文章目录
- 1.引入的方式
- 1.1作为HTML的标签属性
- 1.2style标签
- 1.3link标签外部引入css文件
- 2.基础选择器
- 2.1标签选择器
- 2.2类选择器
- 2.3id选择器
- 2.4通配符选择器
- 3.复合选择器
- 3.1后代选择器
- 3.2子选择器
- 3.3并集选择器
- 3.4伪类选择器
- 4.设置样式
- 4.1字体
- 4.2文本
- 4.3背景
- 4.4圆角
- 5.显示模式
- 6.盒模型
- 7.页面布局(弹性布局)
1.引入的方式
1.1作为HTML的标签属性
针对单个元素,无法针对多个元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="height: 50px; background-color: coral;"></div>
</body>
</html>
1.2style标签
可以针对多个元素,但是比较耦合,因为是在HTML代码中写CSS代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style>
div {
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
1.3link标签外部引入css文件
推荐的写法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="3.css">
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
/* 3.css */
div {
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
2.基础选择器
2.1标签选择器
选择某个标签的所有元素,不能差异性选择
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
h2 {
color: red;
}
p {
color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>1</h2>
<p>11111</p>
<h2>2</h2>
<p>22222</p>
<h2>3</h2>
<p>33333</p>
</body>
</html>

2.2类选择器
(1)可以为任意的HTML标签设置class,这样一个class就可以绑定多个元素,选择某个类就可以为该类的元素设置样式
(2)通过.+类名来选择类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2 class="red">1</h2>
<p>11111</p>
<h2 class="red">2</h2>
<p>22222</p>
<h2>3</h2>
<p>33333</p>
</body>
</html>

2.3id选择器
(1)HTML元素,可以设置id,但是必须全局唯一
(2)通#+id的值来选择某个id的元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#red {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2 id="red">1</h2>
<p>11111</p>
<h2>2</h2>
<p>22222</p>
<h2>3</h2>
<p>33333</p>
</body>
</html>

2.4通配符选择器
所有的元素都会被匹配上,特殊情况下才使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>1</h2>
<p>11111</p>
<h2>2</h2>
<p>22222</p>
<h2>3</h2>
<p>33333</p>
</body>
</html>

3.复合选择器
3.1后代选择器
(1)选择的可以是儿子,也可以是孙子
(2)语法:基础选择器1 基础选择器2{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ul li{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
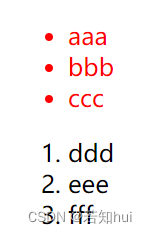
<ul>
<li>aaa</li>
<li>bbb</li>
<li>ccc</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>ddd</li>
<li>eee</li>
<li>fff</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ul li a {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>aaa</li>
<li>bbb</li>
<li>ccc<br><a>会变色</a></li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>ddd</li>
<li>eee</li>
<li>fff</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>

3.2子选择器
(1)选择的只能是儿子
(2)语法:基础选择器1>基础选择器2{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.two>a {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="two">
<a href="#">链接1</a>
<p>
<a href="#">链接2</a>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>

3.3并集选择器
(1)多个选择器的并集
(2)选择器1,选择器2{}
(3)这里的选择器可以是基础选择器,也可以是复合选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div,h3,ul li {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>苹果</div>
<h3>香蕉</h3>
<ul>
<li>鸭梨</li>
<li>橙子</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>

3.4伪类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 未被访问时候的样式 */
a:link {
color: black;
/* 去掉 a 标签的下划线 */
text-decoration: none;
}
/* 已经被访问后的样式 */
a:visited {
color: green;
}
/* 鼠标放上去的时候的样式 */
a:hover {
color: red;
}
/* 鼠标按下去未弹起来时候的样式 */
a:active {
color: blue;
}
/* 鼠标聚焦的时候的样式 */
.three>input:focus {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#">小猫</a>
<div class="three">
<input type="text">
<input type="text">
<input type="text">
<input type="text">
</div>
</body>
</html>
4.设置样式
4.1字体
(1)字体系列:font-family,引号包裹,多个字体之间“,”间隔
(2)字体大小:font-size,值可以使用px(像素),也可以使用rem(字体的正常大小是1rem,如果设置成2rem就是把原来的字体放大2倍)
(3)字体粗细:font-weight,值的范围是100-900,400就是正常粗细,700就是粗体
(4)字体样式:font-style,值为italic就是设置倾斜字体,值为normal就是取消倾斜
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.font-family .one {
/* 字体显示为隶书 */
font-family: '隶书','Microsoft YaHei';
/* 字体大小设置为30px */
font-size: 30px;
}
.font-family .two {
/* 字体显示为宋体 */
font-family: '宋体';
/* 字体大小设置为2rem(原来字体的2倍) */
font-size: 2rem;
/* 字体的粗细为400(正常粗细) */
font-weight: 400;
/* 字体样式为倾斜 */
font-style: italic;
}
.three {
/* 取消字体倾斜 */
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="font-family">
<div class="one">
这是隶书
</div>
<div class="two">
这是宋体
</div>
<em class="three">
这是倾斜字体
</em>
</div>
</body>
</html>

4.2文本
(1)文本对齐:text-algin,值为center就是居中对齐,值为left就是靠左,值为right就是靠右
(2)文本颜色:color,值可以是英文单词、16进制的数字、rgb(三个整数)(三原色写法)
(3)文本装饰:text-decoration,值为none表示什么都没有,一般用于a链接标签去除默认的下划线
(4)文本缩进:text-index,一般缩进为2个文字,值设置为2em
(5)行高:line-height,使用的最多的是将文本垂直居中(注意:文本所在的元素行高设置为该行元素高度)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
/* 通过rbg设置文本颜色 */
color: rgb(230, 17, 17);
}
.one {
/* 让文本左对齐 */
text-align: left;
/* 去除链接的下划线 */
text-decoration: none;
}
.two {
/* 让文本右对齐 */
text-align: right;
text-decoration: underline;
}
.three {
/* 让文本居中对齐 */
text-align: center;
/* 上划线 */
text-decoration: overline;
}
.four {
/* 下划线 */
text-decoration: line-through;
}
#indent {
/* 文本缩进2个文字 */
text-indent: 2em;
}
#line-height {
/* 整体高度 */
height: 50px;
/* 背景颜色 */
background-color:red;
/* 行高 */
line-height: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>要开心</p>
<h2>div对齐</h2>
<div class="one">左对齐</div>
<div class="two">右对齐</div>
<div class="three">居中对齐</div>
<h2>span不会对齐</h2>
<span class="one">左对齐</span>
<br>
<span class="two">右对齐</span>
<br>
<span class="three">居中对齐</span>
<h2>文本装饰</h2>
<div class="one">啥都没有</div>
<div class="two">下划线</div>
<div class="three">上划线</div>
<div class="four">删除线</div>
<h2>文本缩进</h2>
<p id="indent">要快乐</p>
<h2>行高</h2>
<div id="line-height">每天</div>
</body>
</html>
4.3背景
(1)背景色:background-color,值为颜色值
(2)背景图片:background-image,值为url(图片路径)
(3)背景平铺:background-repeat,值为no-repeat表示不平铺,默认的是repeat表示x轴和y轴都会平铺
(4)背景位置:background-position:x值,y值(x值:top(顶)、bottom(底)、px(像素)、百分比)(y值:left(左)、right(右)、center(居中)、px、百分比)
(5)背景尺寸:background-size,值可以是px、百分比、cover(x轴占满)、contain(包含整个背景)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#d1 {
width: 220px;
height: 220px;
/* 背景图片 */
background-image: url(花花.jpg);
}
#d2 {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
/* 背景图片 */
background-image: url(花花.jpg);
/* 背景平铺:repeat表示x轴和y轴都会平铺 */
background-repeat: repeat;
}
#d3 {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
/* 背景图片 */
background-image: url(花花.jpg);
/* 背景平铺:no-repeat表示不平铺 */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/* 背景的位置 */
/* background-position: center bottom; */
background-position: 50% 50%;
}
#d4 {
width: 800px;
height: 500px;
/* 背景图片 */
background-image: url(花花.jpg);
/* 背景平铺:no-repeat表示不平铺 */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/* 背景尺寸:contain表示包含整个背景,cover表示x轴占满,但是可能不会包含全部图片 */
background-size: contain;
/* background-size: cover; */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>背景图片</h2>
<div id="d1">开心</div>
<br>
<h2>图片平铺</h2>
<div id="d2">开心</div>
<h2>图片位置</h2>
<div id="d3">开心</div>
<h2>图片尺寸</h2>
<div id="d4">开心</div>
</body>
</html>
4.4圆角
border-radius,值设置为50%就是圆形
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
background-color: red;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
}
#r10px {
/* 圆角10px */
border-radius: 10px;
}
#r50px {
/* 圆形 */
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>没有设置圆角</h2>
<div></div>
<h2>圆角10px</h2>
<div id="r10px"></div>
<h2>圆形</h2>
<div id="r50px"></div>
</body>
</html>
5.显示模式
display,值可以为block(块级)、inline(内联)、none(隐藏不显示)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.div {
/* div默认是block(块级) */
display: inline;
}
.span {
/* span默认是inline(内联) */
display: block;
}
.none {
/* 隐藏不显示 */
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>div</h2>
<div class="div">1</div>
<div class="div">2</div>
<div class="div">3</div>
<h2>span</h2>
<span class="span">1</span>
<span class="span">2</span>
<span class="span">3</span>
<h2>display: none</h2>
<div class="none">1</div>
</body>
</html>
6.盒模型
(1)边框:border:粗细 样式 颜色
(2)内边距:padding:上 右 下 左(表示内容和边框距离,值可以是px)(padding-top:顶的内边距;padding-bottom:底的内边距;padding-left:左边的内边距;padding-right:右边的内边距)
(3)外边距:margin:上 右 下 左(表示外边元素和自己的距离,值是0 auto表示块级元素水平居中)
(4)记得去除浏览器的边距的默认值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
background-color:red;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
#d1 {
/* 设置边框:粗细 样式 颜色 */
border: 2px solid red;
}
#d2 {
/* 内边距 */
padding: 5px
}
.m {
/* 设置边框:粗细 样式 颜色 */
border: 2px solid red;
/* 外边距 */
margin: 50px;
}
.auto {
/* 设置边框:粗细 样式 颜色 */
border: 2px solid red;
/* 块级元素居中对齐 */
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* 去除浏览器的默认值 */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>边框</h2>
<div id="d1"></div>
<h2>内边距</h2>
<div id="d2">111111111111111111111111111111111111111</div>
<h2>外边距</h2>
<div class="m"></div>
<div class="m"></div>
<div class="auto"></div>
</body>
</html>
7.页面布局(弹性布局)
(1)display:flex(设置为弹性布局)
(2)写在父盒子上,作用在子元素上,控制子元素的位置和排列方式,不含孙子元素
(3)内联元素设置高,宽不会生效,使用弹性布局,宽就有效了
(4)使用了弹性布局,子元素是内联还是块级元素,效果是一样的
(5)主轴假设是x轴(默认),子元素如果没有设置高度,默认就是父元素整个高度
(6)把父盒子称为flex容器,子元素称为flex item子元素排列的方向主轴
(7)设置主轴排列方式:justify-content:前,后,居中,间隔
(8)设置侧轴排列方式:align-items:前,后,居中,间隔
创建一个 div, 内部包含三个span
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: red;
}
div>span {
background-color: green;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>1</span>
<span>2</span>
<span>3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>

加上display: flex;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: red;
/* 设置为弹性布局 */
display: flex;
}
div>span {
background-color: green;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>1</span>
<span>2</span>
<span>3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>

再给 div 加上 justify-content: space-around
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: red;
/* 设置为弹性布局 */
display: flex;
/* 设置主轴排列方式:flex-end(向后排列);space-around(间隔排列,行前行后都有距离);flex-start(向前排列);center(居中排列);space-between(行与行之间有间距) */
justify-content: space-around;
}
div>span {
background-color: green;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>1</span>
<span>2</span>
<span>3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>

主轴和侧轴一起设置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#container {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: red;
/* 设置为弹性布局 */
display: flex;
/* 设置主轴的排列方式(默认是x轴) */
justify-content: space-around;
/* 设置侧轴的排列方式 */
align-items: center;
}
#container>div {
background-color: green;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>