Vuex是vue中的一种状态管理模式,就是一个 状态仓库,仓库做什么?存储状态、管理状态(数据)的变化、提供状态获取窗口。
本文中一些测试用例基于@vue/composition-api@1.7.1 , vuex@3.6.2, vue@2.6.10 做的验证。 Vue3 和 vuex@4.x 用法有所不同。
用来干什么,能做什么用?
可用于全局数据存储,跨层级组件通讯,动态路由。
在通讯的关键是,一方通知后,另一方怎么知晓。在vue2中利用 mapMutations, mapActions 解析出来,则可直接使用解析后的方法进行通知,另外一方 根据 mapGetters, mapState 解析出来的 属性、方法做接收,达到互通目的。
大体剖析
大致理解如下图:
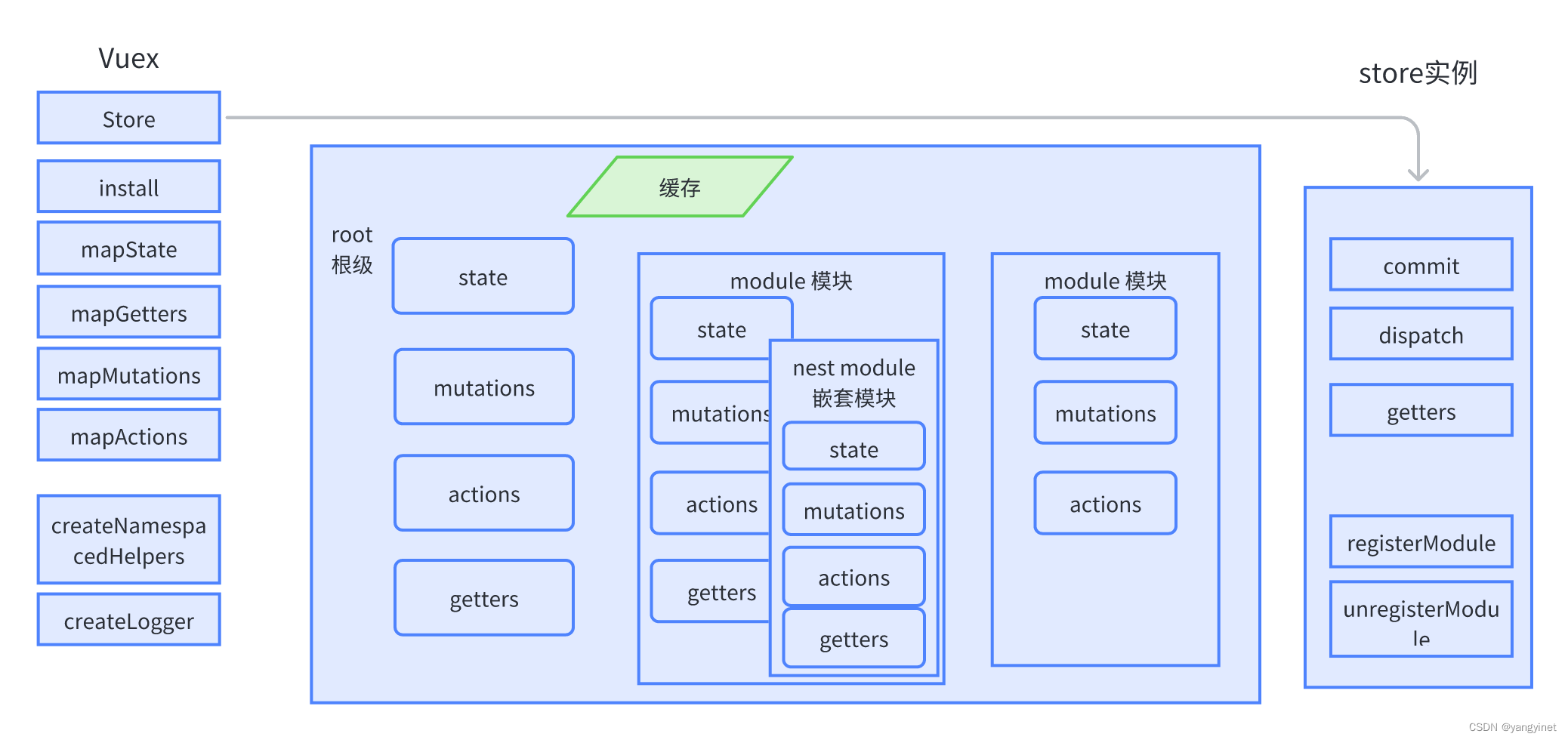
1.Vuex 的 install 对Vue提供use 接入, 利用Vuex.Store 产生实例化对象,具体实例化的规则通过配置的 state, getters, mutations, actions,namespaced 确定。
2.mutations对应及时同步更新仓库数据,对应 store实例的.commit方法
3.actions 对应异步延时更新数据,对应store实例 的.dispatch方法。
4.commit 和 dispatch 函数所带参数,可以是指定type属性的对象,也可以利用参数1直接type类型。 ({type: "mutations中的项目", payload}) 或者 ("actions中的项目")
5. 关于响应式,vue2 直接用 mapState, mapGetter。 compositon-api 中可以直接使用 store示例对象下的 { 变量 } = toRefs(store.state)
6. 针对有命名空间模块,采用 “命名空间名(modules下挂接的属性名)/ ” 进行使用。
6.支持常量类型。为了让大家都清楚,提供了哪些mutation,action, 独立一个 _types ,在types中定义好类型名字,做store 的配置时,直接使用 [_types.XXX]
7. 针对state\ 非函数式getter,数据会进行缓存。
针对Vue3 组合式,对应Vuex4.x 版本, 其使用方式方法有所不同, 产生 store 用CreateStore, 示例使用 app.use(store),不是属性挂接,使用 useStore。
以前觉得vuex的使用必须按常规挂到主 Vue示例上,其实是着相了。 不管是 vuex 还是其他库、框架,本质都是基于某种语言实现的。vuex一样,我们常常使用 Vue.use(Vuex), 在 主Vue实例上挂接 {store: new Vuex.Store({state, getters, matutions, actions})}, 利用 $store 去访问。
那么既然都是js,是不是可以直接使用 store实例就好,答案是可以的,但在某些地方使用时会很不方便,比如vue2直接使用 mapXXX解析,为什么?因为Vuex中提供的映射 mapXXXX 函数内部采用的就是 this.$store 对象进行相关操作。
使用compostion-api时,直接引入 利用 store.js 中生成的 store 示例,不绑定到vue上,也可直接使用。
PS: Vue.use(Vuex) 不能省略,否则出现错误 must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store instance.
具体用法 vue2 + vuex + compostion-api
针对 不采用 compositon-api 的,利用 mapXXX在对应属性上映射即可,方便快捷。
安装背负(Vue.use(Vuex)) -> 指腹为婚(new Vue({store: new Vuex.Store({}) })) -> 开支散叶 (...mapXXX)
直接访问比如
export default {
computed: {
...mapState({
// 箭头函数可使代码更简练
count: state => state.count,
// 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
countAlias: 'count',
// 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数
countPlusLocalState (state) {
return state.count + this.localCount
}
}),
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
}),
...mapActions({
add: 'add' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('add')`
})
}
}不做映射 使用 this.$store 访问, 而composition-api 比较类似这种做法。
vue2 + vuex + compostion-api
基础使用过程:利用Vue.use(Vuex) 将vuex安装到vue上,背上vuex,开始vuex之旅。利用 new Vuex.Store() 创建 store 示例, 无需挂载到 Vue主示例的 store上。需要触发状态值维护的地方,直接 store.commit , store.dispatch 即可,需要 接收状态值的地方,使用 toRefs(store.state.模块) 的方式接收即可。
注意,如果要使用getter,取根级getter相对方便, store.getters.。 启用了命名空间的getter, 相对麻烦,可使用 store._wrappedGetters 获取,且都是函数式的。
代码如下:
store.js store生成文件
import Vue from "vue"
import Vuex from "vuex"
import app from "./modules/app"
import calc from "./modules/calc"
Vue.use(Vuex) // 必须在 new Vuex.Store 之前
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
app,
calc
},
// 这里启用了模块,注意:启用了模块管理于根root上配置不冲突
state(){ // 用函数可以避免 污染
return {}
},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {}
})
export default storeapp 模块配置.js
// 为方便 mutation actions 的 外部使用,可使用 动态属性名
const app = {
// namespaced: true, // 启用命名空间后, getter 直接通过 store 实例对象是无法直接通过 store.getter获取到的
state(){ // 状态
return {
count: 1
}
},
getters: {
getMoreUseAttr(state, getters){
return state.count + 10
},
getMoreUseMethod: state => more => { // 函数式getter, 在使用时 函数调用
return state.count + more
}
},
mutations: { // 加工、维护。只能同步。 为方便
// 外部使用 .commit(mutationName, playload) 或者对象方式 {type, ...payload}
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload?.count
}
},
actions: { // 行为。 异步维护。
// 第一个参数是store模块上下文 conctext,外部使用使用.dispatch(actionName, payload)或者({type: actionName, ...payload}) payload一般建议使用对象,可常量。
addAsync({commit}, payload){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit({type: "increment", ...payload})
resolve(payload)
}, 2000)
})
}
}
}
export default app启用命名空间后, getter 直接通过 store 实例对象是无法直接通过 store.getter获取到的
calc 模块配置
const calc = {
namespaced: true,
state(){
return {
count: 2
}
},
mutations: {
increment(state, payload){ // 注意,这是与app配置中重名的。
state.count += payload.count
}
},
actions:{
addAsync:{
root: true, // 注意,这是与app配置中重名的。并提升到root根级
handler(context, payload){
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit("increment", payload)
}, 1000)
})
}
}
}
}
export default calc在启用命名空间的情况,mutation 或 action 也可使用 root: true 的方式提升到根级root上。
当多个模块 有重名mutation 或 actions 时, 如果启用命名空间,则互不关系,访问时指定命名空间,如果未启用命名空间或提升到了根级,在访问时,所有同名的都会被调用。
// 入口文件 main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
import store from "./components/store/index.js"
new Vue({
render: function (h) { return h(App) },
// store 不挂接
}).$mount('#app')状态值维护组件:/components/vuex/index.vue
<template>
<div>
BusIndex
<button @click="changeData">改变数据</button>
<button @click="asynChangeData">异步改变</button>
<div>
<button>获取更大值</button>
更大值 {{more}}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {onMounted, ref, computed, getCurrentInstance} from "@vue/composition-api"
import store from "./store/store.js"
export default {
name: "VuexIndex",
setup(props, ctx){
const changeData = () => {
store.commit("increment", {count: 2})
store.commit("calc/increment", {count: 5})
}
const asynChangeData = () => {
store.dispatch("addAsync", {count: 10}, { root: true })
}
// 访问根级的getMoreUseAttr
const more = computed(() => store.getters.getMoreUseAttr)
return {
changeData, asynChangeData, asynChangePowerData, more
}
}
}
</script>
状态值接收组件 /components/vuex/comp1.vue
<template>
<div>
状态值 app.count: {{count}} calc.count: {{count1}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {onMounted, ref, toRefs} from "@vue/composition-api"
import store from "./store/store.js"
export default {
name: "BusComp1",
setup(props, ctx){
const st = store
const {count} = toRefs(st.state.app)
const {count: count1} = toRefs(st.state.calc)
return {
count,
count1
}
}
}
</script>
主容器组件App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div>
vuex 测试
<vuexIndex></vuexIndex>
<vuexcomp1></vuexcomp1>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import vuexIndex from "./components/vuex/index.vue"
import vuexcomp1 from "./components/vuex/comp1.vue"
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
vuexIndex, vuexcomp1
}
}
</script>官网地址: Vuex 是什么? | Vuex
关键词回顾:(至此,可以回想下这些关键词是干啥用的)
vuex, store, state, mutations, actions, getters;
mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters;
modules, namespaced,registerModule;