一、安装Prometheus
1.1 部署并配置Prometheus
#主机基础配置
[root@node4~]# systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld
[root@node4~]# sed -i 's/=enforcing/=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config && setenforce 0
#上传prometheus安装包并解压
[root@node4 ~]# tar -zxvf prometheus-2.37.6.linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@node4 ~]# mv prometheus-2.37.6.linux-amd64 /usr/local/prometheus
#备份原始配置文件
[root@node4 ~]# cd /usr/local/prometheus/
[root@node4 prometheus]# cp prometheus.yml prometheus.yml_bak
[root@node4 prometheus]# cat /usr/local/prometheus/prometheus.yml | grep -v "^#"
#配置文件详情
global: #用于prometheus的全局配置,比如采集间隔,抓取超时时间等
scrape_interval: 15s # 采集目标主机监控数据的时间间隔,默认为1m
evaluation_interval: 15s # 触发告警生成alert的时间间隔,默认是1m
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
alerting: #用于alertmanager实例的配置,支持静态配置和动态服务发现的机制
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
# - alertmanager:9093
rule_files: #用于加载告警规则相关的文件路径的配置,可以使用文件名通配机制
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
scrape_configs: #用于采集时序数据源的配置
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus" #每个被监控实例的集合用job_name命名,支持静态配置(static_configs)和动态服务发现的机制
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs: #静态目标配置,固定从某个target拉取数据
- targets: ["192.168.40.165:9090"]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#第一种配置系统启动文件,设置systemctl start prometheus 方式启动
[root@node4 prometheus]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/prometheus.service
[Unit] #服务单元
Description=Prometheus Server
Documentation=https://prometheus.io
After=network.target #依赖关系
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/prometheus/prometheus \ #启动目录
--config.file=/usr/local/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ #配置文件
--storage.tsdb.path=/usr/local/prometheus/data/ \ #数据目录
--storage.tsdb.retention=15d \ #保存时间
--web.enable-lifecycle #开机热加载
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID #重载
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
#第二种启动方式
[root@node4 prometheus]# cd /usr/local/prometheus
[root@node4 prometheus]# ./prometheus
#启动并访问网页
[root@node4 prometheus]# systemctl start prometheus
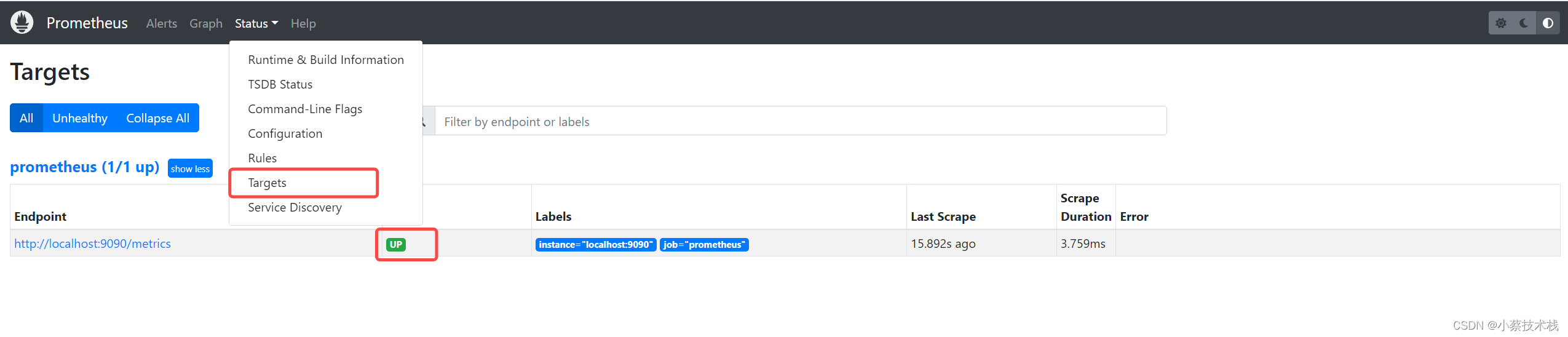
1.2 查看监控节点状态
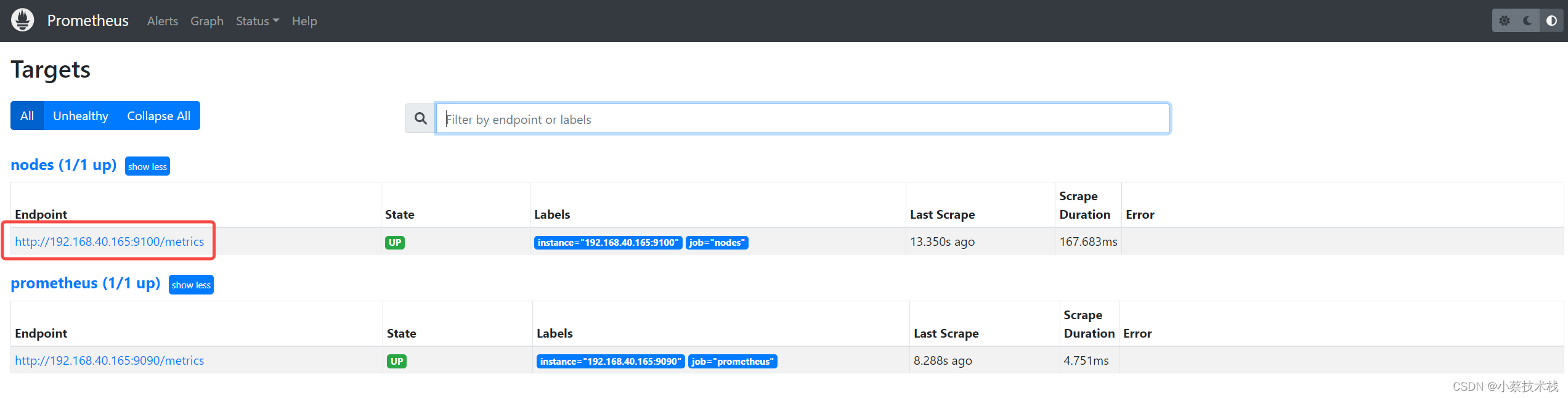
1.3 通过 http:// 服务器 IP:9090/metrics 可以查看到监控指标的数据

二、安装node_exporter
2.1 部署并配置node_exporter 采集监控数据并给到prometheus
#解压配置文件
[root@node4 ~]# tar -zxvf node_exporter-1.5.0.linux-amd64_\(1\).tar.gz
[root@node4 ~]# mv node_exporter-1.5.0.linux-amd64 /usr/local/node_exporter
#第一种配置系统启动文件,设置systemctl start prometheus 方式启动
[root@node4 ~]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
[Unit]
Description=node_exporter
Documentation=https://prometheus.io/
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/node_exporter/node_exporter \
--collector.ntp \
--collector.mountstats \
--collector.systemd \
--collector.tcpstat
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
#第二种启动方式
cd /usr/local/node_exporter/
./node_exporter
#浏览器输入 http://192.168.40.165:9100/metrics 并访问

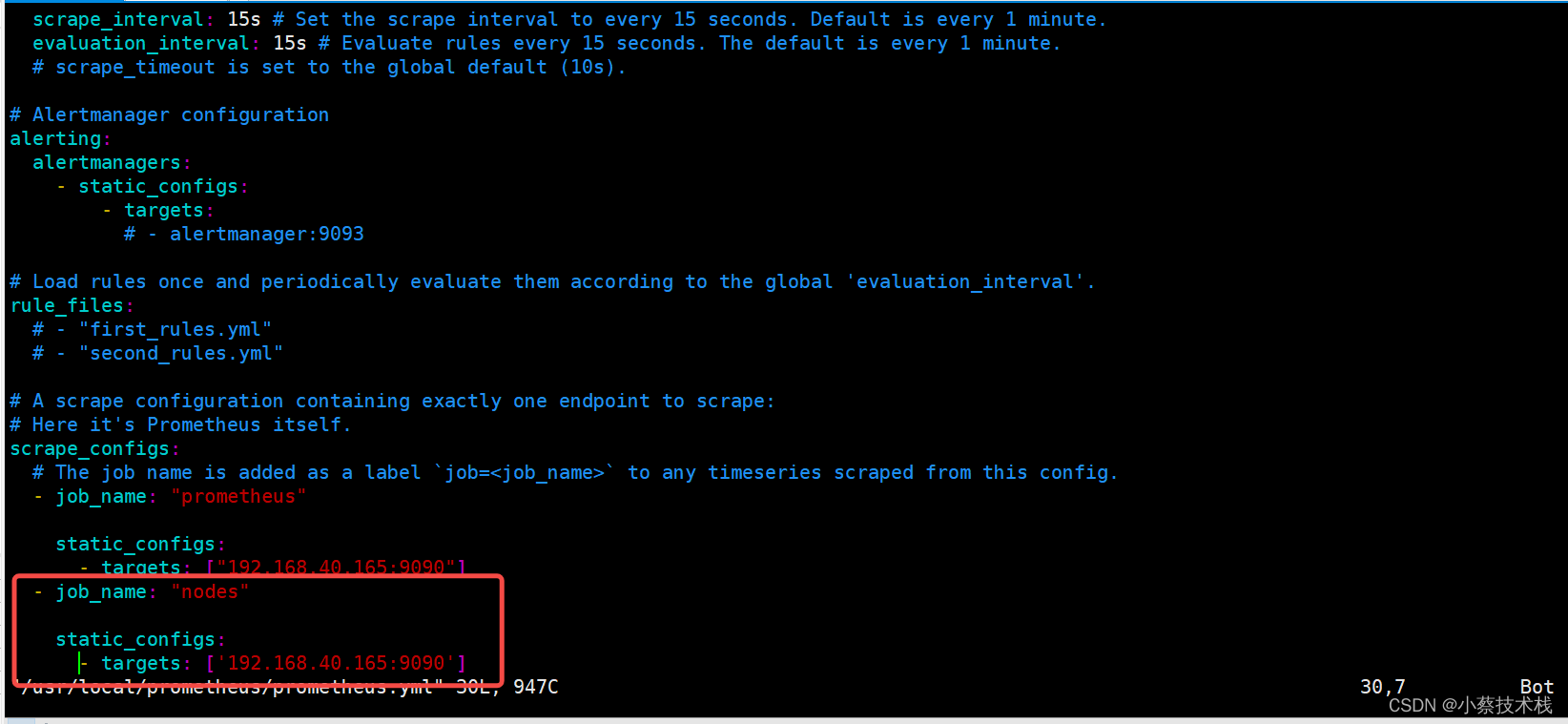
2.2 在prometheus服务配置prometheus.yml文件 添加target用于拉取主机数据
#添加以下节点
[root@node4 ~]# vim /usr/local/prometheus/prometheus.yml
- job_name: "nodes"
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.40.165:9090']
三、Grafana仪表板展示监控信息
3.1 部署Grafana
#下载并直接安装 Grafana
[root@node4 ~]# sudo yum install -y https://dl.grafana.com/enterprise/release/grafana-enterprise-9.4.7-1.x86_64.rpm
#配置文件存放位置,因为是用yum 安装的所以在/etc/目录下面
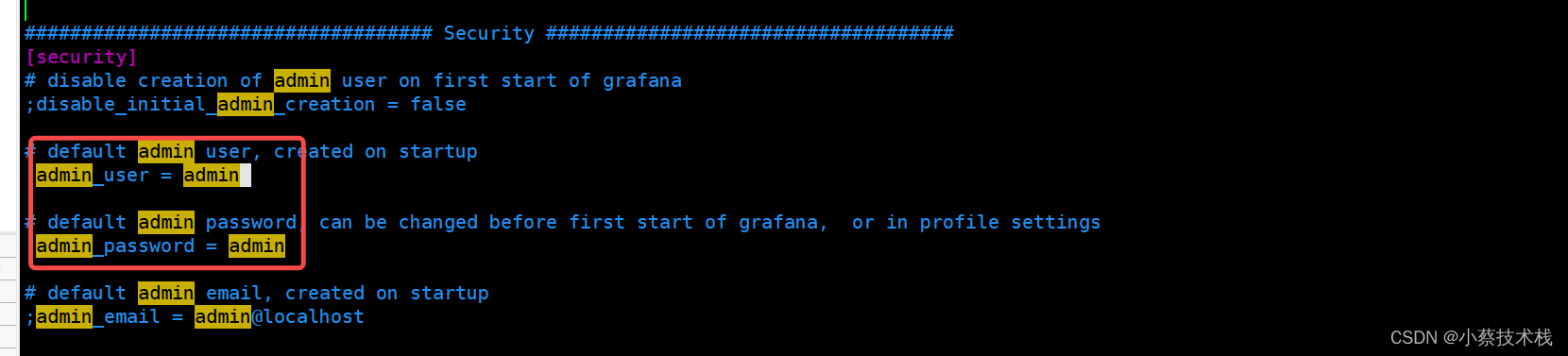
[root@node4 ~]# cat /etc/grafana/grafana.ini
#默认用户名和密码为admin, 浏览器访问 IP:3000
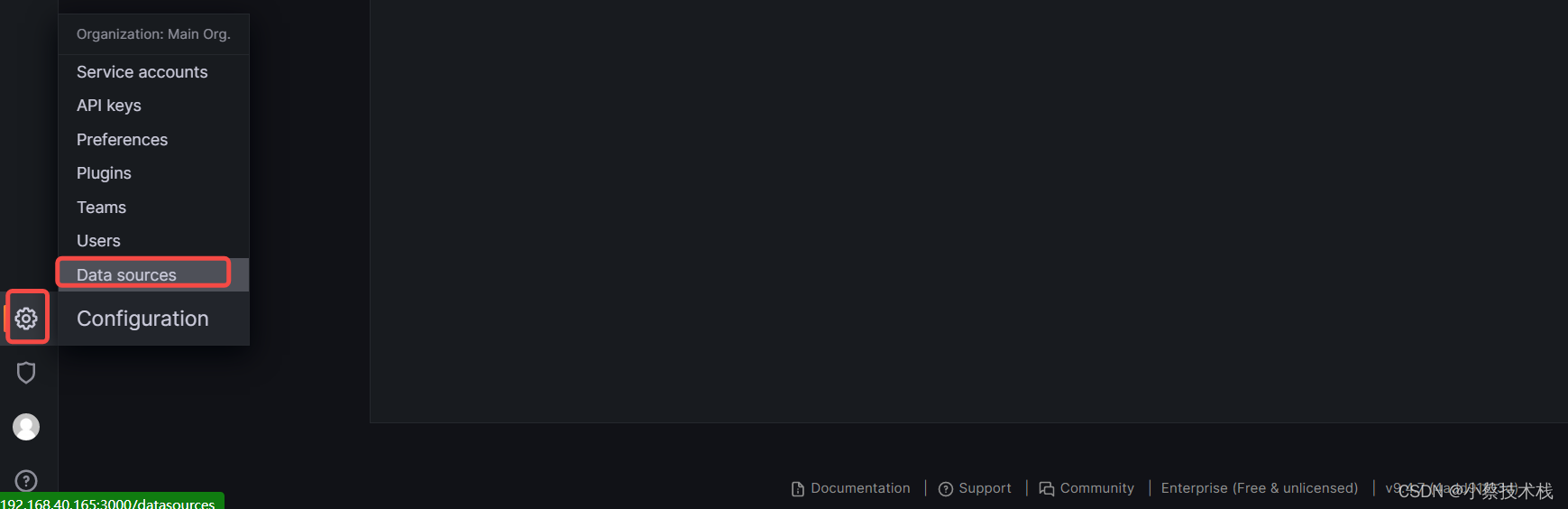
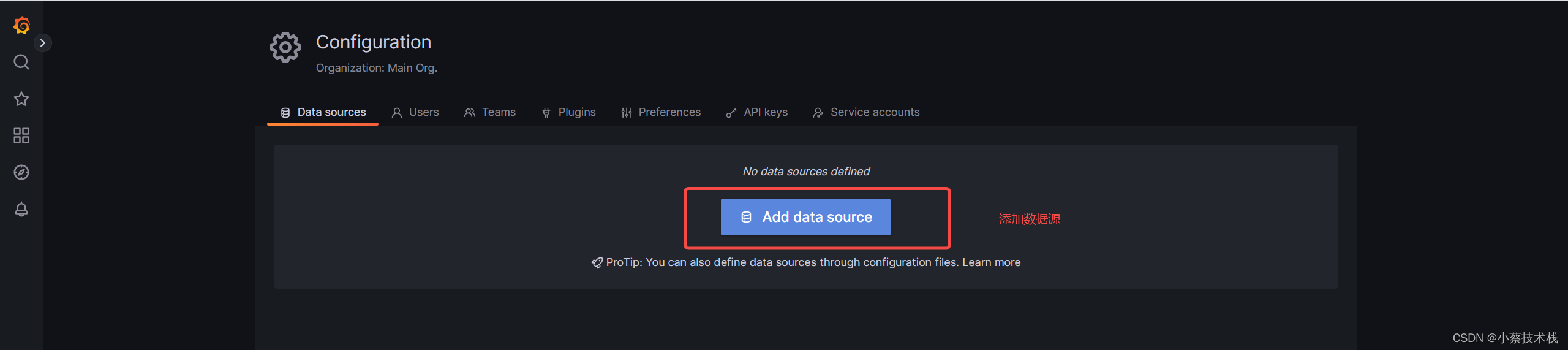
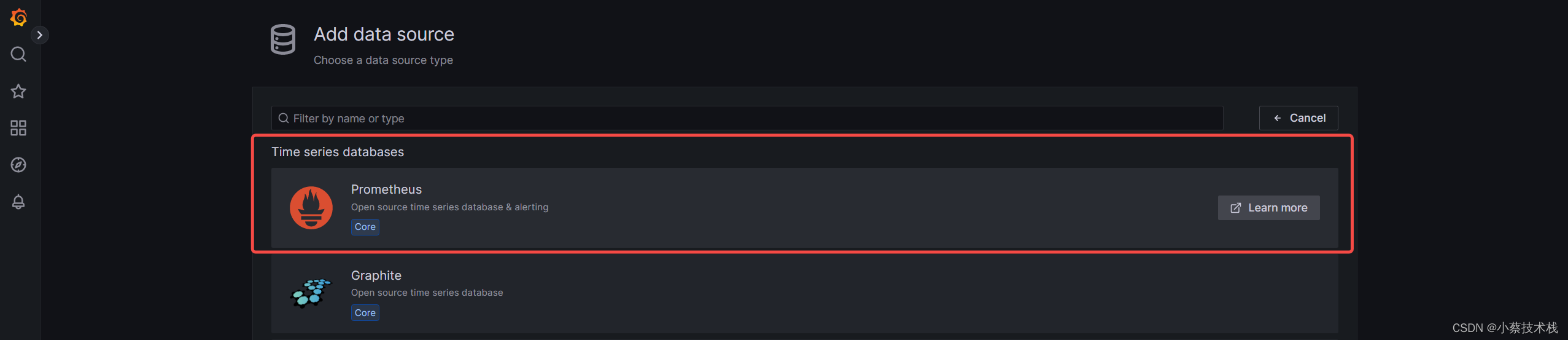
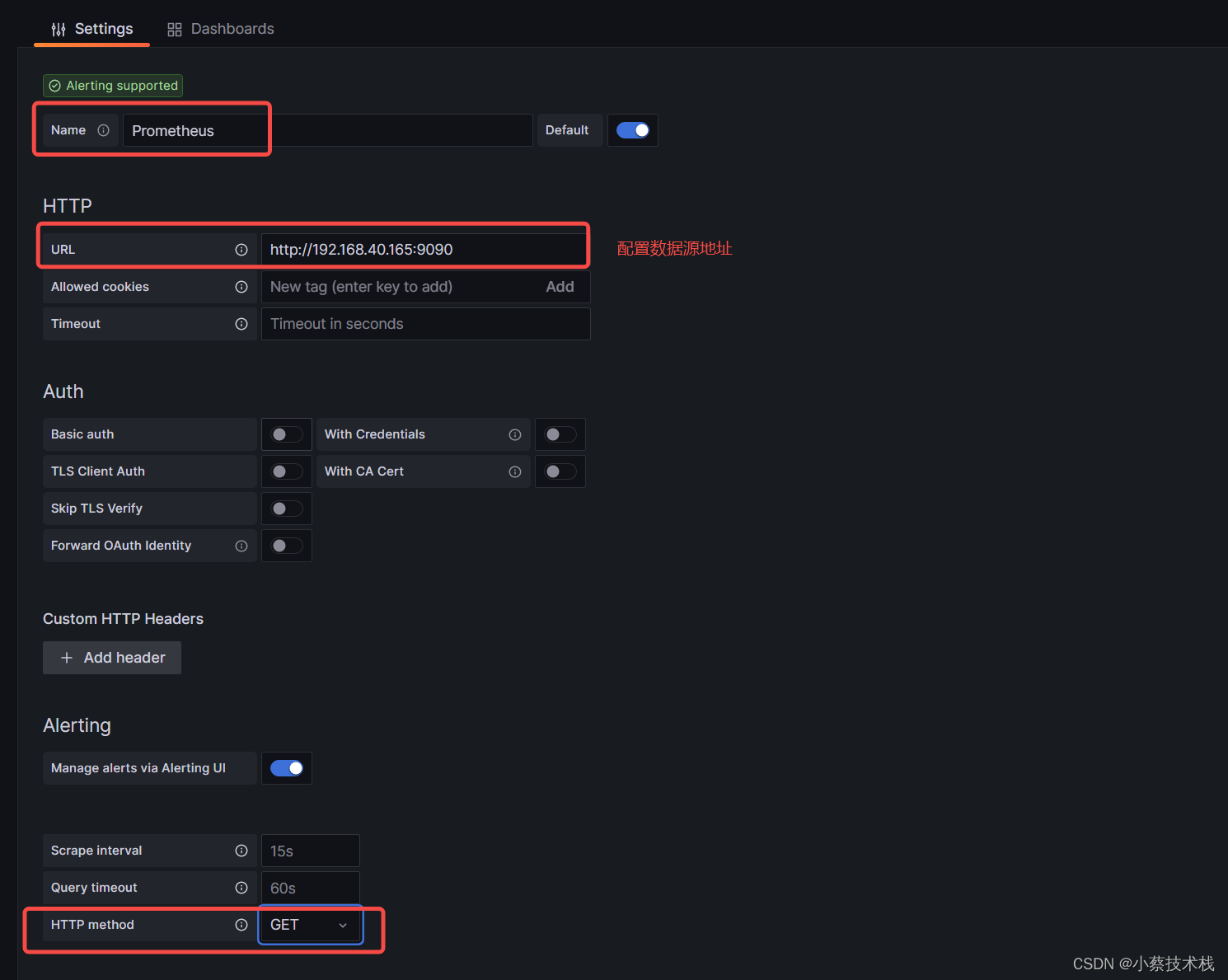
3.2 创建数据源,关联prometheus端,下面我们把 Prometheus 服务器收集的数据做为一个数据源添加到 grafana,让 grafana 可以得到 Prometheus 的数据。
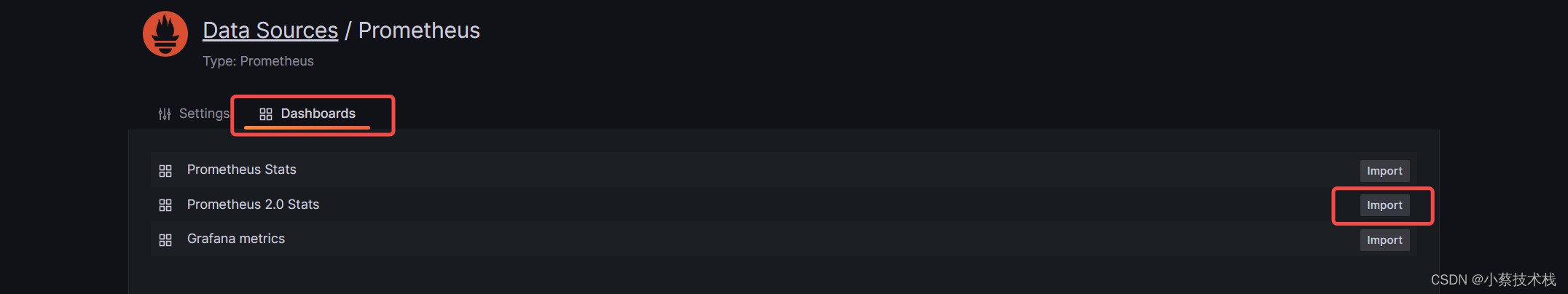
3.3 这里我们 Import 一个模板查看下效果,Grafana 自带多种模板供大家选择
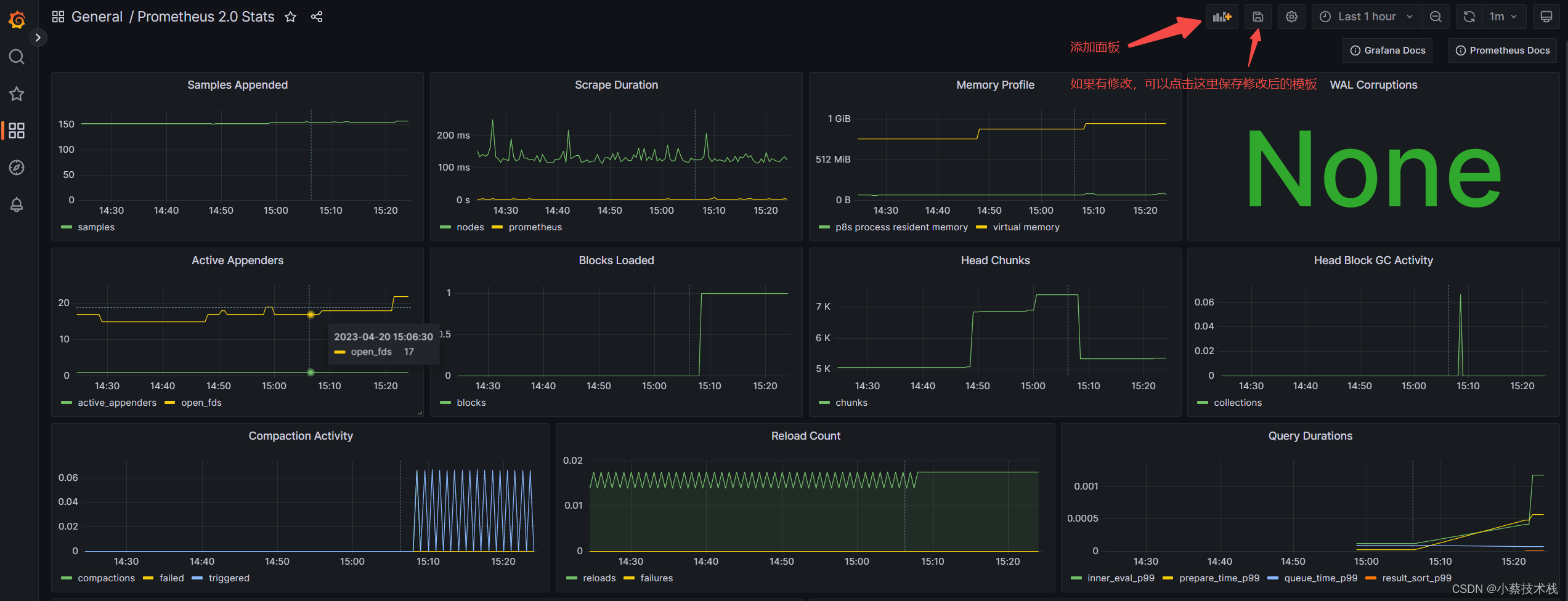
可以扩展配置 通过注册consul 用于服务发现接入到监控中
四、夜莺用于发送告警信息
4.1 安装 mariadb 数据库
[root@node4 ~]# yum -y install mariadb*
[root@node4 ~]# systemctl start mariadb && systemctl enable mariadb
#设置用户名和密码
[root@node4 ~]# mysql -e "SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('1234');"
4.2 安装 Redis 数据库
#安装阿里云镜像源
[root@node4 ~]# mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
[root@node4 ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
#清理缓存
[root@node4 ~]# yum clean all && yum makecache
[root@node4 ~]# yum install epel-release
#安装Redis
[root@node4 ~]# yum install -y redis
4.3 安装夜莺
[root@node4 ~]# mkdir -p /opt/n9e && cd /opt/n9e
# 去 https://github.com/didi/nightingale/releases 找最新版本的包,文档里的包地址可能已经不是最新的了
[root@node4 ~]# wget https://github.com/ccfos/nightingale/releases/n9e-v6.0.0-ga.4.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
#解压缩包
[root@node4 ~]# [root@node4 ~]# tar -zxvf n9e-v6.0.0-ga.4.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
#导入数据表
[root@node4 ~]# mysql -uroot -p1234 < docker/initsql/a-n9e.sql
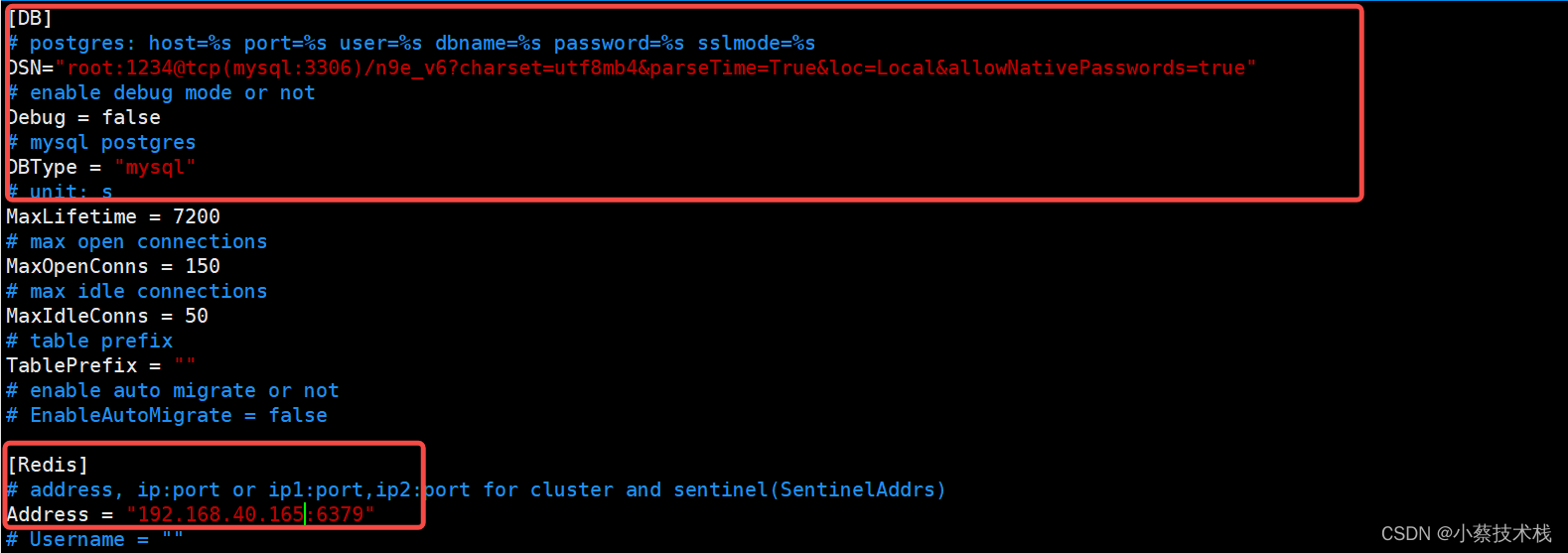
#修改 N9e 的配置文件,在当前目录 文件中,修改url 为prometheus的地址 (版本不一样配置文件路径也不一样)
[root@node4 n9eetc]# vim etc/config.toml
[[Pushgw.Writers]]
Url = "http://127.0.0.1:9090/api/v1/write"
如果启动成功,server 默认会监听在 19000 端口,webapi 会监听在 18000 端口,且日志没有报错。上面使用 nohup 简单演示,生产环境建议用 systemd 托管,相关 service 文件可以在 etc/service 目录下,配置文件etc/server.conf和etc/webapi.conf中都含有 mysql 的连接地址配置,检查一下用户名和密码,prometheus 如果使用上面的脚本安装,默认会监听本机 9090 端口,server.conf 和webapi.conf 中的 prometheus 相关地址都不用修改就是对的,如果使用贵司之前已有的 Prometheus,就要检查这俩配置文件中的时序库的配置了,把 127.0.0.1:9090 改成你的 Prometheus。

#启动服务
nohup ./n9e server &> server.log &
nohup ./n9e webapi &> webapi.log &
4.4 访问夜莺WebUI IP:17000 默认密码 root/root.2020

4.5 安装 Categraf 是一个监控采集 Agent,会将采集到的信息推送到 TSDB。
#下载
[root@node4 ~]# wget https://download.flashcat.cloud/categraf-v0.2.38-linux-amd64.tar.gz
#解压
[root@node4 ~]# tar -zxvf categraf-v0.2.38-linux-amd64.tar.gz
#转移到opt下面
[root@node4 ~]# mv categraf-v0.2.38-linux-amd64 /opt/categraf && cd /opt/categraf
#修改配置文件,在 conf/config.toml 中,修改的部分如下
[root@node4 categraf]# vim conf/config.toml
[[writers]] #改成夜莺地址IP:17000
url = "http://192.168.40.165:17000/prometheus/v1/write"
[heartbeat]
enable = true
#将文件放到系统命令里,然后启动categraf
[root@node4 categraf]# cp conf/categraf.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/
[root@node4 categraf]# systemctl start categraf.service
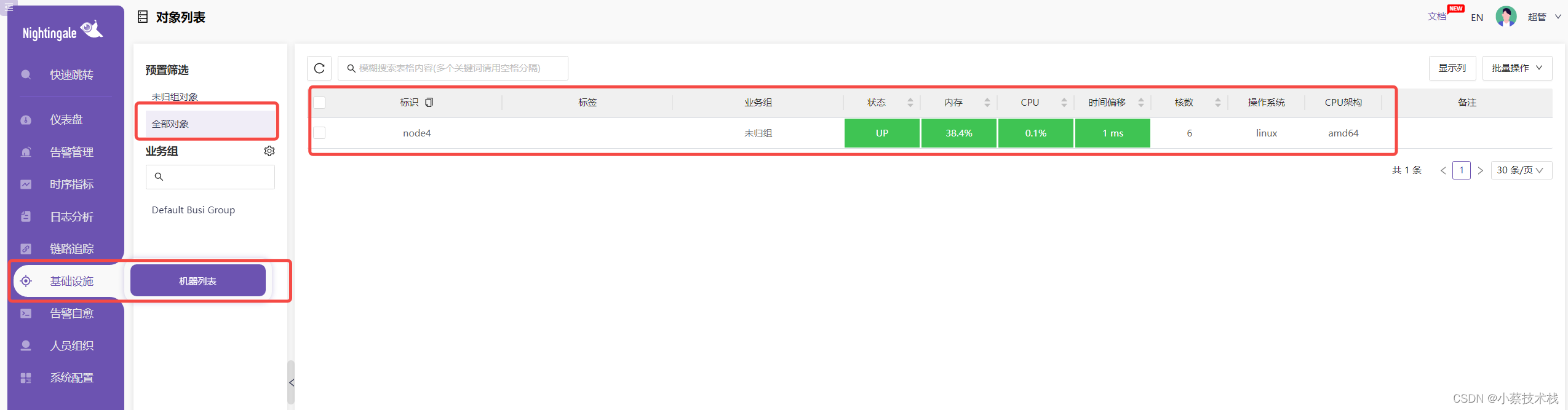
4.6 添加数据源 现在如果去查看时序数据指标,是查询不到的,因为没有添加数据源。
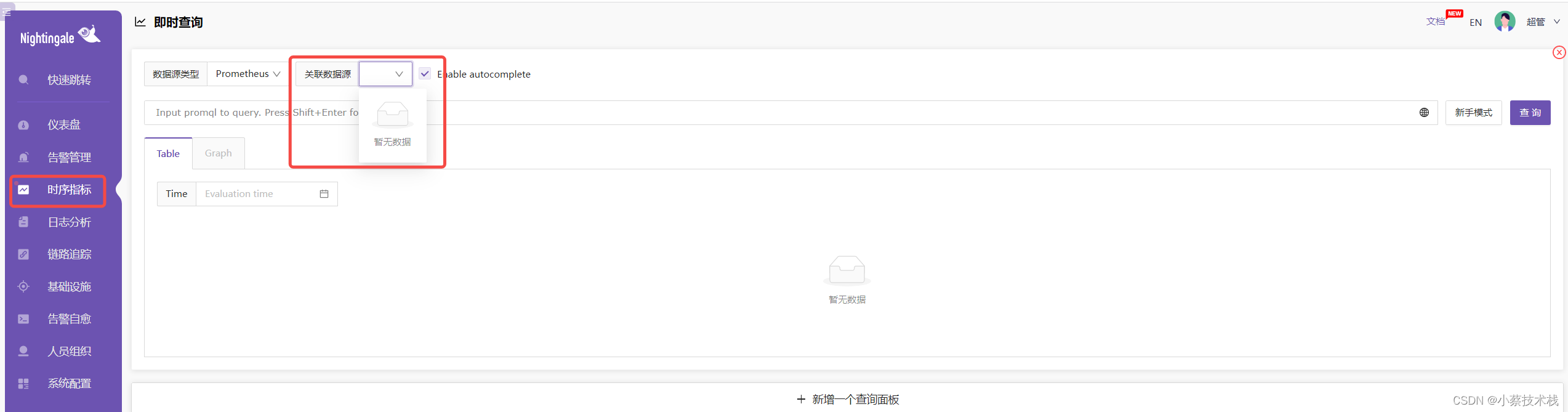
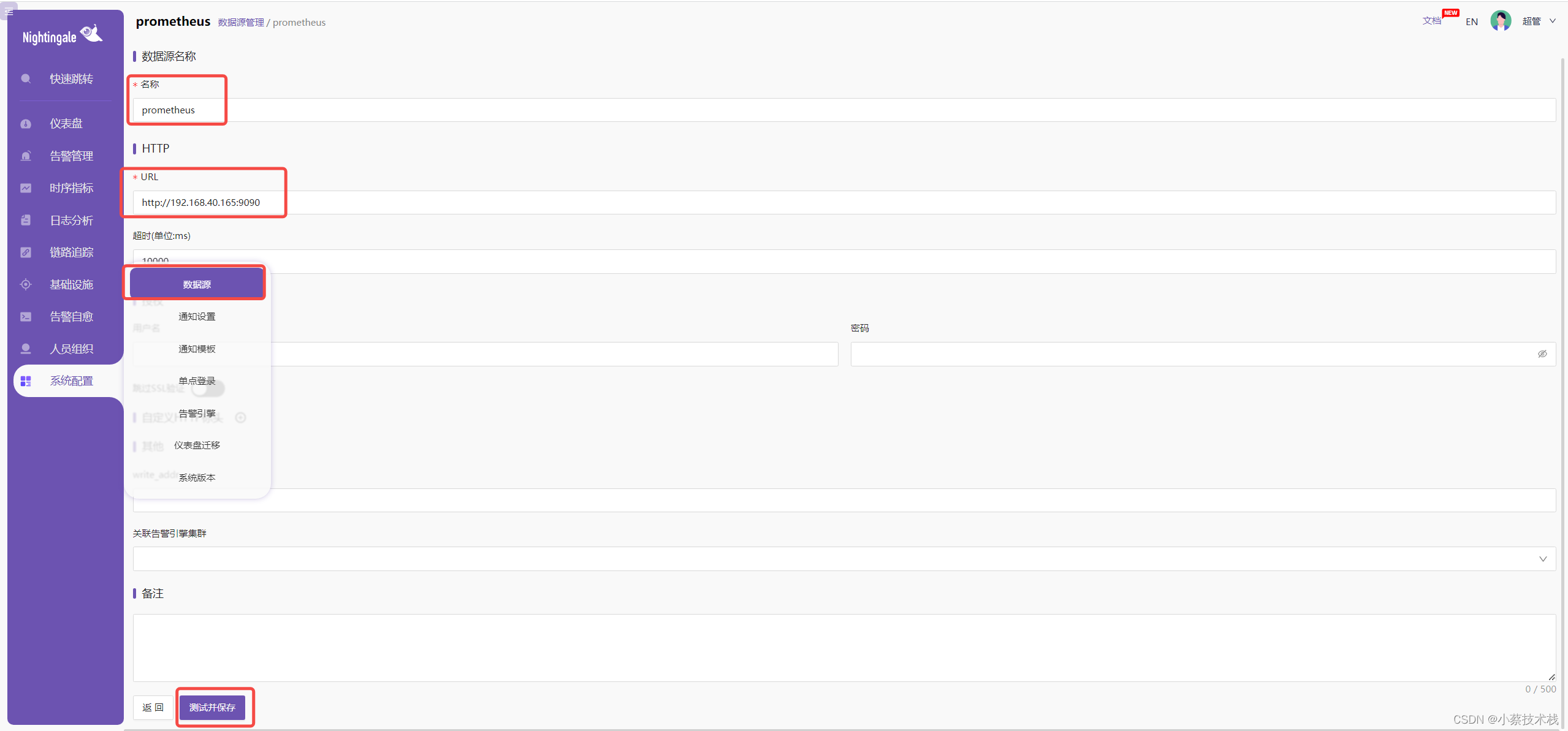
4.7在系统配置->数据源处添加数据源,如下:
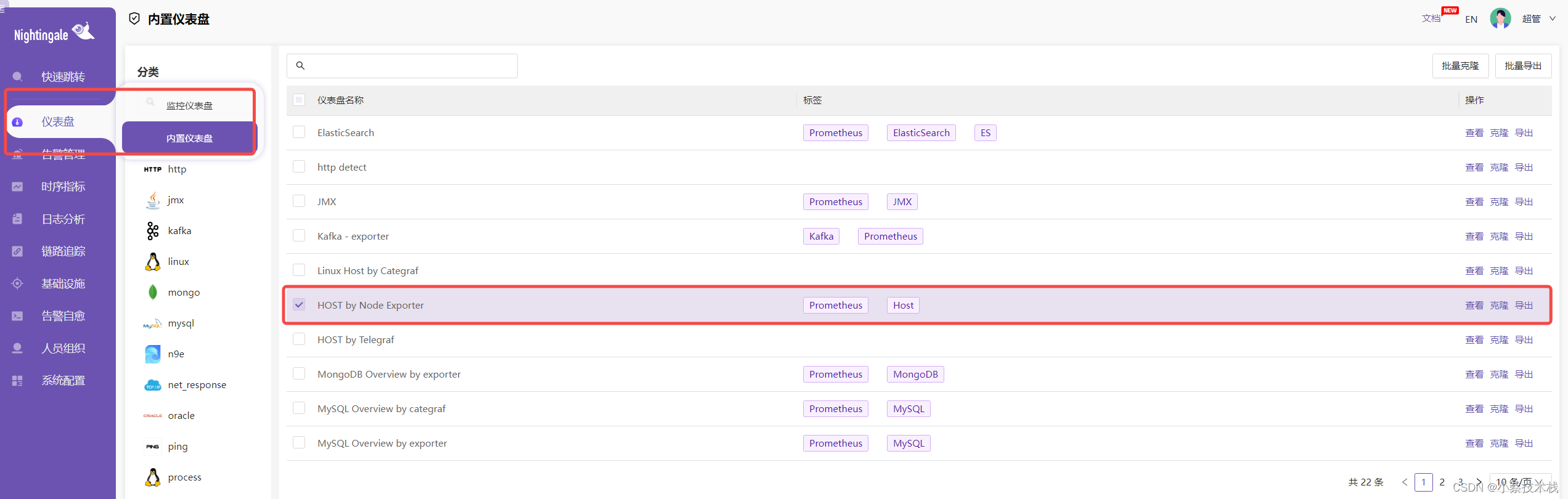
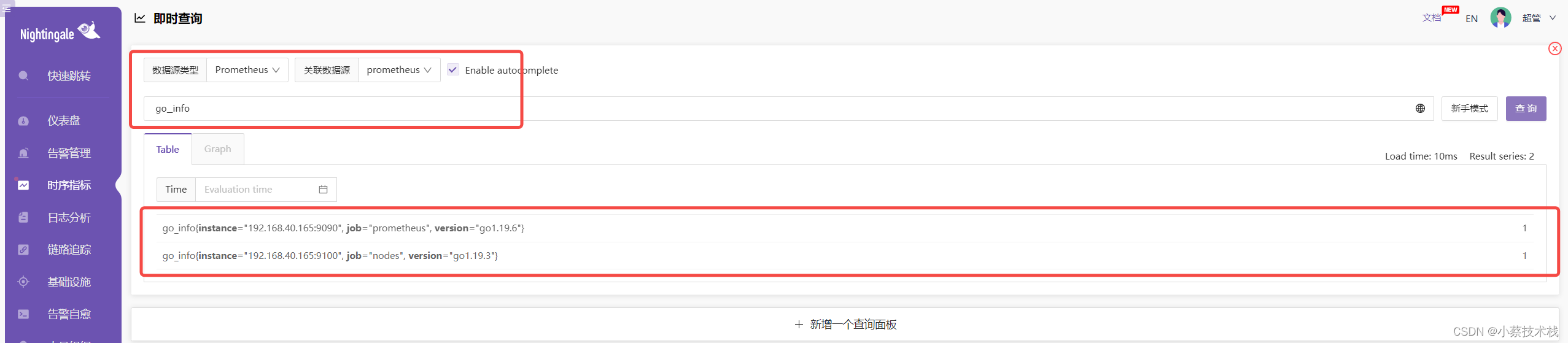
4.8 这里就可以选择数据源,然后就能看到对应的指标数据了
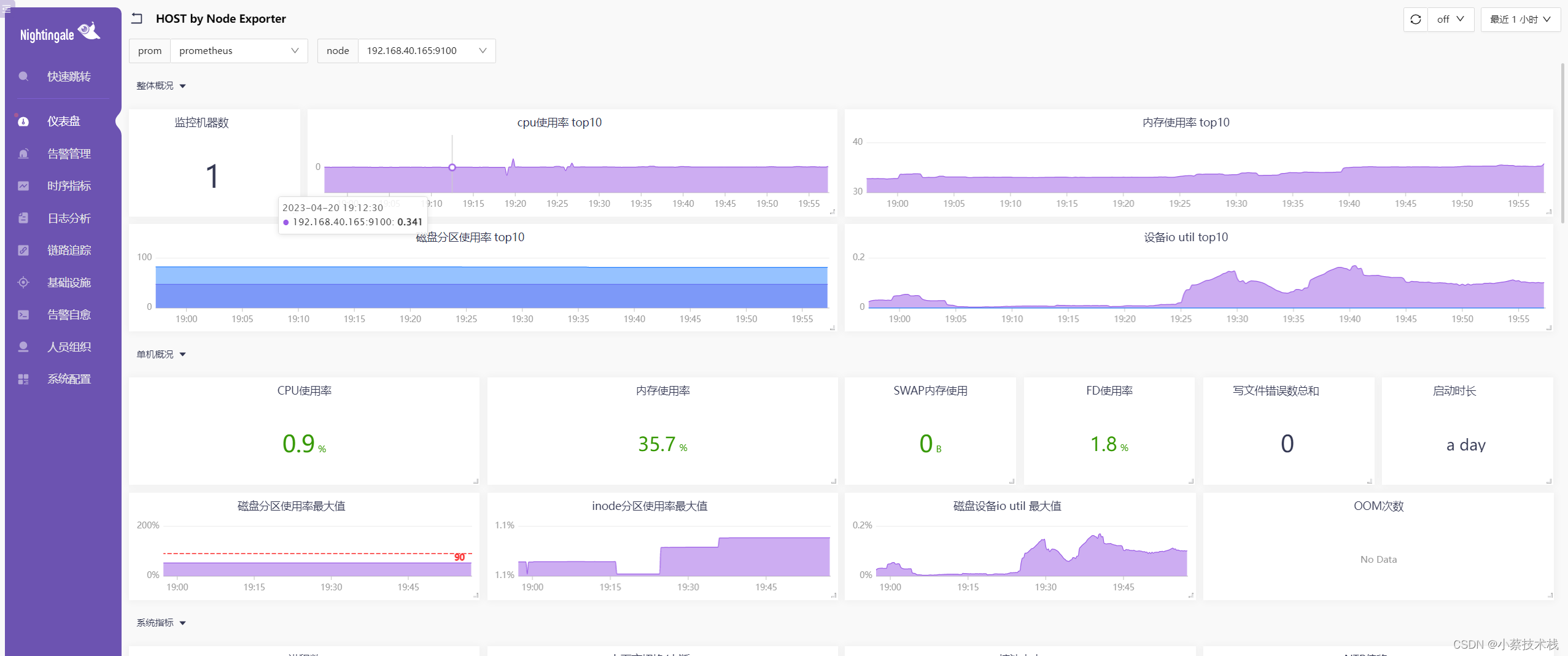
4.9 也可以通过内置的仪表盘查看主机的监控数据,如下: