map< int,int >和map< int,int >::iterator
- 一、map<int,int>、map<string, string>的含义
- 二、map<int,int>::iterator的作用
- 三、map<int,XXX>的自动升序特点
一、map<int,int>、map<string, string>的含义
map容器是C++STL的一种。
map<int,int>是int型的map容器,会形成key为int, value为int的键值对。
// 创建一个int型的map容器
map<int, int> num;
// 当键为1时,里面的值是10
num[1] = 10;
cout << "num[1] = " << num[1] << endl;
运行结果:

map<string, string>是string型的map容器,形成key为string, value为string的键值对。
// 创建一个string型的map容器
map<string, string> fruit;
// 当键为apple时,里面的值是red
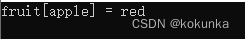
fruit["apple"] = "red";
cout << "fruit[apple] = " << fruit["apple"] << endl;
运行结果:
举一反三,你想要创建<xxx, xxx>的map容器都是可以的,区别是形成不同类型的键值对罢了。
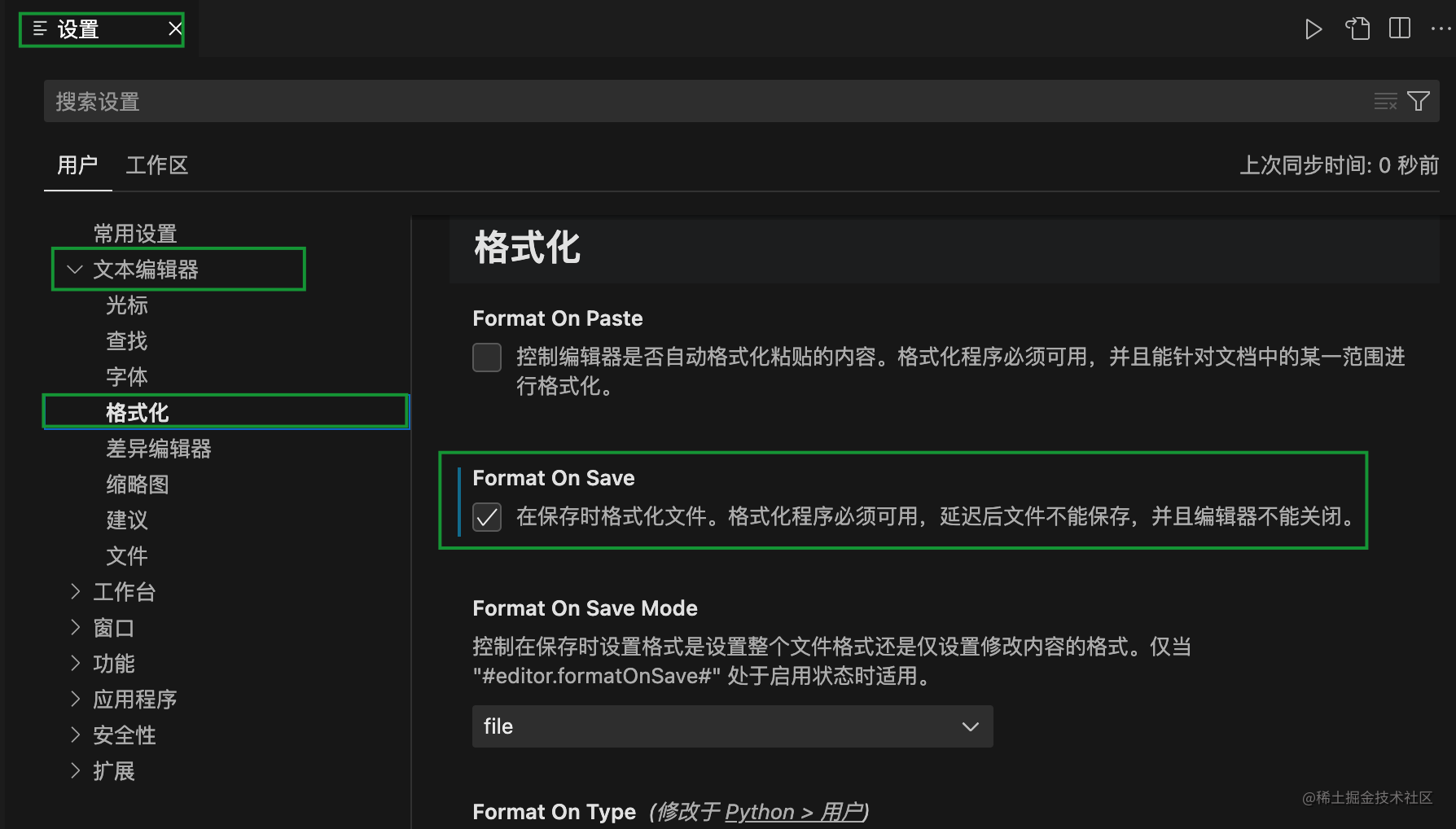
二、map<int,int>::iterator的作用
iterator是一个迭代器,我们想要遍历map容器的时候,就可以使用它。
map<string, int> score;
int max_score = 0;
string max_score_subject;
// 创建对应的键值对
score["Chinese"] = 100;
score["math"] = 97;
score["English"] = 98;
// it->first:对应map容器的键
// it->second:对应map容器的值
for(map<string, int>::iterator it = score.begin(); it!=score.end(); it++) {
if(it->second > max_score) {
max_score = it->second;
max_score_subject = it->first;
}
}
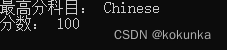
cout << "最高分科目: " << max_score_subject << "\n分数: " << max_score << endl;
运行结果:
三、map<int,XXX>的自动升序特点
当map容器是int型时,它会将键名按照升序排序。
int a[5];
int a[5];
map<int,int>M;
// 依次使用到的键名分别是:M[10]、M[1]、M[10]、 M[20]、M[30]、 M[20]
// map<int,int>容器中所有的键所对应的值的初始值都是为0
a[0]=10; M[a[0]]++;
cout << "M[a[0]] = M[10] = " << M[a[0]] << endl;
a[1]=1; M[a[1]]++;
cout << "M[a[1]] = M[1] = " << M[a[1]] << endl;
a[2]=10; M[a[2]]++;
cout << "M[a[2]] = M[10] = " << M[a[2]] << endl;
a[3]=20; M[a[3]]++;
cout << "M[a[3]] = M[20] = " << M[a[3]] << endl;
a[4]=30; M[a[4]]++;
cout << "M[a[4]] = M[30] = " << M[a[4]] << endl;
a[5]=20; M[a[5]]++;
cout << "M[a[5]] = M[20] = " << M[a[5]] << endl << "\n----------------\n" << endl;
map<int,int>::iterator it;
for(it=M.begin(); it!=M.end(); it++)
cout<<it->first<<' '<<it->second<<endl;
运行结果: