尽量理论来理解代码。
完整代码或者\native\examples里面
说到前面的话
两段官方的话


大致意思就是,这个库有门槛,需要先学会同态的概念,提供的例子必须要看要理解。必看的例子如下,
代码解析
基础加密
参数设置
三个核心参数
首先要知道这里的BFV代码是基于RLWE的,也就是涉及到多项式运算,同时它只能加密整数。
回忆一下RLWE的实例
(
b
=
a
s
+
e
,
a
)
(b=as+e,a)
(b=as+e,a)中的部分是取自于多项式环
R
q
=
Z
q
[
x
]
/
f
(
x
)
R_q = \mathbb{Z}_q[x]/f(x)
Rq=Zq[x]/f(x)(其中
f
(
x
)
=
x
N
+
1
f(x)=x^N+1
f(x)=xN+1),明文空间是
R
t
R_t
Rt。
那么由此将得到三个十分重要的加密参数,即多项式阶数模
N
N
N、多项式系数模数
q
q
q、明文模数
t
t
t
第三个参数仅有bfv需要(BGV的明文空间是
R
2
R_2
R2,CKKS是浮点数和复数)。
- poly_modulus_degree (degree of polynomial modulus);
- coeff_modulus ([ciphertext] coefficient modulus);
- plain_modulus (plaintext modulus; only for the BFV scheme);
同态方案设置
设置当前使用的方案是bfv
EncryptionParameters parms(scheme_type::bfv);
多项式阶数模设置
多项式的阶数模必须是2的正整数次幂,设置得越大,那么密文将越大,相应的计算就会更慢,但是能使用更复杂的计算。另外,官方推荐的至少大于等于1024。这个例子用的4096。
size_t poly_modulus_degree = 4096;
parms.set_poly_modulus_degree(poly_modulus_degree);
多项式系数模设置
接下来设置多项式的系数模,这是多个大素数相乘得到的大整数,每个素数最大为60bits(计算机目前64位,没法直接表示这个大整数,所以用多个相乘),每个素数是由一个类的实例表示的向量,系数的最大位长为它的素数因子位长之和。系数模越大,那么计算能力更强,但它的位长受限于多项式的阶数模,如下
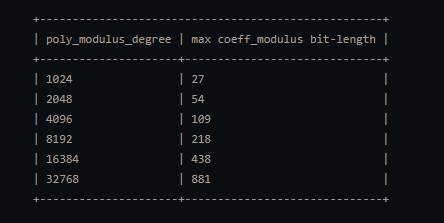
上面的数字可通过查看native/src/seal/util/hestdparms.h 或者调用函数
- CoeffModulus::MaxBitCount(poly_modulus_degree);
也可以直接调用默认的
- CoeffModulus::BFVDefault(poly_modulus_degree);
所以设置多项式系数模就可以像下面一样设置
parms.set_coeff_modulus(CoeffModulus::BFVDefault(poly_modulus_degree));
明文模数设置
明文模数在bfv中不受限制,可以是任意的正整数,比如这里就取2的幂次可以使得运算简化。
明文的模数决定明文数据类型的size和乘法中的噪声预算的消耗,回想一下bfv中的密文是使用了类似模交换操作的,也就是乘以了
t
/
q
t/q
t/q来进行噪声缩放,从而达到控制噪声的目的,所以容易知道明文模数
t
t
t越大,将导致每一次乘法的噪声越大,也就是噪声预算消耗得越大,所以需要它尽可能的小来获取更好的性能。
这里估算的噪声预算大致是log2(coeff_modulus/plain_modulus) (bits)(
log
q
/
t
\log q/t
logq/t)
每一次乘法消耗的噪声预算大致是log2(plain_modulus) + (other terms)()
parms.set_plain_modulus(1024);
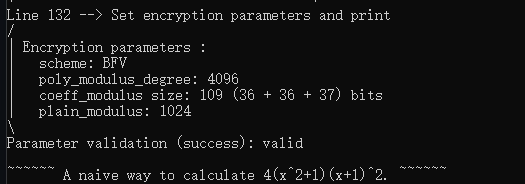
参数可用性校验
参数设置完成后,需要校验一下已设置的参数是否可用,本代码的例子计算的是
4
(
x
2
+
1
)
(
x
+
1
)
2
=
4
x
4
+
8
x
3
+
8
x
2
+
8
x
+
4
4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2=4x^4+8x^3+8x^2+8x+4
4(x2+1)(x+1)2=4x4+8x3+8x2+8x+4
SEALContext context(parms);
/*Print the parameters that we have chosen.*/
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Set encryption parameters and print" << endl;
print_parameters(context);
cout << "Parameter validation (success): " << context.parameter_error_message() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "~~~~~~ A naive way to calculate 4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2. ~~~~~~" << endl;
校验结果如图
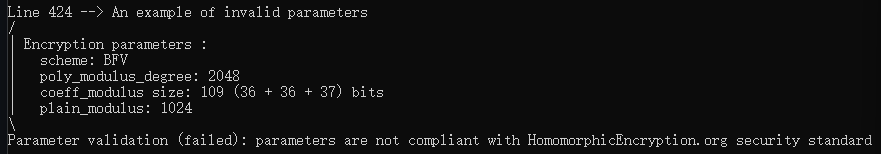
代码的最后(本来在代码的最后位置,这里我提到这里来了),展示了如果设置的参数有问题,seal库会输出为什么有问题。。。相当于一个不错的辅助作用,能帮助修改参数。
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "An example of invalid parameters" << endl;
parms.set_poly_modulus_degree(2048);
context = SEALContext(parms);
print_parameters(context);
cout << "Parameter validation (failed): " << context.parameter_error_message() << endl << endl;
校验结果如图
密钥生成
主要位公钥 s k = s sk=s sk=s、私钥 p k = ( b = a s + e , a ) pk=(b=as+e,a) pk=(b=as+e,a)、评估密钥evk的生成,首先需要一个密钥生成类的实例来创建一个自动生成私钥的生成器,接着利用私钥来生成公钥。
公钥和私钥生成
KeyGenerator keygen(context);
SecretKey secret_key = keygen.secret_key();
PublicKey public_key;
keygen.create_public_key(public_key);
创建加密器
创建加密器,实例化一个加密器类
Encryptor encryptor(context, public_key);
同态计算生成
同态计算密文的时候需要用到这个类(实际运用中,它不会由私钥拥有方来构建)
Evaluator evaluator(context);
创建解密器
创建解密器,实例化一个解密器类
Decryptor decryptor(context, secret_key);
加密
再次说明这里加密的例子是
4
x
4
+
8
x
3
+
8
x
2
+
8
x
+
4
4x^4+8x^3+8x^2+8x+4
4x4+8x3+8x2+8x+4,这里设置了x=6。在RLWE问题中我们可以把明文消息看作多项式的系数,这里的明文就是6,也就是只有一项常数项。另外,别忘了明文的模数是1024。
明文创建
下面的代码创建了一个包含常量6的明文多项式,接着将明文多项式变为一个字符串,其中多项式的系数为十六进制。
print_line(__LINE__);
uint64_t x = 6;
Plaintext x_plain(uint64_to_hex_string(x));
cout << "Express x = " + to_string(x) + " as a plaintext polynomial 0x" + x_plain.to_string() + "." << endl;
输出结果如下

加密操作
密文由两个或多个多项式形如(
c
t
=
(
c
0
,
c
1
)
)
c_t=(c_0,c_1))
ct=(c0,c1)))组成的,系数要模多项式系数模数,也就是模(
q
q
q)
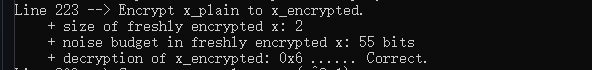
print_line(__LINE__);
Ciphertext x_encrypted;
cout << "Encrypt x_plain to x_encrypted." << endl;
encryptor.encrypt(x_plain, x_encrypted);
密文的大小由Ciphertext::size()给出,新加密的密文大小都是2
cout << " + size of freshly encrypted x: " << x_encrypted.size() << endl;
查看噪声预算
cout << " + noise budget in freshly encrypted x: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(x_encrypted) << " bits"
<< endl;
解密
调用解密器
Plaintext x_decrypted;
cout << " + decryption of x_encrypted: ";
decryptor.decrypt(x_encrypted, x_decrypted);
cout << "0x" << x_decrypted.to_string() << " ...... Correct." << endl;
输出结果如下
这里没有输出加密后的密文,我试了半天没输出成功(太菜了😇),找了一下原因是输出结果是二进制形式不是可阅读的,所以Ciphertexts类里面只提供了save(可以通过stringstream来保存为一个文件)和load(从文件里导出)方法,它没有提供一个类似Plaintext类里的to_string方法。
这是Ciphertexts里的save方法的说明。
同态计算
因为噪声预算会随着乘法深度(次数)的增加而增加,所以为了能够完成更多次的计算,一般选择最小化乘法次数
所以这里计算多项式
4
x
4
+
8
x
3
+
8
x
2
+
8
x
+
4
4x^4+8x^3+8x^2+8x+4
4x4+8x3+8x2+8x+4的时候,选择使用
4
(
x
2
+
1
)
(
x
+
1
)
2
4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2
4(x2+1)(x+1)2,这样对比直接计算能将乘法的深度从4降到了2。
首先是计算
x
2
+
1
x^2+1
x2+1
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Compute x_sq_plus_one (x^2+1)." << endl;
Ciphertext x_sq_plus_one;
evaluator.square(x_encrypted, x_sq_plus_one);//Squares a ciphertext
Plaintext plain_one("1");
evaluator.add_plain_inplace(x_sq_plus_one, plain_one);//Add a ciphertext and a plaintext
同态乘法会导致密文扩张,精确的说,如果输出的两个密文大小为M和N,那么同态乘法后的密文大小将变为M+N-1,下面的代码输出了密文扩张大小和噪声消耗。
cout << " + size of x_sq_plus_one: " << x_sq_plus_one.size() << endl;
cout << " + noise budget in x_sq_plus_one: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(x_sq_plus_one) << " bits"
<< endl;
输出一下解密的结果
Plaintext decrypted_result;
cout << " + decryption of x_sq_plus_one: ";
decryptor.decrypt(x_sq_plus_one, decrypted_result);
cout << "0x" << decrypted_result.to_string() << " ...... Correct." << endl;
输出结果如下
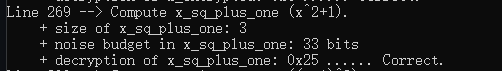
可以看到这里乘法后,密文从2项变到了3项,而噪声消耗了55-33=22个比特,因为还有噪声预算能够消耗,也就是还没达到噪声界限,所以能够正确解密。
接着计算 ( x + 1 ) 2 (x+1)^2 (x+1)2
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Compute x_plus_one_sq ((x+1)^2)." << endl;
Ciphertext x_plus_one_sq;
evaluator.add_plain(x_encrypted, plain_one, x_plus_one_sq);
evaluator.square_inplace(x_plus_one_sq);
cout << " + size of x_plus_one_sq: " << x_plus_one_sq.size() << endl;
cout << " + noise budget in x_plus_one_sq: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(x_plus_one_sq) << " bits"
<< endl;
cout << " + decryption of x_plus_one_sq: ";
decryptor.decrypt(x_plus_one_sq, decrypted_result);
cout << "0x" << decrypted_result.to_string() << " ...... Correct." << endl;
这里需要提一下的是add_plain_inplace()、square_inplace(0与add_plain()、square()函数的区别,带有inplace的是需要指定一个参数用来接收结果的,不带的就是直接保存在第一个参数里的。
输出结果如下
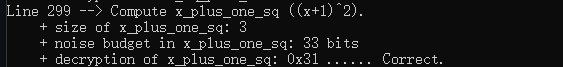
这里的噪声消耗也是22比特
最后是计算两个的乘积
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Compute encrypted_result (4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2)." << endl;
Ciphertext encrypted_result;
Plaintext plain_four("4");
evaluator.multiply_plain_inplace(x_sq_plus_one, plain_four);
evaluator.multiply(x_sq_plus_one, x_plus_one_sq, encrypted_result);
cout << " + size of encrypted_result: " << encrypted_result.size() << endl;
cout << " + noise budget in encrypted_result: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(encrypted_result) << " bits"
<< endl;
cout << "NOTE: Decryption can be incorrect if noise budget is zero." << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "~~~~~~ A better way to calculate 4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2. ~~~~~~" << endl;
这里本来是没有输出结果的,看到噪声预算还有剩余,就加了点代码看看结果。输出结果如下
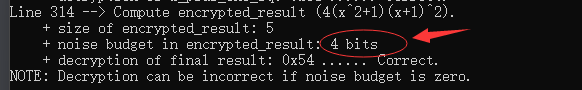
大概消耗了33-4=29比特的噪声预算,式子越复杂消耗的越多。两个三项的相乘会得到五项。
x
=
6
x=6
x=6,表达式是
4
x
4
+
8
x
3
+
8
x
2
+
8
x
+
4
=
4
(
x
2
+
1
)
(
x
+
1
)
2
4x^4+8x^3+8x^2+8x+4=4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2
4x4+8x3+8x2+8x+4=4(x2+1)(x+1)2,我们期待解密结果是
4
×
37
×
49
=
7252
m
o
d
1024
=
84
4\times37\times49=7252 \mod 1024 = 84
4×37×49=7252mod1024=84换算为十六进制就是0x54,所以解密正确。
重线性化
重线性化是为了减少密文的规模扩张,并将密文规模还原到近似乘法之前的状况。
重线性化需要重线性化密钥rlk(其他方案里也叫做evk),它是由一层一层计算出来的一连串的密钥链,每一层都需要对应每一层的密钥,主要是用来消除密钥乘积的二次项,但是会诞生一定的噪声。
假设一个二阶的密文为
[
c
0
,
c
1
,
c
2
]
[\mathbf c_0,\mathbf c_1,\mathbf c_2]
[c0,c1,c2],线性化的目的是将它变成一阶的
[
c
0
′
,
c
1
′
]
[\mathbf c'_0,\mathbf c'_1]
[c0′,c1′]即
[
c
0
+
c
1
⋅
s
+
c
2
⋅
s
2
]
q
=
[
c
0
′
+
c
1
′
⋅
s
+
r
]
q
\left[\mathbf{c}_{0}+\mathbf{c}_{1} \cdot \mathbf{s}+\mathbf{c}_{2} \cdot \mathbf{s}^{2}\right]_{q}=\left[\mathbf{c}_{0}^{\prime}+\mathbf{c}_{1}^{\prime} \cdot \mathbf{s}+\mathbf{r}\right]_{q}
[c0+c1⋅s+c2⋅s2]q=[c0′+c1′⋅s+r]q,其中
r
\mathbf r
r很小。
首先需要生成重线性化密钥rlk
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Generate relinearization keys." << endl;
RelinKeys relin_keys;
keygen.create_relin_keys(relin_keys);
接下来重新计算 4 ( x 2 + 1 ) ( x + 1 ) 2 4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2 4(x2+1)(x+1)2,并在每一次乘法后都调用重线性化,还原密文规模。
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Compute and relinearize x_squared (x^2)," << endl;
cout << string(13, ' ') << "then compute x_sq_plus_one (x^2+1)" << endl;
Ciphertext x_squared;
evaluator.square(x_encrypted, x_squared);
cout << " + size of x_squared: " << x_squared.size() << endl;
evaluator.relinearize_inplace(x_squared, relin_keys);
cout << " + size of x_squared (after relinearization): " << x_squared.size() << endl;
evaluator.add_plain(x_squared, plain_one, x_sq_plus_one);
cout << " + noise budget in x_sq_plus_one: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(x_sq_plus_one) << " bits"
<< endl;
cout << " + decryption of x_sq_plus_one: ";
decryptor.decrypt(x_sq_plus_one, decrypted_result);
cout << "0x" << decrypted_result.to_string() << " ...... Correct." << endl;
print_line(__LINE__);
Ciphertext x_plus_one;
cout << "Compute x_plus_one (x+1)," << endl;
cout << string(13, ' ') << "then compute and relinearize x_plus_one_sq ((x+1)^2)." << endl;
evaluator.add_plain(x_encrypted, plain_one, x_plus_one);
evaluator.square(x_plus_one, x_plus_one_sq);
cout << " + size of x_plus_one_sq: " << x_plus_one_sq.size() << endl;
evaluator.relinearize_inplace(x_plus_one_sq, relin_keys);
cout << " + noise budget in x_plus_one_sq: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(x_plus_one_sq) << " bits"
<< endl;
cout << " + decryption of x_plus_one_sq: ";
decryptor.decrypt(x_plus_one_sq, decrypted_result);
cout << "0x" << decrypted_result.to_string() << " ...... Correct." << endl;
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Compute and relinearize encrypted_result (4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2)." << endl;
evaluator.multiply_plain_inplace(x_sq_plus_one, plain_four);
evaluator.multiply(x_sq_plus_one, x_plus_one_sq, encrypted_result);
cout << " + size of encrypted_result: " << encrypted_result.size() << endl;
evaluator.relinearize_inplace(encrypted_result, relin_keys);
cout << " + size of encrypted_result (after relinearization): " << encrypted_result.size() << endl;
cout << " + noise budget in encrypted_result: " << decryptor.invariant_noise_budget(encrypted_result) << " bits"
<< endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "NOTE: Notice the increase in remaining noise budget." << endl;
接着是看看解密的结果
print_line(__LINE__);
cout << "Decrypt encrypted_result (4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2)." << endl;
decryptor.decrypt(encrypted_result, decrypted_result);
cout << " + decryption of 4(x^2+1)(x+1)^2 = 0x" << decrypted_result.to_string() << " ...... Correct." << endl;
cout << endl;
来看看输出的结果
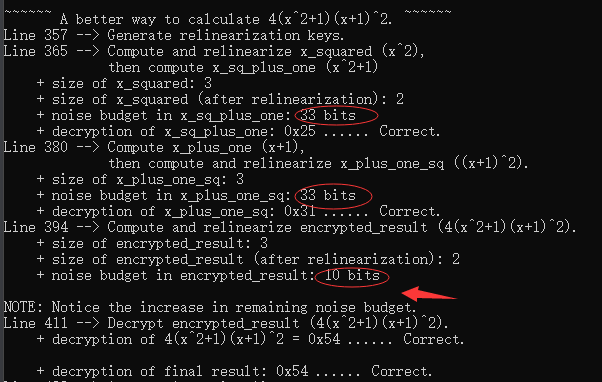
可以看到由于多了重线性化操作,密文的大小也有5减少到了2,而最终表达式的噪声预算还剩下10比特多于没有重线性化的4比特。(怎么两个因子消耗的预算还是没变化~~~😅,算了,whatever,最后的结果是优化了的)。