Know-Evolve: Deep Temporal Reasoning for Dynamic Knowledge Graphs
Rakshit Trivedi 1 Hanjun Dai 1 Yichen Wang 1 Le Song 1
知识背景
Temporal Knowledge Graph : facts occur,recur or evolve over time in these graphs,and each edge in the graphs have temporal information associated with it
knowledge evolution : evolve entities and their dynamically changing relationships over time
存在的问题
static graph 缺点:lack ability to use rich temporal dynamics available in underlying data represented by temporal knowledge graphs
论文提出方法
Know-Evolve
主要做法:the occurrence of a fact(edge) is modeled as a multivariate point process whose intensity function is modulated by th score for that fact computed based on the learned entity embeddings
论文主要贡献
1.propose a novel deep learning architecture : evolve over time based on availability of new facts
2.ability to predict time when the fact may potentially occur(⭐比其他论文的优点)
3.support Open World Assumption as missing links are not considered to be false and may potentially occur in time + support prediction over unseen entities due to its novel dynamic embedding process(⭐没发生的事件不能说是错误的)
4.temporal point process framework(⭐⭐⭐论文重要方法)
预备知识
预备知识1-Temporal Point Process
1.random process
2.consist of a list of events localized in time
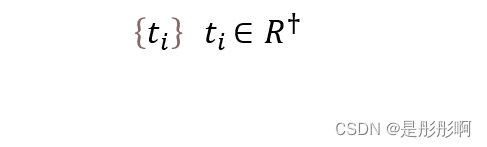
3.temporal point process = counting process N(t) : the number of events before time t
4.
typically assume that only one event can happen in a small window of size dt
dN(t) ∈ {0,1}
5.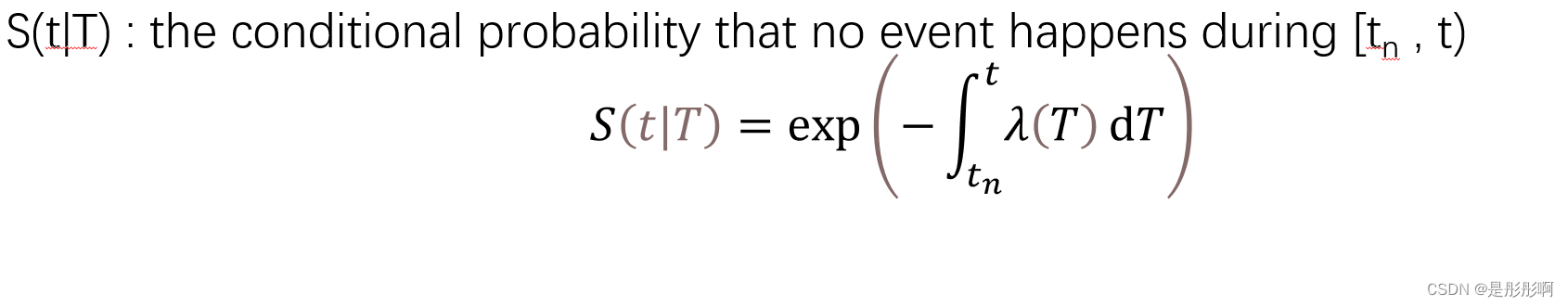
6.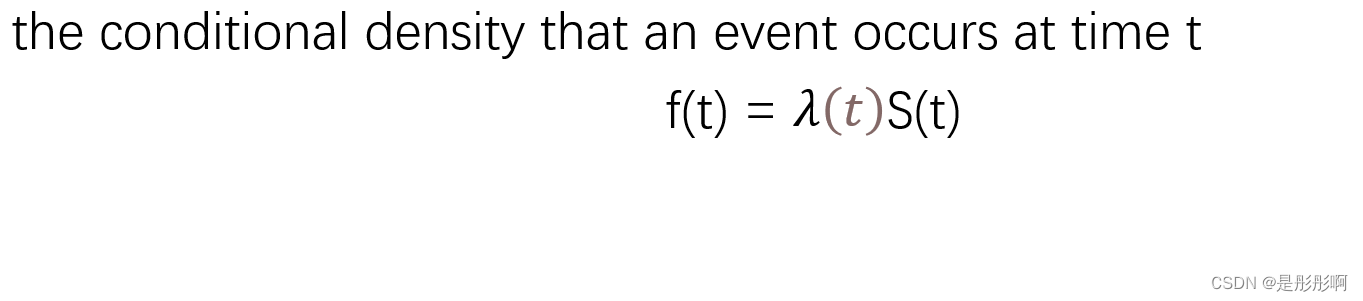
预备知识2-Temporal Knowledge Graph representation
1.
2.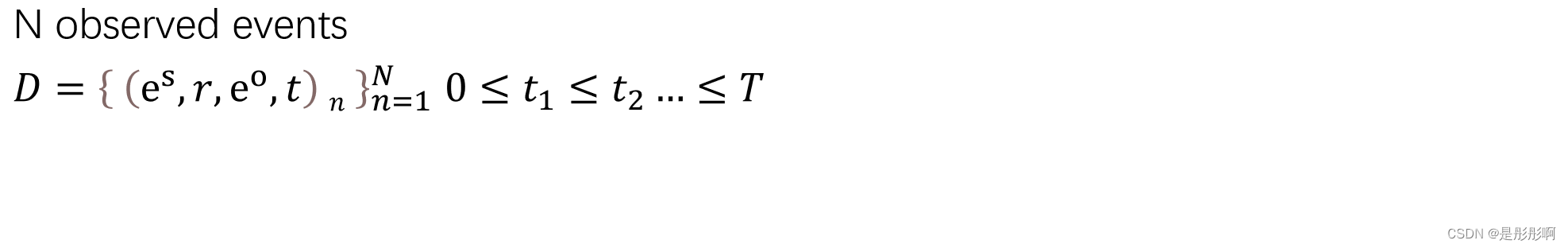
Evolutionary Knowledge Network
1.Temporal Process
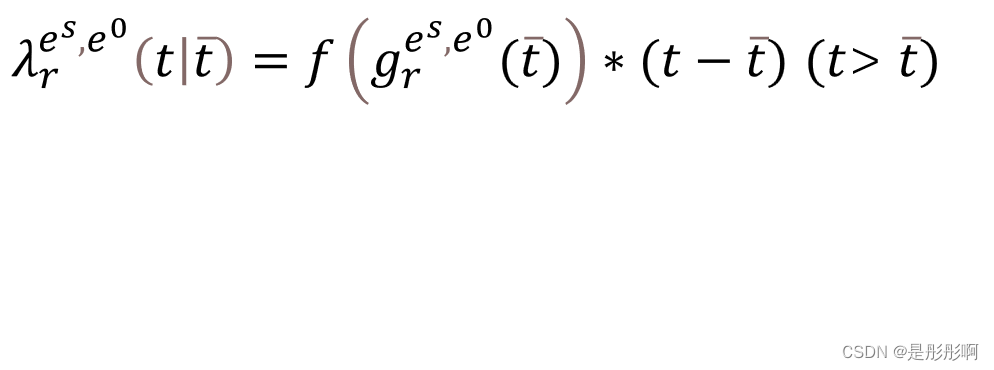

this modulates the intensity of current event based on most recent activity on either entities’ timeline and allows to capture scenarios like non-periodic events and previously unseen events
2.Relational Score Function
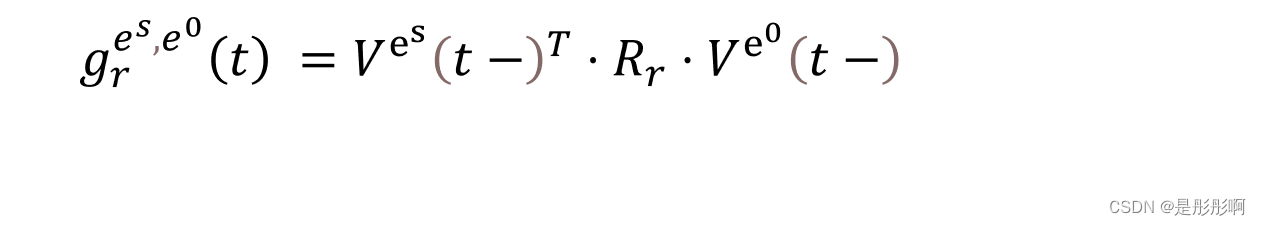

3.Dynamically Evolving Entity Representations

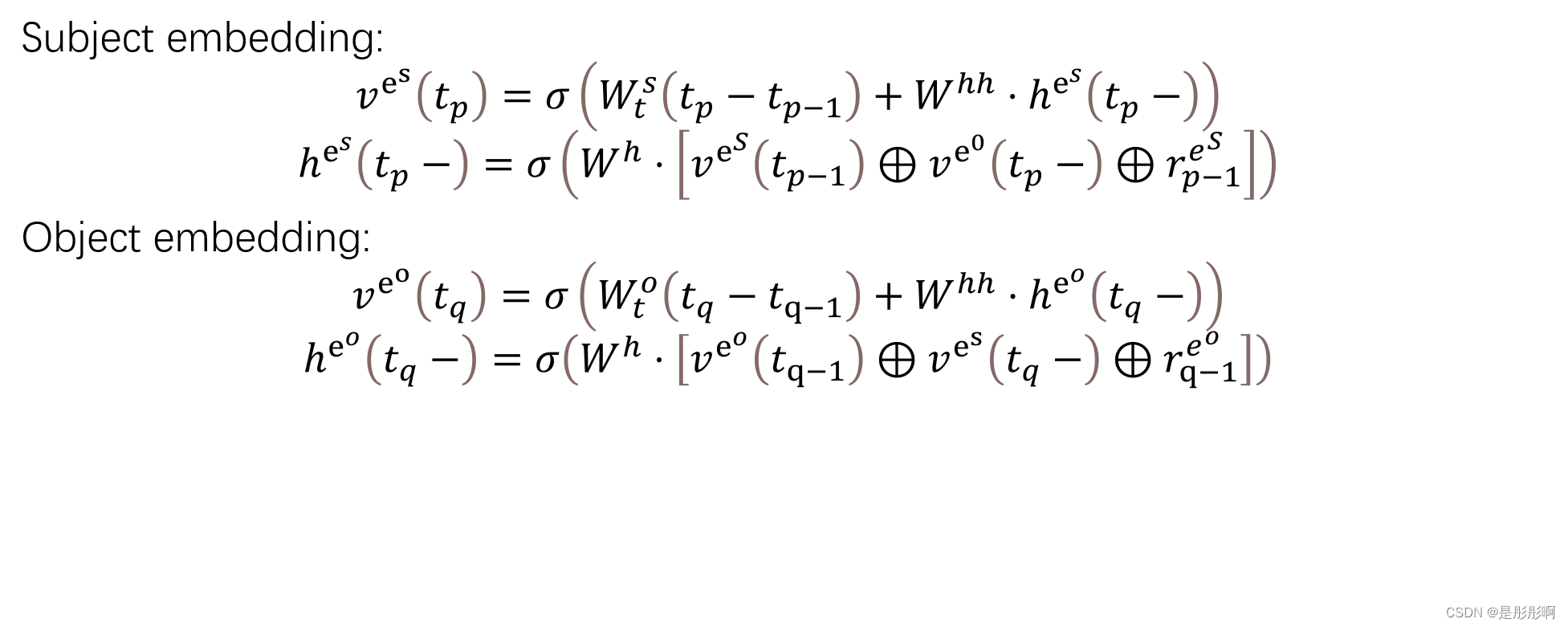


Understanding Unified View of Know-Evolve
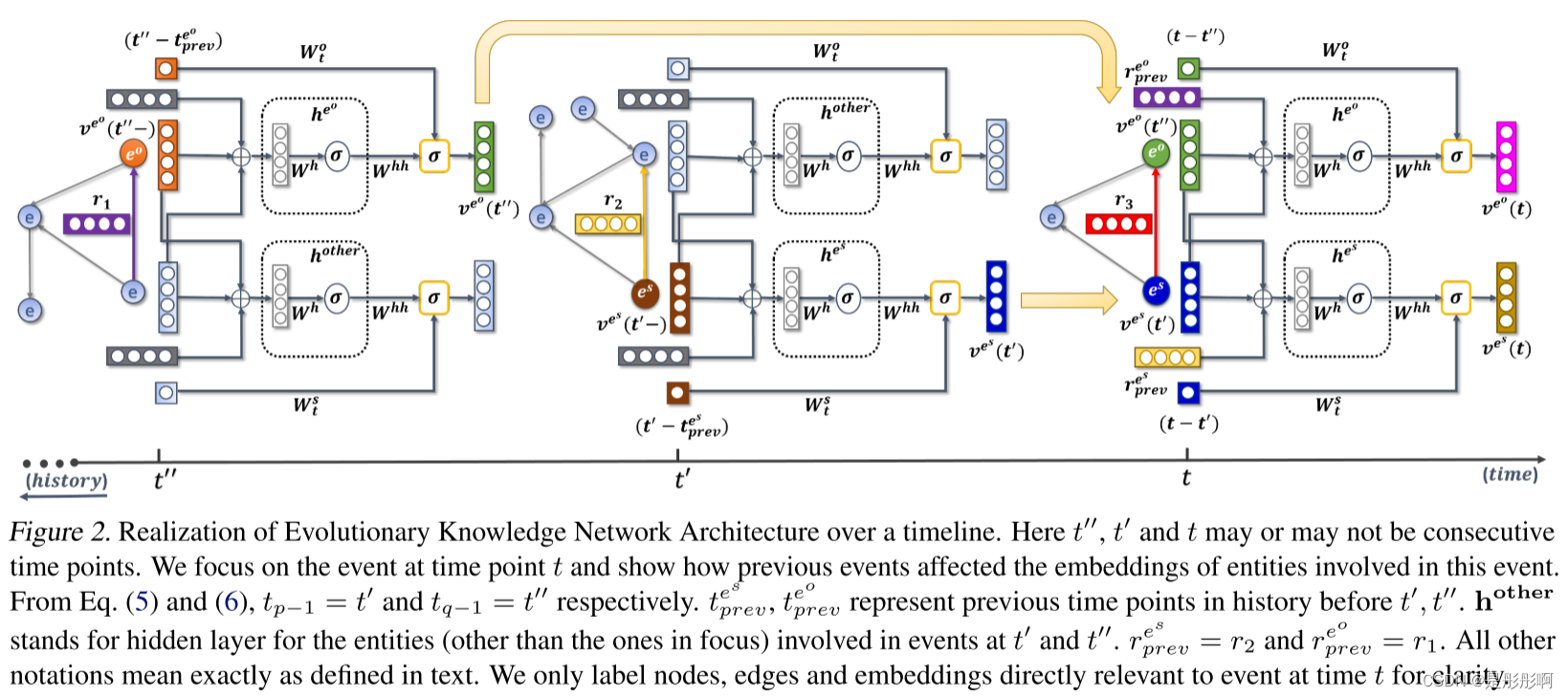

实验
实验数据集
1.Global Database of Events, Language,and Tone (GDELT)
2.Integrated Crisis Early Warning System (ICEWS)
对比方法
there are no existing relational learning approaches that can predict time for a new fact
->hence we devised two baseline methods for evaluation time prediction performance
1.Multi-dimensional Hawkes process (MHP)
具体方法:an entity pair constitues a dimension and for each pair we collect sequence of events on its dimension and train and test on that sequence.
relationship is not modeled in this setup
2.Recurrent Temporal Point Process (RTPP)
具体方法:we concatenate static entity and relationship embeddings and augmented the resulting vector with temporal feature.This agumented unit is uaed as input to global RNN which produces output vector ht.During test time,for a given triplet,we use this vector ht to compute conditional intensity of the event given history which is further used to predict next event time.
主要用于time prediction
实验结果
link prediction
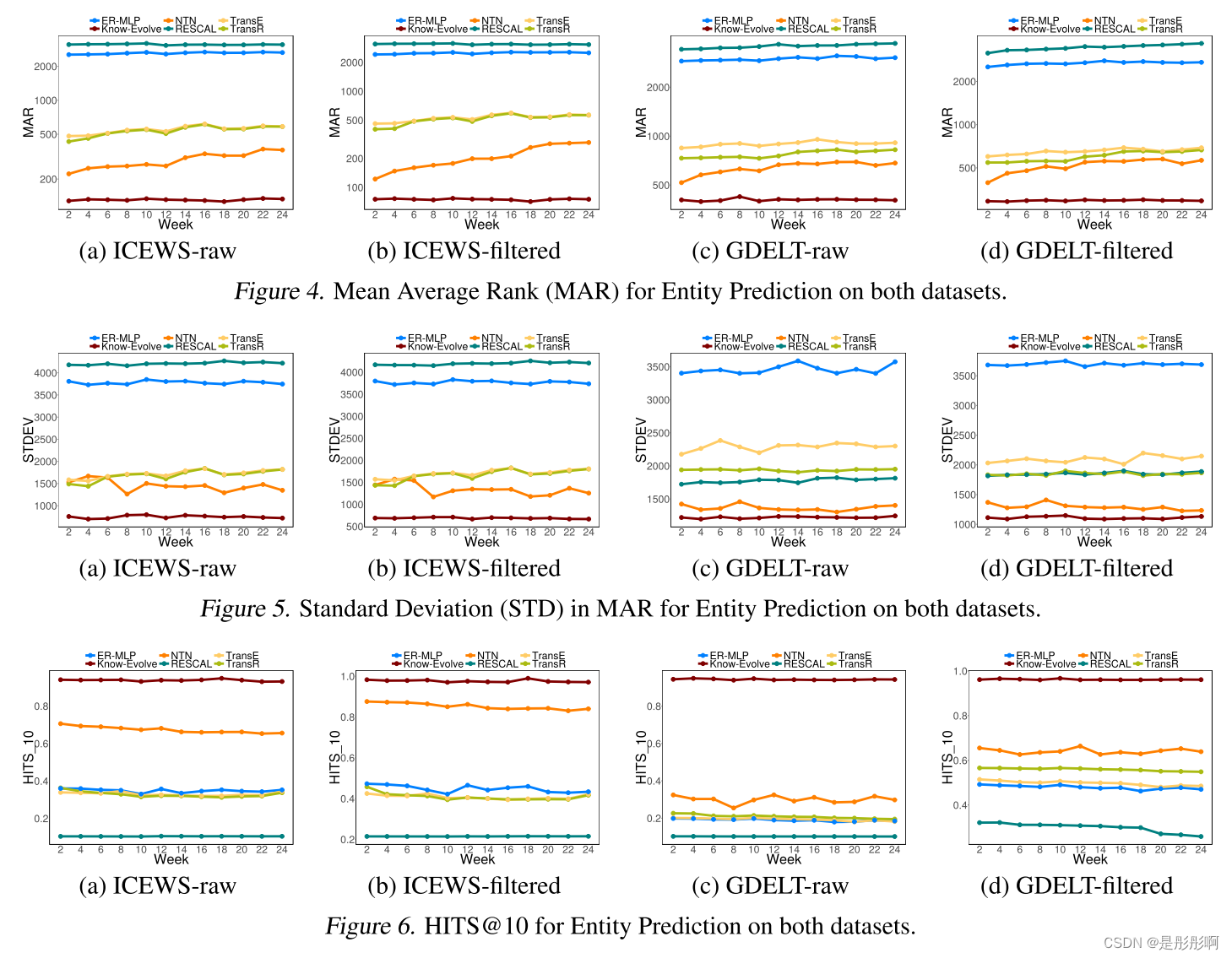
可以看出Know-Evolve比其他方法都有效
time prediction
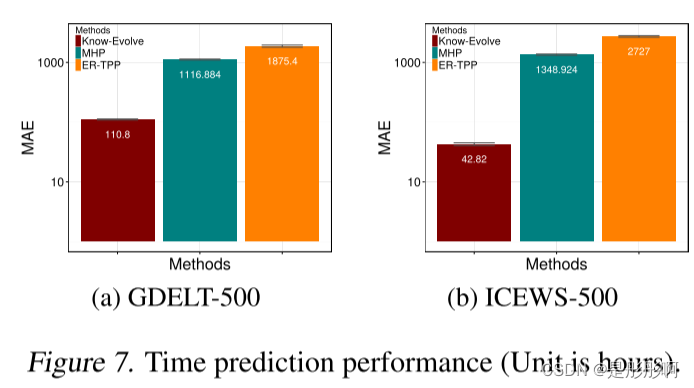
总结思考
1.论文相较于之前的方法,提出图谱是动态进化的,是时序的
2.在加入时间的概念之后,不仅可以link prediction 还可以 time prediction(预测事件再次发生的时间)
3.文章中提到的new fact 我认为指的是实体库中subject 和 object 重新组合的结果,并没有生成一个entity,是图谱的更新存储的问题
比如 (小王,课代表,初一二班,2001) new fact 指(小王,班长,初一二班,2002)
而不会指(小李,班长,初一二班,2002)当小李不在实体库中