目录
一、概述
1.1概念(树形结构)
1.2区别
1.3步骤
1.4回溯法模板
1.5应用
1.6回溯三部曲
二、组合问题
2.1组合
回溯算法
优化剪枝操作
2.2组合总和
2.3组合总和2
2.4组合总和3
2.5电话号码的字母组合
三、切割问题
3.1分割回文串
3.2.复原IP地址
四、子集问题
4.1子集
4.2子集2
4.3递增子序列
五、排列问题
5.1全排列
5.2全排列 II
六、棋盘问题
6.1N皇后
6.2解数独
一、概述
1.1概念(树形结构)
回溯算法是一种系统地搜索问题的解的方法。某个问题的所有可能解的称为问题的解空间,若解空间是有限的,则可将解空间映射成树结构。回溯算法的基本思想是:从一条路往前走,能进则进,不能进则退回来,换一条路再试。
回溯是递归的副产品,只要有递归就会有回溯。
回溯法就是暴力搜索,并不是什么高效的算法,最多在剪枝一下。
1.2区别
回溯算法和深度优先搜索(DFS)有很多相似之处,但也有不同之处。回溯算法在搜索过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。而DFS则是在搜索过程中遍历所有可能的路径,直到找到问题的解
1.3步骤
- 状态表示:需要定义状态表示方式,以便在搜索过程中能够正确地扩展状态。
- 决策生成:需要确定当前状态下的所有可能决策,以便进行进一步的搜索。
- 解空间剪枝:需要根据问题的特点,对搜索过程中无用的状态进行剪枝,以提高算法效率。
- 解的输出:需要根据问题的要求,确定如何输出符合要求的解。
1.4回溯法模板
result = []
def backtrack(路径, 选择列表):
if 满足结束条件:
result.add(路径)
return
for 选择 in 选择列表:
做选择
backtrack(路径, 选择列表)
撤销选择其中,
result存储结果,backtrack是回溯函数,路径是已经做出的选择,选择列表是当前可以做出的选择。
1.5应用
- 组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合
- 排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
- 切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
- 子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
- 棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等。
1.6回溯三部曲
回溯算法三部曲是指:1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值;2. 确定终止条件;3. 确定单层搜索的过程。 回溯算法是一种暴力搜索算法,它通过不断地尝试所有可能的结果来解决问题。在回溯算法中,我们需要对每个可能的结果进行判断,如果符合条件就加入到结果集中,否则就回溯到上一步,继续尝试其他可能的结果。
二、组合问题
2.1组合
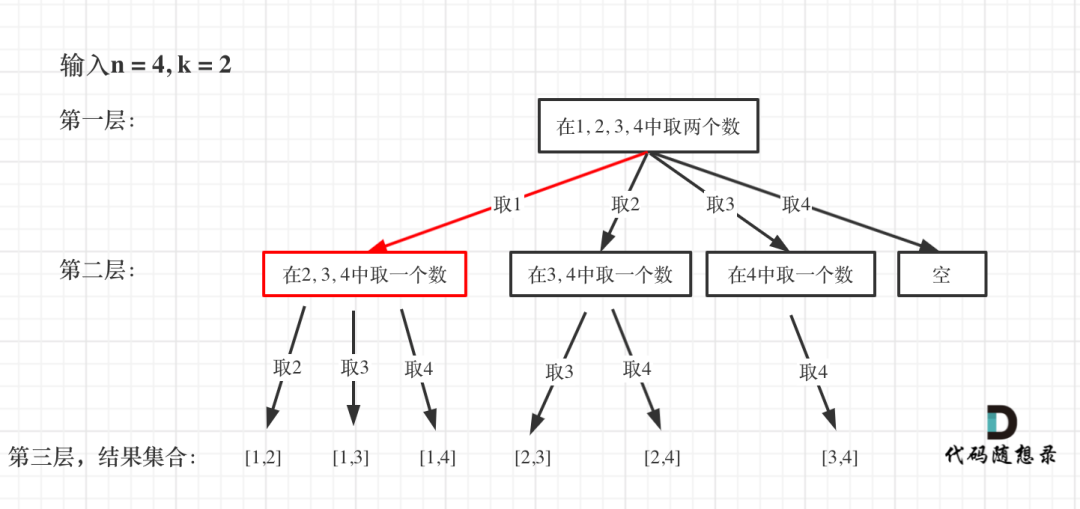
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
#include<stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100;
int a[N];
int n, k;
void dfs(int cur, int cnt) {
if (cnt == k) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = cur; i <= n; i++) {
a[cnt] = i;
dfs(i + 1, cnt + 1);
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> k;
dfs(1, 0);
return 0;
}
回溯算法
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
// 回溯函数
private void backtracking(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> path, int n, int k, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() == k) { // 如果path中的元素个数等于k,说明找到了一组符合条件的组合
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 将该组合加入结果集中
return; // 返回上一层递归
}
// 枚举所有可能的数
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
path.add(i); // 将当前数加入path中,进行处理
backtracking(result, path, n, k, i + 1); // 递归处理下一个数
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 撤销处理的数,回溯到上一层状态
}
}
// 组合函数
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储符合条件的结果集
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储符合条件的组合
backtracking(result, path, n, k, 1); // 开始回溯,从数字1开始
return result; // 返回结果集
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户输入的n
int k = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户输入的k
scanner.close(); // 关闭Scanner
Solution solution = new Solution(); // 创建Solution对象
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.combine(n, k); // 调用组合函数,得到符合条件的结果集
for (List<Integer> list : result) { // 遍历结果集
for (int num : list) { // 遍历组合
System.out.print(num + " "); // 输出组合中的元素
}
System.out.println(); // 输出换行,用于分隔每个组合
}
}
}
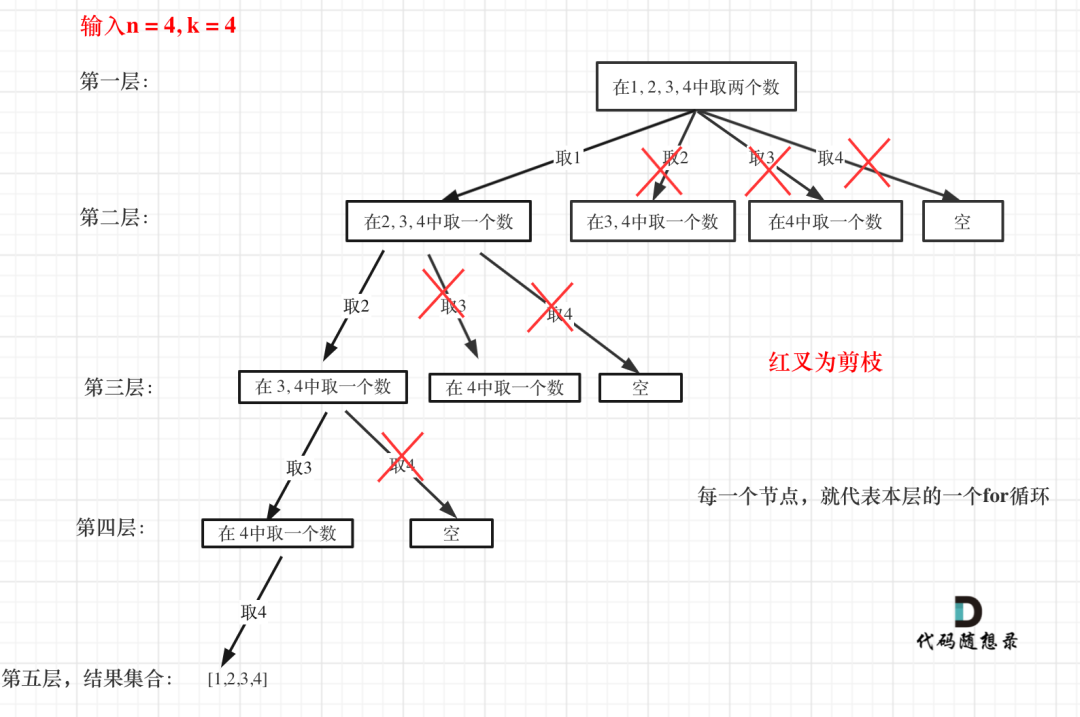
优化剪枝操作
剪枝操作是回溯算法的一种优化方法,可以排除不满足解的情况来提高算法的执行效率。在回溯算法中,剪枝操作可以有多种方式,例如对for循环选择的起始范围的剪枝,或者在递归过程中判断是否需要继续递归等等
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
// 回溯函数
private void backtracking(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> path, int n, int k, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() == k) { // 如果path中的元素个数等于k,说明找到了一组符合条件的组合
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 将该组合加入结果集中
return; // 返回上一层递归
}
// 枚举所有可能的数
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++) {//优化的地方
path.add(i); // 将当前数加入path中,进行处理
backtracking(result, path, n, k, i + 1); // 递归处理下一个数
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 撤销处理的数,回溯到上一层状态
}
}
// 组合函数
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储符合条件的结果集
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储符合条件的组合
backtracking(result, path, n, k, 1); // 开始回溯,从数字1开始
return result; // 返回结果集
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户输入的n
int k = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户输入的k
scanner.close(); // 关闭Scanner
Solution solution = new Solution(); // 创建Solution对象
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.combine(n, k); // 调用组合函数,得到符合条件的结果集
for (List<Integer> list : result) { // 遍历结果集
for (int num : list) { // 遍历组合
System.out.print(num + " "); // 输出组合中的元素
}
System.out.println(); // 输出换行,用于分隔每个组合
}
}
}
2.2组合总和
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
说明:
所有数字都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]
思路
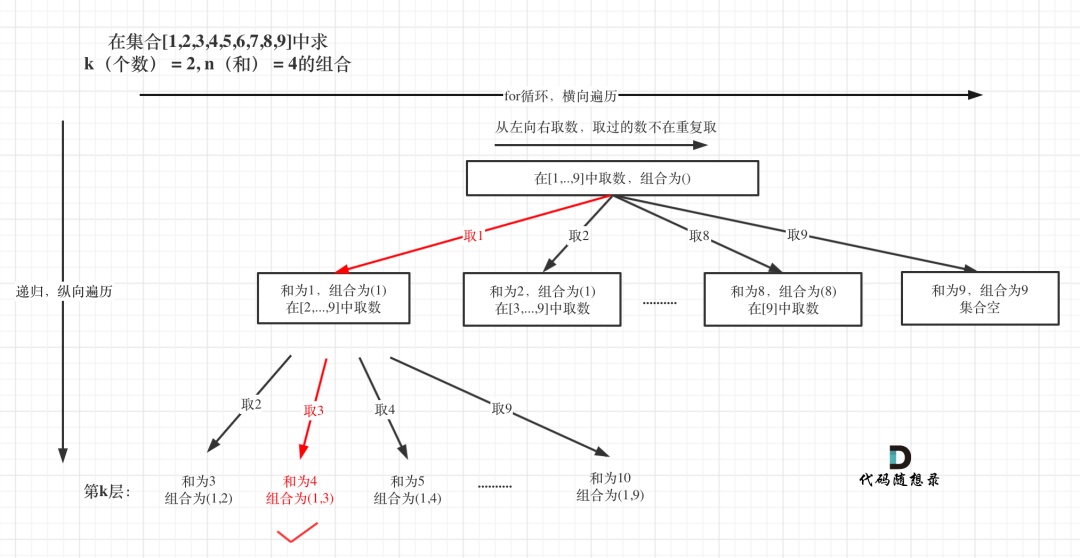
本题就是在[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]这个集合中找到和为n的k个数的组合。
相对于上题,无非就是多了一个限制,本题是要找到和为n的k个数的组合,而整个集合已经是固定的了[1,...,9]。
例如 k = 2,n = 4的话,就是在集合[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]中求 k(个数) = 2, n(和) = 4的组合。
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result; // 存放结果集
private List<Integer> path; // 符合条件的结果
/**
* backtracking - 回溯算法
*
* @param targetSum 目标和,也就是题目中的n。
* @param k 题目中要求k个数的集合。
* @param sum 已经收集的元素的总和,也就是path里元素的总和。
* @param startIndex 下一层for循环搜索的起始位置。
*/
private void backtracking(int targetSum, int k, int sum, int startIndex) {
// 剪枝操作:如果path里的元素个数已经等于k,且当前元素总和不等于目标和targetSum,直接返回。
if (path.size() == k && sum != targetSum) {
return;
}
// 如果path里的元素个数已经等于k,且当前元素总和等于目标和targetSum,说明已经找到了符合条件的结果,加入到结果集中并返回。
if (path.size() == k && sum == targetSum) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9; i++) {
sum += i; // 处理
path.add(i); // 处理
backtracking(targetSum, k, sum, i + 1); // 注意i+1调整startIndex
sum -= i; // 回溯
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
path = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(n, k, 0, 1);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int k = scanner.nextInt(); // 读取sin
int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 读取n
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.combinationSum3(k, n);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
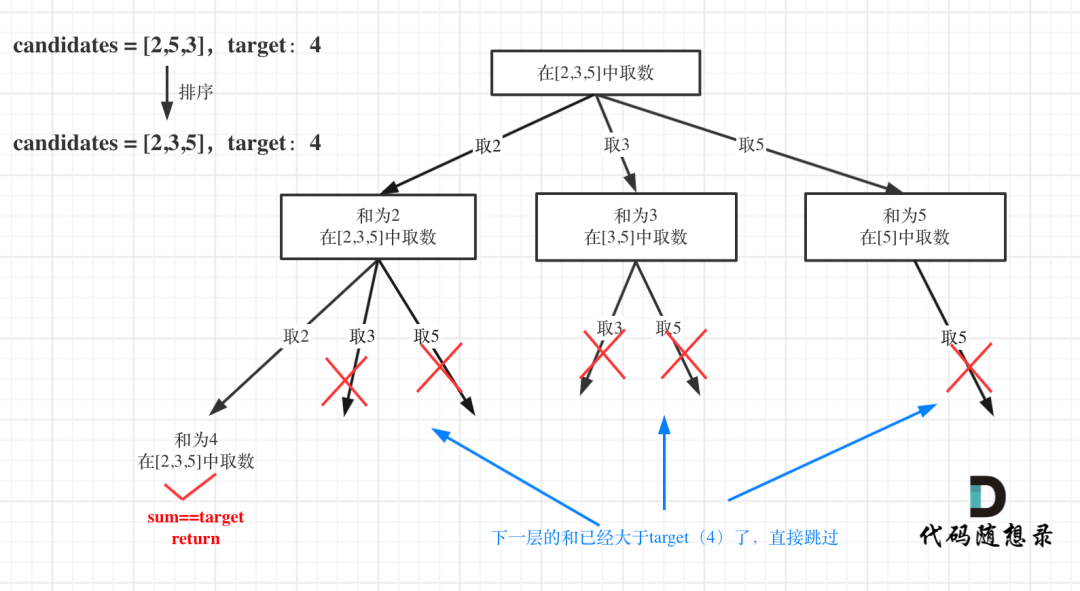
2.3组合总和2
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7, 所求解集为:[ [7], [2,2,3] ]
提示
组合没有数量要求
元素可无限重复选
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先进行排序
backtracking(res, new ArrayList<>(), candidates, target, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void backtracking(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path, int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int idx) {
// 找到了数字和为 target 的组合
if (sum == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 如果 sum + candidates[i] > target 就终止遍历
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) break;
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(res, path, candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯,移除路径 path 最后一个元素
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution s = new Solution();
int[] candidates1 = {2, 3, 6, 7};
int target1 = 7;
List<List<Integer>> res1 = s.combinationSum(candidates1, target1);
System.out.println(res1); // [[7], [2, 2, 3]]
int[] candidates2 = {2, 3, 5};
int target2 = 8;
List<List<Integer>> res2 = s.combinationSum(candidates2, target2);
System.out.println(res2); // [[2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 3, 3], [3, 5]]
}
}
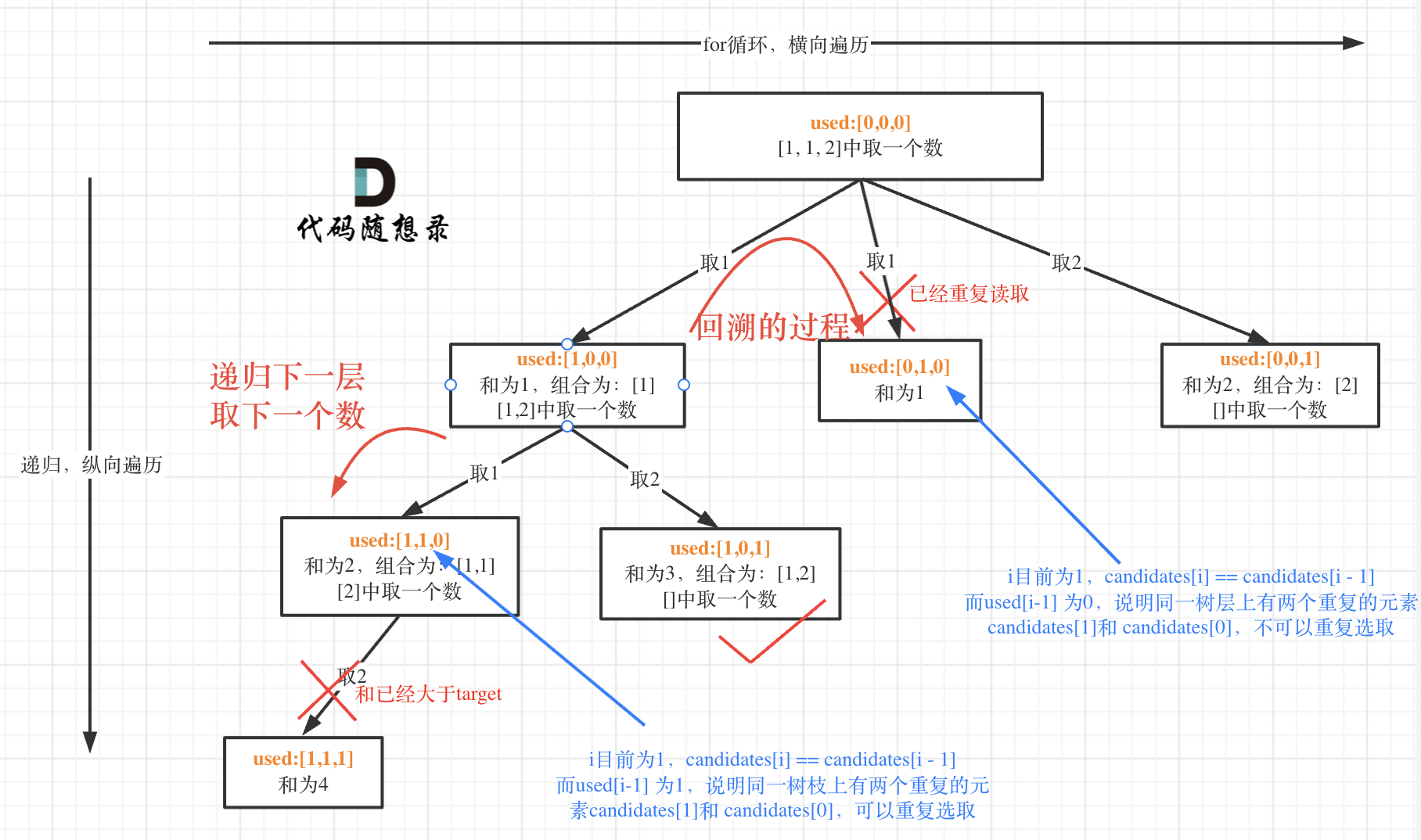
2.4组合总和3
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明: 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
- 示例 1:
- 输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
- 所求解集为:
[ [1, 7], [1, 2, 5], [2, 6], [1, 1, 6] ]
思路
- 本题candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
- 本题数组candidates的元素是有重复的
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used;
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
used = new boolean[candidates.length];
// 加标志数组,用来辅助判断同层节点是否已经遍历
Arrays.fill(used, false);
// 为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backTracking(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
private void backTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) {
break;
}
// 出现重复节点,同层的第一个节点已经被访问过,所以直接跳过
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
// 每个节点仅能选择一次,所以从下一位开始
backTracking(candidates, target, i + 1);
used[i] = false;
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution s = new Solution();
int[] candidates = {10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5};
int target = 8;
List<List<Integer>> result = s.combinationSum2(candidates, target);
System.out.println(result); // expected: [[1, 1, 6], [1, 2, 5], [1, 7], [2, 6]]
}
}
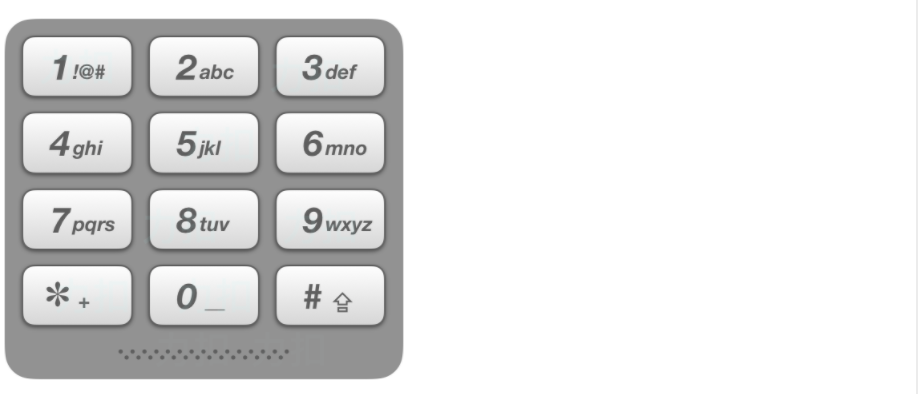
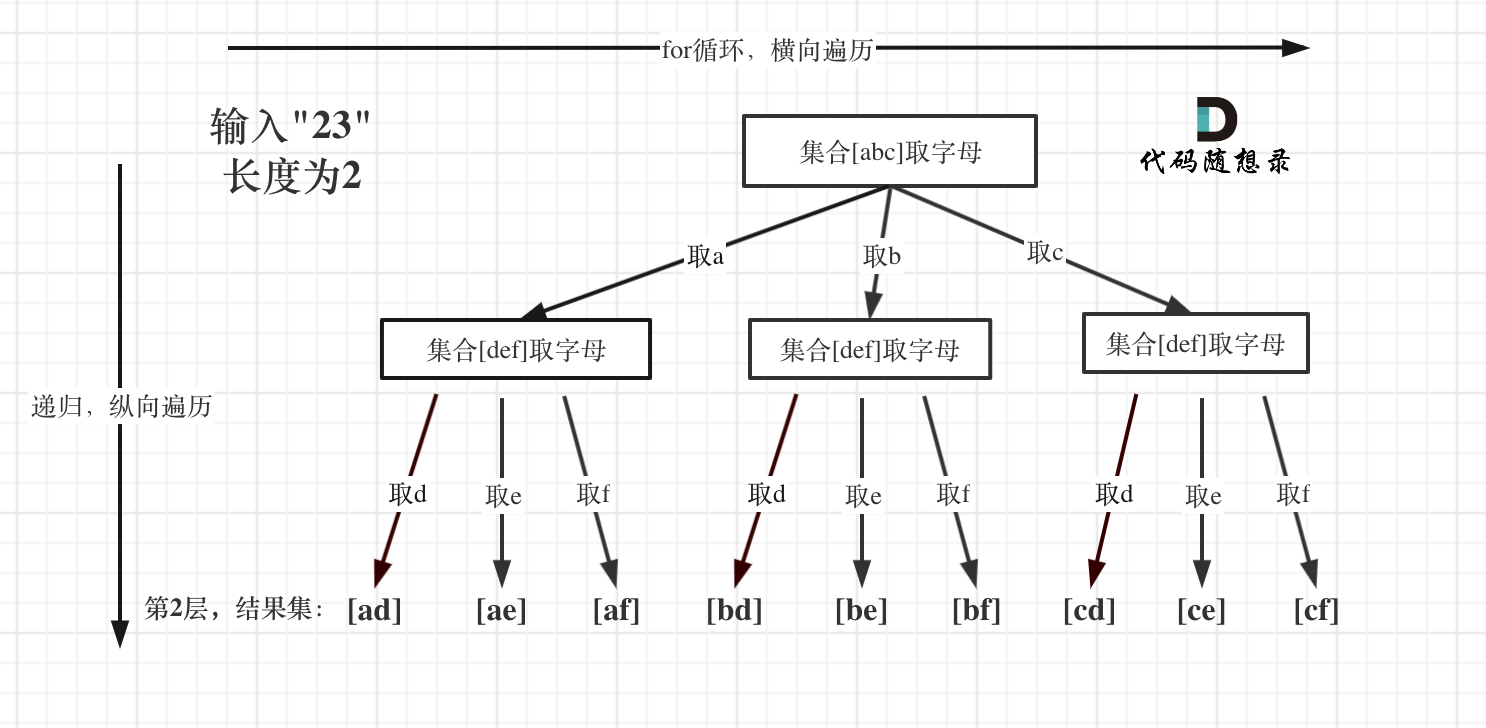
2.5电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例:
- 输入:"23"
- 输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
说明:尽管上面的答案是按字典序排列的,但是你可以任意选择答案输出的顺序。
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
// 字母映射表
private final String[] letterMap = {
"", // 0
"", // 1
"abc", // 2
"def", // 3
"ghi", // 4
"jkl", // 5
"mno", // 6
"pqrs", // 7
"tuv", // 8
"wxyz" // 9
};
private List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储所有结果
private StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); // 存储每个组合
private void backtracking(String digits, int index) {
if (index == digits.length()) { // 当处理到最后一个数字时,将s加入result中
result.add(s.toString());
return;
}
int digit = digits.charAt(index) - '0'; // 将当前数字转为int
String letters = letterMap[digit]; // 找出数字对应的字符集
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length(); i++) {
s.append(letters.charAt(i)); // 将当前字符加入s
backtracking(digits, index + 1); // 递归到下一个数字
s.deleteCharAt(s.length() - 1); // 回溯,将最后一个字符删除
}
}
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
result.clear(); // 清空result
s.setLength(0); // 清空s
if (digits.length() == 0) { // 边界条件,当输入为空时,直接返回result
return result;
}
backtracking(digits, 0); // 从第一个数字开始处理
return result;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol = new Solution();
String digits1 = "23";
List<String> res1 = sol.letterCombinations(digits1);
System.out.println(res1);
String digits2 = "";
List<String> res2 = sol.letterCombinations(digits2);
System.out.println(res2);
String digits3 = "2";
List<String> res3 = sol.letterCombinations(digits3);
System.out.println(res3);
}
}三、切割问题
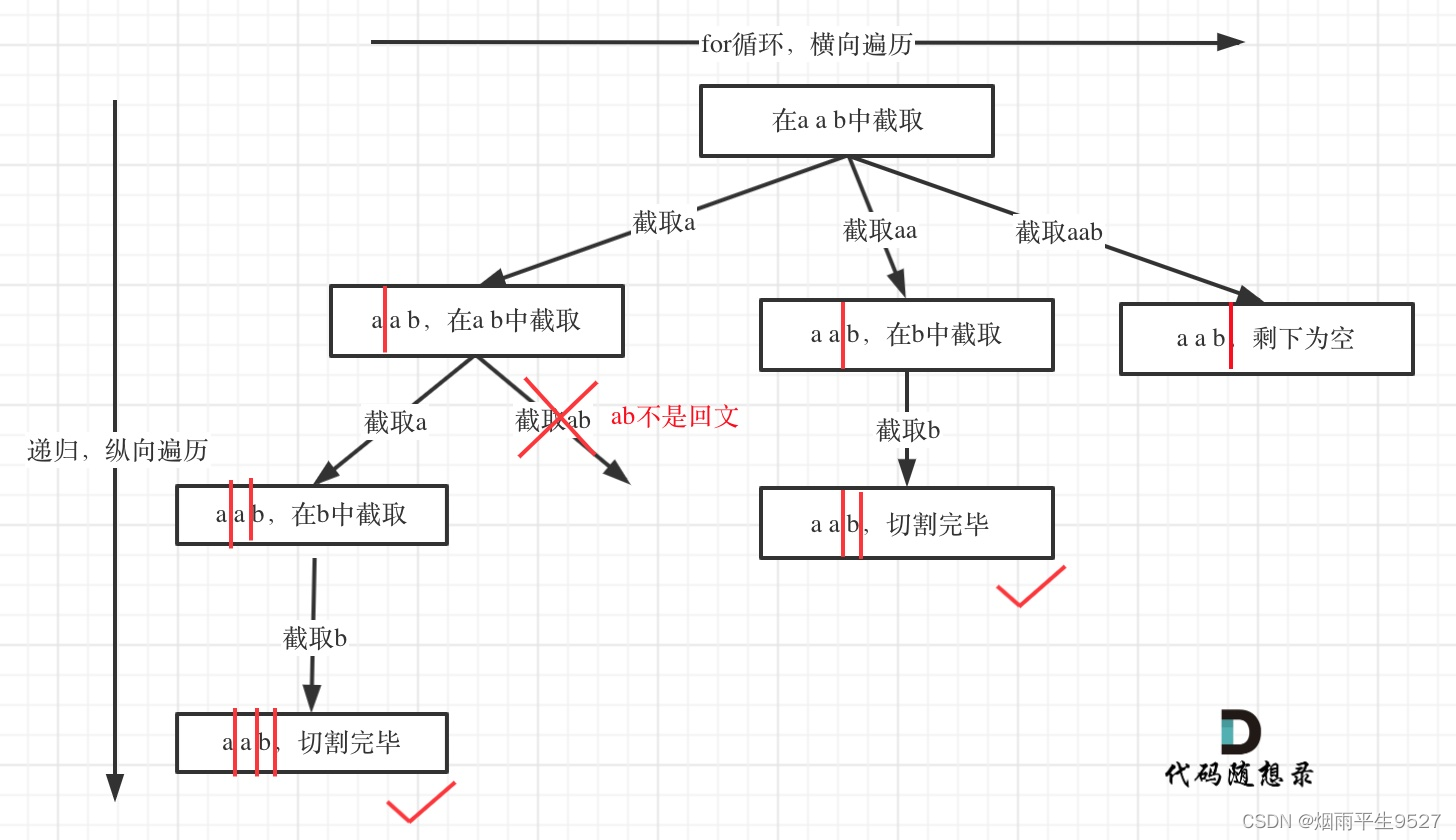
3.1分割回文串
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例: 输入: "aab" 输出: [ ["aa","b"], ["a","a","b"] ]
思路
- 切割问题,有不同的切割方式
- 判断回文
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<String> path = new ArrayList<>(); // 存放已经回文的子串
private void backtracking(String s, int startIndex) {
// 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
if (startIndex >= s.length()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) { // 是回文子串
// 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
path.add(str);
} else { // 不是回文,跳过
continue;
}
backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经填在的子串
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {
// 判断从start到end的子串是否是回文子串
while (start < end) {
if (s.charAt(start++) != s.charAt(end--)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(s, 0);
return result;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol = new Solution();
List<List<String>> res1 = sol.partition("aab");
System.out.println(res1);
List<List<String>> res2 = sol.partition("a");
System.out.println(res2);
List<List<String>> res3 = sol.partition("racecar");
System.out.println(res3);
}
}3.2.复原IP地址
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。
有效的 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 '.' 分隔。
例如:"0.1.2.201" 和 "192.168.1.1" 是 有效的 IP 地址,但是 "0.011.255.245"、"192.168.1.312" 和 "192.168@1.1" 是 无效的 IP 地址。
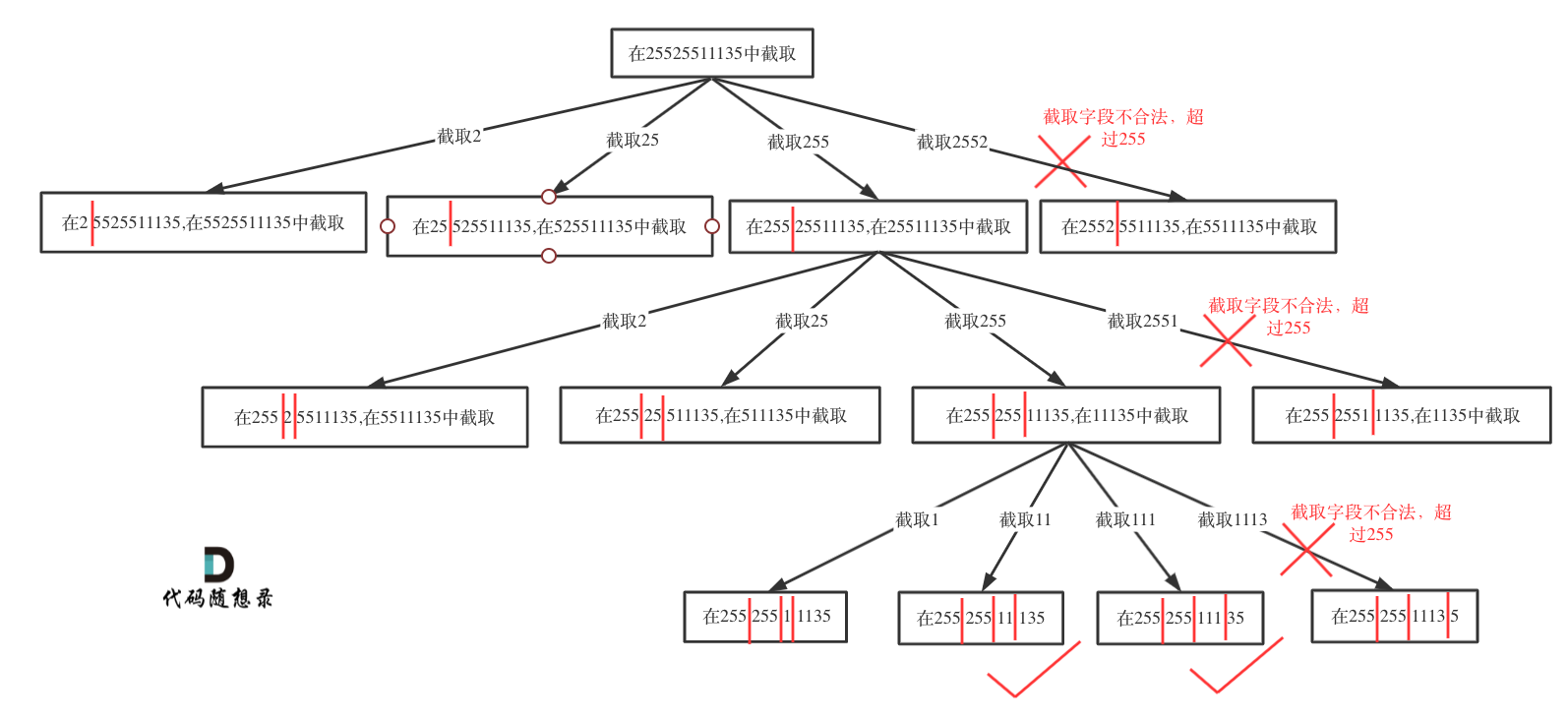
示例 1:
- 输入:s = "25525511135"
- 输出:["255.255.11.135","255.255.111.35"]
示例 2:
- 输入:s = "0000"
- 输出:["0.0.0.0"]
提示
切割问题就可以使用回溯搜索法把所有可能性搜出来
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录结果
// startIndex: 搜索的起始位置,pointNum:添加逗点的数量
private void backtracking(String s, int startIndex, int pointNum) {
if (pointNum == 3) { // 逗点数量为3时,分隔结束
// 判断第四段子字符串是否合法,如果合法就放进result中
if (isValid(s, startIndex, s.length() - 1)) {
result.add(s);
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isValid(s, startIndex, i)) { // 判断 [startIndex,i] 这个区间的子串是否合法
s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + "." + s.substring(i + 1); // 在i的后面插入一个逗点
pointNum++;
backtracking(s, i + 2, pointNum); // 插入逗点之后下一个子串的起始位置为i+2
pointNum--; // 回溯
s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + s.substring(i + 2); // 回溯删掉逗点
} else {
break; // 不合法,直接结束本层循环
}
}
}
// 判断字符串s在左闭右闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
private boolean isValid(String s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
}
if (s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end) { // 0开头的数字不合法
return false;
}
int num = 0;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) > '9' || s.charAt(i) < '0') { // 遇到非数字字符不合法
return false;
}
num = num * 10 + (s.charAt(i) - '0');
if (num > 255) { // 如果大于255了不合法
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
result.clear();
if (s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12) {
return result; // 算是剪枝了
}
backtracking(s, 0, 0);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<String> result = solution.restoreIpAddresses("25525511135");
System.out.println(result); // ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]
}
}
四、子集问题
4.1子集
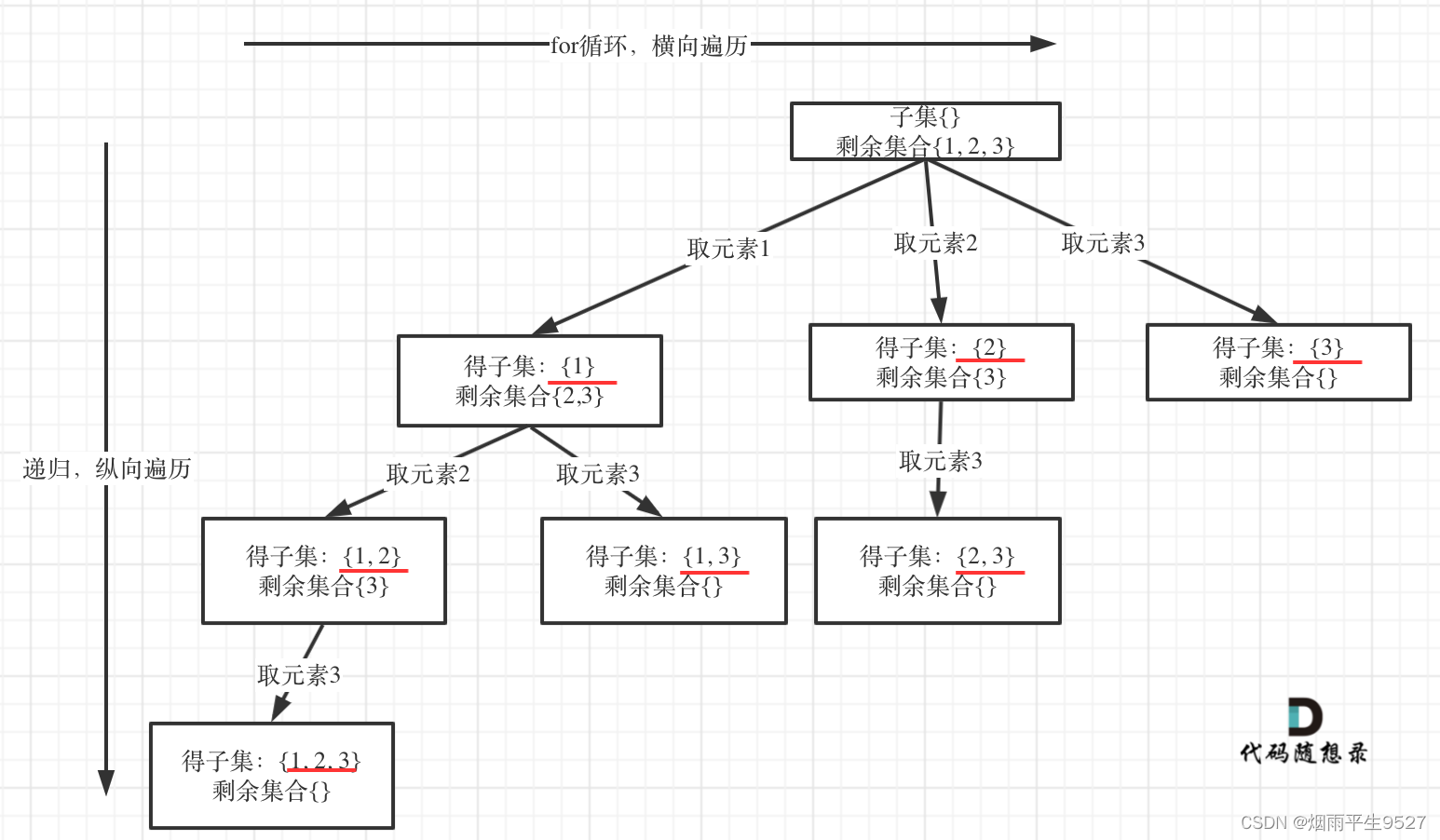
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例: 输入: nums = [1,2,3] 输出: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ]
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储所有的子集
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储当前正在生成的子集
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
private void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 加入当前生成的子集
if (startIndex == nums.length) { // 终止条件
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1); // 从i+1开始搜索,避免重复
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3};
List<List<Integer>> subsets = solution.subsets(nums);
for (List<Integer> subset : subsets) {
System.out.println(subset);
}
}
}
4.2子集2
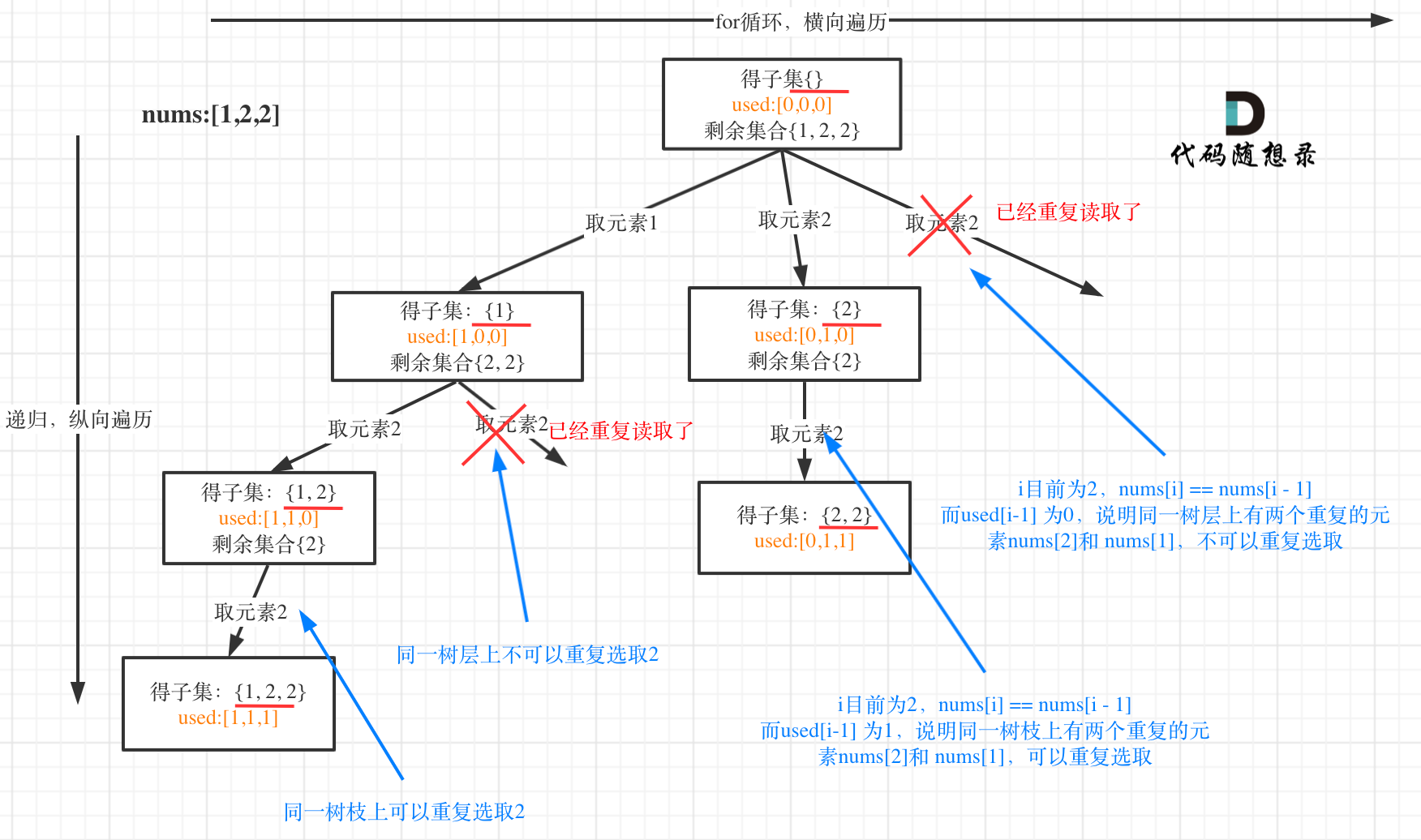
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
- 输入: [1,2,2]
- 输出: [ [2], [1], [1,2,2], [2,2], [1,2], [] ]
思路
集合里有重复元素了,而且求取的子集要去重。
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result;
private List<Integer> path;
private void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 收集子集
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果这个元素和上一个元素一样,并且上一个元素没有被选中,那么这个元素也不用选
if (i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
path = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums); // 数组排序
backtracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] nums = {1, 2, 2};
List<List<Integer>> subsets = solution.subsetsWithDup(nums);
for (List<Integer> subset : subsets) {
System.out.println(subset.toString());
}
}
}
4.3递增子序列
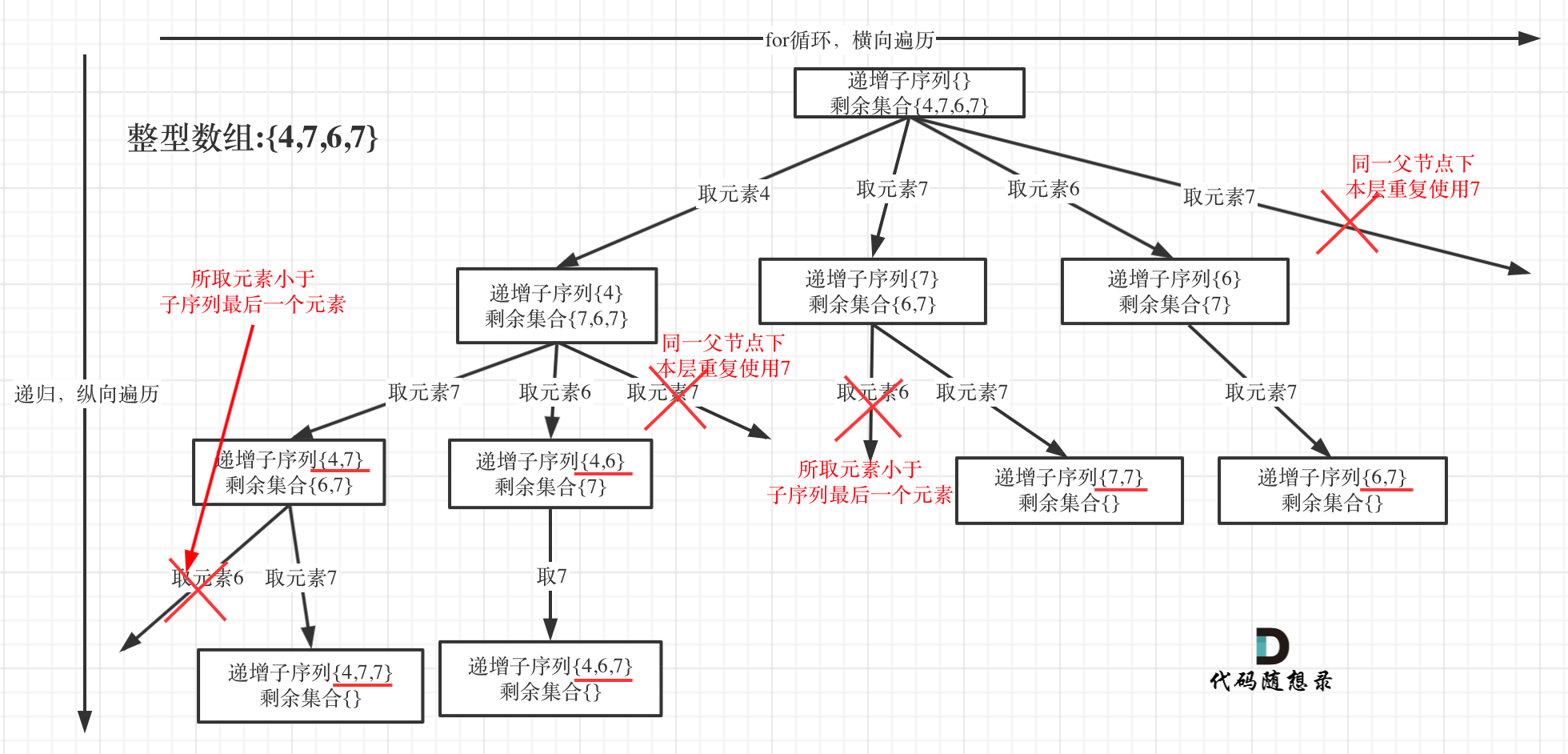
给定一个整型数组, 你的任务是找到所有该数组的递增子序列,递增子序列的长度至少是2。
示例:
- 输入: [4, 6, 7, 7]
- 输出: [[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 7, 7], [6, 7], [6, 7, 7], [7,7], [4,7,7]]
说明:
- 给定数组的长度不会超过15。
- 数组中的整数范围是 [-100,100]。
- 给定数组中可能包含重复数字,相等的数字应该被视为递增的一种情况。
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
private void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() > 1) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 注意这里要new一个新的list
// 注意这里不要加return,要取树上的节点
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); // 使用set对本层元素进行去重
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
if ((!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.get(path.size() - 1))
|| set.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
set.add(nums[i]); // 记录这个元素在本层用过了,本层后面不能再用了
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] nums = {4, 6, 7, 7};
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.findSubsequences(nums);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
五、排列问题
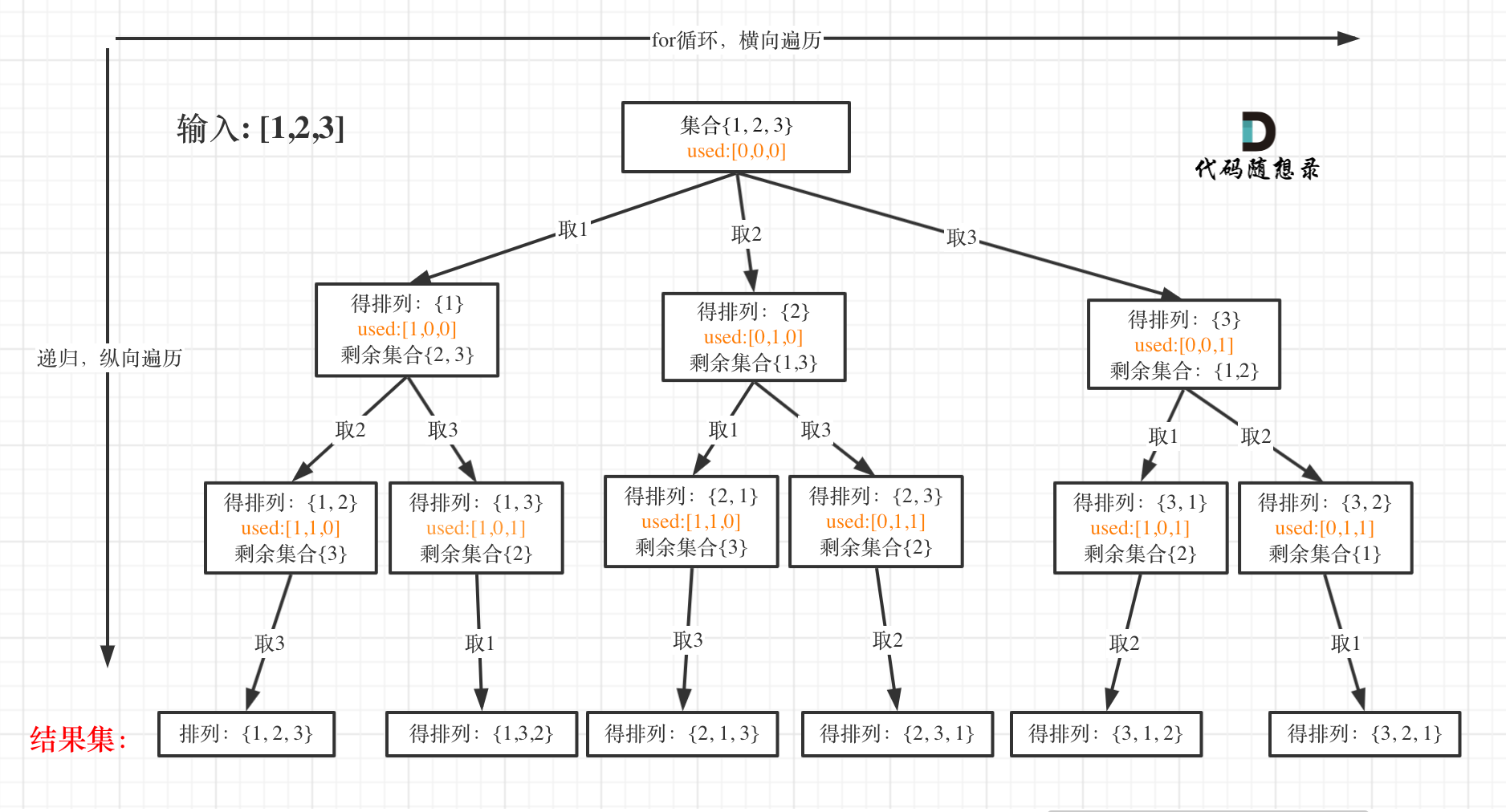
5.1全排列
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
- 输入: [1,2,3]
- 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ]
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
// 回溯算法
public void backtracking(List<Integer> nums, boolean[] used) {
// 如果当前path中的数字数量等于nums中的数字数量,则已经找到一组答案
if (path.size() == nums.size()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 枚举nums中所有的数字
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 如果当前数字已经使用过,则跳过
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
// 标记当前数字已经使用过
used[i] = true;
// 将当前数字加入到path中
path.add(nums.get(i));
// 继续递归查找
backtracking(nums, used);
// 回溯
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(List<Integer> nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.size()];
backtracking(nums, used);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.permute(nums);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
asList是Java中的一个方法,它可以将数组转换为List。返回的List是由指定数组支持的固定大小的列表。 该方法可以作为基于数组和基于集合的API之间的桥梁
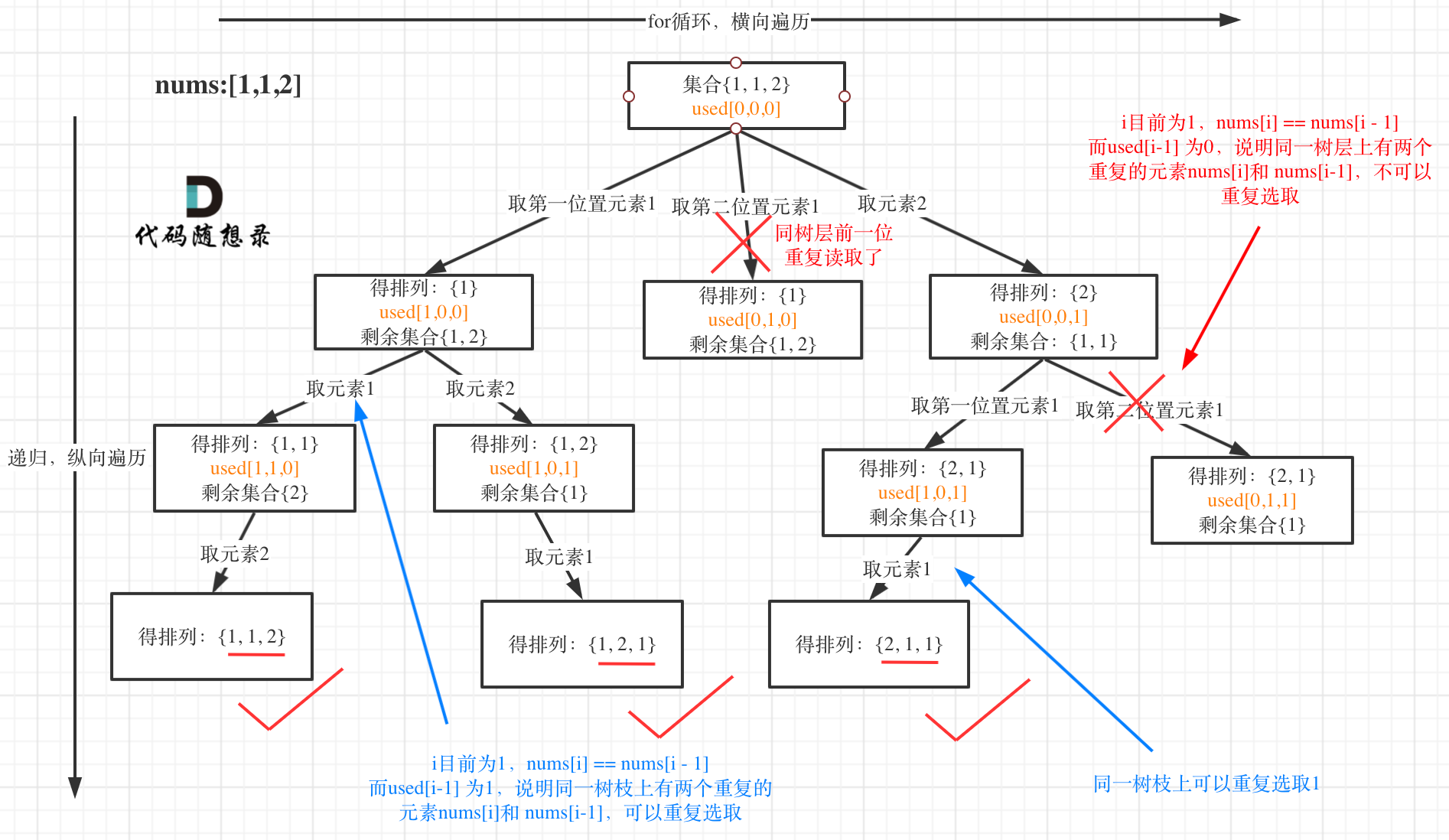
5.2全排列 II
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
- 输入:nums = [1,1,2]
- 输出: [[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
private void backtracking(int[] nums, boolean[] used) {
// 如果当前组合中的数字数量等于数组的长度,说明找到了一组,加入结果集中
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 注意需要新建一个ArrayList,否则结果会受到后续操作的影响
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果当前数字已经被使用过,跳过
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
// 如果当前数字和前一个数字相同,并且前一个数字没有被使用过,则跳过
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && !used[i-1]) {
continue;
}
// 将当前数字加入组合中
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true; // 标记当前数字已经被使用过
// 继续搜索
backtracking(nums, used);
// 回溯,将当前数字从组合中删除,并标记为未使用过
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
result.clear(); // 清空结果集
path.clear(); // 清空当前组合
Arrays.sort(nums); // 对数组进行排序,方便判断重复数字
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length]; // 标记每个数字是否被使用过
backtracking(nums, used); // 开始搜索
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] nums = {1, 1, 2};
List<List<Integer>> result = solution.permuteUnique(nums);
System.out.println(result);
}
}六、棋盘问题
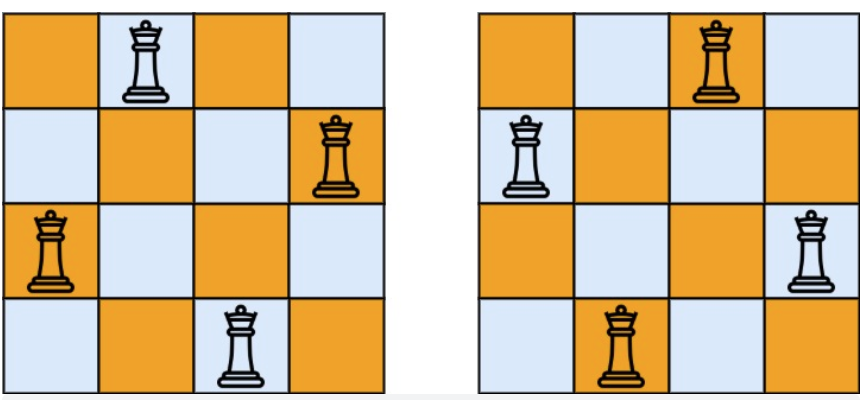
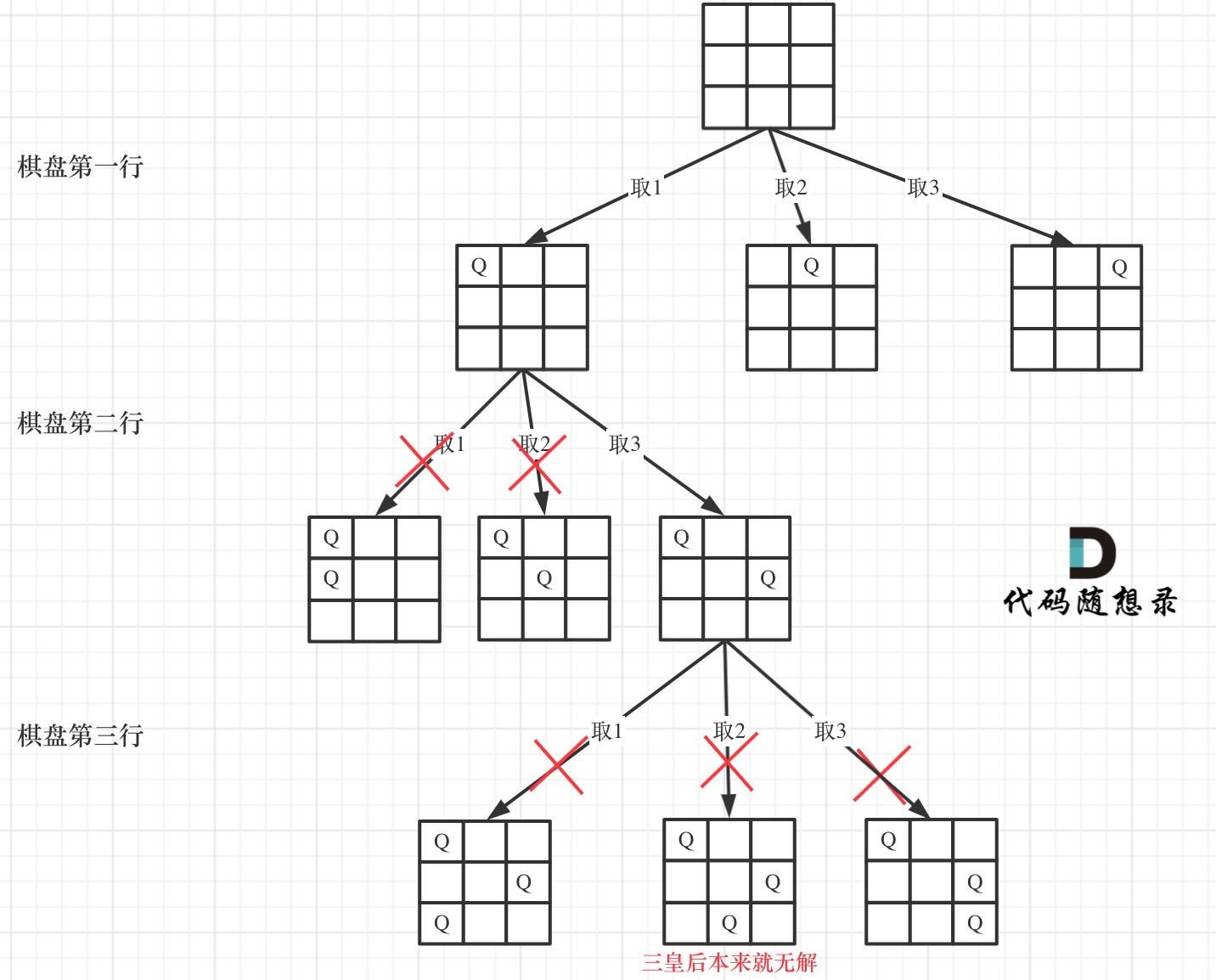
6.1N皇后
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例 1:
- 输入:n = 4
- 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
- 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
提示
首先来看一下皇后们的约束条件:
- 不能同行
- 不能同列
- 不能同斜线
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
private List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// n 为输入的棋盘大小
// row 是当前递归到棋盘的第几行了
private void backtracking(int n, int row, char[][] chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
result.add(charToStringList(chessboard));
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
}
}
}
private boolean isValid(int row, int col, char[][] chessboard, int n) {
// 检查列
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 45度角是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 135度角是否有皇后
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private List<String> charToStringList(char[][] chessboard) {
List<String> board = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] row : chessboard) {
board.add(new String(row));
}
return board;
}
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
result.clear();
char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
chessboard[i][j] = '.';
}
}
backtracking(n, 0, chessboard);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int n = 4;
List<List<String>> result = solution.solveNQueens(n);
for (List<String> board : result) {
for (String row : board) {
System.out.println(row);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}6.2解数独
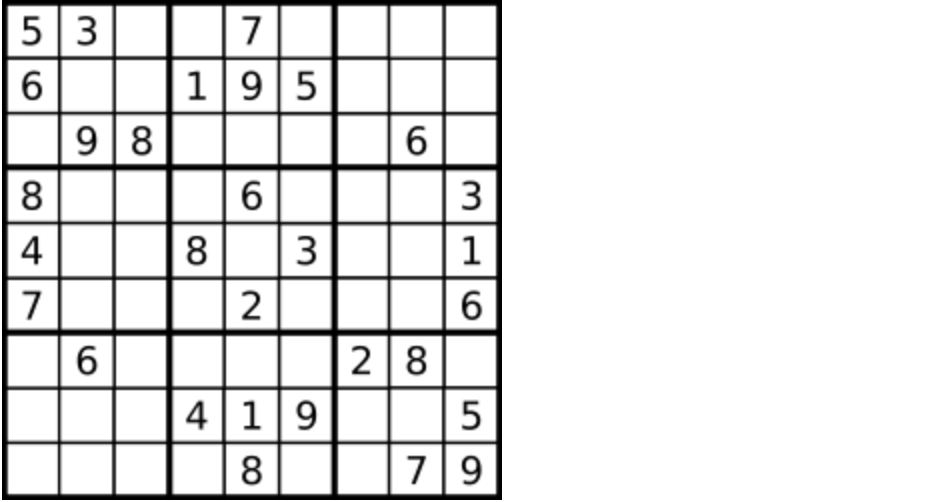
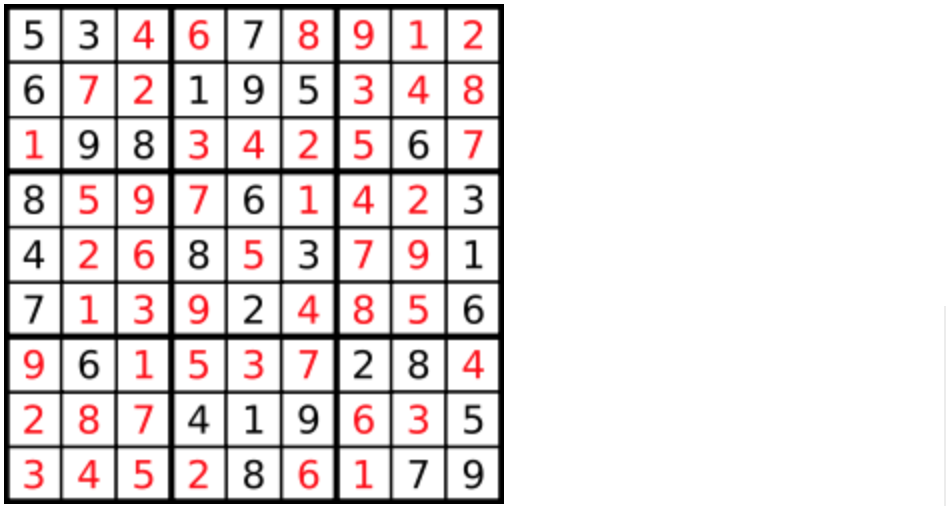
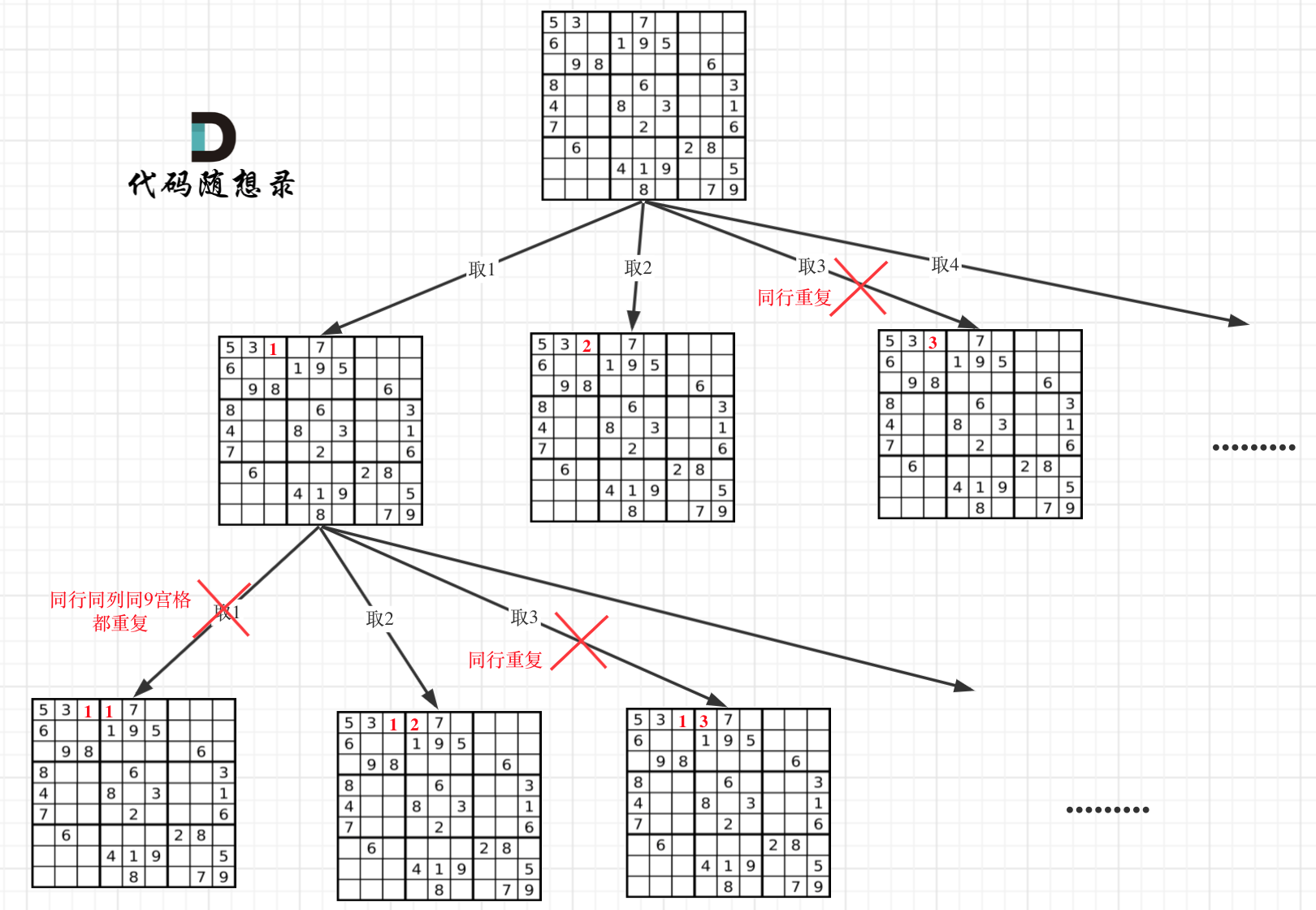
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
一个数独的解法需遵循如下规则: 数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。 数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。 数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。 空白格用 '.' 表示。
一个数独。
答案被标成红色。
提示:
- 给定的数独序列只包含数字 1-9 和字符 '.' 。
- 你可以假设给定的数独只有唯一解。
- 给定数独永远是 9x9 形式的。
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private boolean backtracking(char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) { // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) { // 遍历列
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++) { // (i, j) 这个位置放k是否合适
if (isValid(i, j, k, board)) {
board[i][j] = k; // 放置k
if (backtracking(board)) {
return true; // 如果找到合适一组立刻返回
}
board[i][j] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销k
}
}
return false; // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
}
}
}
return true; // 遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了
}
private boolean isValid(int row, int col, char val, char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // 判断行里是否重复
if (board[row][i] == val) {
return false;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { // 判断列里是否重复
if (board[j][col] == val) {
return false;
}
}
int startRow = (row / 3) * 3;
int startCol = (col / 3) * 3;
for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++) { // 判断9方格里是否重复
for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == val) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
backtracking(board);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol = new Solution();
char[][] board = new char[][]{
{'5','3','.','.','7','.','.','.','.'},
{'6','.','.','1','9','5','.','.','.'},
{'.','9','8','.','.','.','.','6','.'},
{'8','.','.','.','6','.','.','.','3'},
{'4','.','.','8','.','3','.','.','1'},
{'7','.','.','.','2','.','.','.','6'},
{'.','6','.','.','.','.','2','8','.'},
{'.','.','.','4','1','9','.','.','5'},
{'.','.','.','.','8','.','.','7','9'}
};
sol.solveSudoku(board);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(board[i]));
}
}
}