文章目录
- HDR and tone mapping
- 1.什么是HDR?
- 2.为什么需要HDR?
- 3.hdr文件格式
- 4.tone mapping
- 4.1 aces tone mapping
- 4.2 Fast Bilateral Filtering for the Display of High-Dynamic-Range Images
- 5 参考
HDR and tone mapping
1.什么是HDR?
就是高动态图像。如何体现
查看 https://www.easyhdr.com/examples/ 这个网站上的例子:

3张曝光融合为一张, 似乎是挑出不同曝光图像中比较清晰的部分 进行融合。
比如选了 第一张欠曝图像中 的高光蓝天部分, 选了第二三张过曝图像 中的 一些低亮度 海岸部分。 最终融合一张 整体亮度适中的 HDR图像:这样既能看清蓝天,也能看清海岸。
那么是不是可以通过调整第二张图像的亮度来达到 HDR的效果呢? 比如压制高光蓝天,提亮低光海岸。答案也是可以的,有一些深度学习的方法也是这么做的,单张HDR或者图像增强。
如下面的例子:

2.为什么需要HDR?
因为现实场景的动态范围非常大,人眼的动态范围也比较宽广, HDR技术可以更好的表达场景,更好的符合人眼感知
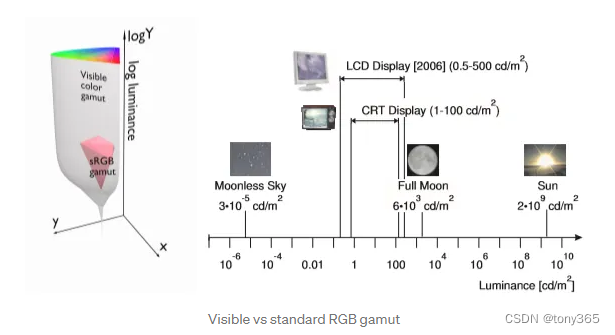
sdr和 hdr图像:
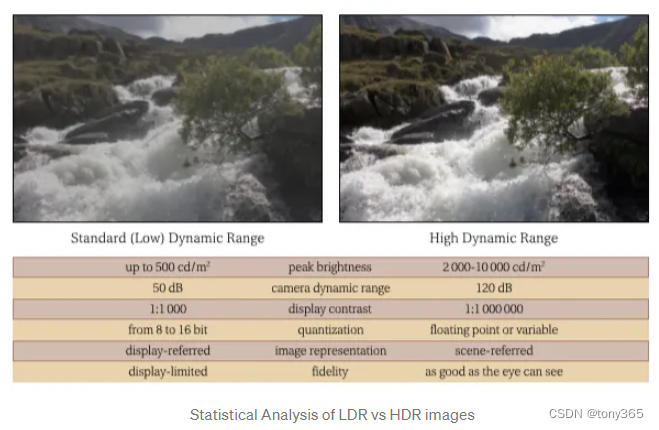
3.hdr文件格式
hdr文件 是 float32类型,记录的是场景的亮度,与辐射是线性关系。
在 改网站上可以显示hdr图像:https://viewer.openhdr.org/
比如拖入nave.hdr文件可以得到:

右上角是曝光调节,可以看到不同曝光条件下的 图像。
这里我用python 实现了上面网站类似的效果:
根据不同的ev, 提取一定范围内直方图的数据,展示图片。
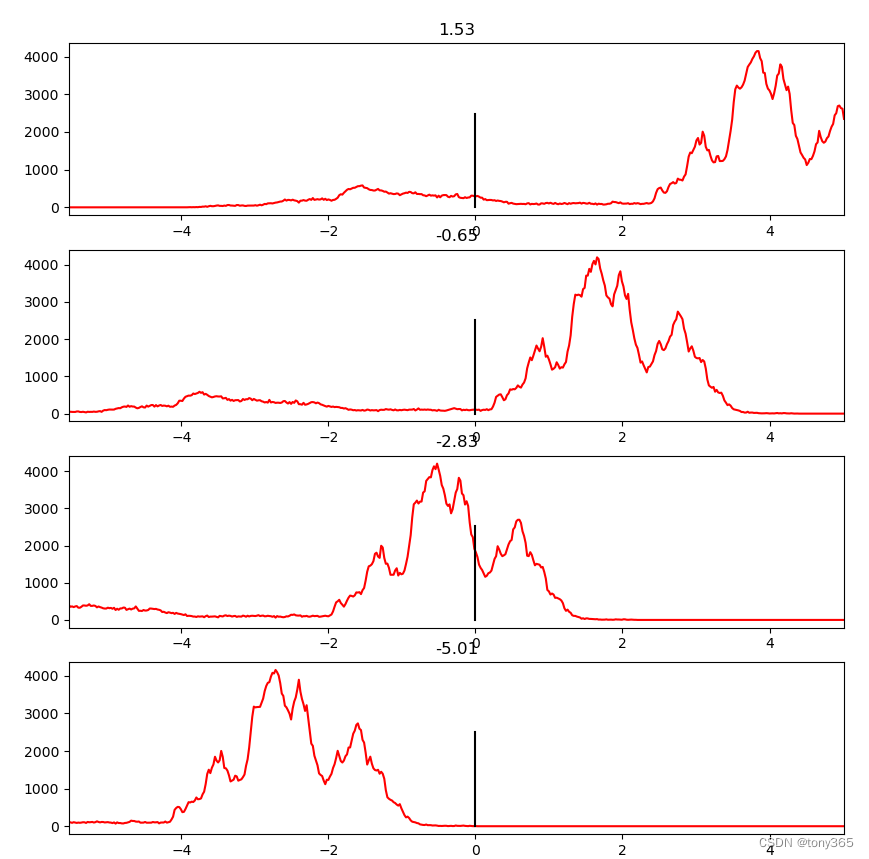
提取 乘上(2^ev)之后的[0, 1]范围内数据
img = np.clip(data * (2 ** ev), 0, 1) ** (1/2.2)
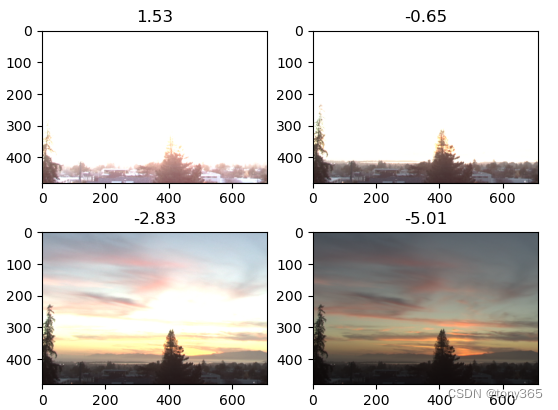
完整code:
def compute_luminance(input: np.ndarray):
luminance = 0.2126 * input[:, :,
0] + 0.7152 * input[:, :,
1] + 0.0722 * input[:, :, 2]
return luminance
def map_luminance(input: np.ndarray, luminance: np.ndarray,
new_luminance: np.ndarray):
output = np.zeros(input.shape)
output[:, :, 0] = input[:, :, 0] * new_luminance / luminance
output[:, :, 1] = input[:, :, 1] * new_luminance / luminance
output[:, :, 2] = input[:, :, 2] * new_luminance / luminance
return output
if __name__ == "__main__"
file = r'D:\code_color\HDR-Tone-Mapping-and-Image-Upscaling-main\test image\hdr_images\vinesunset.hdr'
data = cv2.imread(file, cv2.IMREAD_ANYDEPTH)[..., ::-1]
print('rgb data info ')
print(data.shape, data.dtype, data.min(), data.max(), data.mean())
L = compute_luminance(data)
print('L info ')
print(L.shape, L.dtype, L.min(), L.max(), L.mean())
L_log = np.log2(L)
print('L log info ')
print(L_log.shape, L_log.dtype, L_log.min(), L_log.max(), L_log.mean())
bin_low = L_log.min()
bin_high = L_log.max()
bins_num = 500
hist2, bins2 = np.histogram(L_log, bins_num, [bin_low, bin_high])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3))
plt.title("complete hist")
plt.plot(np.linspace(bin_low, bin_high, bins_num), hist2, 'r-')
plt.show()
num_ev = 4
hist_s = []
img_s = []
evs = -np.linspace(bin_low+4, bin_high, num_ev)
print('evs : ', evs)
for ev in evs:
L0 = L * (2 ** ev)
hist, bins= np.histogram(np.log2(L0), bins_num, [bin_low, bin_high])
print(L0.min(), L0.max())
img = np.clip(data * (2 ** ev), 0, 1) ** (1/2.2)
hist_s.append(hist)
img_s.append(img)
# 画图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3*num_ev))
for i in range(len(evs)):
ev = evs[i]
hist = hist_s[i]
ax = plt.subplot(num_ev, 1, i+1)
ax.plot(np.linspace(bin_low, bin_high, bins_num), hist, 'r-')
ax.plot((0, 0), (0, 0.6*hist.max()), 'k-')
ax.set_title(str(np.round(ev, 2)))
plt.xlim([bin_low, bin_high])
plt.figure()
for i in range(len(evs)):
ev = evs[i]
img = img_s[i]
ax = plt.subplot(2, (num_ev+1)//2, i+1)
ax.set_title(str(np.round(ev, 2)))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
4.tone mapping
hdr的数据 覆盖的亮度比较大,而一般的传统设备可能无法显示 hdr数据(比如只能显示8bit的 sdr数据)
可以想到的是直接对hdr数据进行归一化,然后乘上255进行显示。但是这样显示有一个问题,就是比如一个hdr数据很多细节都在 比较小的数据上,如下图直方图所示:
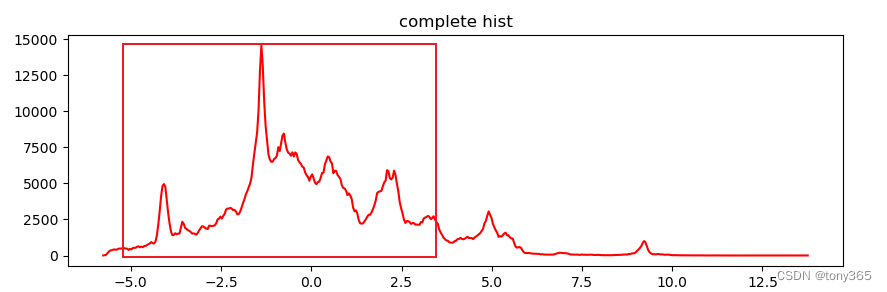
这个时候线性归一化后,图像会整体比较暗,如下图:

一个正常的tone mapping方法可以得到正常的图像:

tone mapping 就是将hdr数据映射到 sdr设备上的方法。
在 这篇博客中有介绍一些常见的tone mapping方法:
比如Reinhard tone mapping, aces tone mapping等, 好像都是S-curve形状。
4.1 aces tone mapping
这里实现aced tone mapping 看下效果
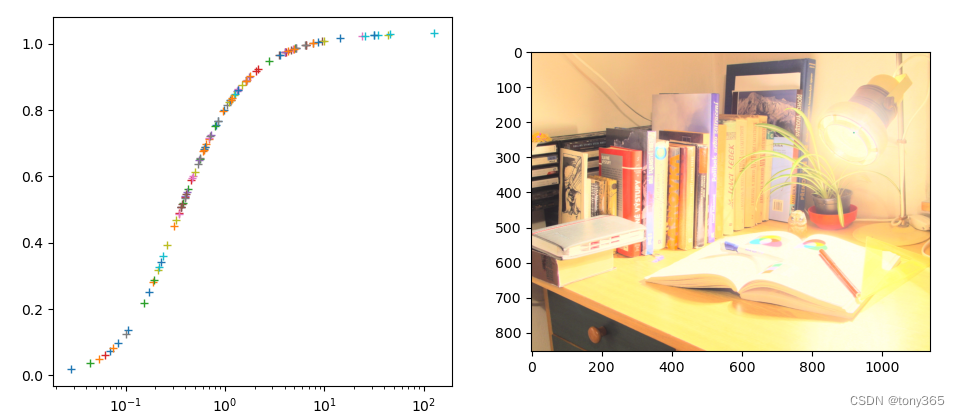
def aces_tone_mapping(x):
a = 2.51
b = 0.03
c = 2.43
d = 0.59
e = 0.14
return (x * (a * x + b)) / (x * (c * x + d) + e)
def map_luminance(input, luminance, new_luminance, s=1):
output = ((input / luminance[..., None])**s) * new_luminance[..., None]
output = np.clip(output, 0, 1)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__"
# aces tone mapping
x = L
y = aces_tone_mapping(x)
out_aces = map_luminance(data, x, y, 1)
out_aces = out_aces ** (1 / 2.2)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(121)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.plot(x[::100, ::100], y[::100, ::100], '+')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(out_aces)
plt.show()
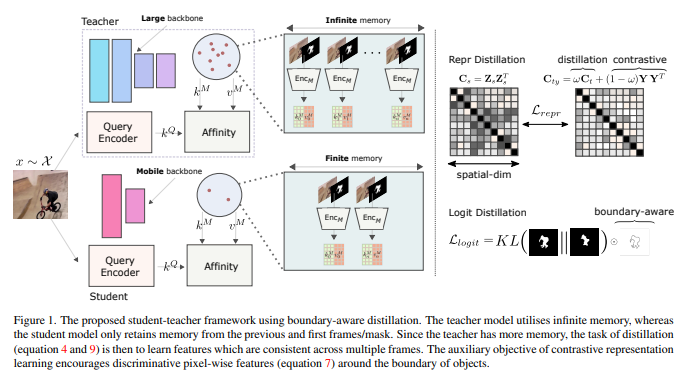
4.2 Fast Bilateral Filtering for the Display of High-Dynamic-Range Images
Durand and Julie Dorsey 基于 滤波 和 分层的 tone mapping方法
算法原理如下:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-IjkwRsN2-1682410919356)(2023-04-25-15-17-55.png)]
仿真实验效果:
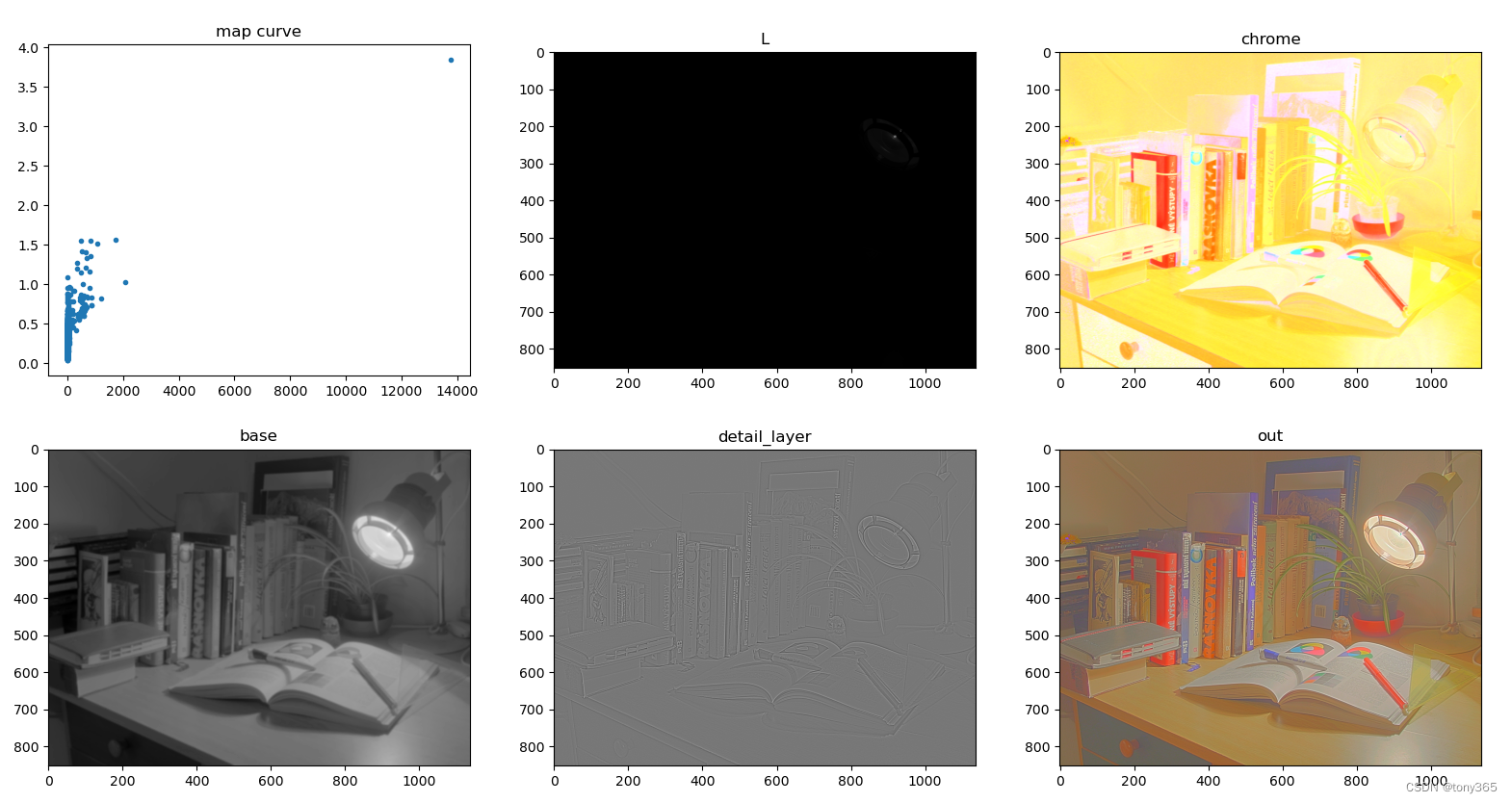
python code:
def fast_bilateral_tone_mapping(data):
contrast = 10
L = compute_luminance(data)
chrome = data / L[..., None]
log_intensity = np.log10(L)
base_layer = bilateral_filter(log_intensity, 7, 50, 50)
detail_layer = log_intensity - base_layer
compression_factor = np.log10(contrast) / (base_layer.max() - base_layer.min())
log_abs_scale = base_layer.max() * compression_factor
out_log_lum = base_layer * compression_factor + detail_layer - log_abs_scale
out_lum = np.power(10, out_log_lum)
out = chrome * out_lum[..., None]
out = np.clip(out, 0, 1) ** (1 / 2.2)
print('out : ', out.min(), out.max())
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(231)
plt.title('map curve')
plt.plot(L.reshape(-1)[::100], out_lum.reshape(-1)[::100], '.')
plt.subplot(232)
plt.title('L')
plt.imshow(L, 'gray')
plt.subplot(233)
plt.title('chrome')
plt.imshow(chrome)
plt.subplot(234)
plt.title('base')
plt.imshow(base_layer, 'gray')
plt.subplot(235)
plt.title('detail_layer')
plt.imshow(detail_layer, 'gray')
plt.subplot(236)
plt.title('out')
plt.imshow(out)
plt.show()
return out
fast_bilateral_tone_mapping(data)
https://sites.google.com/site/ianschillebeeckx/cse555/hmwk1
5 参考
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1167088?areaSource=103001.6&traceId=r3KPIA5AV5GmTN3HDENpZ 色域映射介绍: HDR关键技术—色域映射
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1358173?areaSource=103001.5&traceId=r3KPIA5AV5GmTN3HDENpZ HDR关键技术:逆色调映射
本文主要介绍和了解hdr文件,以及tone mapping概念。
关于如何生成 HDR , tone mapping 算法, inverse tone mapping 方法等没有过多的介绍。