1.什么要做python连接mysql,一般是解决什么问题的
做自动化测试时候,注册了一个新用户,产生了多余的数据,下次同一个账号就无法注册了,这种情况怎么办呢?自动化测试都有数据准备和数据清理的操作,如果因此用例产生了多余数据,就需要清理数据,可以用Pyhthon连接Mysql直接删除多余的数据就可以了。
Python3如何连接Mysql呢?PyMySQL是在Py3版本用于连接Mysql
2.python连接mysql的模块安装
在线安装
pip install PyMySQL
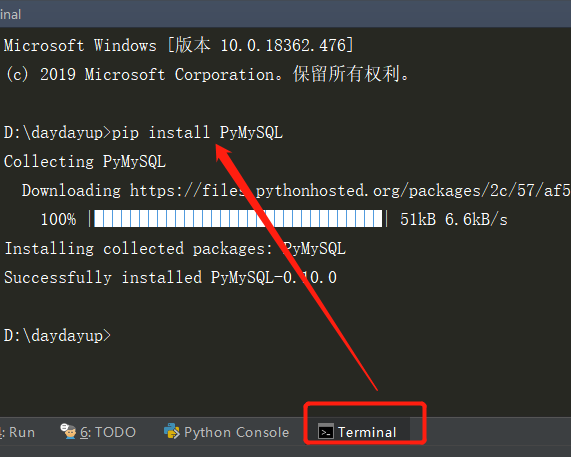
在Pycharm—点击–Terminal—输入pip install PyMySQL等待完装完毕即可,如图所示
离线安装
有时候在线安装第三方模块的时,会因为网络原因总是装不上,那怎么办呢?那就手动安装
1.下载所需要的模块包
2.解压该文件
3.将文件名改短,然后放入非C盘且放在根目录
4.打开cmd---->E:---->cd xlrd---->python setup.py install
5.等待完装完毕
6.导入模块 import xlrd,运行如果没报错就说明安装正常
3.连接MySql
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# 使用 execute() 方法执行 SQL 查询
cursor.execute("SELECT VERSION()")
# 使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据.
data = cursor.fetchone()
print("Database version : %s " % data)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
4.数据库基本操作
增加数据
insert 语句可以用来将一行或多行数据插到数据库表中, 使用的一般形式如下:
insert [into] 表名 [(列名1, 列名2, 列名3, ...)] values (值1, 值2, 值3, ...);
其中 [ ] 内的内容是可选的, 例如, 要给study_date数据库中的 studys 表插入一条记录, 执行语句:
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
insert_sql =
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute("insert into studys(id, name, age) values(3, '骑着乌龟赶猪', 35)")
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit() cursor.execute("select * from studys")
# 查看表里所有数据
data = cursor.fetchall()
print(data) # 关闭数据库连接 db.close()
再运行一次上以代码,运行后报错,两个重要错误信息
1、错误在哪一行

2、这个错误原因
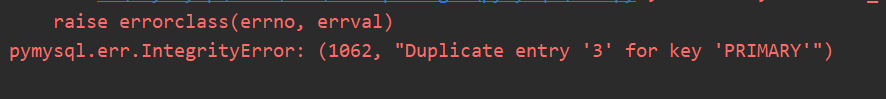
为防止插入数据时出现异常,所以加上try…except
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
insert_sql = "insert into studys(id, name, age) values(3, '骑着乌龟赶猪', 35)"
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(insert_sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
cursor.execute("select * from studys")
# 查看表里所有数据
data = cursor.fetchall()
print(data)
except:
print("数据插入失败,请查检try语句里的代码")
# 关闭数据库连接
# 如果想知道报了啥错,可以主动抛出异常
# raise
db.close()
5.删除数据
delete 语句用于删除表中的数据
delete from 表名称 where 删除条件;
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
check_sql = 'select * from studys'
# SQL 删除数据
del_sql = "delete from studys where id=3"
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(del_sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
cursor.execute(check_sql)
# 查看表里所有数据
data = cursor.fetchall()
print(data)
except:
# 如果发生错误则回滚
db.rollback()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
6.修改数据
update 语句可用来修改表中的数据
update 表名称 set 列名称=新值 where 更新条件;
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
check_sql = 'select * from studys'
# SQL 修改数据
updata_sql = "update studys set age=30 where id=2"
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(updata_sql)
# 提交到数据库执行
db.commit()
cursor.execute(check_sql)
# 查看表里所有数据
data = cursor.fetchall()
print(data)
except:
# 如果发生错误则回滚
db.rollback()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
7.查询数据
查询单条数据
语法:
fetchone()
例如要查询 students 表中所有学生的名字和年龄, 输入语句
select name, age from studys
fetchone()获取一行数据
# 导入模块
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接 数据库地址
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# 使用 execute()方法执行 SQL 查询
# 通配符,意思是查询表里所有内容
cursor.execute("select * from studys")
#Python小白学习交流群:711312441
# 使用 fetchone() 方法获取一行数据.
data = cursor.fetchone()
print(data)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
查询多条数据
fetchall()获取所有数据
# 导入模块,固定写法
import pymysql
# 打开数据库连接 数据库地址
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "111223", "study_date")
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
# 使用 execute() 方法执行 SQL 查询
cursor.execute("select * from studys")
# 使用 fetchall() 方法获取所有数据.以元组形式返回
data = cursor.fetchall()
print(data)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()






![[oeasy]python0140_导入_import_from_as_namespace_](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/e19f7e6297ba4f1c175df5e0c3b9054d.png)