目录
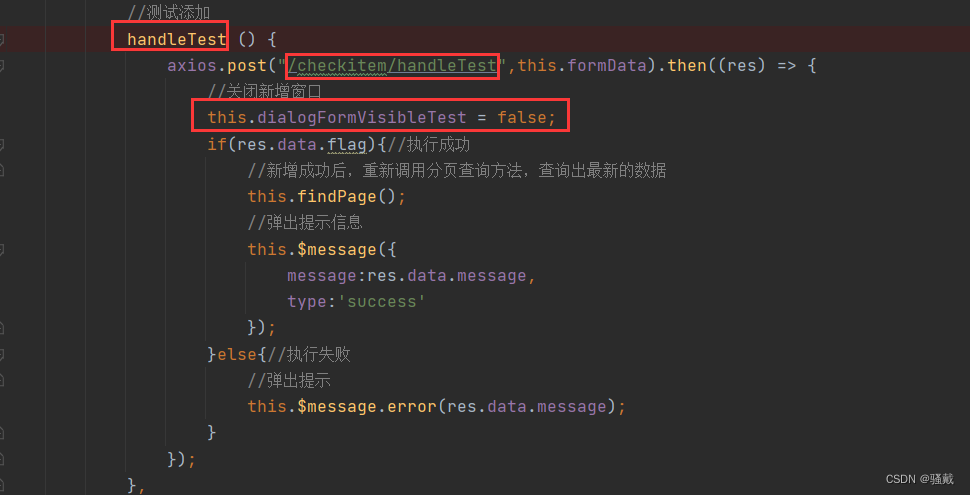
第一题
代码
输出流程分析
运行结果
考察知识点
第二题
代码
流程分析
运行结果
第三题
题目要求
我的代码
代码改进
第一题
代码
package com.hspedu.extends_.exercise;
public class ExtendsExercise01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
}
}
class A {
A(){//默认的无参构造器
System.out.println("a");
}
A(String name){
System.out.println("a name");
}
}
class B extends A {
B(){
//已经有this就不会有super了
this("abc");
System.out.println("b");
}
B(String name){
super();
System.out.println("b name");
}
}
输出流程分析
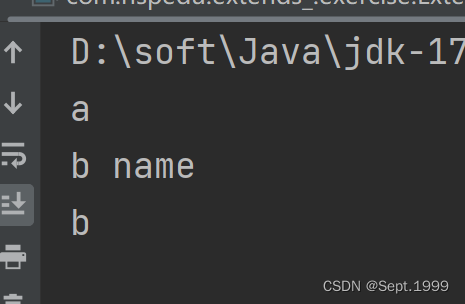
1)调用B类无参构造器,因为构造器内第一行有this(),所以不会再调用父类的无参构造器
2)执行this("abc");
3)执行super();
4)执行父类即A类的无参构造器,输出a(第一次输出)
5)输出b name(第二次输出)
6)输出 b (第三次输出)
运行结果
考察知识点
1)当创建子类对象时, 不管使用子类的哪个构造器, 默认情况下总会去调用父类的无参构造器
2)在构造器中,this()和super()不能同时使用
第二题
代码
package com.hspedu.extends_.exercise;
public class ExtendsExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
C1 c1 = new C1();
}
}
class A1 {
public A1(){
System.out.println("我是A类");
}
}
class B1 extends A1 {
public B1(){
System.out.println("我是B类的无参构造");
}
public B1(String name) {
System.out.println(name + "我是B类的有参构造");
}
}
class C1 extends B1 {
public C1() {
this("hello");
System.out.println("我是c类的无参构造");
}
public C1(String name) {
super("hahah");
System.out.println("我是c类的有参构造");
}
}流程分析
1)调用this("hello");
2)调用super("hahah");
3)调用
public B1(String name) {
System.out.println(name + "我是B类的有参构造");
}
需要先调用这个子类的父类的无参构造器
4)调用
class A1 {
public A1(){
System.out.println("我是A类");
}
}
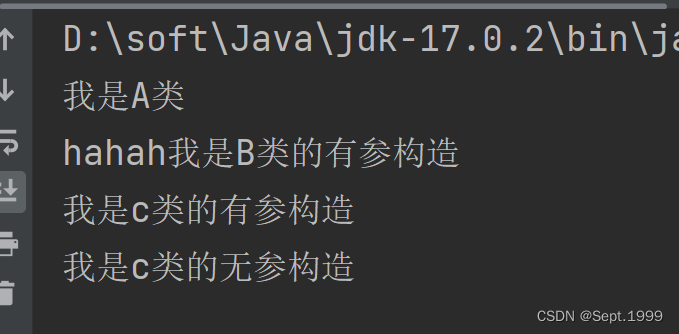
第一次输出:我是A类
第二次输出:hahah我是B类的有参构造
第三次输出:我是c类的有参构造
第四次输出:我是c类的无参构造
运行结果
第三题
题目要求
1)编写 Computer 类, 包含 CPU、 内存、 硬盘等属性, getDetails 方法用于返回 Computer 的详细信息
2)编写 PC 子类, 继承 Computer 类, 添加特有属性【品牌 brand】
3)编写 NotePad 子类, 继承 Computer 类, 添加特有属性【color】
4)编写ExtendsExercise03类, 在 main 方法中创建 PC 和 NotePad 对象, 分别给对象中特有的属性赋值(即在创建对象的时候就完成对象属性的初始化), 以及从 Computer 类继承的属性赋值, 并使用方法并打印输出信息(在子类中创建打印信息的方法,然后调用)
我的代码
package com.hspedu.extends_.exercise;
public class Computer {
//编写 Computer类,包含 CPU、 内存、 硬盘等属性,
// getDetails 方法用于返回 Computer 的详细信息
private String cpu;
private int memory;
private int disk;
//有参构造器,完成对象属性的初始化
public Computer(String cpu, int memory, int disk) {
this.cpu = cpu;
this.memory = memory;
this.disk = disk;
}
//全是private属性,创建public方法访问
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public int getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public int getDisk() {
return disk;
}
public String getDetails(){
return "电脑CPU " + cpu + " 内存" + memory
+ " 硬盘" + disk;
}
}
package com.hspedu.extends_.exercise;
//因为子类默认加载父类的无参构造器,但是父类定义了有参构造器,所以此处会报错
//解决方法:用super()指定构造器
public class PC extends Computer{
private String brand;
public PC(String cpu, int memory, int disk, String brand) {
super(cpu, memory, disk);
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println(getDetails() + " 品牌" + brand);
}
}
package com.hspedu.extends_.exercise;
public class NotePad extends Computer{
private String color;
//根据继承的规则,此处会自动调用父类的构造器
//即父类构造器完成父类属性的初始化
//子类构造器完成子类属性的初始化
public NotePad(String cpu, int memory, int disk, String color) {
super(cpu, memory, disk);
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println(getDetails() + " 颜色" + color);
}
}
运行类
package com.hspedu.extends_.exercise;
// 在main方法中创建PC和NotePad对象,分别给对象中特有的属性赋值,
//以及从Computer类继承属性赋值,并使用方法并打印输出信息
//题目含义:创建PC类和NotePad对象,分别给他们的父类属性和子类属性赋值
//打印出这两个对象的属性信息
public class ExtendsExercise03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
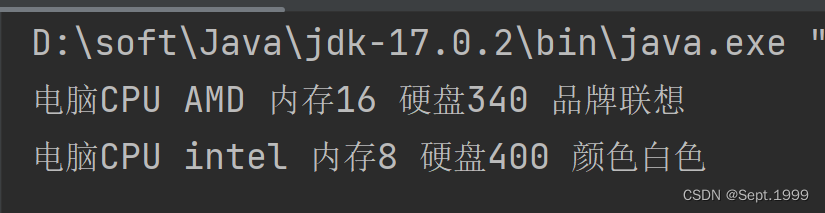
PC pc = new PC("AMD",16,340,"联想");
pc.showInfo();
NotePad notePad = new NotePad("intel", 8, 400, "白色");
notePad.showInfo();
}
}
结果
代码改进
用get和set方法完成封装
父类:Computer
package com.hspedu.extends_.exerciseteacher;
public class Computer {
private String CPU;
private int memory;
private int disk;
//构造器
public Computer(String CPU, int memory, int disk) {
this.CPU = CPU;
this.memory = memory;
this.disk = disk;
}
//封装
public String getCPU() {
return CPU;
}
public void setCPU(String CPU) {
this.CPU = CPU;
}
public int getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public void setMemory(int memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
public int getDisk() {
return disk;
}
public void setDisk(int disk) {
this.disk = disk;
}
//返回信息
public String getDetails(){
return "CPU=" + CPU + " memory=" + memory +
" disk=" + disk;
}
}
子类:PC
package com.hspedu.extends_.exerciseteacher;
public class PC extends Computer{
private String brand;
public PC(String CPU, int memory, int disk, String brand) {
super(CPU, memory, disk);
this.brand = brand;
}
//封装
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
//返回信息
public void printInfo(){
System.out.println("======PC信息如下======");
System.out.println(getDetails() + " brand=" + brand);
}
}
子类:NotePad
package com.hspedu.extends_.exerciseteacher;
public class NotePad extends Computer{
private String color;
public NotePad(String CPU, int memory, int disk, String color) {
super(CPU, memory, disk);
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void printInfo(){
System.out.println("======NotePad信息如下======");
System.out.println(getDetails() + " color=" + color);
}
}
package com.hspedu.extends_.exerciseteacher;
public class ExtendsExercise03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
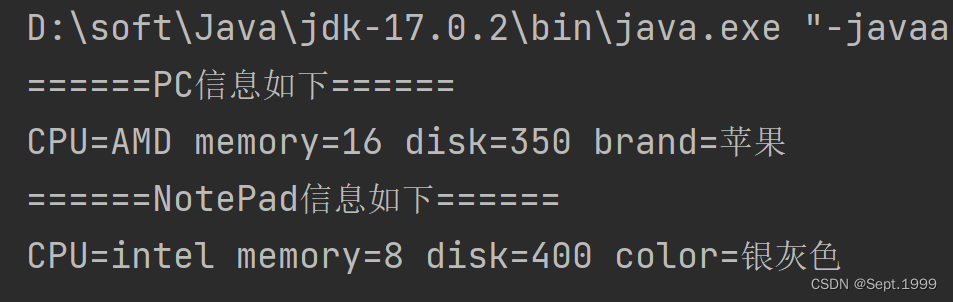
PC pc = new PC("AMD", 16, 350, "苹果");
pc.printInfo();
NotePad notePad = new NotePad("intel", 8, 400, "银灰色");
notePad.printInfo();
}
}
运行结果



![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于Java的校园二手平台交易系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7f7553af40dd489c9d83c4f8d343578b.png)