目录
vector介绍
常见接口
构造函数
迭代器
容量操作
元素访问
增删查改
模拟实现
模拟实现要点图解
整体代码
迭代器失效问题
内部失效
外部失效
深浅拷贝问题
vector介绍
vector是表示可变大小数组的序列式容器。vector采用连续的空间存储元素,大小通过动态增长的方式改变,元素的访问比较高效。
常见接口
构造函数

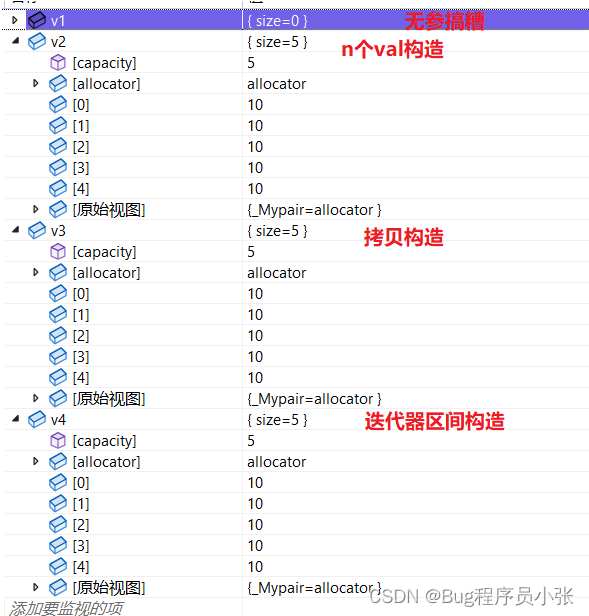
//构造函数测试 void Vector_Test1() { //无参构造 vector<int> v1; //初始化n个val构造 vector<int> v2(5, 10); //拷贝构造 vector<int> v3(v2); //迭代器区间构造 vector<int> v4(v3.begin(), v3.end()); }
迭代器

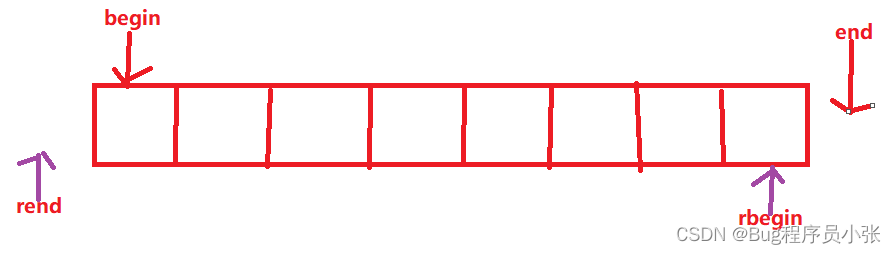
如上图所示,正向迭代器的begin指向首元素的迭代器位置,end指向末尾元素的下一个位置,【左闭,右开)。反向迭代器正好相反。
//迭代器测试 void Vector_Test2() { vector<int> vv={ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; //vector<int>::iterator it = vv.begin(); auto it = vv.begin(); cout << "正向迭代:>" << endl; while (it != vv.end()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } cout << endl; auto rit = vv.rbegin(); cout << "反向迭代:>" << endl; while (rit != vv.rend()) { cout << *rit << " "; rit++; } cout << endl; }
容量操作
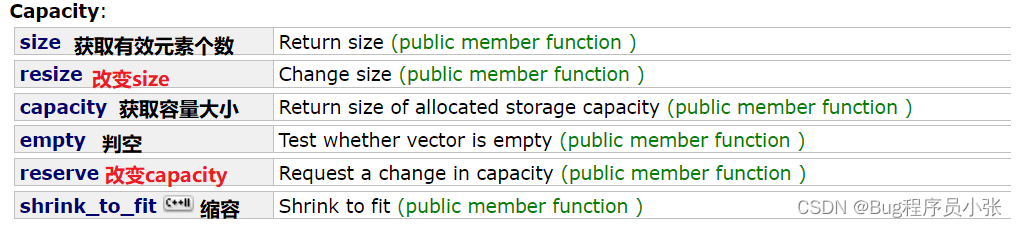
简单接口测试:
//容量测试 void Vector_Test3() { vector<int> vv(10,985); cout <<"size:>" << vv.size() << endl; cout << "capacity:>" << vv.capacity() << endl; cout << "empty? :>" << vv.empty() << endl; }
resize和reserve分析:
resize和reserve都有的共同点就是不会进行缩容,给我空间可以,想缩容,没门!
resize:
void Printf(vector<int> vv) { auto it = vv.begin(); while (it != vv.end()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } cout << endl; } void Vector_Test4() { vector<int> vv = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; vv.resize(15,1); cout << "newsize>size:" << endl; cout << "size:" << vv.size() << endl; cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; Printf(vv); vv.reserve(20); vv.resize(20, 100); cout << "newsize在容量范围内:" << endl; cout << "size:" << vv.size() << endl; cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; Printf(vv); vv.resize(5); cout << "newsize<size:" << endl; cout << "size:" << vv.size()<<endl; cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; Printf(vv); }
reserve:新容量大扩容,新容量下不变!
void Vector_Test5() { vector<int> vv = {1,2,3,4,5}; cout << "----------容量增加,扩容-----------" << endl; cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; vv.reserve(10); cout << "newcapacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; cout << "----------容量减少,不变-----------" << endl; cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; vv.reserve(5); cout << "newcapacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; }
默认扩容机制测试: vs下测试,默认按照1.5倍扩容!
void TestVectorExpand() { size_t sz; vector<int> v; //记录每次扩容后的容量大小 sz = v.capacity(); int cnt = 1; for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) { v.push_back(i); if (sz != v.capacity()) { sz = v.capacity(); cout << "第" << cnt++<<"次扩容: " << sz << '\n'; } } }
c++11提供的接口,调用后缩容。
void Vector_Test6() { vector<int> vv; cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; vv.reserve(20); cout << "capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; vv.resize(10); vv.shrink_to_fit(); cout << "shrink_to_fit_capacity:" << vv.capacity() << endl; }
元素访问

上述两个接口的功能类似,在底层实现上【】检查越界的方式是断言,在release断言会失效。at接口底层检查越界的方式是抛异常,使用上可读性没有【】直观,因为我们比较习惯【】的使用。
void Vector_Test7() { vector<int> vv = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; cout <<"[]:>" << vv[3] << endl; cout <<"at:>"<< vv.at(5) << endl; }
增删查改

assign:将新内容赋给向量,替换其当前内容,并相应地修改其大小。
void Vector_Test8() { vector<int> vv = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; vector<int> vv2; vv2.assign(vv.begin(), vv.end()); Printf(vv); vv.assign(12, 1); Printf(vv); }
上述剩余接口都比较常用,需要注意的是,在使用插入或者删除后如果后序还要使用it,需要重写接收一下insert和erase返回的迭代器位置,否则会出现迭代器失效的问题,后面会详细讨论。
void Vector_Test9() { vector<int> vv = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; auto it = vv.begin(); vv.insert(it,5); vv.insert(it, 5); vv.insert(it, 5); vv.insert(it, 5); it++; *it = 10; }
查找接口统一使用算法中(algorithm)的查找,vector容器中并没有提供查找接口。
模拟实现
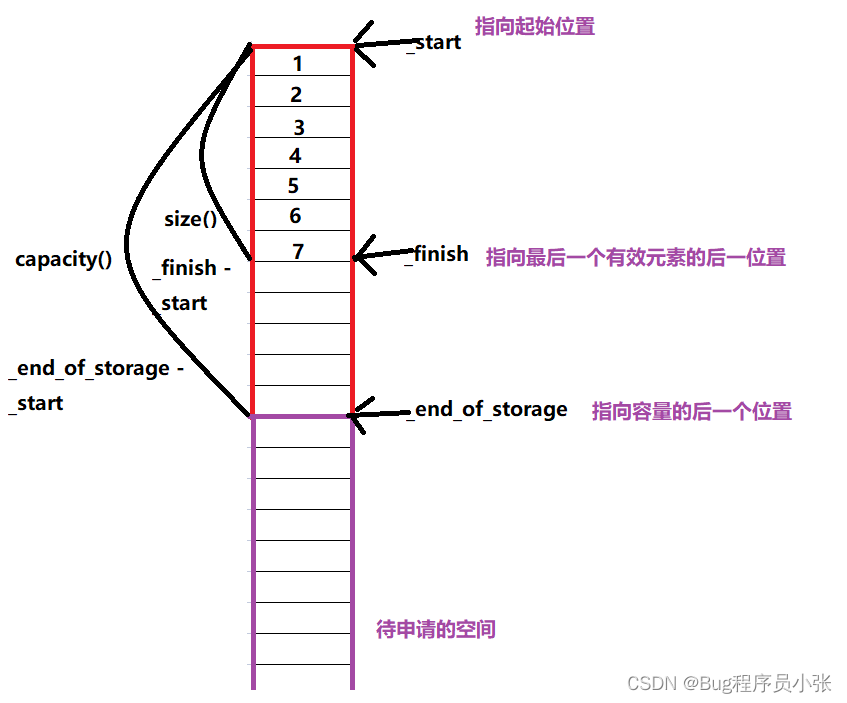
模拟实现要点图解
整体代码
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
iterator being()
{
return _start;
}
iterator end()
{
return _finish;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _start;
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _finish;
}
T& operator[](size_t pos)
{
return _start[pos];
}
T& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
return _start[pos];
}
//无参构造
vector()
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _end_of_storage(nullptr)
{}
//初始化n个val
vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
vector(int n, const T & val = T())
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
//代代器区间
template <class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
//拷贝构造
vector(const vector<T>& v)
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _end_of_storage(nullptr)
{
//调用构造
vector<T> tmp(v.begin(),v.end());
//将构造好的交换给this
swap(tmp);
}
//赋值,这里不能给引用,不然赋值变成交换
vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v)
{
swap(v);
return *this;
}
//析构
void swap(vector<T>& v)
{
std::swap(_start,v._start);
std::swap(_finish, v._finish);
std::swap(_end_of_storage,v._end_of_storage);
}
~vector()
{
delete[] _start;
_start = _finish = _end_of_storage = nullptr;
}
//扩容
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
//扩容
T* tmp = new T[n];
size_t oldsize = size();
if (_start)
{
//浅拷贝
//memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * oldsize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < oldsize; i++)
{
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start;
}
//_start的地址变成了新的
_start = tmp;
_finish = tmp + oldsize;//_finish的计算要注意
_end_of_storage = tmp + n;
}
}
//调整size
void resize(size_t n, T val = T())
{
if(n>capacity())
{
//扩容
reserve(n);
}
if (n > size())
{
//填数据
while (_finish < _start + n)
{
* _finish = val;
++_finish;
}
}
else
{
//删除数据
_finish = _start + n;
}
}
//返回容量
size_t capacity() const
{
return _end_of_storage - _start;
}
//返回size
size_t size() const
{
return _finish - _start;
}
//尾插
void push_back(const T& val)
{
if (_finish == _end_of_storage)
{
//扩容
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity();
reserve(newcapacity);
_end_of_storage = _start + newcapacity;
}
*_finish = val;
_finish++;
}
//尾删
void pop_back()
{
assert(size()>0);
--_finish;
}
//迭代器失效问题
//插入
iterator insert(iterator pos,const T& val)
{
assert(pos >= _start);
assert(pos <= _finish);
if (_finish == _end_of_storage)
{
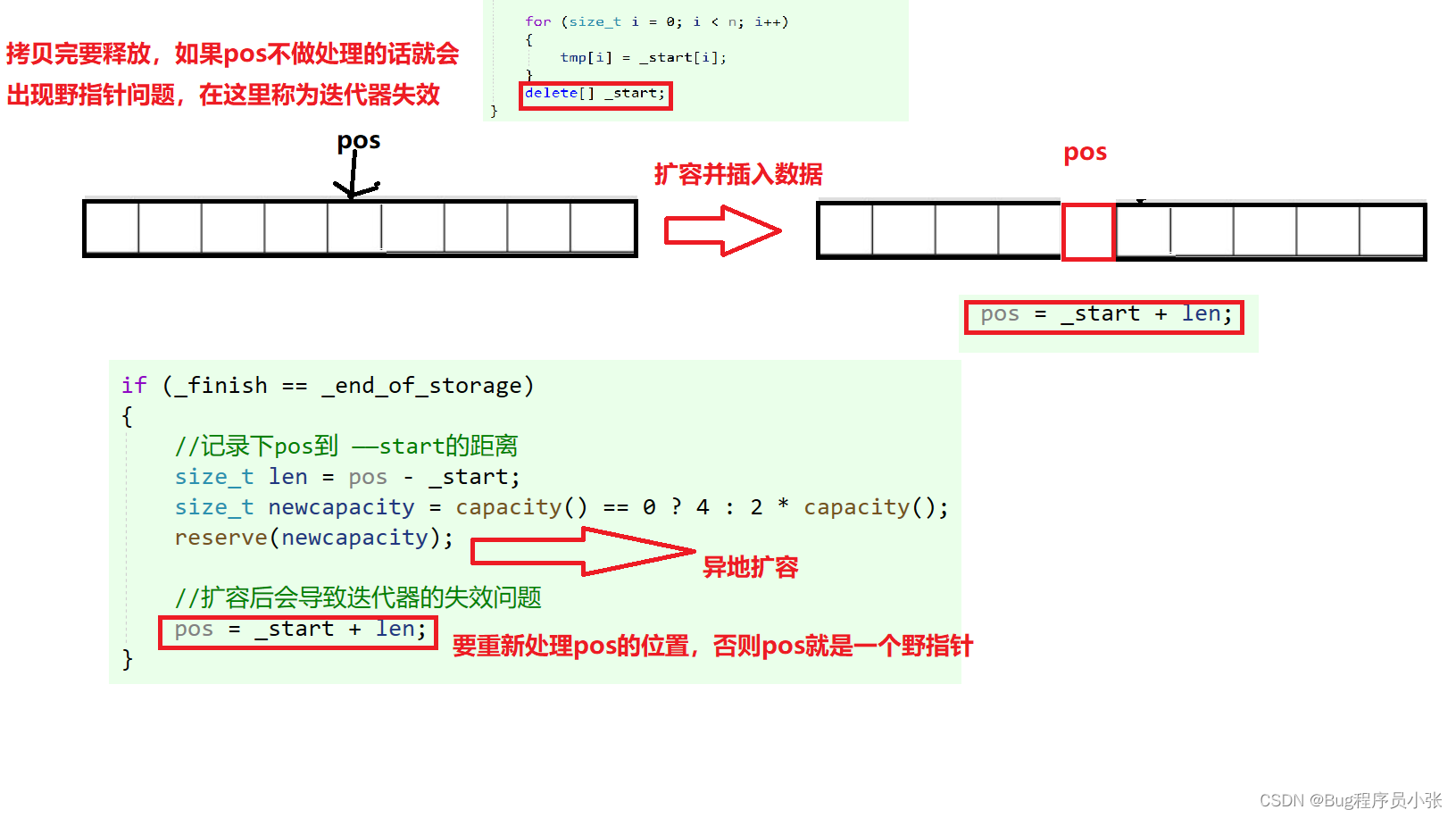
//记录下pos到 ——start的距离
size_t len = pos - _start;
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity();
reserve(newcapacity);
//扩容后会导致迭代器的失效问题
pos = _start + len;
}
//向后挪动数据
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end+1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = val;
++_finish;
return pos;
}
//删除
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos >= _start);
assert(pos < _finish);
iterator begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < _finish)
{
*(begin - 1) = *(begin);
++begin;
}
--_finish;
return pos;
}
//清除数据
void clear()
{
_finish = _start;
}
//判断空
bool empty() const
{
return _start == _finish;
}
private:
iterator _start;
iterator _finish;
iterator _end_of_storage;
};迭代器失效问题
内部失效
外部失效
int main()
{
vector<int> vv;
auto it = vv.begin();
vv.insert(it, 1);
//读
cout << *it << endl;
//cout << (*it)++ << endl;
return 0;
}上述代码中用的是库中的vector,但是同样存在迭代器失效的问题,调用insert接口插入数据后会发生扩容,外部迭代器指向的空间已经被释放了,此时该迭代器已经失效了,当对该位置进行读写操作时就会出现错误!
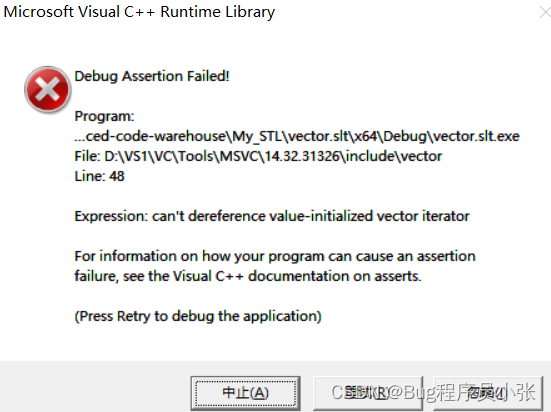
如果仍然要再次使用it的话,在使用前对it重新赋值就好了。
深浅拷贝问题
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
//扩容
T* tmp = new T[n];
size_t oldsize = size();
if (_start)
{
//浅拷贝
//memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * oldsize);
delete[] _start;
}
//_start的地址变成了新的
_start = tmp;
_finish = tmp + oldsize;//_finish的计算要注意
_end_of_storage = tmp + n;
}
}void testcopy()
{
zxy::vector<string> v1;
string ss("abc");
v1.push_back(ss);
v1.push_back(ss);
v1.push_back(ss);
v1.push_back(ss);
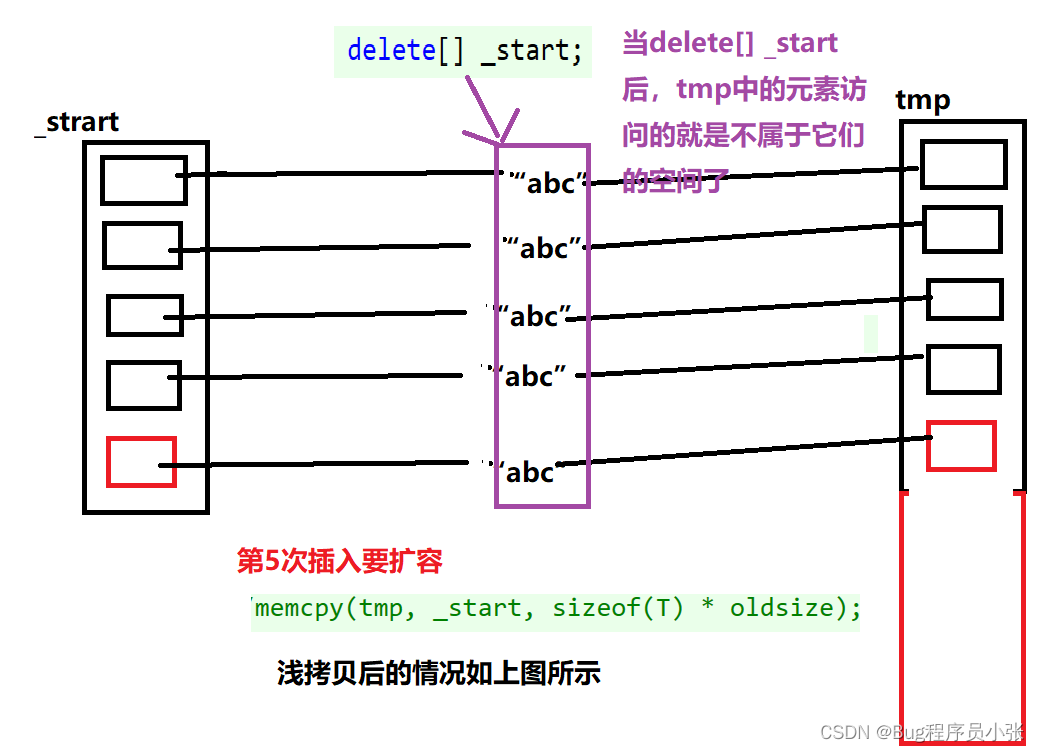
//第5次插入发生扩容
v1.push_back(ss);
}
问题分析:
当第5次插入数据,发生了扩容。string是自定义类型,并且有资源的申请。浅拷贝完成后,手动的delete[] _start。当析构函数调用时会在次释放该空间,所以这里不能用浅拷贝。
解决办法:换成深拷贝
//扩容
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
//扩容
T* tmp = new T[n];
size_t oldsize = size();
if (_start)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < oldsize; i++)
{
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start;
}
//_start的地址变成了新的
_start = tmp;
_finish = tmp + oldsize;//_finish的计算要注意
_end_of_storage = tmp + n;
}
}