1.红黑树中的迭代器
operator++是关键 迭代需要走中序 如何走中序?
_node从左子树的最左结点开始遍历走中序
分两类情况:
-
如果右树不为空 那么中序的下一个就是右子树的最左结点
-
如果右树为空 那么表示_node所在的子树已经完成 在一个结点的祖先去找
沿着路径往上孩子是它的左的那个祖先
//迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
__TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
//++如何走?
Self& operator++()
{
//STL给了头结点 左孩子指向最左结点 右孩子指向最右结点
//_node为左子树的最左结点 从这开始
//1.如果右不为空 中序的下一个就是右子树的最左结点
//2.如果右为空 表示_node所在的子树已经放完成 在一个结点的祖先去找
//沿着路径往上孩子是它的左的那个祖先
//右树不为空
if (_node->_right)
{
//中序的下一个就是右子树的最左结点
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
//右树为空
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//右孩子就停下来 去找最左结点
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
//与++相反
//右根左
//1.如果左不为空 就访问左树的最右结点
//2.如果左为空 找为右孩子的那个祖先
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
整颗红黑树
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Colour
{
BLACK,
RED,
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _col(RED)
{}
};
//迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
__TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
//++如何走?
Self& operator++()
{
//STL给了头结点 左孩子指向最左结点 右孩子指向最右结点
//_node为左子树的最左结点 从这开始
//1.如果右不为空 中序的下一个就是右子树的最左结点
//2.如果右为空 表示_node所在的子树已经放完成 在一个结点的祖先去找
//沿着路径往上孩子是它的左的那个祖先
//右树不为空
if (_node->_right)
{
//中序的下一个就是右子树的最左结点
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
//右树为空
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//右孩子就停下来 去找最左结点
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
//与++相反
//右根左
//1.如果左不为空 就访问左树的最右结点
//2.如果左为空 找为右孩子的那个祖先
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class KOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
//插入
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点必须是黑色
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true); //插入成功
}
KOfT koft;
//二叉搜索树
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (koft(data) < koft(cur->_data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (koft(data) > koft(cur->_data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
//将结点插入
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
if (koft(cur->_data) < koft(parent->_data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
//------------------------
//新增结点红的 or 黑的
//破坏b还是c 破坏b较轻
//1.只影响一条路径
//2.还不一定破坏规则
//所以选红的
cur->_col = RED;
//-------------------------------
//调色
//第一种情况:cur为红 p为红 g为黑 只要u存在且为红-> p和u变黑 g变红 继续往上处理 如果到根 根要变回黑
//ps:需要注意的是 这里只关注颜色 而p g u几个结点在左边或者右边是一样的
//最后就是为了防止连续的红和保持每条支路黑的结点数量一样
//-------------------------------------
//第二种情况:cur为红 p为红 g为黑 u不存在/u为黑 直线
//1.如果u不存在 那么cur就是新增结点
//旋转+变色
//旋转:左单旋 or 右单旋
//变色:g变红 p变黑
//---------------------------------------
//2.如果u存在且为黑 那么cur一定不是新增
//你要保证每条路黑色结点数量一样->cur一定是黑的
//cur变红的话就是第一种情况
//---------------------------------------
//第三种情况:cur为红 p为红 g为黑 u不存在/u为黑 折线
//旋转:左右双旋 or 右左双旋
//变色:g变红 cur变黑
//-------------------------------------
//parent为红
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) //情况1:uncle存在且为红
{
//颜色调整
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续往上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //情况2+情况3:uncle不存在 + uncle存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else //cur == parent->_right
{
RotateLR(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
break; //子树旋转后,该子树的根变成了黑色,无需继续往上进行处理
}
}
else //parent是grandfather的右孩子
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) //情况1:uncle存在且为红
{
//颜色调整
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续往上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //情况2+情况3:uncle不存在 + uncle存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateRL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else //cur == parent->_right
{
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
break; //子树旋转后,该子树的根变成了黑色,无需继续往上进行处理
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK; //根结点的颜色为黑色(可能被情况一变成了红色,需要变回黑色)
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
//左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
//需要处理subR的parent left
//需要处理subRL的parent
//需要处理parent的right parent
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == parentParent->_left)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
//右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == parentParent->_left)
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
//左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
}
//右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
}
//中序遍历
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_Inorder(root->_left);
//cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
//判断是否为红黑树
bool ISRBTree()
{
if (_root == nullptr) //空树是红黑树
{
return true;
}
if (_root->_col == RED)
{
cout << "error:根结点为红色" << endl;
return false;
}
//找最左路径作为黑色结点数目的参考值
Node* cur = _root;
int BlackCount = 0;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
BlackCount++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
int count = 0;
return _ISRBTree(_root, count, BlackCount);
}
bool _ISRBTree(Node* root, int count, int BlackCount)
{
if (root == nullptr) //该路径已经走完了
{
if (count != BlackCount)
{
cout << "error:黑色结点的数目不相等" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "error:存在连续的红色结点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
count++;
}
return _ISRBTree(root->_left, count, BlackCount) && _ISRBTree(root->_right, count, BlackCount);
}
//查找函数
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
KOfT koft;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (koft(data) < koft(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (koft(data) > koft(cur->_data))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return iterator(cur);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
2.MySet和MyMap
如何使用一颗红黑树实现map和set
利用模板 KOfT 传K的时候返回K 传pair<K,V>的时候也返回K
这样就可以同时满足set和map
MySet
#pragma once
#include "RBTree1.h"
namespace szh
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& k)
{
return k;
}
};
public:
//编译器会找不到 没有实例化 加上typename 告诉编译器这里是类型名称
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& k)
{
return _t.Insert(k);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
s.Insert(3);
s.Insert(4);
s.Insert(1);
s.Insert(2);
s.Insert(5);
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto k: s)
{
cout << k << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
MyMap
#pragma once
#include "RBTree1.h"
namespace szh
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//编译器会找不到 没有实例化 加上typename 告诉编译器这里是类型名称
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
//为了实现operator[] 多加一个迭代器返回 返回value
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));//缺省
return ret.first->second;
//ret.first拿到迭代器 迭代器->second对应value
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
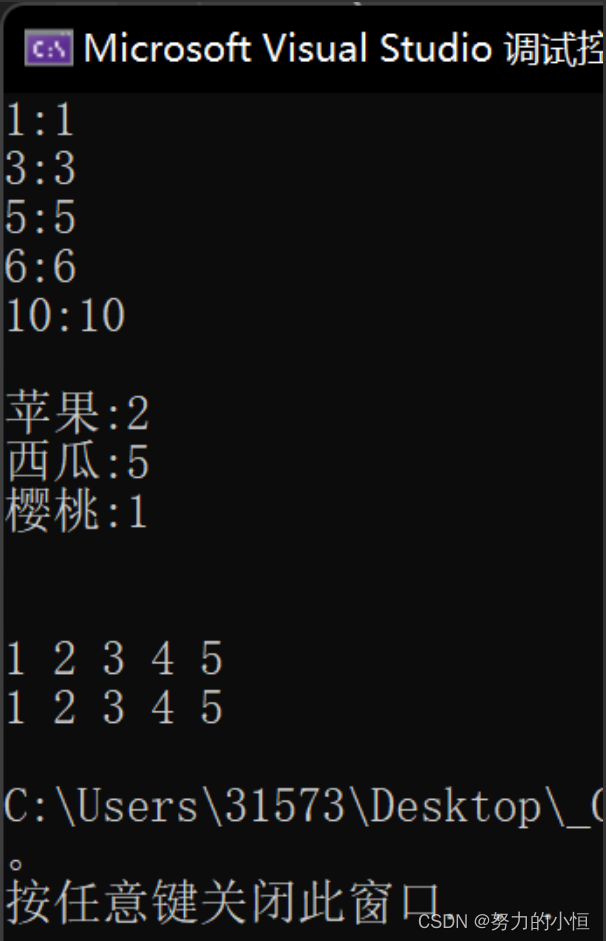
void test_map()
{
map<int, int> m;
m.Insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.Insert(make_pair(3, 3));
m.Insert(make_pair(10, 10));
m.Insert(make_pair(5, 5));
m.Insert(make_pair(6, 6));
map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//支持范围for
//for (auto kv : m)
//{
// cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
//}
//cout << endl;
//统计次数
string strs[] = { "西瓜","樱桃","西瓜","苹果","西瓜","西瓜","西瓜","苹果" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : strs)
{
countMap[str]++;
//第一次出现会先插入并同时返回Key所在的Value 然后value++
//第二次只返回Key所在的Value 然后value++
}
for (auto kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
范围for以及计数都可以使用
3.测试
#include "MyMap.h"
#include "MySet.h"
int main()
{
szh::test_map();
cout << endl;
szh::test_set();
return 0;
}
【C++】17.map和set的模拟实现 完