前言
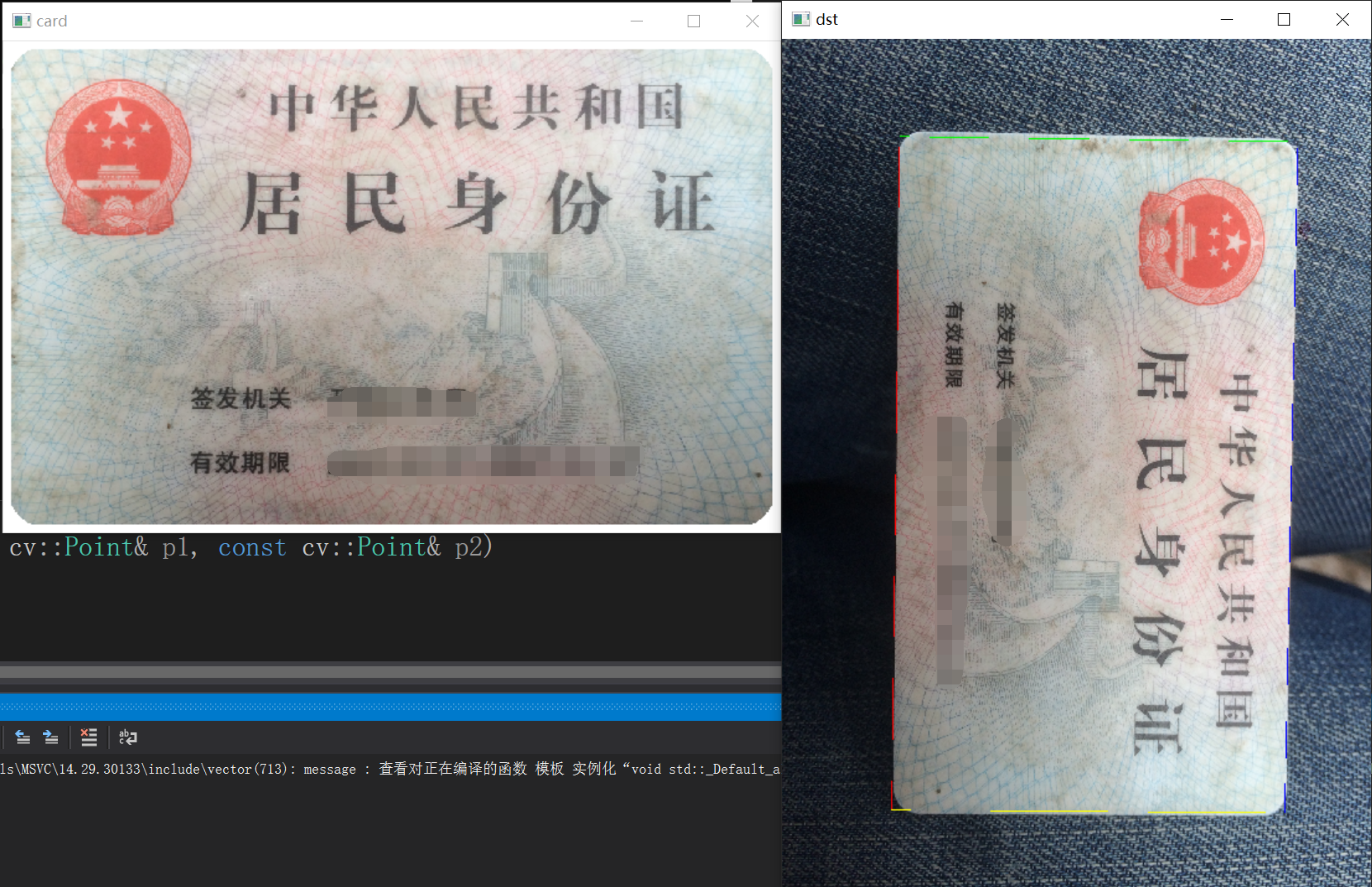
1.用拍照的证件照片正反面,实现用证件去复印到A4纸上的效果,还有证件的格式化识别。

图1:把拍照的证件1比1还原证件到A4纸上

图2:证件OCR格式化识别
2.使用Yolo做目标识别,Enet做边缘检测,Paddle OCR做文字识别,OpenCV做处理图像,当前的开发环境为开发环境是win10,显卡RTX3080,cuda11.2,cudnn8.1,OpenCV4.5,ncnn,IDE 是Vs2019,界面是Qt 写的。
一、目标识别
1.要识别的证卡有身份证正反面、银行卡正反面、社保卡正反面、港澳通行证正反面、护照、驾驶证、居住证等,这些数据都涉及到个人数据安全,所以很难找到可以使用的数据集,但训练模型又不能没有数据集,解决的办法是从网上获取一些公开的证件样本数据集,然后使用生成对抗(GAN)生成可以训练的数据集。
2.使用yolov5训练目标识别模型,关于yolov5的如果训练模型,可以看我之前的博客《深度学习目标检测(YoloV5)项目——完整记录从数据处理开始到项目落地部署》![]() https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/118598706?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501。
https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/118598706?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501。
3.身份证的正面和社保卡、居住证特征很像,目标识别时往往会错检,为了更好的区分,在标注的时候,把头像,国徽这些统一的特征也标注出来,做目标识别时,再做逻辑判断。比如当前识别到身份证的背面时,要去判断有没有同时识别到国徽,国徽是否在背面识别框内。
static void mergeFrameRect(std::vector<cv::Rect> r1, std::vector<cv::Rect> r2, std::vector<cv::Rect>& r_m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < r1.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < r2.size(); j++)
{
if (computRectJoinUnion(r1.at(i), r2.at(j)))
{
r_m.push_back(r1.at(i));
}
}
}
}
int filterTarget(std::vector<ObjectFlag>& objects, std::map<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>& rect_frame)
{
std::vector<cv::Rect> IDF_Frame, IDB_Frame, SSCB_Frame, SSCF_Frame, BCF_Frame, BCB_Frame, CNPF_Frame, RPF_Frame, DLF_Frame, OWPF_Frame, OWPB_Frame;
std::vector<cv::Rect> AC, BD, CNPF, DLF, OWPB, OWPF, RPF, SSCB, SSCF, UPAY, BCF, BCB, IDF, IDB, CNM, PTT;
//"AC标识", "书本", "护照", "驾驶证", "港澳通行证背面", "港澳通行证正面", "居住证",
//"社保卡背面", "社保卡正面", "银联标示", "银行卡正面", "银行卡背面", "身体证正面", "身体证背面", "国徽", "头像"
///目标识别返回标志位///
//AC芯片 0 AC
//书本 1 BD
//护照正面 2 CNPF
//驾驶证 3 DLF
//港澳通行证背面 4 OWPB
//港澳通行证正面 5 OWPF
//居住证 6 RPF
//社保卡反面 7 SSCB
//社保卡正面 8 SSCF
//银联标志 9 UPAY
//银行卡正面 10 BCF
//银行卡反面 11 BCB
//身份证正面 12 IDF
//身份证反面 13 IDB
//国徽 14 CNM
//头像 15 PTT
for (int i = 0; i < objects.size(); i++)
{
const ObjectFlag obj = objects[i];
if (obj.prob >= 0.4)
{
switch (obj.label)
{
case 0:
AC.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 1:
BD.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 2:
CNPF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 3:
DLF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 4:
OWPB.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 5:
OWPF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 6:
RPF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 7:
SSCB.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 8:
SSCF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 9:
UPAY.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 10:
BCF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 11:
BCB.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 12:
IDF.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 13:
IDB.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 14:
CNM.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
case 15:
PTT.push_back(obj.rect);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
if (BD.size() > 0)//书本
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(10, BD));
}
if (IDF.size() > 0 && PTT.size() > 0)//身份证正面
{
mergeFrameRect(IDF, PTT, IDF_Frame);
if (IDF_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(20, IDF_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (IDB.size() > 0 && CNM.size() > 0)//身份证反面
{
mergeFrameRect(IDB, CNM, IDB_Frame);
if (IDB_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(21, IDB_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (SSCF.size() > 0 && AC.size() > 0 && PTT.size() > 0) //社保卡正面
{
std::vector<cv::Rect> RECT;
mergeFrameRect(SSCF, AC, RECT);
if (RECT.size() > 0)
{
mergeFrameRect(RECT, PTT, SSCF_Frame);
}
if (SSCF_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(30, SSCF_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (SSCB.size() > 0 && CNM.size() > 0)//社保卡反面
{
mergeFrameRect(SSCB, CNM, SSCB_Frame);
if (SSCB_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(31, SSCB_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (CNPF.size() > 0 && PTT.size() > 0)//护照正面
{
mergeFrameRect(CNPF, PTT, CNPF_Frame);
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(40, CNPF_Frame));
}
if (BCF.size() > 0 && UPAY.size()>0)//银行卡正面
{
mergeFrameRect(BCF, UPAY, BCF_Frame);
if (BCF_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(50, BCF_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (BCB.size() > 0 && UPAY.size()>0)//银行卡反面
{
mergeFrameRect(BCB, UPAY, BCB_Frame);
if (BCB_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(51, BCB_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (RPF.size() > 0 && PTT.size()>0)//居住证
{
mergeFrameRect(RPF, PTT, RPF_Frame);
if (RPF_Frame.size())
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(60, RPF_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (OWPF.size() > 0 && PTT.size()>0)//港澳通行证正面
{
mergeFrameRect(OWPF, PTT, OWPF_Frame);
if (OWPF_Frame.size())
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(70, OWPF_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
if (OWPB.size())//港澳通行证背面
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(71, OWPB));
}
if (DLF.size() > 0 && PTT.size()>0)//驾驶证
{
mergeFrameRect(DLF, PTT, DLF_Frame);
if (DLF_Frame.size() > 0)
{
rect_frame.insert(std::pair<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>(80, DLF_Frame));
}
else
{
return -2;
}
}
return 0;
}
int screeningTarget(cv::Rect& rect_out, std::map<int, std::vector<cv::Rect>>& rect_frame)
{
std::vector<cv::Rect> IDF_Frame, IDB_Frame, SSCB_Frame, SSCF_Frame, BCF_Frame, BCB_Frame, CNPF_Frame, BD_Frame, RPF_Frame, DLF_Frame, OWPF_Frame, OWPB_Frame;
std::vector<int> indes;
for (auto i = rect_frame.begin(); i != rect_frame.end(); i++)
{
int index = i->first;
//std::cout << index << std::endl;
switch (index)
{
case 10:
BD_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(BD_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 20:
IDF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(IDF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 21:
IDB_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(IDB_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 30:
SSCF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(SSCF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 31:
SSCB_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(SSCB_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 40:
CNPF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(CNPF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 50:
BCF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(BCF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 51:
BCB_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(BCB_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 60:
RPF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(RPF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 70:
OWPF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(OWPF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 71:
OWPB_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(OWPB_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
case 80:
DLF_Frame = i->second;
indes.push_back(atoi((std::to_string(i->first) + std::to_string(DLF_Frame.size())).c_str()));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (indes.size() > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < indes.size(); i++)
{
int index = std::stoi(std::to_string(indes.at(i)).substr(0, 2));
switch (index)
{
case 10:
{
rect_out = BD_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 20:
{
rect_out = IDF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 21:
{
rect_out = IDB_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 30:
{
rect_out = SSCF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 31:
{
rect_out = SSCB_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 40:
{
rect_out = CNPF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 50:
{
rect_out = BCF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 51:
{
rect_out = BCB_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 60:
{
rect_out = RPF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 70:
{
rect_out = OWPF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 71:
{
rect_out = OWPB_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
case 80:
{
rect_out = DLF_Frame.at(0);
return indes.at(i);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
识别效果如下:



二、边缘提取与校正
1.获取当前目标之后,要对当前目标进行语义分割,为了分割速度,这里先择了Enet做目标分割,关于Enet网络的训练步骤可以参考我之前的博客《轻量化实时语义分割LiteSeg——从算法原理到模型训练与部署![]() https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/124539667?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502》,ENet的训练框架是Pytorch,可以使用git上的这个源码进行训练:GitHub - davidtvs/PyTorch-ENet: PyTorch implementation of ENetPyTorch implementation of ENet. Contribute to davidtvs/PyTorch-ENet development by creating an account on GitHub.
https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/124539667?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502》,ENet的训练框架是Pytorch,可以使用git上的这个源码进行训练:GitHub - davidtvs/PyTorch-ENet: PyTorch implementation of ENetPyTorch implementation of ENet. Contribute to davidtvs/PyTorch-ENet development by creating an account on GitHub.![]() https://github.com/davidtvs/PyTorch-ENet 。
https://github.com/davidtvs/PyTorch-ENet 。
2.训练好模型之后,把模型量化成FP16以提升速度,用NCNN实现模型推理
/// <summary>
/// 语义分割
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ncnn_net">分割模型</param>
/// <param name="cv_src">输入图像</param>
/// <param name="cv_enet">输出分割后的图像</param>
/// <param name="threadsm">阈值</param>
/// <param name="image_size">推理尺寸大小</param>
/// <returns></returns>
static int enetSegmentation(cv::Mat& cv_src, cv::Mat& cv_enet, ncnn::Net& ncnn_net, int threadsm, int image_size)
{
if (cv_src.empty())
{
return -20;
}
ncnn::Mat in = ncnn::Mat::from_pixels_resize(cv_src.data, ncnn::Mat::PIXEL_BGR, cv_src.cols, cv_src.rows, image_size, image_size);
const float norm_vals[3] = { 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f };
in.substract_mean_normalize(0, norm_vals);
ncnn::Extractor ex = ncnn_net.create_extractor();
ex.set_num_threads(threadsm);
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.input("input.1", in);
ex.extract("887", out);
cv::Mat cv_seg = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(out.w, out.h), CV_8UC1);
for (int i = 0; i < out.h; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < out.w; ++j)
{
const float* bg = out.channel(0);
const float* fg = out.channel(1);
if (bg[i * out.w + j] < fg[i * out.w + j])
{
cv_seg.data[i * out.w + j] = 255;
}
}
}
cv::resize(cv_seg, cv_enet, cv::Size(cv_src.cols, cv_src.rows), cv::INTER_LINEAR);
return 0;
}分割效果:
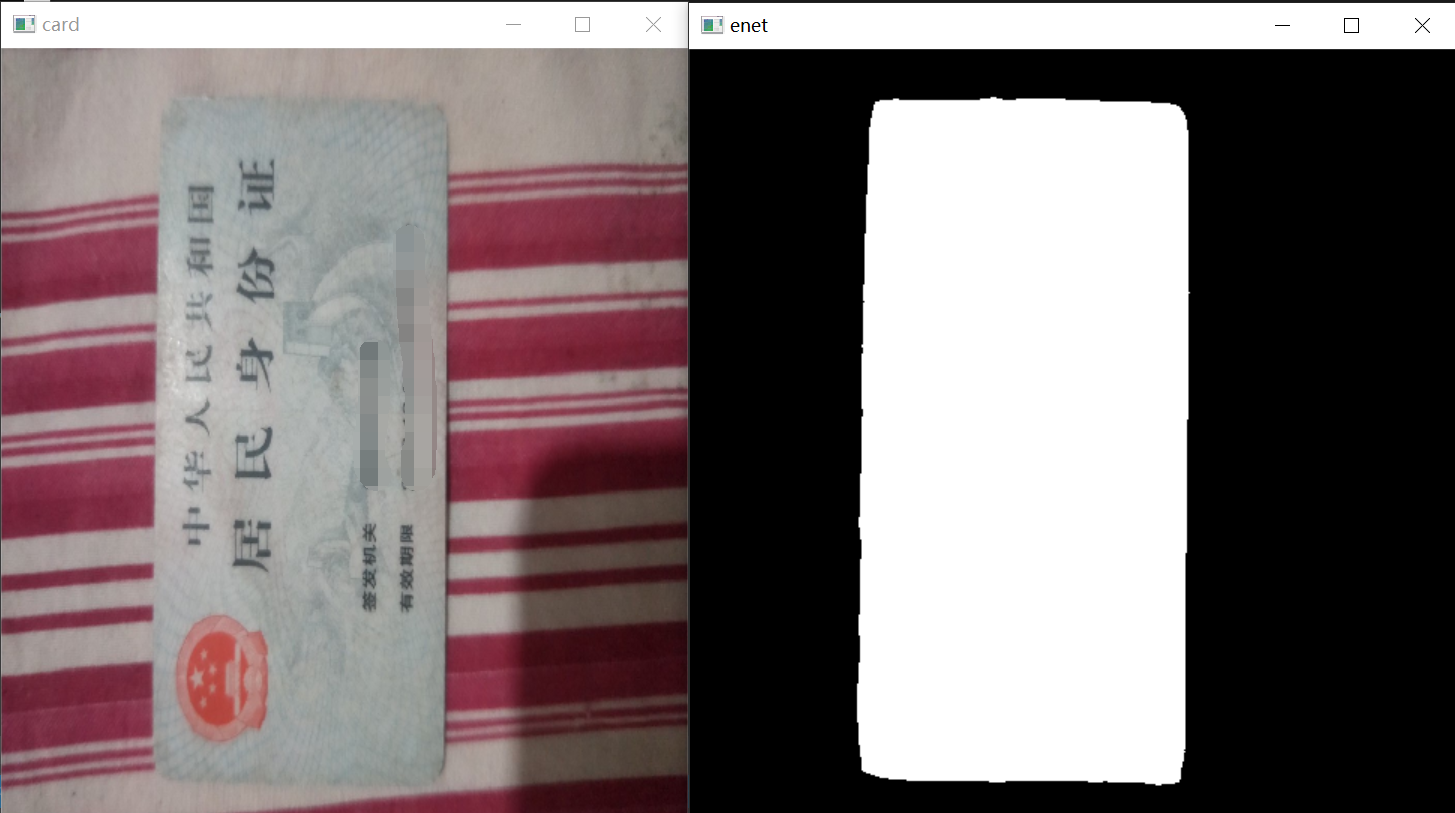
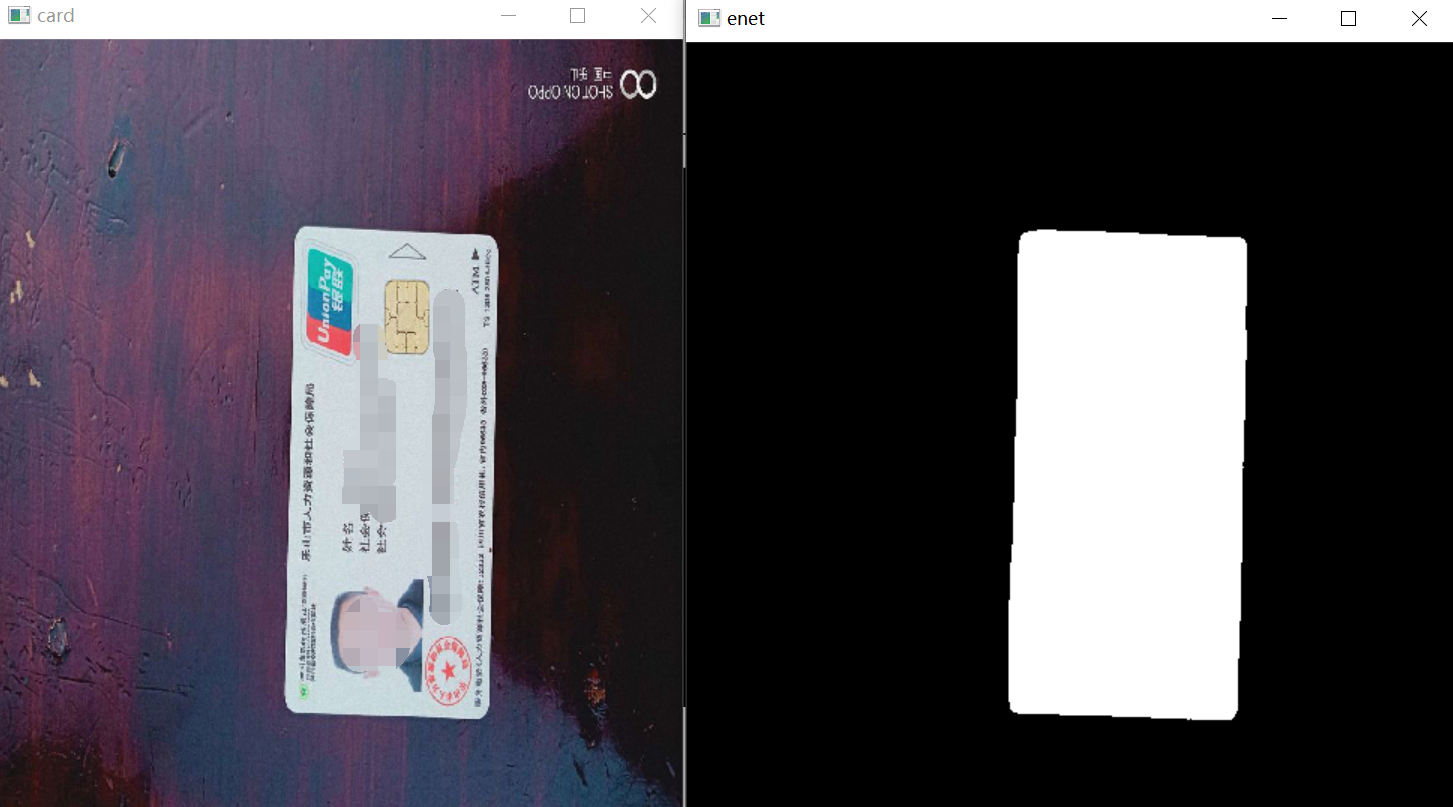
3.获取目标的分割位置之后要对目标的连边缘进行提取,要进行直线检测,直线可以用传统算法,OpenCV的霍夫曼直接检测,也可以用基于深度学习的M-LSD,如果用M-LSD也可以直接省掉语义分割的这一步,直线检测效果的对比可以看我之前的博客《直线检测——对比M-LSD直线检测(基于深度学习)与霍夫曼直线检测![]() https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/124362068?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502》。
https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/124362068?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502》。
直线检测与拟合边缘点:
static int getCorrectionPoint(cv::Mat cv_edge, cv::Mat& cv_enet, std::vector<cv::Point>& points_out,
double theta = 50, int threshold = 30, double minLineLength = 10)
{
std::vector<cv::Vec4f> lines;
HoughLinesP(cv_edge, lines, 1, CV_PI * 1 / 180, theta, threshold, minLineLength);
if (lines.size() <= 3)
{
int mask = enetLinesToPoint(cv_enet, points_out);
return std::stoi(std::to_string(42) + std::to_string(mask));
}
std::vector<Line> horizontals, verticals;
linesDichotomy(lines, horizontals, verticals, cv_edge);
if (horizontals.size() < 2 || verticals.size() < 2)
{
int mask = enetLinesToPoint(cv_enet, points_out);
return std::stoi(std::to_string(43) + std::to_string(mask));
}
std::vector<Line> lines_out;
screenLines(horizontals, verticals, lines_out, 40);
if (lines_out.size() < 4)
{
int mask = enetLinesToPoint(cv_enet, points_out);
return std::stoi(std::to_string(44) + std::to_string(mask));
}
if (decideAngle(lines_out))
{
int mask = enetLinesToPoint(cv_enet, points_out);
return std::stoi(std::to_string(45) + std::to_string(mask));
}
std::vector<cv::Point> points;
points.push_back(computeIntersect(lines_out.at(0), lines_out.at(2)));
points.push_back(computeIntersect(lines_out.at(0), lines_out.at(3)));
points.push_back(computeIntersect(lines_out.at(2), lines_out.at(1)));
points.push_back(computeIntersect(lines_out.at(1), lines_out.at(3)));
if (decodeArea(cv_enet, points, 4))
{
int mask = enetLinesToPoint(cv_enet, points_out);
return std::stoi(std::to_string(46) + std::to_string(mask));
}
if (((points.at(1).x - points.at(0).x) < 60) || ((points.at(3).x - points.at(2).x) < 60) ||
((points.at(2).y - points.at(0).y) < 60) || ((points.at(3).y - points.at(1).y) < 60))
{
int mask = enetLinesToPoint(cv_enet, points_out);
return std::stoi(std::to_string(47) + std::to_string(mask));
}
points_out = points;
return 400;
}
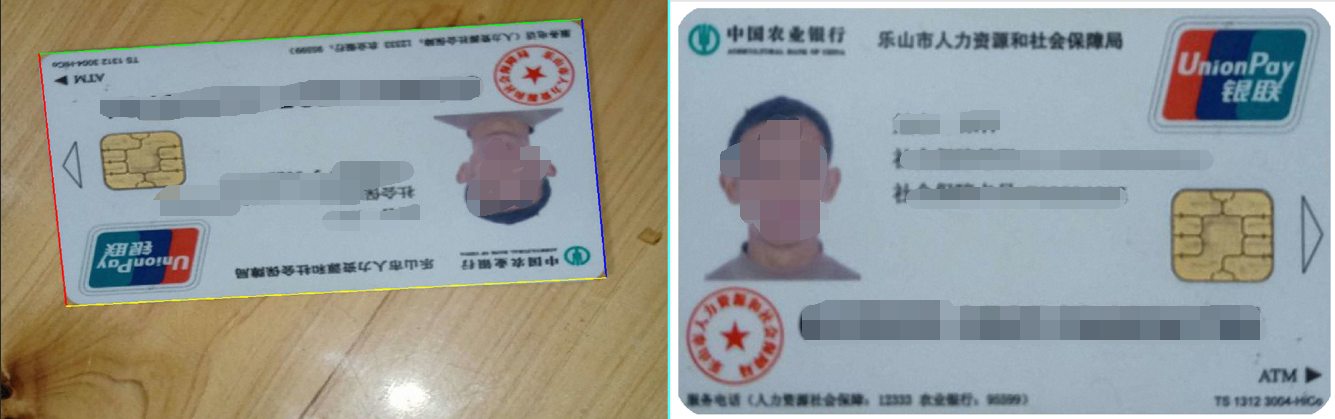
4.获取边缘之后,要对边缘进行校正,校正就是把边缘的四个点重新映射到平面上,为了更智能化的处理,在这里加上了文字检测与文字角度检测,为了达到,不管用户拍照的证件照不管是什么方向,最终得到的校正后图像文字都是正过来的,避免用户过多的参与操作。
int reviseImage(cv::Mat& cv_src, cv::Mat& cv_dst, ncnn::Net& db_net,
ncnn::Net& angle_net, std::vector<cv::Point>& in_points)
{
int val = verify();
if (val != 0)
{
return val;
}
if (cv_src.empty())
{
return -20;
}
cv::Mat cv_warp = cv_src.clone();
if (in_points.size() != 4)
{
return -444;
}
cv::Point point_f, point_b;
point_f.x = (in_points.at(0).x < in_points.at(2).x) ? in_points.at(0).x : in_points.at(2).x;
point_f.y = (in_points.at(0).y < in_points.at(1).y) ? in_points.at(0).y : in_points.at(1).y;
point_b.x = (in_points.at(3).x > in_points.at(1).x) ? in_points.at(3).x : in_points.at(1).x;
point_b.y = (in_points.at(3).y > in_points.at(2).y) ? in_points.at(3).y : in_points.at(2).y;
//2020.8.24更新了比例不对的问题,加了点到点之间的距离运算,最终取水平与垂直线最长线
float l_1 = getDistance(in_points.at(0), in_points.at(1));
float l_2 = getDistance(in_points.at(2), in_points.at(3));
float l_3 = getDistance(in_points.at(1), in_points.at(3));
float l_4 = getDistance(in_points.at(0), in_points.at(2));
int width = l_1 >= l_2 ? l_1 : l_2;
int height = l_3 >= l_4 ? l_3 : l_4;
//旧代码取目标的最小外接矩形,但倾斜45度时会出现比例变形的现象
//cv::Rect rect(point_f, point_b);
cv_dst = cv::Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC3);
std::vector<cv::Point2f> dst_pts;
dst_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(0, 0));
dst_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(width - 1, 0));
dst_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(0, height - 1));
dst_pts.push_back(cv::Point2f(width - 1, height - 1));
std::vector<cv::Point2f> tr_points;
tr_points.push_back(in_points.at(0));
tr_points.push_back(in_points.at(1));
tr_points.push_back(in_points.at(2));
tr_points.push_back(in_points.at(3));
cv::Mat transmtx = getPerspectiveTransform(tr_points, dst_pts);
cv::Mat cv_revise;
cv::warpPerspective(cv_warp, cv_revise, transmtx, cv_dst.size());
std::vector<cv::Mat> cv_dsts;
int vh = cutTextLines(cv_revise, db_net, cv_dsts);
int angle = directionTextLines(cv_dsts, angle_net);
//std::cout << angle << std::endl;
int rotate_angle = 0;
if (vh == 7 && angle == 1)//横排文字竖放从上到下
{
rotate_angle = 90;
}
if (vh == 7 && angle == 0)//横排文字竖放从下到上
{
rotate_angle = 270;
}
if (vh == 4 && angle == 0)//横排文字颠倒
{
rotate_angle = 180;
}
if (vh == 7 && angle == 3)//竖排文字正常
{
rotate_angle = 0;
}
if (vh == 4 && angle == 2)//竖排文字横放从下到上
{
rotate_angle = 90;
}
if (vh == 4 && angle == 3)//竖排文字横放从上到下
{
rotate_angle = 270;
}
if (vh == 7 && angle == 2)//竖排文字颠倒
{
rotate_angle = 180;
}
if (vh == 4 && angle == 1)//横排文字正常
{
rotate_angle = 0;
}
if (vh == 7 && angle < 0)//横排文字检测不到多于3行的文字
{
rotate_angle = 0;
}
if (vh == 4 && angle < 0)//竖排文字检测不到多于3行的文字
{
rotate_angle = 90;
}
switch (rotate_angle)
{
case 0:
cv_dst = cv_revise;
break;
case 90:
cv_dst = rotateMat(cv_revise, 0);
break;
case 180:
cv_dst = rotateMat(cv_revise, -1);
//flip(cv_revise, cv_dst, -1);
break;
case 270:
cv_dst = rotateMat(cv_revise, 1);
break;
default:
break;
}
return std::stoi(std::to_string(vh) + std::to_string(angle));
} 
三、正反面合并
1、按正常扫描逻辑,合并扫描时,正面的那张一般都是放在最上边,这里做了判断,如果合并的时同一类型的证件,比如只合并身份证,不混着合并身份证和银行卡,那么身份证的下面照片就放在上面。
void KL_SmartOffice::merge_imgae()
{
ui.label_r->setMaximumWidth(0);
ui.widget_d->setMaximumHeight(0);
if (btnGroup->checkedId() == 1)
{
if (!cv_dis_1.empty() && !cv_dis_2.empty())
{
if (od_index_1 == 20 && od_index_2 == 21)
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_1, cv_dis_2, cv_merge);
}
else if (od_index_1 == 21 && od_index_2 == 20)
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_2, cv_dis_1, cv_merge);
}
else if (od_index_1 ==30 && od_index_2 == 31)
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_1, cv_dis_2, cv_merge);
}
else if (od_index_1 == 31 && od_index_2 == 30)
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_2, cv_dis_1, cv_merge);
}
else if (od_index_1 == 50 && od_index_2 == 51)
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_1, cv_dis_2, cv_merge);
}
else if (od_index_1 == 51 && od_index_2 == 50)
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_2, cv_dis_1, cv_merge);
}
else
{
scan.merge_a4(cv_dis_1, cv_dis_2, cv_merge);
}
}
ui.pushButton_save->setEnabled(true);
ui.pushButton_style->setEnabled(false);
ui.pushButton_rotate->setEnabled(false);
ui.pushButton_merge->setEnabled(false);
ui.pushButton_ocr->setEnabled(false);
}
}2.合并到A4纸上,300dpi,如果太低了,合并出来的照片就是很模糊。
void ScanJia::merge_a4(const cv::Mat& cv_src_1, const cv::Mat& cv_src_2, cv::Mat& cv_dst)
{
cv::Mat cv_1, cv_2;
cv::resize(cv_src_1, cv_1, cv::Size(1031, 658));
cv::resize(cv_src_2, cv_2, cv::Size(1031, 658));
cv_dst = cv::Mat(3508, 2479, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255));
cv::Mat cv_one = cv_dst(cv::Rect(724, 700,cv_1.cols, cv_1.rows));
cv_1.copyTo(cv_one);
cv::Mat cv_two = cv_dst(cv::Rect(724, 2058,cv_2.cols, cv_2.rows));
cv_2.copyTo(cv_two);
}
合并的效果如下,社保卡正反面合并:

身份证正反面合并:

四、OCR文字识别
1.证件的识别相对于场景简单一引起,使用的是paddle离线版本,为了库的统一,关于paddle模型转ncnn模型可以参考:
https://github.com/FeiGeChuanShu/ncnn_paddleocr ![]() https://github.com/FeiGeChuanShu/ncnn_paddleocr
https://github.com/FeiGeChuanShu/ncnn_paddleocr
2.NCNN推理代码
OcrResult OcrLite::detect(const cv::Mat& mat, int padding, int maxSideLen,
float boxScoreThresh, float boxThresh, float unClipRatio, bool doAngle, bool mostAngle)
{
cv::Mat originSrc = mat;
int originMaxSide = (std::max)(originSrc.cols, originSrc.rows);
int resize;
if (maxSideLen <= 0 || maxSideLen > originMaxSide) {
resize = originMaxSide;
}
else {
resize = maxSideLen;
}
resize += 2 * padding;
cv::Rect paddingRect(padding, padding, originSrc.cols, originSrc.rows);
cv::Mat paddingSrc = makePadding(originSrc, padding);
ScaleParam scale = getScaleParam(paddingSrc, resize);
OcrResult result;
result = detect(NULL, NULL, paddingSrc, paddingRect, scale,
boxScoreThresh, boxThresh, unClipRatio, doAngle, mostAngle);
return result;
}
std::vector<cv::Mat> OcrLite::getPartImages(cv::Mat& src, std::vector<TextBox>& textBoxes)
{
std::vector<cv::Mat> partImages;
for (int i = 0; i < textBoxes.size(); ++i)
{
cv::Mat partImg = getRotateCropImage(src, textBoxes[i].boxPoint);
partImages.emplace_back(partImg);
}
return partImages;
}
OcrResult OcrLite::detect(const char*, const char*,
cv::Mat& src, cv::Rect& originRect, ScaleParam& scale,
float boxScoreThresh, float boxThresh, float unClipRatio, bool doAngle, bool mostAngle) {
cv::Mat textBoxPaddingImg = src.clone();
int thickness = getThickness(src);
double startTime = getCurrentTime();
std::vector<TextBox> textBoxes = dbNet.getTextBoxes(src, scale, boxScoreThresh, boxThresh, unClipRatio);
double endDbNetTime = getCurrentTime();
double dbNetTime = endDbNetTime - startTime;
drawTextBoxes(textBoxPaddingImg, textBoxes, thickness);
//---------- getPartImages ----------
std::vector<cv::Mat> partImages = getPartImages(src, textBoxes);
std::vector<Angle> angles;
angles = angleNet.getAngles(partImages, doAngle, mostAngle);
//Rotate partImgs
for (int i = 0; i < partImages.size(); ++i) {
if (angles[i].index == 1) {
partImages.at(i) = matRotateClockWise180(partImages[i]);
}
}
std::vector<TextLine> textLines = crnnNet.getTextLines(partImages);
std::vector<TextBlock> textBlocks;
for (int i = 0; i < textLines.size(); ++i) {
std::vector<cv::Point> boxPoint = std::vector<cv::Point>(4);
int padding = originRect.x;//padding conversion
boxPoint[0] = cv::Point(textBoxes[i].boxPoint[0].x - padding, textBoxes[i].boxPoint[0].y - padding);
boxPoint[1] = cv::Point(textBoxes[i].boxPoint[1].x - padding, textBoxes[i].boxPoint[1].y - padding);
boxPoint[2] = cv::Point(textBoxes[i].boxPoint[2].x - padding, textBoxes[i].boxPoint[2].y - padding);
boxPoint[3] = cv::Point(textBoxes[i].boxPoint[3].x - padding, textBoxes[i].boxPoint[3].y - padding);
TextBlock textBlock{ boxPoint, textBoxes[i].score, angles[i].index, angles[i].score,
angles[i].time, textLines[i].text, textLines[i].charScores, textLines[i].time,
angles[i].time + textLines[i].time };
textBlocks.emplace_back(textBlock);
}
double endTime = getCurrentTime();
double fullTime = endTime - startTime;
//cropped to original size
cv::Mat textBoxImg;
if (originRect.x > 0 && originRect.y > 0) {
textBoxPaddingImg(originRect).copyTo(textBoxImg);
}
else {
textBoxImg = textBoxPaddingImg;
}
std::string strRes;
for (int i = 0; i < textBlocks.size(); ++i) {
strRes.append(textBlocks[i].text);
strRes.append("\n");
}
return OcrResult{ dbNetTime, textBlocks, textBoxImg, fullTime, strRes };
}
}
3.识别的效果