文章目录
- 1. list的使用
- 1. 构造函数
- 2.迭代器的使用和数据访问
- 3. 容量相关
- 4. 数据修改
- 1.数据插入
- 2. 数据删除
- 5.其他接口
1. list的使用
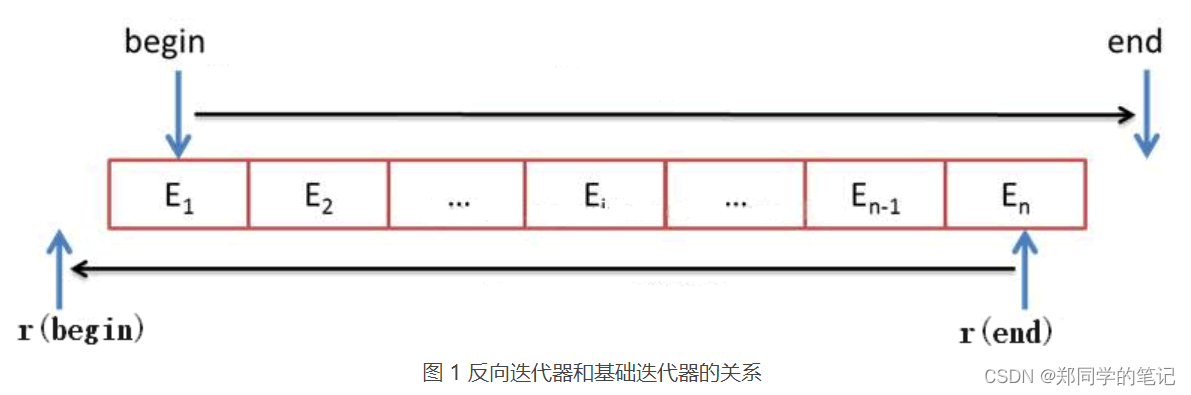
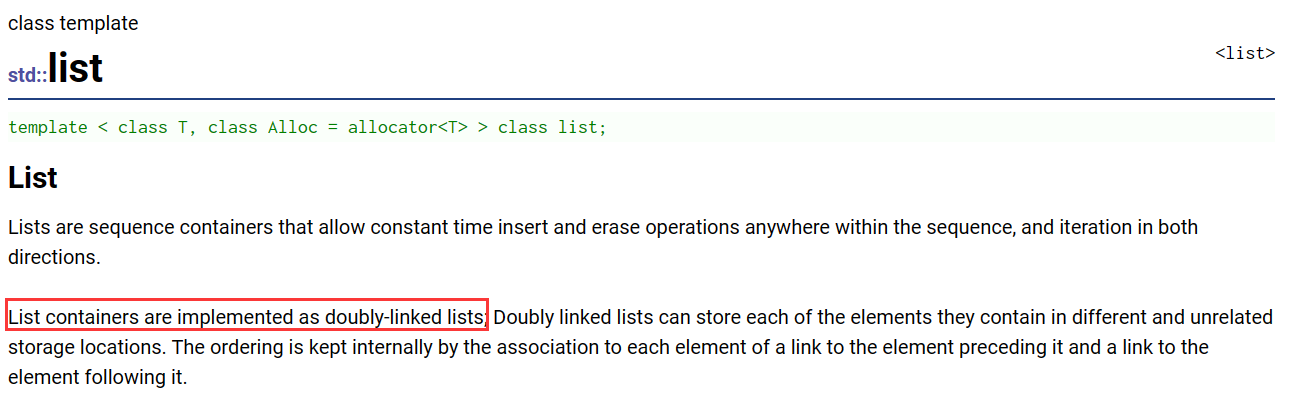
首先,在使用list之前,我们得先了解list到底是个什么东西,查看文档可以了解到,list的底层是一个带头双向循环链表。
按照顺序,我们首先来了解一下list的默认成员函数,这里我们不关注后面关于allocator的参数。
1. 构造函数
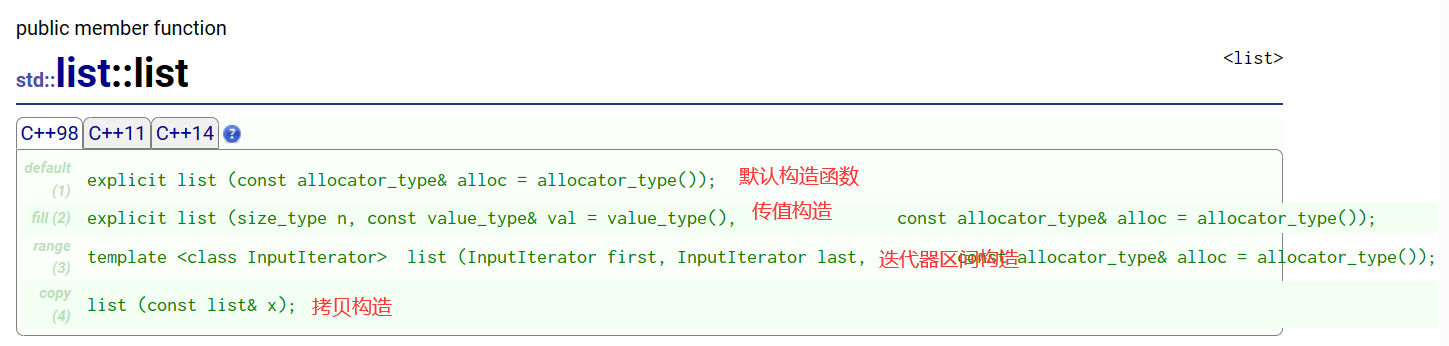
接下来通过一段代码来了解一下:
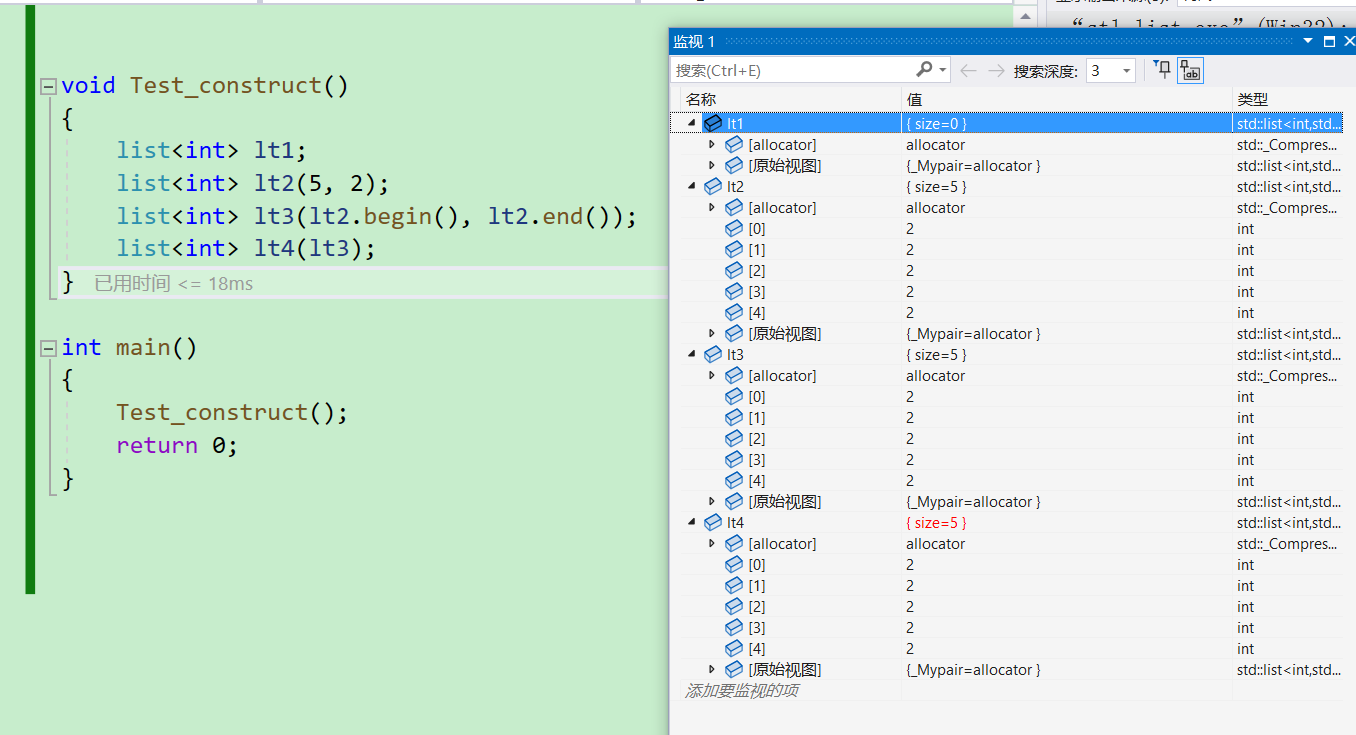
void Test_construct()
{
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2(5, 2);
list<int> lt3(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
list<int> lt4(lt3);
}
2.迭代器的使用和数据访问
我们知道,迭代器设计模式的出现就是为了让所有的容器都有统一的访问方式,所以这里迭代器的使用与之前讲的string和vector没有任何区别。
void Test_Iterator()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
//写
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
*it *= 10;
++it;
}
//读
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
但是对于string和vector,我们对其中数据访问的方式有三种:[]下标访问,迭代器,范围for。其中使用[]访问的目的是为了访问到任意元素的时间复杂度都为O(1),但是对于list的结构:链表,我们,没办法做到O(1)的访问,所以这里就没有重载[]的必要了所以对于list的访问方式只有迭代器和范围for两种。
3. 容量相关
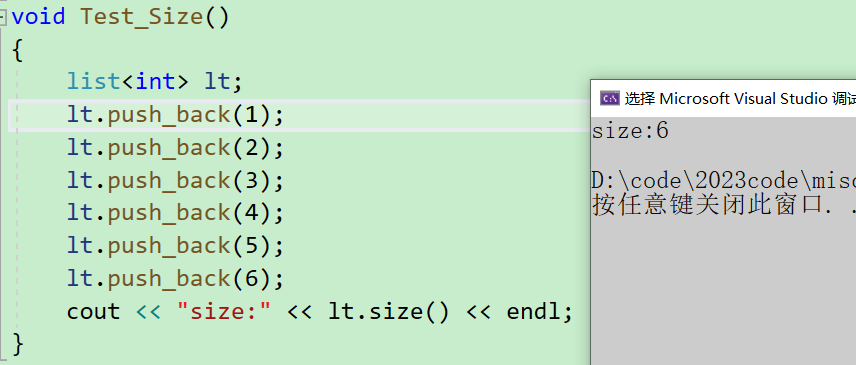
1. size:拿到list的数据个数
由于list的结构,所以不会出现有容量的概念,因为每次插入数据或者删除数据的时候,直接插入或删除一个节点即可。所以这里只提供了size这个接口用于返回数据个数。
2. resize:改变数据个数
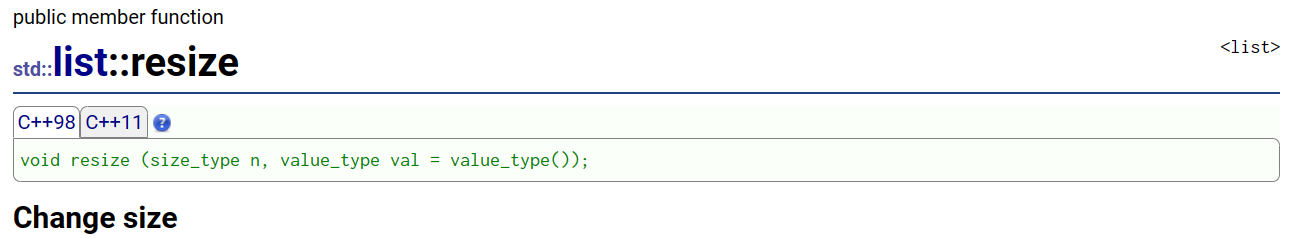
和其他STL容器的接口相同的用法
3. clear:清空容器中的所有数据
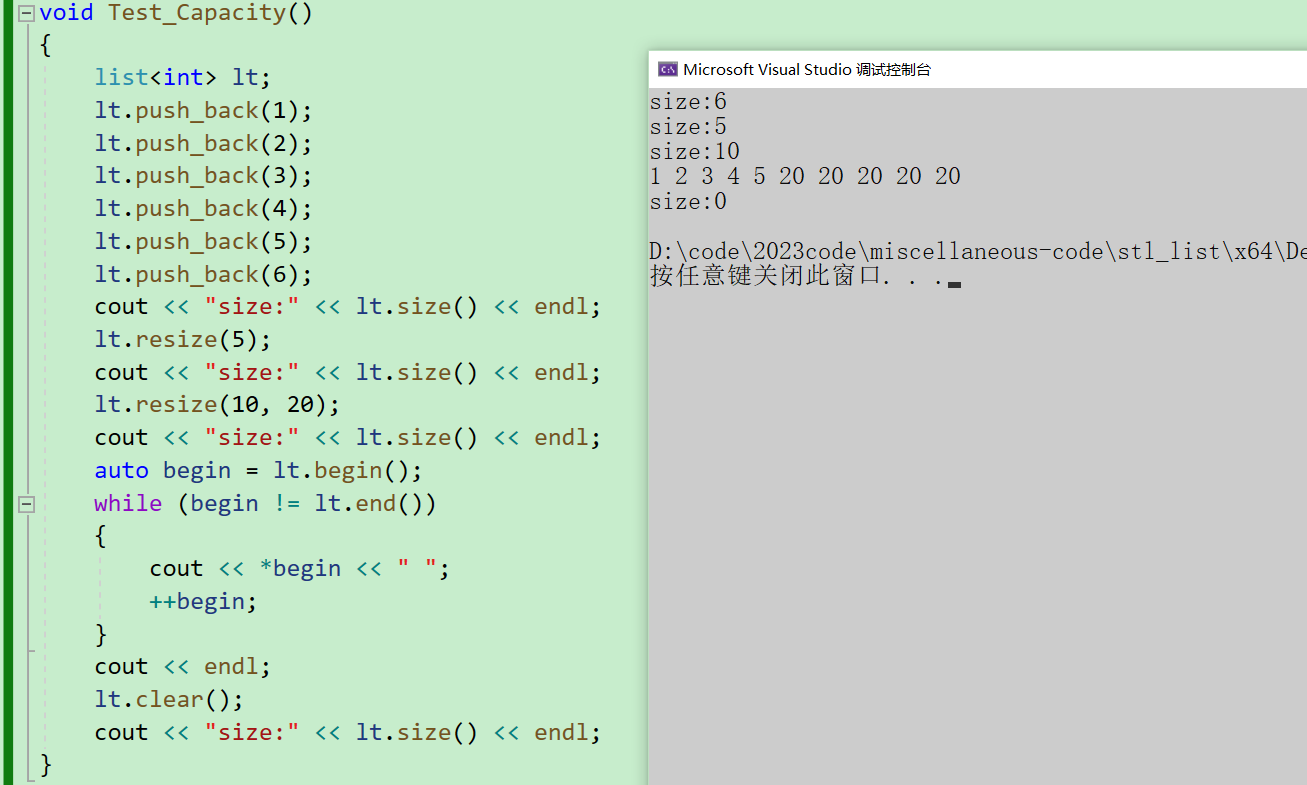
void Test_Capacity()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
cout << "size:" << lt.size() << endl;
lt.resize(5);
cout << "size:" << lt.size() << endl;
lt.resize(10, 20);
cout << "size:" << lt.size() << endl;
auto begin = lt.begin();
while (begin != lt.end())
{
cout << *begin << " ";
++begin;
}
cout << endl;
lt.clear();
cout << "size:" << lt.size() << endl;
}
4. 数据修改
由于链表结构的特殊性,我们可以很方便的头插,尾插或者在任意位置插入,所以在这里库里面对于数据插入提供了很多种方式
1.数据插入
1. push_back:尾插
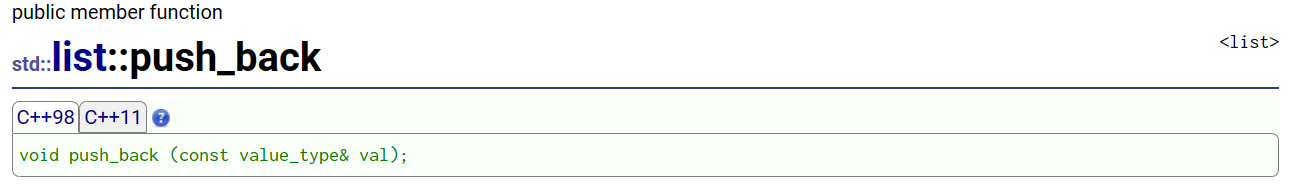
2. push_front:头插

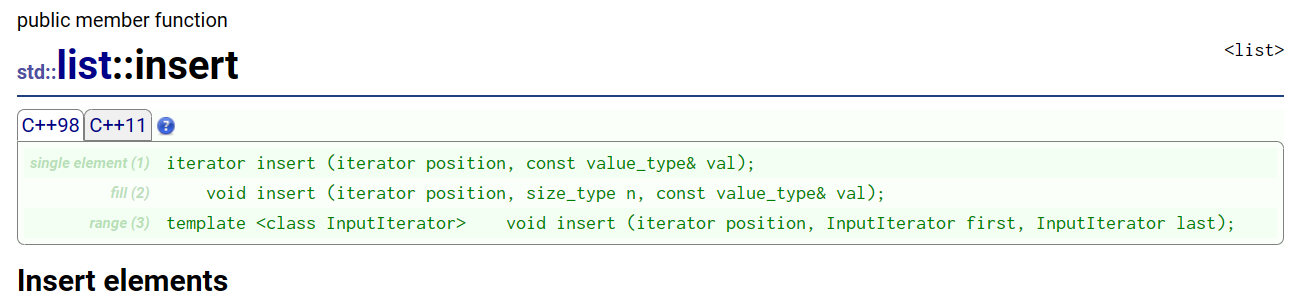
3.insert:在任意位置插入删除
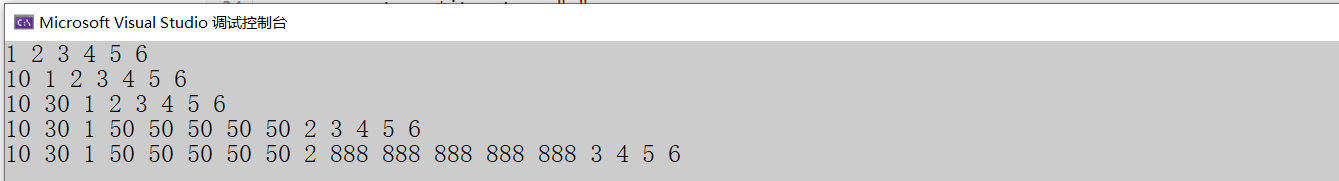
void Test_insert()
{
vector<int> v(5, 888);
list<int> lt;
//尾插
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
auto it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
//头插
lt.push_front(10);
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
//在任意位置插入
auto it_push = ++lt.begin();//从第二个位置开始
lt.insert(it_push, 30);//插入一个值
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
++it_push;
lt.insert(it_push, 5, 50);//插入n个值
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
++it_push;
lt.insert(it_push, v.begin(), v.end());//插入一个迭代器区间
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
}
2. 数据删除
与数据插入相对应的,数据删除也有三个
1. pop_back:尾删

2.pop_front:头删

3.erase:任意位置删除
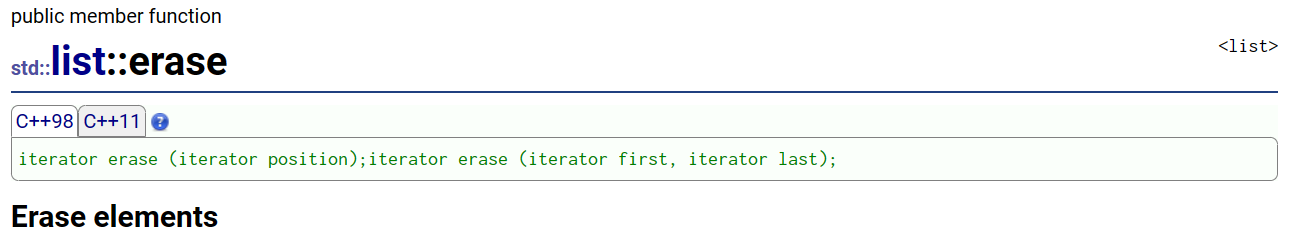
void Test_erase()
{
list<int> lt;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
lt.push_back(i);
}
auto it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
//头删
lt.pop_front();
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
//尾删
lt.pop_back();
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
//任意位置删除
auto pos = ++lt.begin();
pos = lt.erase(pos);//删除某一位置
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
auto start = ++pos;
auto end = ++(++start);
lt.erase(start, end);//删除一个迭代器区间
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
}

5.其他接口
除了上述的接口之外,还有一些我们之前在string和vector中没有见到的接口,下面我们来看看他们的用法
1. remove:删除list中指定值

void Test_remove()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(7);
lt.push_back(8);
auto it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
lt.remove(5);
lt.remove(10);
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
}
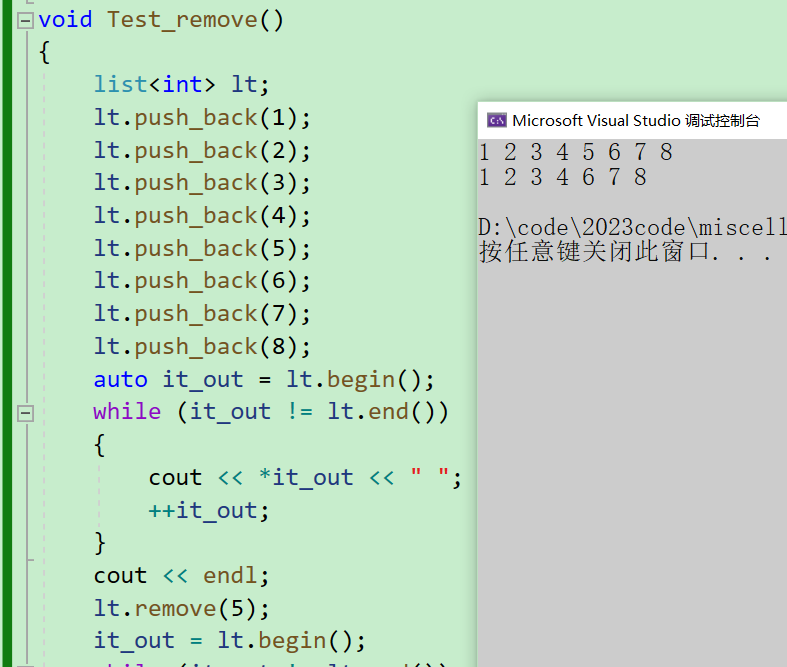
可以看到,remove对于list中不存在的元素不会做任何操作
2. sort:排序list

看到这里肯定会有人有疑惑,sort算法库里面不是实现过吗?为什么又要重新在list里实现一下,我直接用算法库里面的不行吗?
✅答案是:不行,接下来看实验==》

可以看到,在编译的过程就已经报错了,这是因为库里面没有支持list迭代器类型的构造,为啥嘞?因为之前sort对容器内部的元素操作使用了+和-操作,但是list由于结构的限制,不支持迭代器的这个行为,所以对于list,要重新在库里面实现一个sort。
3. unique:删除list中的重复值
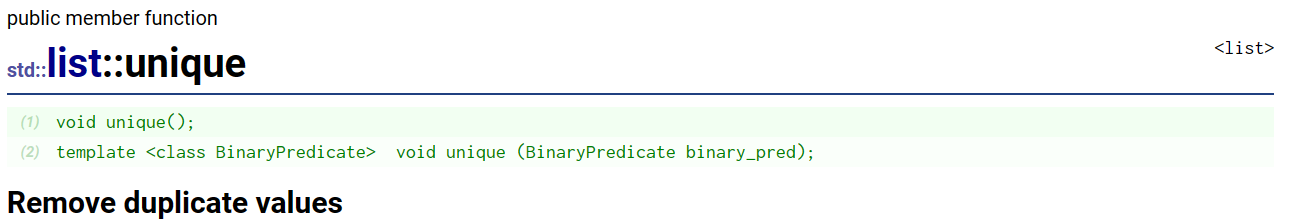
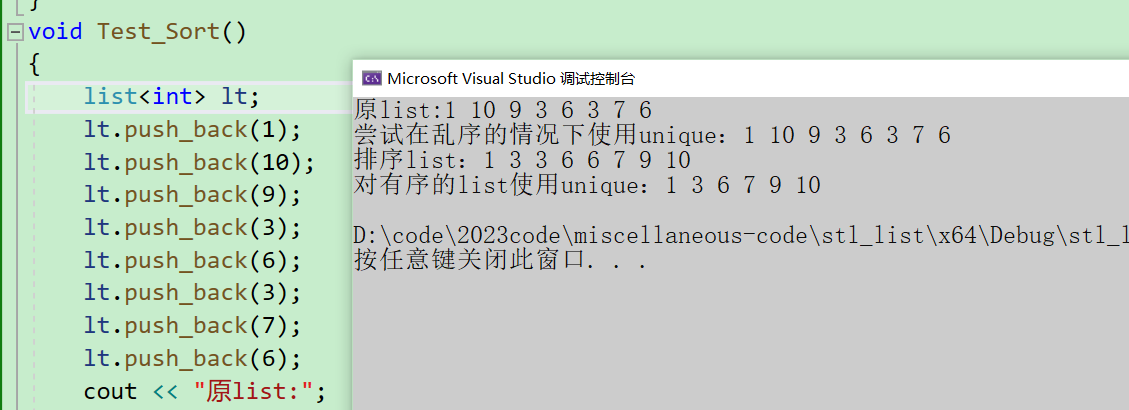
这里注意一下,在使用unique之前要确保list是有序的,否则不能完成删除所有重复值的功能
void Test_Sort()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(9);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(7);
lt.push_back(6);
cout << "原list:";
auto it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
lt.unique();
cout << "尝试在乱序的情况下使用unique:";
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
lt.sort();
cout << "排序list:";
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "对有序的list使用unique:";
lt.unique();
it_out = lt.begin();
while (it_out != lt.end())
{
cout << *it_out << " ";
++it_out;
}
cout << endl;
}