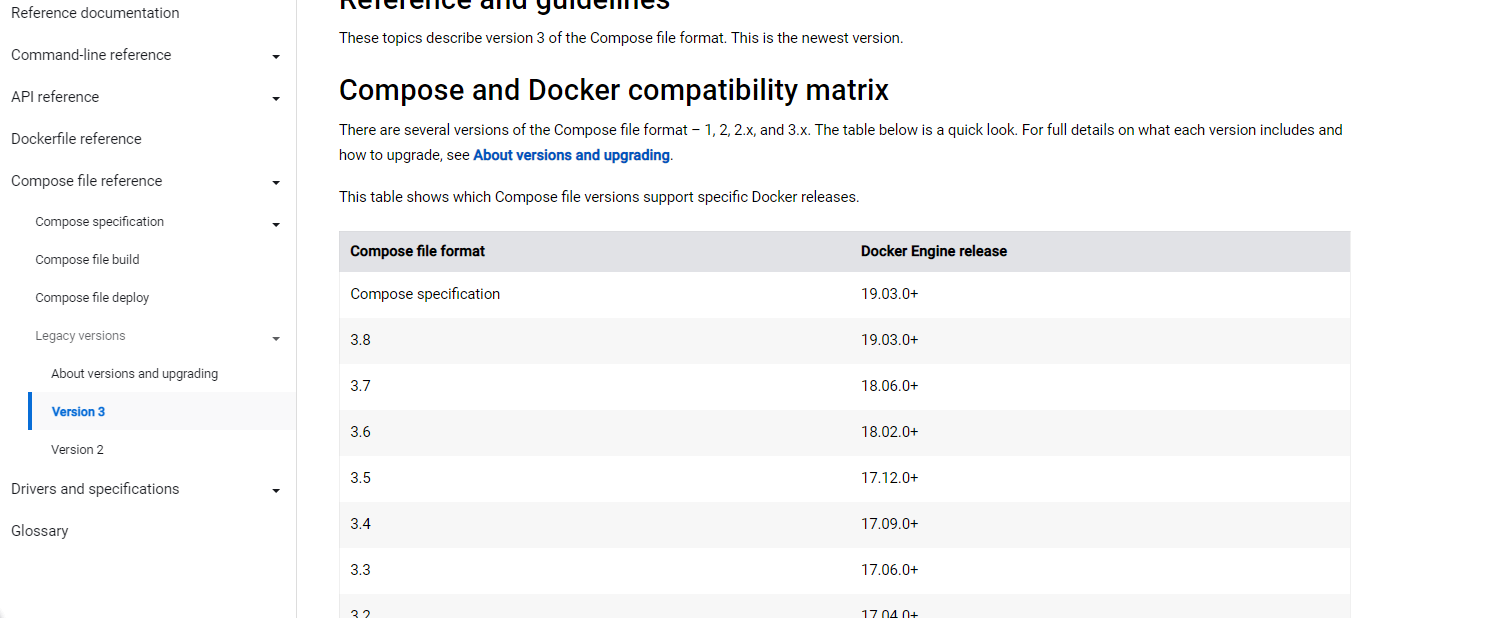
前言
Activity是Android中一个很重要的概念,堪称四大组件之首,关于Activity有很多内容,比如生命周期和启动Flags,这二者想要说清楚,恐怕又要写两篇长文,更何况分析它们的源码呢。不过本文的侧重点不是它们,我要介绍的是一个Activity典型的启动过程,本文会从源码的角度对其进行分析。我们知道,当startActivity被调用的时候,可以启动一个Activity,但是你知道这个Activity是如何被启动的吗?每个Activity也是一个对象,你知道这个对象是啥时候被创建的吗(也就是说它的构造方法是什么时候被调用的)?为什么onCreate是Activity的执行入口?所有的这一切都被系统封装好了,对我们来说是透明的,我们使用的时候仅仅是传递一个intent然后startActivity就可以达到目的了,不过,阅读了本文以后,你将会了解它的背后到底做了哪些事情。在分析之前,我先介绍几个类:
- Activity:这个大家都熟悉,startActivity方法的真正实现在Activity中
- Instrumentation:用来辅助Activity完成启动Activity的过程
- ActivityThread(包含ApplicationThread + ApplicationThreadNative + IApplicationThread):真正启动Activity的实现都在这里。
源码分析
首先看入口
code:Activity#startActivity
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
startActivity(intent, null);
}
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) {
startActivityForResult(intent, requestCode, null);
}
说明:显然,从上往下,最终都是由startActivityForResult来实现的
接着看
code:Activity#startActivityForResult
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
//一般的Activity其mParent为null,mParent常用在ActivityGroup中,ActivityGroup已废弃
if (mParent == null) {
//这里会启动新的Activity,核心功能都在mMainThread.getApplicationThread()中完成
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
//发送结果,即onActivityResult会被调用
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode, ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
if (requestCode = 0) {
// If this start is requesting a result, we can avoid making
// the activity visible until the result is received. Setting
// this code during onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) or onResume() will keep the
// activity hidden during this time, to avoid flickering.
// This can only be done when a result is requested because
// that guarantees we will get information back when the
// activity is finished, no matter what happens to it.
mStartedActivity = true;
}
final View decor = mWindow != null ? mWindow.peekDecorView() : null;
if (decor != null) {
decor.cancelPendingInputEvents();
}
// TODO Consider clearing/flushing other event sources and events for child windows.
} else {
//在ActivityGroup内部的Activity调用startActivity的时候会走到这里,内部处理逻辑和上面是类似的
if (options != null) {
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this method for compatibility with
// existing applications that may have overridden it.
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode);
}
}
}
说明:上述代码关键点都有注释了,可以发现,真正打开activity的实现在Instrumentation的execStartActivity方法中,去看看
code:Instrumentation#execStartActivity
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
//核心功能在这个whoThread中完成,其内部scheduleLaunchActivity方法用于完成activity的打开
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
synchronized (mSync) {
//先查找一遍看是否存在这个activity
final int N = mActivityMonitors.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
final ActivityMonitor am = mActivityMonitors.get(i);
if (am.match(who, null, intent)) {
//如果找到了就跳出循环
am.mHits++;
//如果目标activity无法打开,直接return
if (am.isBlocking()) {
return requestCode = 0 ? am.getResult() : null;
}
break;
}
}
}
}
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess();
//这里才是真正打开activity的地方,核心功能在whoThread中完成。
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, null, options);
//这个方法是专门抛异常的,它会对结果进行检查,如果无法打开activity,
//则抛出诸如ActivityNotFoundException类似的各种异常
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}
说明:我想再说一下这个方法checkStartActivityResult,它也专业抛异常的,看代码,相信大家对下面的异常信息不陌生吧,就是它干的,其中最熟悉的非Unable to find explicit activity class莫属了,如果你在xml中没有注册目标activity,此异常将会抛出。
/
*package*/ static void checkStartActivityResult(int res, Object intent) {
if (res = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
switch (res) {
case ActivityManager.START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED:
case ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND:
if (intent instanceof Intent && ((Intent)intent).getComponent() != null)
throw new ActivityNotFoundException(
"Unable to find explicit activity class "
+ ((Intent)intent).getComponent().toShortString()
+ "; have you declared this activity in your AndroidManifest.xml?");
throw new ActivityNotFoundException(
"No Activity found to handle " + intent);
case ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED:
throw new SecurityException("Not allowed to start activity "
+ intent);
case ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT:
throw new AndroidRuntimeException(
"FORWARD_RESULT_FLAG used while also requesting a result");
case ActivityManager.START_NOT_ACTIVITY:
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"PendingIntent is not an activity");
default:
throw new AndroidRuntimeException("Unknown error code "
+ res + " when starting " + intent);
}
}
接下来我们要去看看IApplicationThread,因为核心功能由其内部的scheduleLaunchActivity方法来完成,由于IApplicationThread是个接口,所以,我们需要找到它的实现类,我已经帮大家找到了,它就是ActivityThread中的内部类ApplicationThread,看下它的继承关系:
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative;
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder implements IApplicationThread;
可以发现,ApplicationThread还是间接实现了IApplicationThread接口,先看下这个类的结构

看完ApplicationThread的大致结构,我们应该能够猜测到,Activity的生命周期中的resume、newIntent、pause、stop等事件都是由它触发的,事实上,的确是这样的。这里,我们为了说明问题,仅仅看scheduleLaunchActivity方法
code:ApplicationThread#scheduleLaunchActivity
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
int procState, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo pendingResults,
List<Intent pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward,
String profileName, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, boolean autoStopProfiler) {
updateProcessState(procState, false);
ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
r.token = token;
r.ident = ident;
r.intent = intent;
r.activityInfo = info;
r.compatInfo = compatInfo;
r.state = state;
r.pendingResults = pendingResults;
r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents;
r.startsNotResumed = notResumed;
r.isForward = isForward;
r.profileFile = profileName;
r.profileFd = profileFd;
r.autoStopProfiler = autoStopProfiler;
updatePendingConfiguration(curConfig);
queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}
说明:上述代码很好理解,构造一个activity记录,然后发送一个消息,所以,我们要看看Handler是如何处理这个消息的,现在转到这个Handler,它有个很短的名字叫做H
code:ActivityThread#H
/
/这个类太长,我只帖出了我们用到的部分
private class H extends Handler {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, " handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
//这里处理LAUNCH_ACTIVITY消息类型
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
//这里处理startActivity消息
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
case RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityRestart");
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
handleRelaunchActivity(r);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityPause");
handlePauseActivity((IBinder)msg.obj, false, msg.arg1 != 0, msg.arg2);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
...
}
}
说明:看来还要看handleLaunchActivity
code:ActivityThread#handleLaunchActivity
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
if (r.profileFd != null) {
mProfiler.setProfiler(r.profileFile, r.profileFd);
mProfiler.startProfiling();
mProfiler.autoStopProfiler = r.autoStopProfiler;
}
// Make sure we are running with the most recent config.
handleConfigurationChanged(null, null);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Handling launch of " + r);
//终于到底了,大家都有点不耐烦了吧,从方法名可以看出,
//performLaunchActivity真正完成了activity的调起,
//同时activity会被实例化,并且onCreate会被调用
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
//看到没,目标activity的onResume会被调用
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) {
// The activity manager actually wants this one to start out
// paused, because it needs to be visible but isn't in the
// foreground. We accomplish this by going through the
// normal startup (because activities expect to go through
// onResume() the first time they run, before their window
// is displayed), and then pausing it. However, in this case
// we do -not- need to do the full pause cycle (of freezing
// and such) because the activity manager assumes it can just
// retain the current state it has.
try {
r.activity.mCalled = false;
//同时,由于新activity被调起了,原activity的onPause会被调用
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
// We need to keep around the original state, in case
// we need to be created again. But we only do this
// for pre-Honeycomb apps, which always save their state
// when pausing, so we can not have them save their state
// when restarting from a paused state. For HC and later,
// we want to (and can) let the state be saved as the normal
// part of stopping the activity.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
r.state = oldState;
}
if (!r.activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to pause activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
r.paused = true;
}
} else {
// If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity
// manager to stop us.
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
说明:关于原activity和新activity之间的状态同步,如果大家感兴趣可以自己研究下,因为逻辑太复杂,我没法把所有问题都说清楚,否则就太深入细节而淹没了整体逻辑,研究源码要的就是清楚整体逻辑。下面看最后一个方法,这个方法是activity的启动过程的真正实现。
code:ActivityThread#performLaunchActivity
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// System.out.println("##### [" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "] ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(" + r + ")");
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
//首先从intent中解析出目标activity的启动参数
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//用ClassLoader(类加载器)将目标activity的类通过类名加载进来并调用newInstance来实例化一个对象
//其实就是通过Activity的无参构造方法来new一个对象,对象就是在这里new出来的。
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, r + ": app=" + app
+ ", appName=" + app.getPackageName()
+ ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName()
+ ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir());
if (activity != null) {
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource()
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
//目标activity的onCreate被调用了,到此为止,Activity被启动了,接下来的流程就是Activity的生命周期了,
//本文之前已经提到,其生命周期的各种状态的切换由ApplicationThread内部来完成
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}
总结
相信当你看到这里的时候,你对Activity的启动过程应该有了一个感性的认识。Activity很复杂,特性很多,本文没法对各个细节进行深入分析,而且就算真的对各个细节都进行了深入分析,那文章要有多长啊,还有人有耐心看下去吗?希望本文能够给大家带来一些帮助,谢谢大家阅读。


![[助人为乐]层次分析法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/97cafb8f46bc4bd6830b2387f19d15db.png)

![[Linux]进程控制精讲,简单实现一个shell](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b8dbd2c1012147468d10aa8e81a401e1.png)