前文了解了线程的创建方式和状态切换,在实际开发时,一个进程中往往有很多个线程,大多数线程之间往往不是绝对独立的,比如说我们需要将A和B 两个线程的执行结果收集在一起然后显示在界面上,又或者比较典型的消费者-生产者模式,在这些场景下,线程间通信成了我们必须使用的手段,那么线程之间怎么通信呢?
线程间通信方式,从实现本质来讲,主要可以分为两大类共享内存和消息传递。
相信大家还记得,在内存模型一节,我们提到多线程并发情况下的三大特性,原子性,有序性,可见性,其所对应的解决方案就可以用来实现线程间通信,这些解决方案的本质就是共享内存。
对于消息传递而言,最经典的实现就是我们的Handler机制,在子线程使用主线程的Handler对象将一些信息发送到主线程以便进行处理。
下面我们来看一些线程间通信的典型实现
Object.wait/Object.notify
对于Object对象而言,其提供了等待/通知机制以便实现线程间通信,由于Object是Java中所有类的父类,也就意味着Java中所有对象都支持通知/等待机制,与该机制关联的主要有五个方法:
| 方法名称 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| wait() | 线程执行中调用对象的wait方法可以使得当前线程进入WAITING状态,只有等待其他线程的通知或被中断才会返回,需要注意的是,调用wait方法后,会释放对象的锁 | / |
| wait(long timeout) | 与wait含义一致,不同的是通过timeout指定了超时时间,如果时间到了还没收到通知就超时返回 | / |
| wait(long timeout, int nanos) | 超时管控更加精确,第二个参数单位为毫微秒 | / |
| notify | 通知一个在对象上等待的线程使其从wait对象返回 | / |
| notifyAll | 通知所有等待在该对象上的线程 | / |
以Object.wait/Object.notify实现一个典型的消息者生产者模型,消费者对变量做-1操作,生产者对变量做+1操作,代码如下:
// 盘子
public class Number {
// 盘子当前容量,是否有内容
private int mCount = 0;
//对盘子容量进行+1操作
public void inc() {
if (mCount != 0) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCount++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",mCount+1,mCount="+mCount);
this.notifyAll();
}
//对盘子容量进行-1操作
public void dec() {
if (mCount == 0) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCount--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",mCount-1,mCount="+mCount);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number number = new Number();
// 生产者线程
Thread incThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
number.inc();
}
});
incThread.setName("Inc Thread");
incThread.start();
// 消费者线程
Thread decThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
number.dec();
}
});
decThread.setName("Dec Thread");
decThread.start();
}
如上述代码备注,其中Inc Thread为生产者线程,当盘子内容为0时,每次向盘子Number中放一个内容,消费者线程Dec Thread当盘子有内容时,消耗内容,让盘子内容变为0.运行输出如下:
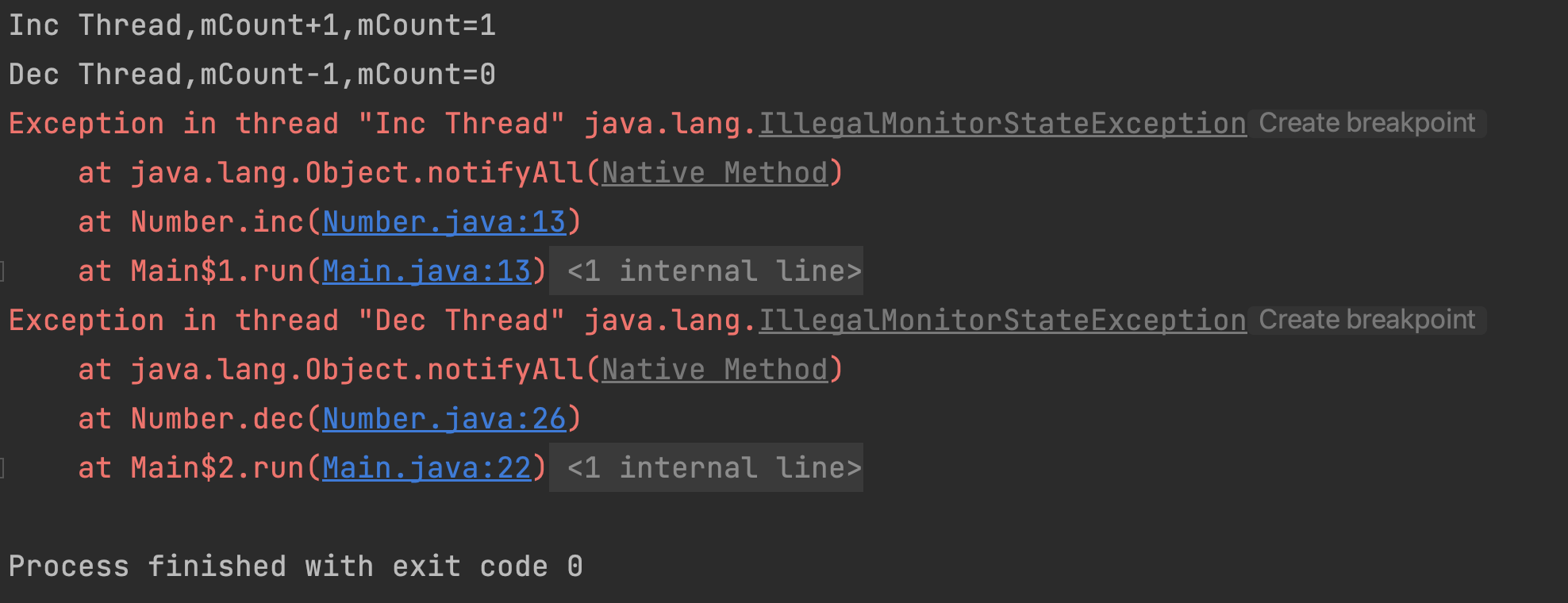
糟糕,正确运行一个循环后,抛出了IllegalMonitorStateException,为什么会这样呢?这个异常是什么意思?
遇事不决看源码,IllegalMonitorStateException的类说明如下:
Thrown to indicate that a thread has attempted to wait on an object’s monitor or to notify other threads waiting on an object’s monitor without owning the specified monitor.
翻译过来的意思就是当线程在没有持有特定的锁的情况下试图等待对象锁或者通知其他线程等待对象锁会抛出此异常,有点拗口,先放置,即然我们调用了wait/notifyAll这两个方法,不妨看下这两个方法的说明,看是否有新的提示,wait方法说明如下:
/** * Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the * {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the * {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object. * In other words, this method behaves exactly as if it simply * performs the call {@code wait(0)}. * <p> * The current thread must own this object's monitor. The thread * releases ownership of this monitor and waits until another thread * notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor to wake up * either through a call to the {@code notify} method or the * {@code notifyAll} method. The thread then waits until it can * re-obtain ownership of the monitor and resumes execution. * <p> * As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are * possible, and this method should always be used in a loop: * <pre> * synchronized (obj) { * while (<condition does not hold>) * obj.wait(); * ... // Perform action appropriate to condition * } * </pre> * This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner * of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a * description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of * a monitor. * * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not * the owner of the object's monitor. * @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the * current thread before or while the current thread * was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted * status</i> of the current thread is cleared when * this exception is thrown. * @see java.lang.Object#notify() * @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll() */ public final void wait() throws InterruptedException { wait(0); }
在上述说明中反复提到 The current thread must own this object’s monitor. This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner of this object’s monitor.也就是说在调用Object.wait方法前,当前线程必须持有该对象的锁,获取锁的方法很简单,wait方法说明中也有,通过synchronized关键词,那么正确的调用代码如下所示:
public class Number {
private int mCount = 0;
public void inc() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mCount != 0) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCount++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",mCount+1,mCount="+mCount);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public void dec() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mCount == 0) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCount--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",mCount-1,mCount="+mCount);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
重新运行代码,输出如下:
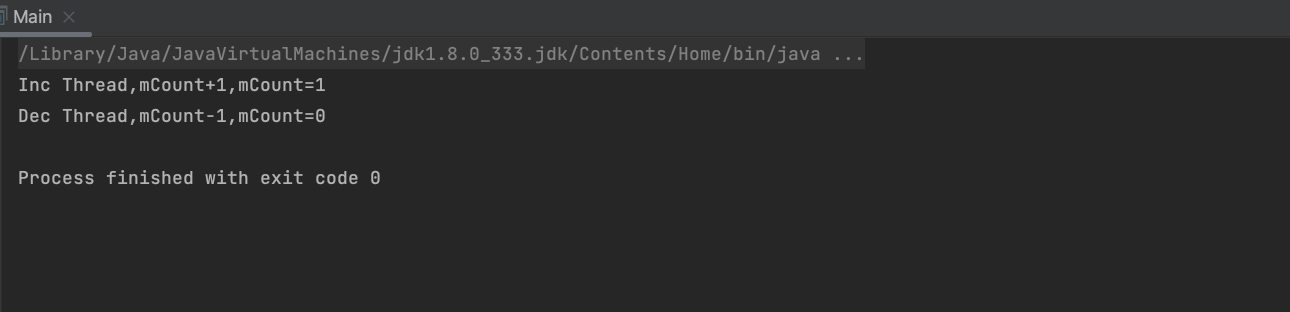
这里可以看出,只运行了一个循环,那么怎么让它一直运行呢?将if修改称while即可,以生产10次为例,如需一直生产消息,使用while(true)即可,代码及输出如下:
public class Number {
private int mCount = 0;
private int mIncTimes = 0;
private int mDecTimes = 0;
public void inc() {
synchronized (this) {
while (mIncTimes < 10) {
if (mCount != 0) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCount++;
mIncTimes ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",mCount+1,mCount="+mCount+",mIncTimes:"+mIncTimes);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
public void dec() {
synchronized (this) {
while (mDecTimes < 10) {
if (mCount == 0) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mCount--;
mDecTimes++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",mCount-1,mCount="+mCount+",mDecTimes:"+mDecTimes);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
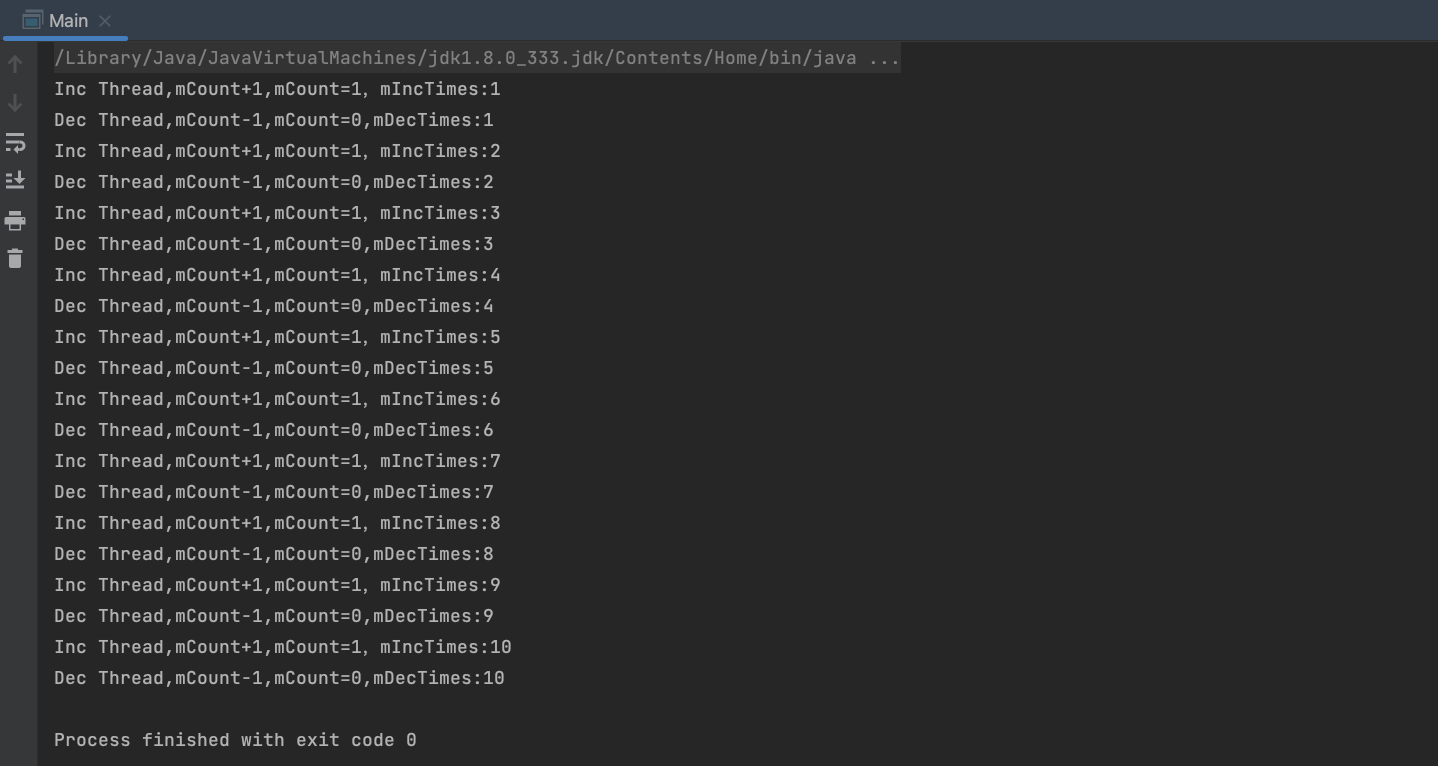
综上,使用Object.wait/Object.notify/Object.notifyAll时,切记其必须先使用关键词获取同个Object的对象锁,否则就会抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
Semaphore
Semaphore翻译为信号量,一个信号量维护一组许可,在调用acquire方法时阻塞,直到获取许可,在调用release的时候释放占用,从而唤醒阻塞的某个线程。信号量操作类似于停车场车辆管理,初始时停车场有5个车位,当停车场内部5个车位全占满时,此时可用资源为0,即信号量可用许可数量为0,其他车辆想停车就只能在停车场外排队阻塞(相当于调用acquire),当一辆车辆从停车场驶出时(相当于调用release方法),此时信号量许可数量为1,唤醒一个等待停车的车辆进入停车辆,自身可用许可数量再次为0,依此往复。
对于只有一个许可的信号量而言,其可用许可数量为0或1,故被称为二进制信号量,对于有多个正整数可用许可数据的信号量而言,其被称为通用信号量。需要注意在执行acquire时信号量本身并不会持有同步锁,因为这样会影响被释放的许可进入可用许可池中。
二进制信号量,不同于其他锁机制,要求释放锁的线程和获取锁的线程是同一个,也就意味着我们可以在其他线程释放二进制信号量以完成死锁恢复。
下面我们以二进制信号量实现消费者生产者模式,代码如下(生产消费4次即停止):
public class Counter {
private int mCount = 0;
public void incCount() {
mCount ++;
}
public void decCount() {
mCount--;
}
public int getCount() {
return mCount;
}
}
// Main主类代码
private static int mIncTimes = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);
Thread incThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (mIncTimes < 4) {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
if (counter.getCount() == 0) {
counter.incCount();
mIncTimes ++;
System.out.println("Inc Thread ++,current count is:" + counter.getCount());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
});
incThread.setName("Inc Thread");
incThread.start();
Thread decThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (mIncTimes < 4) {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
if (counter.getCount() != 0) {
counter.decCount();
System.out.println("Dec Thread --,current count is:" + counter.getCount());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
});
decThread.setName("Dec Thread");
decThread.start();
}
运行结果如下:
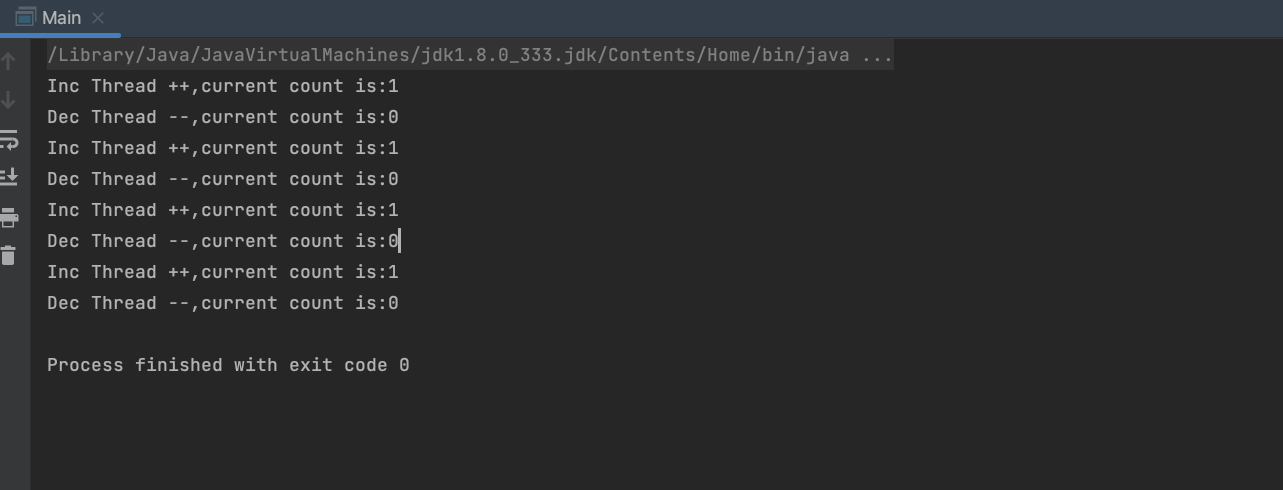
内存一致性影响,要求一个线程中的release操作和另一个线程中的acquire操作必须存在happen-before关系