstra并不能计算出正确的结果。而prim算法是构建最小生成树的一种策略。
Dijkstra 求单源最短路径时,我们要给定一个顶点,去找到其他结点的最短路径,而最小生成树是任意选择一个顶点开始。
Dijkstra 算法适用于有向图,而Prim更适合无向图(我认为主要是有向图在两个节点来回可能权重不同)
4.代码
- 在dijkstra中主要分为三个for循环,一个大的for循环:一次循环就可以确定从v0顶点到某个顶点的最短路径,在大循环中的第一个循环是找出v0结点到剩余未访问结点中的最短路径,第三个循环是:已经确定某个顶点是最短路径,去更新tempDistanceArray,tempParentArray这两个数组。
public int[] dijikstra(int paraSource) {
// Step 1. Initialize.
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(paraSource, i);
}
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, paraSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[paraSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraSource] = true;
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
}
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
}
}
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
}
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
}
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
}
}
// For test
System.out.println("The distance to each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
}
// Step 3. Output for debug.
System.out.println("Finally");
System.out.println("The distance to each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
return tempDistanceArray;
}
- 在prim算法中,与dijkstra算法最大的区别在与第三个循环中,在更新tempDistanceArray是累加之前的边,而在prim算法中则不需要累加,只需要判断从这个已选结点出发到其他结点的距离是否需要更新
public int prim() {
// Step 1. Initialize.
// Any node can be the source.
int tempSource = 0;
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempSource, i);
}
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, tempSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[tempSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[tempSource] = true;
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
}
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
}
}
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
}
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
}
// Attention: the difference from the Dijkstra algorithm.
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
}
}
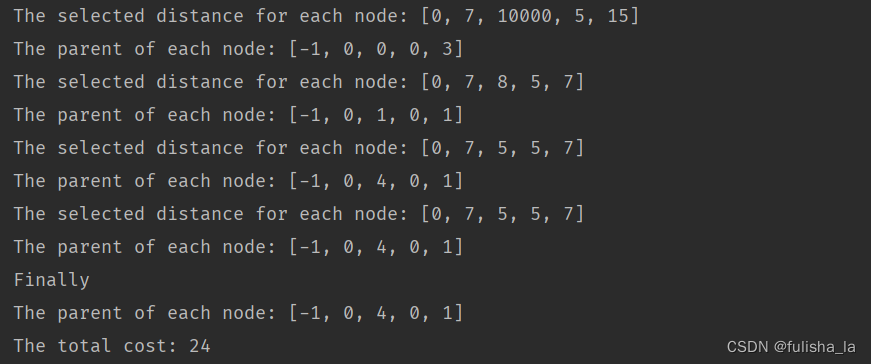
// For test
System.out.println(
"The selected distance for each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
}
int resultCost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
resultCost += tempDistanceArray[i];
}
// Step 3. Output for debug.
System.out.println("Finally");
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
System.out.println("The total cost: " + resultCost);
return resultCost;
}
-
单元测试
-
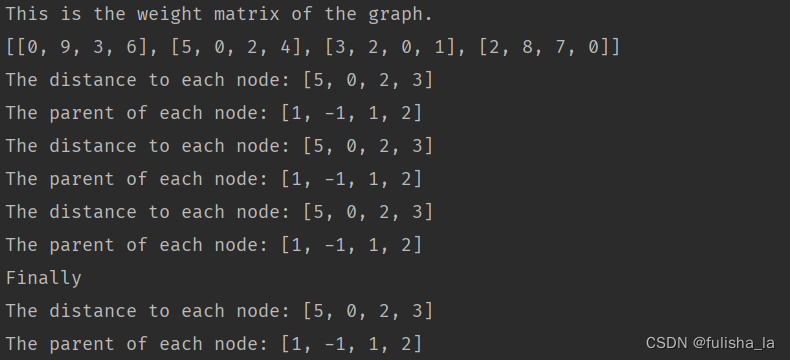
dijkstra算法(从顶点0出发)
-
prim算法