栈和队列
1 栈的基础应用:20.括号匹配
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') {
stack.push(c);
} else {
// 还有字符串但是栈已经为空了,肯定是非法表达式
if (stack.size()==0){
return false;
}
char cPop = stack.pop();
if(cPop == '('){
if (c !=')'){
return false;
}
}else if (cPop == '['){
if (c != ']'){
return false;
}
}else if (cPop== '{'){
if (c != '}'){
return false;
}
}
}
}
if (stack.size() != 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
本节类似问题:150、71
150.逆波兰表达式求值
71.简化路径
##2 栈和递归的关系,以二叉树的前、中、后序遍历为例(图的深度优先遍历DFS原理是一样的)
参考Part2Basic/第06章_二分搜索树BST.md的6.6和6.7
144.二叉树前序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preorder(root, list);
return list;
}
/// 遍历以node作为根节点的子树
private void preorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> list){
// 1.递归终止条件
if(node == null){
return;
}
// 2.递归具体逻辑
list.add(node.val);
preorder(node.left, list);
preorder(node.right, list);
}
}
94.二叉树中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, list);
return list;
}
/// 遍历以node作为根节点的子树
private void inorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> list){
// 1.递归终止条件
if(node == null){
return;
}
// 2.递归具体逻辑
inorder(node.left, list);
list.add(node.val);
inorder(node.right, list);
}
}
145.二叉树后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, list);
return list;
}
/// 遍历以node作为根节点的子树
private void postorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> list){
// 1.递归终止条件
if(node == null){
return;
}
// 2.递归具体逻辑
postorder(node.left, list);
postorder(node.right, list);
list.add(node.val);
}
}
589.n叉树前序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preorder(root, list);
return list;
}
private void preorder(Node node, List<Integer> list){
// 1.递归终止条件
if(node == null){
return;
}
// 2.递归具体逻辑
list.add(node.val);
for(Node child : node.children){
preorder(child, list);
}
}
}
590.n叉树后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, list);
return list;
}
private void postorder(Node node, List<Integer> list){
// 1.递归终止条件
if(node == null){
return;
}
// 2.递归具体逻辑
for(Node child : node.children){
postorder(child, list);
}
list.add(node.val);
}
}
##3 使用栈模拟递归
递归实际是一种系统栈调用
341.扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* public interface NestedInteger {
*
* // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* public boolean isInteger();
*
* // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* public Integer getInteger();
*
* // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* public List<NestedInteger> getList();
* }
*/
public class NestedIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
// 定义一个队列
private Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 根据文件头各个函数的注释进行合理的递归调用
private void init(List<NestedInteger> nestedList){
for(NestedInteger nestedInteger : nestedList){
if(nestedInteger.isInteger()){
queue.add(nestedInteger.getInteger());
}else {
init(nestedInteger.getList());
}
}
}
public NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
init(nestedList);
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
return queue.remove();
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return !queue.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i = new NestedIterator(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) v[f()] = i.next();
*/
##4 队列的典型应用:二叉树的层序遍历以及图的BFS
102.二叉树的层序遍历
可以记住第几层的BFS
给定一个二叉树,返回其按层次遍历的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
例如:
给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
// 一次性把当前层的节点全部弹出
List<Integer> levelList = new ArrayList<>();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
levelList.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
list.add(levelList);
}
return list;
}
}
不用记住第几层的BFS
class Solution {
public List<Integer> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 一次性把当前层的节点全部弹出
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
return list;
}
}
此外还有107、103、199
107.二叉树的层次遍历 II
相比102实际就加了
Collections.reverse(list);这一行
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
// 一次性把当前层的节点全部弹出
List<Integer> levelList = new ArrayList<>();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
levelList.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
list.add(levelList);
}
// 相比102就加了下面一行
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
}
103.二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
相比102实际只加了下面几行,用于偶数行逆序
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> listCur = list.get(i);
if (i % 2 == 1) {
Collections.reverse(listCur);
}
}
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
// 一次性把当前层的节点全部弹出
List<Integer> levelList = new ArrayList<>();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
levelList.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
list.add(levelList);
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> listCur = list.get(i);
if (i % 2 == 1) {
Collections.reverse(listCur);
}
}
return list;
}
}
199.二叉树的右视图
当到达本层最后一个元素时才加到list中
核心代码:
// 核心,到达本行最后一个元素才加到list里
if (i == size - 1) {
list.add(node.val);
}
完整实现如下:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
int i = 0;
while (i < size) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
// 核心,到达本行最后一个元素才加到list里
if (i == size - 1) {
list.add(node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
i++;
}
}
return list;
}
}
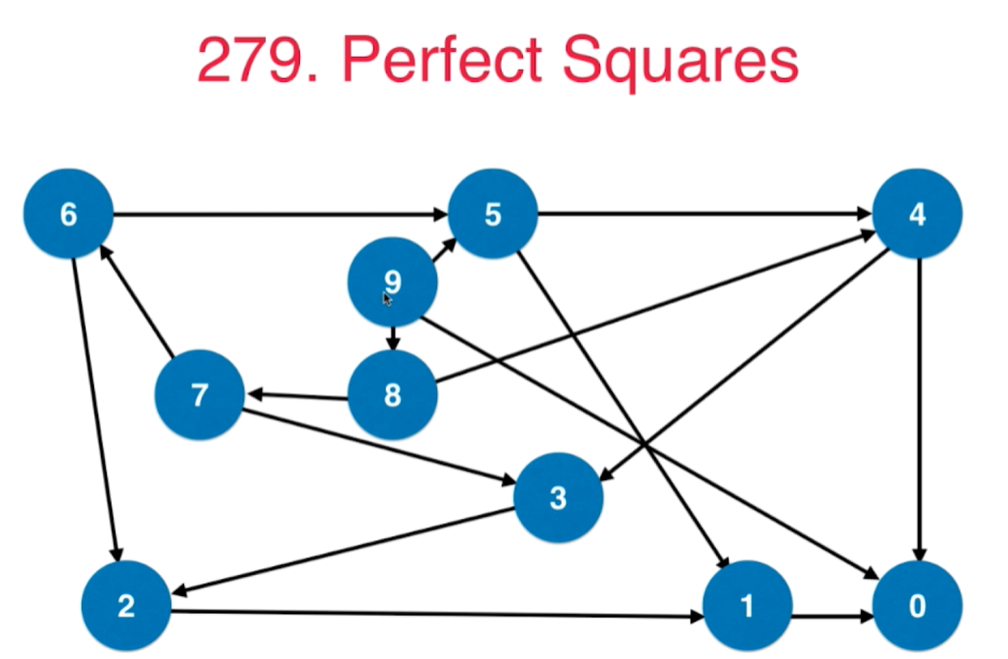
##5 BFS和图的最短路径:279.完全平方数
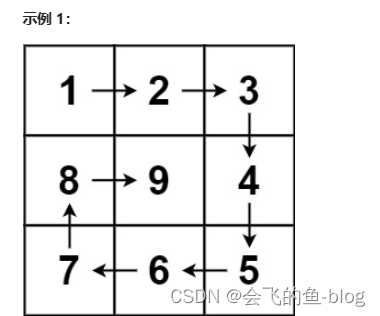
给定正整数 n,找到若干个完全平方数(比如 1, 4, 9, 16, ...)使得它们的和等于 n。你需要让组成和的完全平方数的个数最少。
示例 1:
输入: n = 12
输出: 3
解释: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
示例 2:
输入: n = 13
输出: 2
解释: 13 = 4 + 9.
思路:
- 对问题建模,整个问题转化为一个图论问题。
- 从n到0,每个数组表示一个节点
- 如果两个数字x到y相差一个完全平方数,则连接一条边,我们得到了一个有向无权图。
- 原问题转换为:
求这个无权图从n到0的最短路径,求最短路径一般都用BFS
public class Solution {
private class Node {
/**
* 节点编号
*/
int num;
/**
* 节点到起点的距离
*/
int distance;
public Node(int num, int distance) {
this.num = num;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
public int numSquares(int n) {
// 这里用map表达图中的一个节点,键代表节点,值代表距离起点的距离(无权图可以认为是经过的节点个数)
Queue<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new Node(n, 0));
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.remove();
if (node.num == 0) {
// 这里我们只用到了距离,不需要具体的路径,需要完整路径地话还需要pre数组
return node.distance;
}
// 遍历邻接点,把他们加入到队列中
for (int i = 1; node.num - i * i >= 0; i++) {
if (!visited[node.num - i * i]) {
queue.add(new Node(node.num - i * i, node.distance + 1));
visited[node.num - i * i] = true;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
类似问题:127、126
使用BFS关键是要找到邻接点
127.单词接龙
class Solution {
private class Node {
/**
* 节点对应的单词
*/
String word;
/**
* 当前单词到起点单词的距离
*/
int distance;
public Node(String word, int distance) {
this.word = word;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
/**
* 判断两个单词是否只有一个单词不同
* 两个单词的长度是相等地
*/
private boolean oneCharDiff(String wordA, String wordB) {
// 不同字符的个数
int diffCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < wordA.length(); i++) {
if (wordA.charAt(i) != wordB.charAt(i)) {
diffCnt++;
}
}
return diffCnt == 1;
}
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
// 访问数组
Map<String, Boolean> visited = new HashMap<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new Node(beginWord, 1));
visited.put(beginWord, true);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.remove();
for (String word : wordList) {
if (oneCharDiff(word, node.word) && visited.get(word) == null) {
// 一旦找到目标单词endWord,直接返回
if (word.equals(endWord)) {
return node.distance + 1;
}
// 和父节点相比只有一个节点不同而且还没被访问
queue.add(new Node(word, node.distance + 1));
visited.put(word, true);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
126.单词接龙2之记住所有可达路径,参考博客
第1个。超时的版本,21/39
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// 如果不含有结束单词,直接结束,不然后边会造成死循环
if (!wordList.contains(endWord)) {
return ans;
}
// 利用 BFS 得到所有的邻居节点,以及每个节点的所在层数
HashMap<String, Integer> mapWordDistance = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
bfs(beginWord, endWord, wordList, map, mapWordDistance);
ArrayList<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
// temp 用来保存当前的路径
path.add(beginWord);
dfs(beginWord, endWord, map, mapWordDistance, path, ans);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(String beginWord, String endWord, HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> map,
HashMap<String, Integer> mapWordDistance, List<String> path, List<List<String>> pathList) {
if (beginWord.equals(endWord)) {
pathList.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
ArrayList<String> neighbors = map.getOrDefault(beginWord, new ArrayList<String>());
for (String neighbor : neighbors) {
//判断层数是否符合
if (mapWordDistance.get(beginWord) + 1 == mapWordDistance.get(neighbor)) {
path.add(neighbor);
dfs(neighbor, endWord, map, mapWordDistance, path, pathList);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public void bfs(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList, HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> map, HashMap<String, Integer> distance) {
Queue<String> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(beginWord);
distance.put(beginWord, 0);
boolean isFound = false;
int depth = 0;
Set<String> dict = new HashSet<>(wordList);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
depth++;
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
String temp = queue.poll();
// 一次性得到所有的下一个的节点
ArrayList<String> neighbors = getOneCharDiffWords(temp, dict);
map.put(temp, neighbors);
for (String neighbor : neighbors) {
if (!distance.containsKey(neighbor)) {
distance.put(neighbor, depth);
if (neighbor.equals(endWord)) {
isFound = true;
}
queue.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
if (isFound) {
break;
}
}
}
private ArrayList<String> getOneCharDiffWords(String node, Set<String> dict) {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
char chs[] = node.toCharArray();
for (char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++) {
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
if (chs[i] == ch) {
continue;
}
char old_ch = chs[i];
chs[i] = ch;
if (dict.contains(String.valueOf(chs))) {
res.add(String.valueOf(chs));
}
chs[i] = old_ch;
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* String beginWord = "hit";
* String endWord = "cog";
* String[] words = {"hot","dot","dog","lot","log", "cog"};
* <p>
* String beginWord = "qa";
* String endWord = "sq";
* String[] words = {"si", "go", "se", "cm", "so", "ph", "mt", "db", "mb", "sb", "kr", "ln", "tm", "le", "av", "sm", "ar", "ci", "ca", "br", "ti", "ba", "to", "ra", "fa", "yo", "ow", "sn", "ya", "cr", "po", "fe", "ho", "ma", "re", "or", "rn", "au", "ur", "rh", "sr", "tc", "lt", "lo", "as", "fr", "nb", "yb", "if", "pb", "ge", "th", "pm", "rb", "sh", "co", "ga", "li", "ha", "hz", "no", "bi", "di", "hi", "qa", "pi", "os", "uh", "wm", "an", "me", "mo", "na", "la", "st", "er", "sc", "ne", "mn", "mi", "am", "ex", "pt", "io", "be", "fm", "ta", "tb", "ni", "mr", "pa", "he", "lr", "sq", "ye"};
* <p>
* String beginWord = "cet";
* String endWord = "ism";
* String[] words = {"kid", "tag", "pup", "ail", "tun", "woo", "erg", "luz", "brr", "gay", "sip", "kay", "per", "val", "mes", "ohs", "now", "boa", "cet", "pal", "bar", "die", "war", "hay", "eco", "pub", "lob", "rue", "fry", "lit", "rex", "jan", "cot", "bid", "ali", "pay", "col", "gum", "ger", "row", "won", "dan", "rum", "fad", "tut", "sag", "yip", "sui", "ark", "has", "zip", "fez", "own", "ump", "dis", "ads", "max", "jaw", "out", "btu", "ana", "gap", "cry", "led", "abe", "box", "ore", "pig", "fie", "toy", "fat", "cal", "lie", "noh", "sew", "ono", "tam", "flu", "mgm", "ply", "awe", "pry", "tit", "tie", "yet", "too", "tax", "jim", "san", "pan", "map", "ski", "ova", "wed", "non", "wac", "nut", "why", "bye", "lye", "oct", "old", "fin", "feb", "chi", "sap", "owl", "log", "tod", "dot", "bow", "fob", "for", "joe", "ivy", "fan", "age", "fax", "hip", "jib", "mel", "hus", "sob", "ifs", "tab", "ara", "dab", "jag", "jar", "arm", "lot", "tom", "sax", "tex", "yum", "pei", "wen", "wry", "ire", "irk", "far", "mew", "wit", "doe", "gas", "rte", "ian", "pot", "ask", "wag", "hag", "amy", "nag", "ron", "soy", "gin", "don", "tug", "fay", "vic", "boo", "nam", "ave", "buy", "sop", "but", "orb", "fen", "paw", "his", "sub", "bob", "yea", "oft", "inn", "rod", "yam", "pew", "web", "hod", "hun", "gyp", "wei", "wis", "rob", "gad", "pie", "mon", "dog", "bib", "rub", "ere", "dig", "era", "cat", "fox", "bee", "mod", "day", "apr", "vie", "nev", "jam", "pam", "new", "aye", "ani", "and", "ibm", "yap", "can", "pyx", "tar", "kin", "fog", "hum", "pip", "cup", "dye", "lyx", "jog", "nun", "par", "wan", "fey", "bus", "oak", "bad", "ats", "set", "qom", "vat", "eat", "pus", "rev", "axe", "ion", "six", "ila", "lao", "mom", "mas", "pro", "few", "opt", "poe", "art", "ash", "oar", "cap", "lop", "may", "shy", "rid", "bat", "sum", "rim", "fee", "bmw", "sky", "maj", "hue", "thy", "ava", "rap", "den", "fla", "auk", "cox", "ibo", "hey", "saw", "vim", "sec", "ltd", "you", "its", "tat", "dew", "eva", "tog", "ram", "let", "see", "zit", "maw", "nix", "ate", "gig", "rep", "owe", "ind", "hog", "eve", "sam", "zoo", "any", "dow", "cod", "bed", "vet", "ham", "sis", "hex", "via", "fir", "nod", "mao", "aug", "mum", "hoe", "bah", "hal", "keg", "hew", "zed", "tow", "gog", "ass", "dem", "who", "bet", "gos", "son", "ear", "spy", "kit", "boy", "due", "sen", "oaf", "mix", "hep", "fur", "ada", "bin", "nil", "mia", "ewe", "hit", "fix", "sad", "rib", "eye", "hop", "haw", "wax", "mid", "tad", "ken", "wad", "rye", "pap", "bog", "gut", "ito", "woe", "our", "ado", "sin", "mad", "ray", "hon", "roy", "dip", "hen", "iva", "lug", "asp", "hui", "yak", "bay", "poi", "yep", "bun", "try", "lad", "elm", "nat", "wyo", "gym", "dug", "toe", "dee", "wig", "sly", "rip", "geo", "cog", "pas", "zen", "odd", "nan", "lay", "pod", "fit", "hem", "joy", "bum", "rio", "yon", "dec", "leg", "put", "sue", "dim", "pet", "yaw", "nub", "bit", "bur", "sid", "sun", "oil", "red", "doc", "moe", "caw", "eel", "dix", "cub", "end", "gem", "off", "yew", "hug", "pop", "tub", "sgt", "lid", "pun", "ton", "sol", "din", "yup", "jab", "pea", "bug", "gag", "mil", "jig", "hub", "low", "did", "tin", "get", "gte", "sox", "lei", "mig", "fig", "lon", "use", "ban", "flo", "nov", "jut", "bag", "mir", "sty", "lap", "two", "ins", "con", "ant", "net", "tux", "ode", "stu", "mug", "cad", "nap", "gun", "fop", "tot", "sow", "sal", "sic", "ted", "wot", "del", "imp", "cob", "way", "ann", "tan", "mci", "job", "wet", "ism", "err", "him", "all", "pad", "hah", "hie", "aim", "ike", "jed", "ego", "mac", "baa", "min", "com", "ill", "was", "cab", "ago", "ina", "big", "ilk", "gal", "tap", "duh", "ola", "ran", "lab", "top", "gob", "hot", "ora", "tia", "kip", "han", "met", "hut", "she", "sac", "fed", "goo", "tee", "ell", "not", "act", "gil", "rut", "ala", "ape", "rig", "cid", "god", "duo", "lin", "aid", "gel", "awl", "lag", "elf", "liz", "ref", "aha", "fib", "oho", "tho", "her", "nor", "ace", "adz", "fun", "ned", "coo", "win", "tao", "coy", "van", "man", "pit", "guy", "foe", "hid", "mai", "sup", "jay", "hob", "mow", "jot", "are", "pol", "arc", "lax", "aft", "alb", "len", "air", "pug", "pox", "vow", "got", "meg", "zoe", "amp", "ale", "bud", "gee", "pin", "dun", "pat", "ten", "mob"};
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String beginWord = "hit";
String endWord = "cog";
String[] words = {"hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog"};
List<String> wordList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(words));
List<List<String>> ladders = new Solution().findLadders(beginWord, endWord, wordList);
System.out.println(ladders);
}
}
##6~7 优先队列
Java默认的
java.util.PriorityQueue是基于最小堆实现地
347.前K个高频元素
class Solution {
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
// 元素和出现频次的映射Map
Map<Integer, Integer> mapNumFreq = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : nums) {
// 更新map里面的值
if (mapNumFreq.get(num) == null) {
mapNumFreq.put(num, 1);
} else {
mapNumFreq.put(num, mapNumFreq.get(num) + 1);
}
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer key1, Integer key2) {
// 自定义比较器,找出现频次较高地需要每次弹出最小值
return mapNumFreq.get(key1) - mapNumFreq.get(key2);
}
});
for (Integer key : mapNumFreq.keySet()) {
if (pq.size() == k) {
// 满了需要和栈顶元素比较,比栈顶元素大就加入到队列中
if (mapNumFreq.get(key) > mapNumFreq.get(pq.peek())) {
pq.poll();
pq.add(key);
}
} else {
// 优先队列没满就直接加入
pq.add(key);
}
}
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
result.add(pq.poll());
}
// 从高频到低频
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
23.合并K个排序链表
/***********************************************************
* @Description : 合并K个排序链表
* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)
* @date : 2020/1/20 16:01
* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com
***********************************************************/
import Chapter05LinkedList.ListNode;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (ListNode list : lists) {
cur = list;
while (cur!=null){
pq.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
cur = dummyHead;
while (!pq.isEmpty()){
cur.next = new ListNode(pq.remove());
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}