基于Jetson Nano板子搭建一个无人车,少不了减速电机驱动轮子滚动,那如何驱动呢?
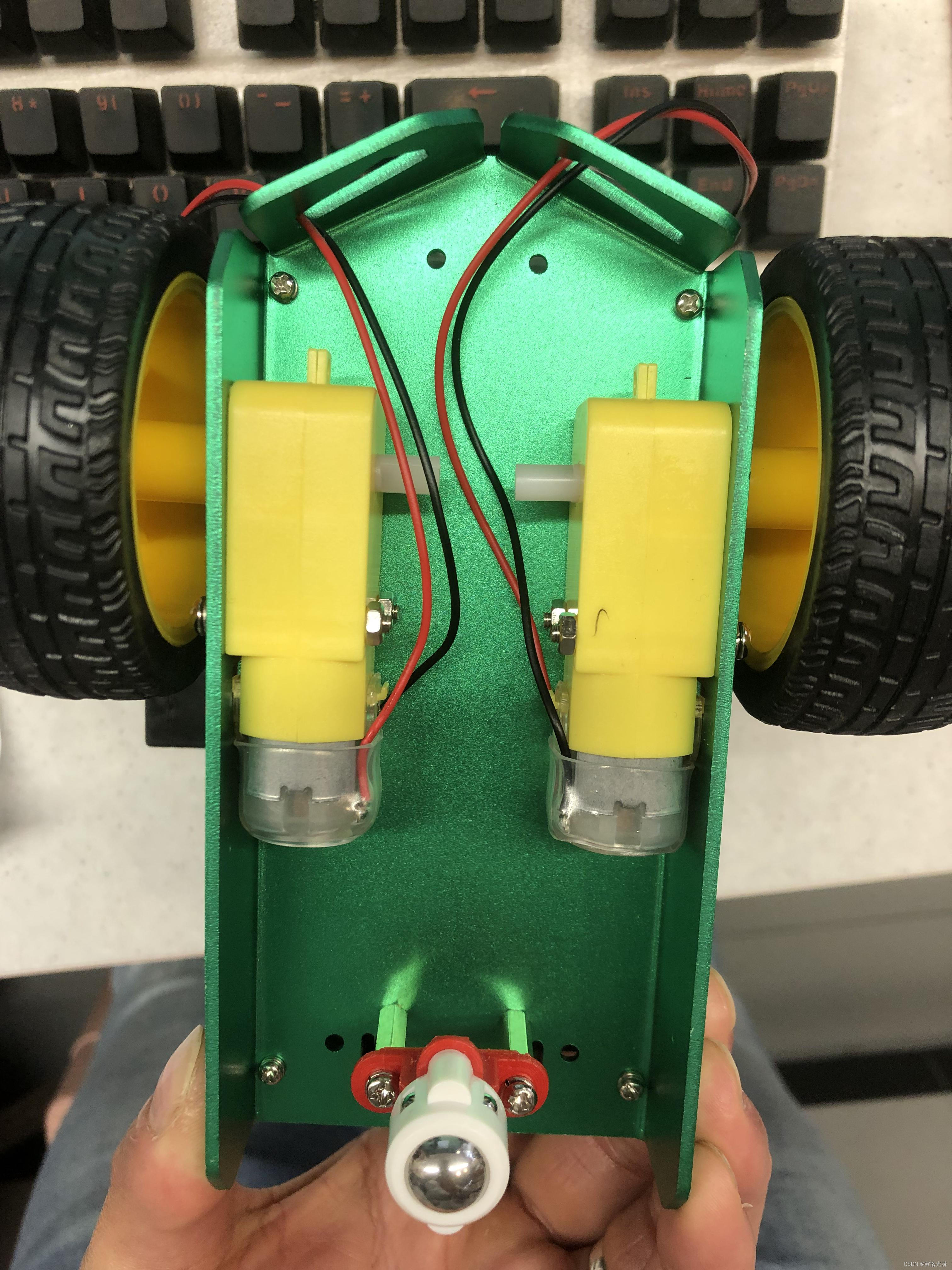
从Jetson.GPIO库文件来说,里面没有支持产生PWM的引脚,也就意味着Jetson nano没有硬件产生PWM的能力,所以我们不得不使用别的方法产生PWM完成驱动控制,而刚好STM8解决了这一问题并且节约了它有限的GPIO资源,我们借助STM8这款MCU作为协处理器,大大增强了Jetson nano的驱动能力,PWM的周期和占空比(在一个脉冲循环内,通电时间相对于总时间所占的比例)都完全可控。
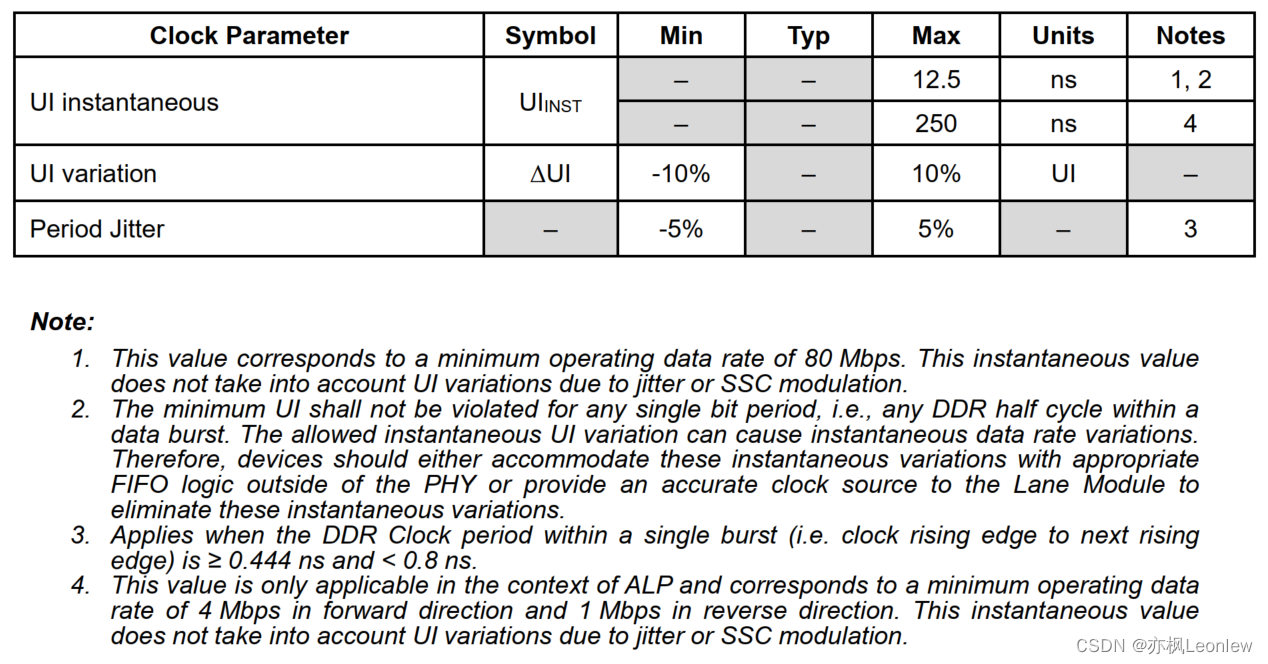
我们来看下它的参数:
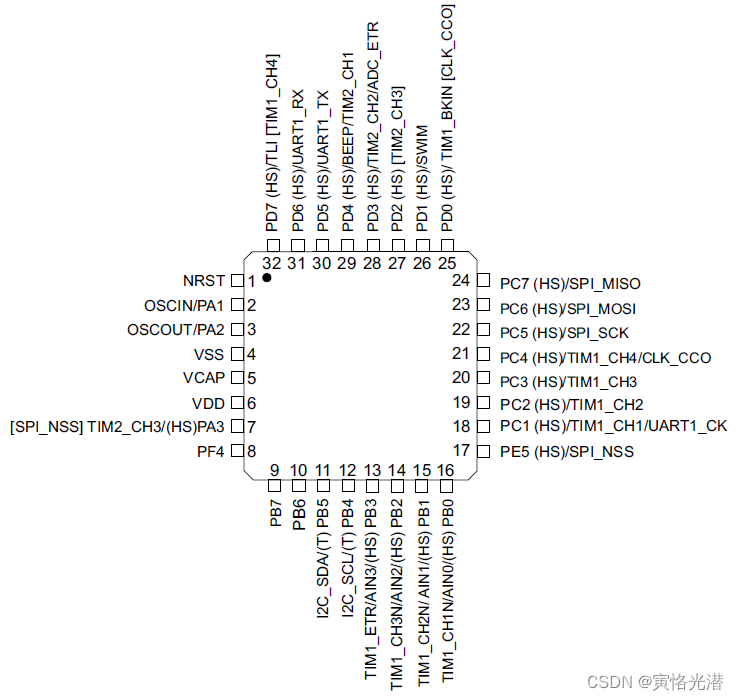
我们使用的是上图所示的QFN20封装的STM8,它主要参数特征如下:
1. I2C接口,支持多路PWM输出
2. 内置16MHz晶振,可不连接外部晶振,也可以连接外部晶振
3. 支持2.95V-5.5V电压,最大耐压值5.5V
4. 具有上电复位,以及软件复位等功能

由上图三极管驱动的有源蜂鸣器电路,而三极管控制引脚接在协处理器可知,开启蜂鸣器只需要通过IIC给协处理器对应的指令即可,下面我们看到通讯协议:

在上一篇文章我们演示的蜂鸣器,我们通过IIC向协处理器(地址0x1B)的寄存器0x06发送1即可打开蜂鸣器,发送0即关闭蜂鸣器
bus.write_byte_data(0x1B,0x06,1或0)
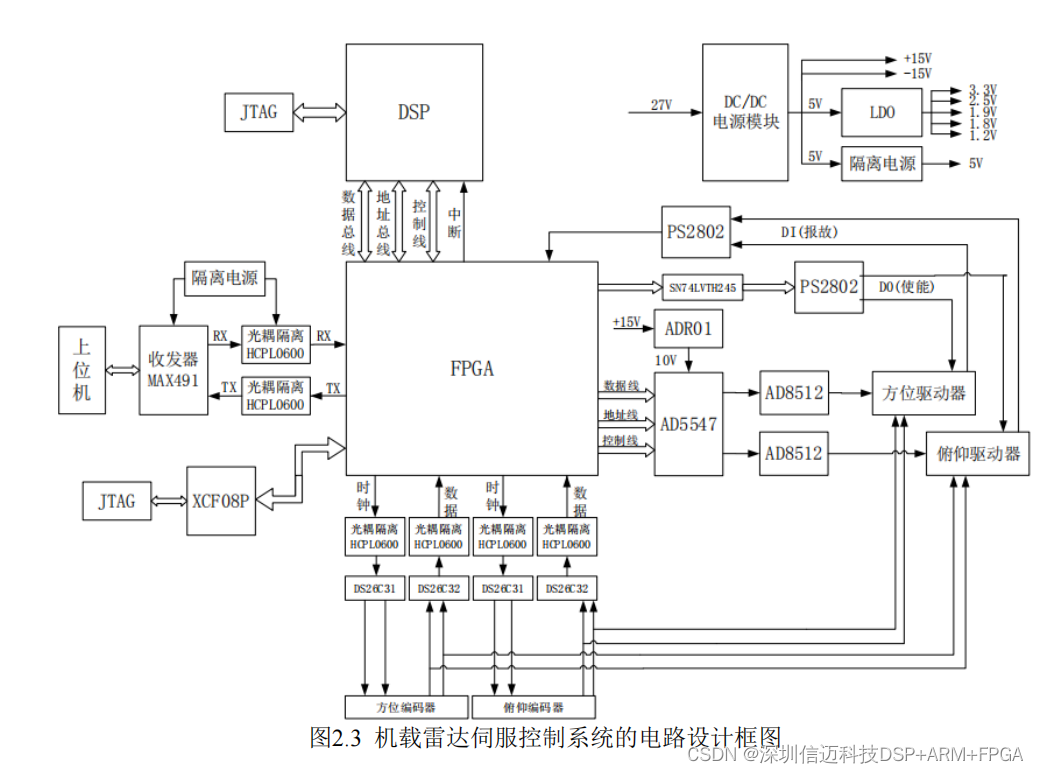
同样的给出两路电机的电路图:
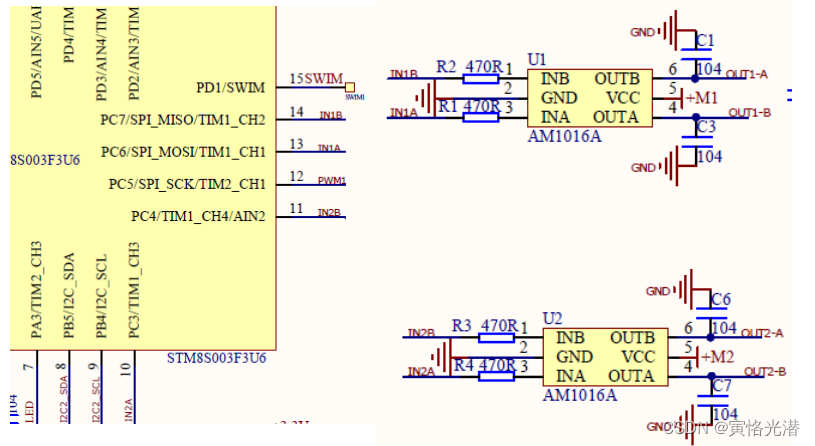
我们来实际驱动电机看下,这里电机控制部分用到了Jetbotmini的库:
from jetbotmini import Robot
import time
robot = Robot()print(dir(robot))
#['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_add_notifiers', '_config_changed', '_cross_validation_lock', '_find_my_config', '_instance', '_load_config', '_log_default', '_notify_trait', '_register_validator', '_remove_notifiers', '_trait_default_generators', '_trait_notifiers', '_trait_validators', '_trait_values', '_walk_mro', 'add_traits', 'backward', 'class_config_rst_doc', 'class_config_section', 'class_get_help', 'class_get_trait_help', 'class_own_trait_events', 'class_own_traits', 'class_print_help', 'class_trait_names', 'class_traits', 'clear_instance', 'config', 'cross_validation_lock', 'forward', 'has_trait', 'hold_trait_notifications', 'i2c_bus', 'initialized', 'instance', 'left', 'left_motor', 'left_motor_alpha', 'left_motor_channel', 'log', 'motor_driver', 'notify_change', 'observe', 'on_trait_change', 'parent', 'right', 'right_motor', 'right_motor_alpha', 'right_motor_channel', 'section_names', 'set_motors', 'set_trait', 'setup_instance', 'stop', 'trait_events', 'trait_metadata', 'trait_names', 'traits', 'unobserve', 'unobserve_all', 'update_config']print(dir(robot.left_motor))
#['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_add_notifiers', '_config_changed', '_cross_validation_lock', '_driver', '_find_my_config', '_load_config', '_motor', '_notify_trait', '_observe_value', '_register_validator', '_release', '_remove_notifiers', '_trait_default_generators', '_trait_notifiers', '_trait_validators', '_trait_values', '_write_value', 'add_traits', 'alpha', 'beta', 'class_config_rst_doc', 'class_config_section', 'class_get_help', 'class_get_trait_help', 'class_own_trait_events', 'class_own_traits', 'class_print_help', 'class_trait_names', 'class_traits', 'config', 'cross_validation_lock', 'has_trait', 'hold_trait_notifications', 'notify_change', 'observe', 'on_trait_change', 'parent', 'section_names', 'set_trait', 'setup_instance', 'trait_events', 'trait_metadata', 'trait_names', 'traits', 'unobserve', 'unobserve_all', 'update_config', 'value']#这个转速的范围是[0,1],不过我设置成0.1也没有转,设置成0.2及以上才转,不知道是不是电量不是很足的原因了。
robot.left_motor.value = 0.8
robot.right_motor.value = 0.8
#这样就可以让电机转动了,很简单,然后做停止电机的操作
robot.left_motor.value = 0
robot.right_motor.value = 0
#或者直接将robot停止也可以
#robot.stop()这段赋值左右马达的意思就是,控制电机速度的值的范围是0~1.0,即代表给出的PWM的占空比为0~100%,所以赋值为0,就是把输出给电机的PWM占空比设置为0,这样就关闭了电机
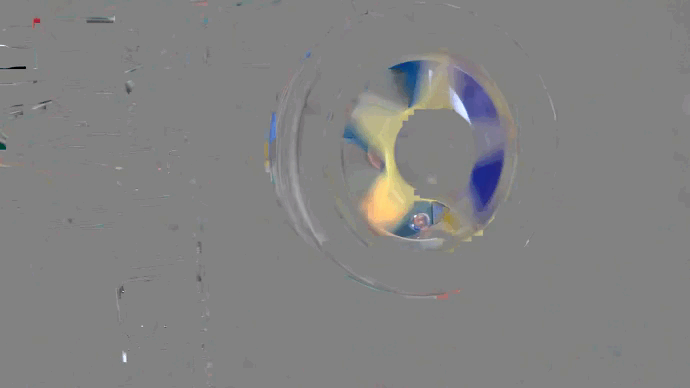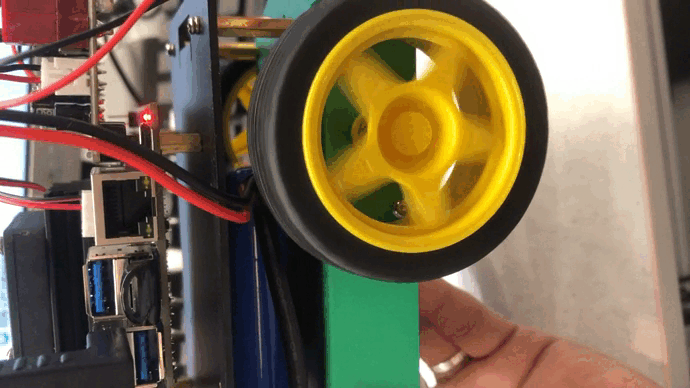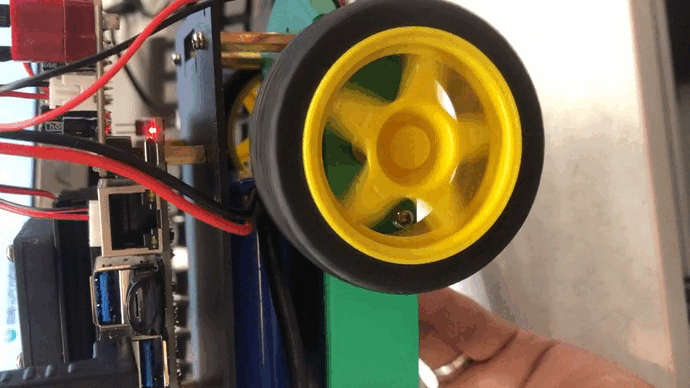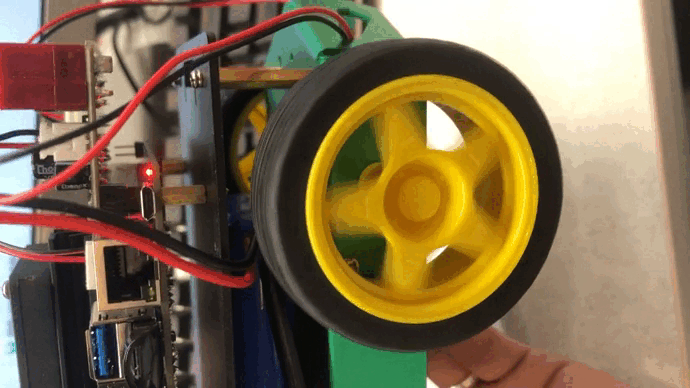
更多的robot实例方法可以自行查阅源码:
Help on Robot in module jetbotmini.robot object:
class Robot(traitlets.config.configurable.SingletonConfigurable)
| A configurable that only allows one instance.
|
| This class is for classes that should only have one instance of itself
| or *any* subclass. To create and retrieve such a class use the
| :meth:`SingletonConfigurable.instance` method.
|
| Method resolution order:
| Robot
| traitlets.config.configurable.SingletonConfigurable
| traitlets.config.configurable.LoggingConfigurable
| traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable
| traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits
| traitlets.traitlets.HasDescriptors
| builtins.object
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, *args, **kwargs)
| Create a configurable given a config config.
|
| Parameters
| ----------
| config : Config
| If this is empty, default values are used. If config is a
| :class:`Config` instance, it will be used to configure the
| instance.
| parent : Configurable instance, optional
| The parent Configurable instance of this object.
|
| Notes
| -----
| Subclasses of Configurable must call the :meth:`__init__` method of
| :class:`Configurable` *before* doing anything else and using
| :func:`super`::
|
| class MyConfigurable(Configurable):
| def __init__(self, config=None):
| super(MyConfigurable, self).__init__(config=config)
| # Then any other code you need to finish initialization.
|
| This ensures that instances will be configured properly.
|
| backward(self, speed=1.0)
|
| forward(self, speed=1.0, duration=None)
|
| left(self, speed=1.0)
|
| right(self, speed=1.0)
|
| set_motors(self, left_speed, right_speed)
|
| stop(self)
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| i2c_bus
| An int trait.
|
| left_motor
| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.
|
| The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.
|
| Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute
|
| left_motor_alpha
| A float trait.
|
| left_motor_channel
| An int trait.
|
| right_motor
| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.
|
| The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.
|
| Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute
|
| right_motor_alpha
| A float trait.
|
| right_motor_channel
| An int trait.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.SingletonConfigurable:
|
| clear_instance() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| unset _instance for this class and singleton parents.
|
| initialized() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Has an instance been created?
|
| instance(*args, **kwargs) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Returns a global instance of this class.
|
| This method create a new instance if none have previously been created
| and returns a previously created instance is one already exists.
|
| The arguments and keyword arguments passed to this method are passed
| on to the :meth:`__init__` method of the class upon instantiation.
|
| Examples
| --------
|
| Create a singleton class using instance, and retrieve it::
|
| >>> from traitlets.config.configurable import SingletonConfigurable
| >>> class Foo(SingletonConfigurable): pass
| >>> foo = Foo.instance()
| >>> foo == Foo.instance()
| True
|
| Create a subclass that is retrived using the base class instance::
|
| >>> class Bar(SingletonConfigurable): pass
| >>> class Bam(Bar): pass
| >>> bam = Bam.instance()
| >>> bam == Bar.instance()
| True
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.LoggingConfigurable:
|
| log
| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.
|
| The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.
|
| Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable:
|
| update_config(self, config)
| Update config and load the new values
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable:
|
| class_config_rst_doc() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Generate rST documentation for this class' config options.
|
| Excludes traits defined on parent classes.
|
| class_config_section() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get the config class config section
|
| class_get_help(inst=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get the help string for this class in ReST format.
|
| If `inst` is given, it's current trait values will be used in place of
| class defaults.
|
| class_get_trait_help(trait, inst=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get the help string for a single trait.
|
| If `inst` is given, it's current trait values will be used in place of
| the class default.
|
| class_print_help(inst=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get the help string for a single trait and print it.
|
| section_names() from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| return section names as a list
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.config.configurable.Configurable:
|
| config
| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.
|
| The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.
|
| Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute
|
| parent
| A trait whose value must be an instance of a specified class.
|
| The value can also be an instance of a subclass of the specified class.
|
| Subclasses can declare default classes by overriding the klass attribute
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits:
|
| __getstate__(self)
|
| __setstate__(self, state)
|
| add_traits(self, **traits)
| Dynamically add trait attributes to the HasTraits instance.
|
| has_trait(self, name)
| Returns True if the object has a trait with the specified name.
|
| hold_trait_notifications(self)
| Context manager for bundling trait change notifications and cross
| validation.
|
| Use this when doing multiple trait assignments (init, config), to avoid
| race conditions in trait notifiers requesting other trait values.
| All trait notifications will fire after all values have been assigned.
|
| notify_change(self, change)
|
| observe(self, handler, names=traitlets.All, type='change')
| Setup a handler to be called when a trait changes.
|
| This is used to setup dynamic notifications of trait changes.
|
| Parameters
| ----------
| handler : callable
| A callable that is called when a trait changes. Its
| signature should be ``handler(change)``, where ``change`` is a
| dictionary. The change dictionary at least holds a 'type' key.
| * ``type``: the type of notification.
| Other keys may be passed depending on the value of 'type'. In the
| case where type is 'change', we also have the following keys:
| * ``owner`` : the HasTraits instance
| * ``old`` : the old value of the modified trait attribute
| * ``new`` : the new value of the modified trait attribute
| * ``name`` : the name of the modified trait attribute.
| names : list, str, All
| If names is All, the handler will apply to all traits. If a list
| of str, handler will apply to all names in the list. If a
| str, the handler will apply just to that name.
| type : str, All (default: 'change')
| The type of notification to filter by. If equal to All, then all
| notifications are passed to the observe handler.
|
| on_trait_change(self, handler=None, name=None, remove=False)
| DEPRECATED: Setup a handler to be called when a trait changes.
|
| This is used to setup dynamic notifications of trait changes.
|
| Static handlers can be created by creating methods on a HasTraits
| subclass with the naming convention '_[traitname]_changed'. Thus,
| to create static handler for the trait 'a', create the method
| _a_changed(self, name, old, new) (fewer arguments can be used, see
| below).
|
| If `remove` is True and `handler` is not specified, all change
| handlers for the specified name are uninstalled.
|
| Parameters
| ----------
| handler : callable, None
| A callable that is called when a trait changes. Its
| signature can be handler(), handler(name), handler(name, new),
| handler(name, old, new), or handler(name, old, new, self).
| name : list, str, None
| If None, the handler will apply to all traits. If a list
| of str, handler will apply to all names in the list. If a
| str, the handler will apply just to that name.
| remove : bool
| If False (the default), then install the handler. If True
| then unintall it.
|
| set_trait(self, name, value)
| Forcibly sets trait attribute, including read-only attributes.
|
| setup_instance(self, *args, **kwargs)
| This is called **before** self.__init__ is called.
|
| trait_metadata(self, traitname, key, default=None)
| Get metadata values for trait by key.
|
| trait_names(self, **metadata)
| Get a list of all the names of this class' traits.
|
| traits(self, **metadata)
| Get a ``dict`` of all the traits of this class. The dictionary
| is keyed on the name and the values are the TraitType objects.
|
| The TraitTypes returned don't know anything about the values
| that the various HasTrait's instances are holding.
|
| The metadata kwargs allow functions to be passed in which
| filter traits based on metadata values. The functions should
| take a single value as an argument and return a boolean. If
| any function returns False, then the trait is not included in
| the output. If a metadata key doesn't exist, None will be passed
| to the function.
|
| unobserve(self, handler, names=traitlets.All, type='change')
| Remove a trait change handler.
|
| This is used to unregister handlers to trait change notifications.
|
| Parameters
| ----------
| handler : callable
| The callable called when a trait attribute changes.
| names : list, str, All (default: All)
| The names of the traits for which the specified handler should be
| uninstalled. If names is All, the specified handler is uninstalled
| from the list of notifiers corresponding to all changes.
| type : str or All (default: 'change')
| The type of notification to filter by. If All, the specified handler
| is uninstalled from the list of notifiers corresponding to all types.
|
| unobserve_all(self, name=traitlets.All)
| Remove trait change handlers of any type for the specified name.
| If name is not specified, removes all trait notifiers.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits:
|
| class_own_trait_events(name) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get a dict of all event handlers defined on this class, not a parent.
|
| Works like ``event_handlers``, except for excluding traits from parents.
|
| class_own_traits(**metadata) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get a dict of all the traitlets defined on this class, not a parent.
|
| Works like `class_traits`, except for excluding traits from parents.
|
| class_trait_names(**metadata) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get a list of all the names of this class' traits.
|
| This method is just like the :meth:`trait_names` method,
| but is unbound.
|
| class_traits(**metadata) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get a ``dict`` of all the traits of this class. The dictionary
| is keyed on the name and the values are the TraitType objects.
|
| This method is just like the :meth:`traits` method, but is unbound.
|
| The TraitTypes returned don't know anything about the values
| that the various HasTrait's instances are holding.
|
| The metadata kwargs allow functions to be passed in which
| filter traits based on metadata values. The functions should
| take a single value as an argument and return a boolean. If
| any function returns False, then the trait is not included in
| the output. If a metadata key doesn't exist, None will be passed
| to the function.
|
| trait_events(name=None) from traitlets.traitlets.MetaHasTraits
| Get a ``dict`` of all the event handlers of this class.
|
| Parameters
| ----------
| name: str (default: None)
| The name of a trait of this class. If name is ``None`` then all
| the event handlers of this class will be returned instead.
|
| Returns
| -------
| The event handlers associated with a trait name, or all event handlers.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasTraits:
|
| cross_validation_lock
| A contextmanager for running a block with our cross validation lock set
| to True.
|
| At the end of the block, the lock's value is restored to its value
| prior to entering the block.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasDescriptors:
|
| __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from traitlets.traitlets.HasDescriptors:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)