CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。
CompletableFuture实现了Future和CompletionStage两个接口
- 通过Future同步等待执行结果
- CompletionStage,增强异步回调的功能。
将CompletableFuture当作简单的Future来使用
可以用一个无参数构造函数创建这个类的实例来表示Future的结果,将它分发给使用者,并在将来的某个时候使用complete方法完成它。使用者可以使用get方法阻塞当前线程,直到获取返回结果。
public Future<String> calculateAsync() throws InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
Executors.newCachedThreadPool().submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(500);
completableFuture.complete("Hello");
return null;
});
return completableFuture;
}
CompletableFuture构建方法
构建一个CompletableFuture有以下四种办法
- supplyAsync(runnable) 异步执行一个任务,提供返回值
- supplyAsync(runnable,Executor executor) 提供返回值
- runAsync(runnable,Executor executor) -> 通过自定义线程池异步执行一个任务,没有返回值
- runAsync(runnable) -> 异步执行一个任务, 默认用ForkJoinPool.commonPool(), 没有返回值
注意在没有返回值的情形下,CompletableFuture也还是提供了get方法来阻塞获取执行结果,只是最后返回的结果为null
CompletionStage
CompletionStage定义了很多方法,大致可以分为以下几类
纯消费类型的方法
纯消费类型的方法,指依赖上一个异步任务的结果作为当前函数的参数进行下一步计算,它的特点是不返回新的计算值,这类的方法都包含 Accept 这个关键字
在CompletionStage中包含9个Accept关键字的方法,这9个方法又可以分为三类:
- 依赖单个CompletionStage任务完成,
- 依赖两个CompletionStage任务都完成
- 依赖两个CompletionStage中的任何一个完成
//当前线程同步执行
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
//使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool线程池执行action
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
//使用自定义线程池执行action
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T>
action,Executor executor);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U>
other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<?
extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<?
extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action,Executor executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T>
other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T>
other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T>
other,Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
有返回值类型的方法
有返回值类型的方法,就是用上一个异步任务的执行结果进行下一步计算,并且会产生一个新的有返回值的CompletionStage对象。
在CompletionStage中,定义了9个带有返回结果的方法,也可以根据依赖几个CompletionStage任务的完成来分成三类
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U>
fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U>
fn,Executor executor);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U>
other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends
U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends
U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T>
other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends
T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends
T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor);
不消费也不返回的方法
该方法的执行,带run关键字,下一步的执行不依赖上一步的执行结果,也不返回结果,只是有执行的先后顺序
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor
executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable
action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?>
other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?>
other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?>
other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?>
other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?>
other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
多任务组合
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends
CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends
CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends
CompletionStage<U>> fn,Executor executor)
并行执行
- allOf():当所有给定的 CompletableFuture 完成时,返回一个新的 CompletableFuture
- anyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletablFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
结果/异常处理
-
whenComplete
whenComplete表示当任务执行完成后,会触发的方法,它的特点是,不论前置的
CompletionStage任务是正常执行结束还是出现异常,都能够触发特定的 action 方法 -
handle
handle表示前置任务执行完成后,不管前置任务执行状态是正常还是异常,都会执行handle中的
fn 函数,它和whenComplete的作用几乎一致,不同点在于,handle是一个有返回值类型的方
法。 -
exceptionally
exceptionally接受一个 fn 函数,当上一个CompletionStage出现异常时,会把该异常作为参数传
递到 fn 函数
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()-> {
// int i=1/0;
System.out.println("执行某些操作");
}).whenComplete((r, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
System.out.println("执行过程出现异常...");
} else {
System.out.println("任务执行完成");
}
});
}
thenCompose和thenApply的异同
thenApply和thenCompose都是对一个CompletableFuture返回的结果进行后续操作,返回一个新的CompletableFuture。
对于thenApply,fn函数是一个对一个已完成的stage或者说CompletableFuture的返回值进行计算、操作;
对于thenCompose,fn函数是对另一个CompletableFuture进行计算、操作
CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100).thenApply(num -> num + " to String");
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100).thenCompose(num -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> num + " to String"));
System.out.println(f1.join()); // 100 to String
System.out.println(f2.join()); // 100 to String
上面thenApply和thenCompose都是将一个CompletableFuture<Integer>转换为CompletableFuture<String>。不同的是,thenApply中的传入函数的返回值是String,而thenCompose的传入函数的返回值是CompletableFuture<String>。就好像stream中学到的map和flatMap。回想我们做过的二维数组转一维数组,使用stream().flatMap映射时,我们是把流中的每个数据(数组)又展开为了流。
CompletableFuture原理介绍
以下述代码为例,简单了解下CompletableFuture的实现原理
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<Void> f = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Hello";
}).thenAccept(e -> {
System.out.println("执行结果为" + e);
});
f.get();
}
先看一下CompletableFuture里定义了哪些重要的变量
//CompletableFuture的结果值或者是一个异常的包装对象AltResult
volatile Object result;
// 依赖操作栈的栈顶
volatile Completion stack; // Top of Treiber stack of dependent actions
然后看下我的例子里调用的supplyAsync方法
supplyAsync
会将我们的Supplier参数封装成AsyncSupply对象,然后交给线程池执行,
AsyncSupply有两个参数,一个是源码里创建的CompletableFuture对象,一个是用户定义的Supplier参数
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
//asyncPool是一个全局的ForkJoinPool.commonPool线程池
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e,
Supplier<U> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//创建一个新的CompletableFuture并返回(1)
CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();
e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));
return d;
}
public void run() {
CompletableFuture<T> d; Supplier<T> f;
//如果dep和fn不为空
if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {
dep = null; fn = null;
//如果CompletableFuture的result为空(表示当前任务还没执行完),则等待直接完成后执行postComplete
if (d.result == null) {
try {
//通过get()方法获取返回结果并设置给result
d.completeValue(f.get());
} catch (Throwable ex) {
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
//在执行完自己的方法获取到返回值之后,会执行所有依赖此任务的其他任务,这些任务存储在一个无锁并发栈里
d.postComplete();
}
}
thenAccept
我们先来看下thenAccept的实现
private CompletableFuture<Void> uniAcceptStage(Executor e,
Consumer<? super T> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>();
//这里的this就是前面supplyAsync方法里创建的CompletableFuture
//如果为异步任务,则将任务压栈后直接返回,因为源任务结束后会触发异步线程执行对应逻辑
//如果为同步任务(e==null)会调用d.uniAccept方法 这个方法的逻辑:如果源任务完成,则直接调用f并返回true,否则进入下面的if代码块
if (e != null || !d.uniAccept(this, f, null)) {
//封装一个UniAccept对象,并压入到栈中
UniAccept<T> c = new UniAccept<T>(e, d, this, f);
push(c);
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
return d;
}
/** Pushes the given completion (if it exists) unless done. */
final void push(UniCompletion<?,?> c) {
if (c != null) {
while (result == null && !tryPushStack(c))
lazySetNext(c, null); // clear on failure
}
}
final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) {
CompletableFuture<Void> d; CompletableFuture<T> a;
if ((d = dep) == null ||
//如果是异步调用(mode>0),传入null。否则传入this
!d.uniAccept(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this))
return null;
dep = null; src = null; fn = null;
return d.postFire(a, mode);
}
final <S> boolean uniAccept(CompletableFuture<S> a,
Consumer<? super S> f, UniAccept<S> c) {
Object r; Throwable x;
//判断当前CompletableFuture是否已完成,如果没有完成则返回false
if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null)
return false;
tryComplete: if (result == null) {
//判断任务执行结果是否为异常类型
if (r instanceof AltResult) {
if ((x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null) {
completeThrowable(x, r);
break tryComplete;
}
r = null;
}
try {
//判断当前任务是否可以执行(d.uniAccept(this, f, null)传入的c为null)
if (c != null && !c.claim())
return false;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") S s = (S) r;
//获取CompletableFuture执行的任务结果并执行consumer
f.accept(s);
completeNull();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
return true;
}
postComplete
再回过头看下在一个任务执行完成后调用的postComplete 方法
/**
* Pops and tries to trigger all reachable dependents. Call only
* when known to be done.
*/
final void postComplete() {
//无锁并发栈,(Completion有一个next指针), 保存的是依赖当前的CompletableFuture的一串任务
CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;
//判断stack是否为空
while ((h = f.stack) != null ||
(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;
//非空则通过CAS出栈
if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) {
//如果f不是this,将刚出栈的h压入this的栈顶
if (f != this) {
//通过CAS入栈
pushStack(h);
continue;
}
// 如果是当前CompletableFuture, 解除头节点与栈的联系, help GC
h.next = null;
}
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;
}
}
}
final void pushStack(Completion c) {
do {} while (!tryPushStack(c));
}
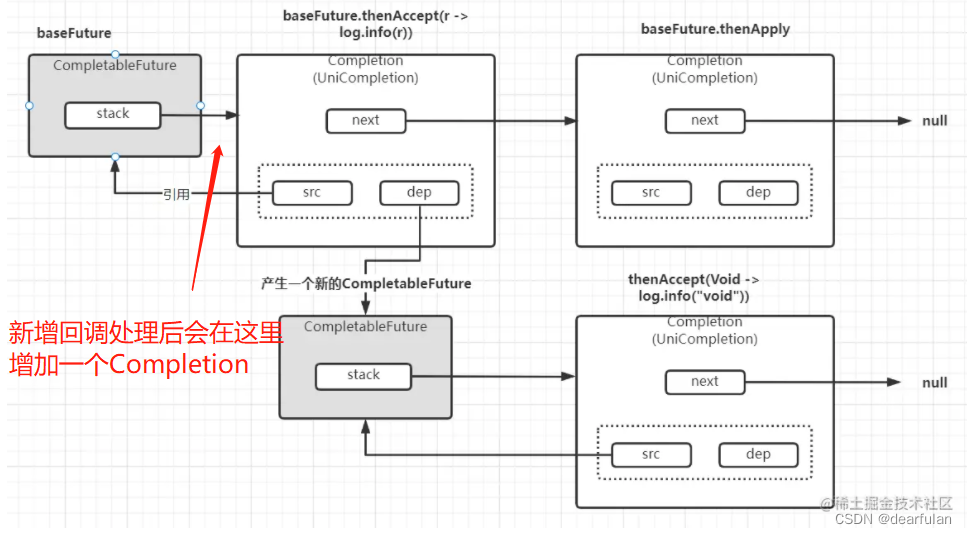
CompletableFuture实现链式调用的核心原理就是通过一个无锁并发栈(Treiber Stack)来存储任务。
依赖任务执行的时候先判断源任务是否完成,如果完成,直接在对应线程执行以来任务(如果是同步,则在当前线程处理,否则在异步线程处理)
如果任务没有完成,直接返回,因为等任务完成之后会通过postComplete去触发调用依赖任务。
借用下在别人的博客看到的原理图:
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> baseFuture = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("Base Future");
log.info(baseFuture.thenApply((r) -> r + " Then Apply").join());
baseFuture.thenAccept((r) -> log.info(r)).thenAccept((Void) -> log.info("Void"));
}
实战例子: 烧水泡茶
CompletableFuture使用详解
全网最详细CompletableFuture使用教程





![[ARM+Linux] 基于wiringPi库的串口通信](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8a4954b6d8eb4f6d870a94f1bdfd9796.png)