视频地址:尚硅谷大数据技术之Scala入门到精通教程(小白快速上手scala)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
- 尚硅谷大数据技术Scala教程-笔记01【Scala课程简介、Scala入门、变量和数据类型、运算符、流程控制】
- 尚硅谷大数据技术Scala教程-笔记02【函数式编程】
- 尚硅谷大数据技术Scala教程-笔记03【面向对象】
- 尚硅谷大数据技术Scala教程-笔记04【集合】
- 尚硅谷大数据技术Scala教程-笔记05【模式匹配、异常、隐式转换、泛型、scala总结】
目录
第08章-模式匹配
P125【125_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(一)_基本概念和用法】10:47
P126【126_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(二)_模式守卫】04:22
P127【127_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(一)_匹配常量】06:03
P128【128_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(二)_匹配类型】07:12
P129【129_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(三)_匹配数组】07:59
P130【130_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(四)_匹配列表】08:56
P131【131_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(五)_匹配元组(一)_基本用法】06:20
P132【132_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(五)_匹配元组(二)_变量声明】05:49
P133【133_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(五)_匹配元组(三)_for推导式中变量】07:30
P134【134_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(六)_匹配对象】10:15
P135【135_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(七)_样例类】04:04
P136【136_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(四)_偏函数】15:50
第09章-异常
P137【137_尚硅谷_Scala_异常处理】08:14
第10章-隐式转换
P138【138_尚硅谷_Scala_隐式转换(一)_基本概念和类型】06:54
P139【139_尚硅谷_Scala_隐式转换(二)_隐式函数和隐式类】07:57
P140【140_尚硅谷_Scala_隐式转换(三)_隐式参数】09:38
第11章-泛型
P141【141_尚硅谷_Scala_泛型(一)_概念和意义】05:56
P142【142_尚硅谷_Scala_泛型(二)_逆变和协变】06:40
P143【143_尚硅谷_Scala_泛型(三)_上下限】06:14
第12章-总结
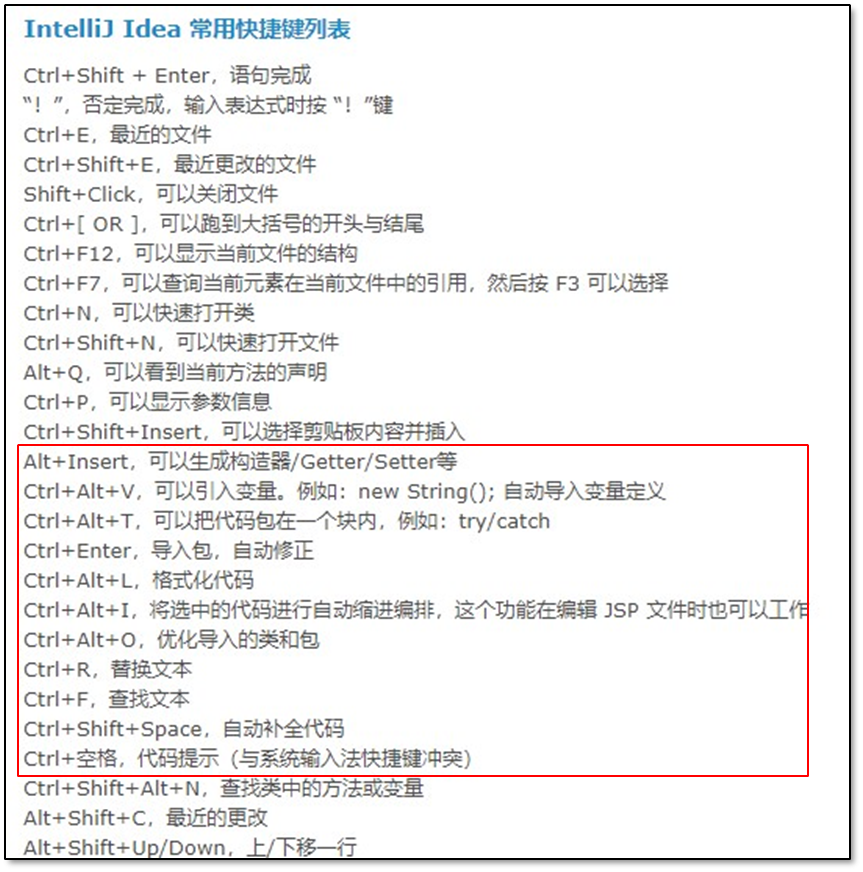
第13章-IDEA快捷键
第08章-模式匹配
P125【125_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(一)_基本概念和用法】10:47
package chapter08
object Test01_PatternMatchBase {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1. 基本定义语法
val x: Int = 5
val y: String = x match {
case 1 => "one"
case 2 => "two"
case 3 => "three"
case _ => "other"
}
println(y) //other
// 2. 示例:用模式匹配实现简单二元运算
val a = 25
val b = 13
def matchDualOp(op: Char): Int = op match {
case '+' => a + b
case '-' => a - b
case '*' => a * b
case '/' => a / b
case '%' => a % b
case _ => -1
}
println(matchDualOp('+')) //38
println(matchDualOp('/')) //1
println(matchDualOp('\\')) //-1
}
}P126【126_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(二)_模式守卫】04:22
package chapter08
object Test01_PatternMatchBase {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 3. 模式守卫
def abs(num: Int): Int = {//求一个整数的绝对值
num match {
case i if i >= 0 => i
case i if i < 0 => -i
}
}
println(abs(67)) //67
println(abs(0)) //0
println(abs(-24)) //24
}
}P127【127_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(一)_匹配常量】06:03
Scala中,模式匹配可以匹配所有的字面量,包括字符串,字符,数字,布尔值等等。
package chapter08
object Test02_MatchTypes {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1. 匹配常量
def describeConst(x: Any): String = x match {
case 1 => "Int one"
case "hello" => "String hello"
case true => "Boolean true"
case '+' => "Char +"
case _ => "~"
}
println(describeConst("hello")) //String hello
println(describeConst('+')) //Char +
println(describeConst(0.3)) //~
}
}P128【128_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(二)_匹配类型】07:12
// 2. 匹配类型
def describeType(x: Any): String = x match {
case i: Int => "Int " + i
case s: String => "String " + s
case list: List[String] => "List " + list
case array: Array[Int] => "Array[Int] " + array.mkString(",")
case a => "Something else: " + a
}
println(describeType(35)) //Int 35
println(describeType("hello")) //String hello
println(describeType(List("hi", "hello"))) //List List(hi, hello)
println(describeType(List(2, 23))) //List List(2, 23)
println(describeType(Array("hi", "hello"))) //Something else: [Ljava.lang.String;@75bd9247
println(describeType(Array(2, 23))) //Array[Int] 2,23P129【129_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(三)_匹配数组】07:59
// 3. 匹配数组
for (arr <- List(
Array(0),
Array(1, 0),
Array(0, 1, 0),
Array(1, 1, 0),
Array(2, 3, 7, 15),
Array("hello", 1, 30),
)) {
val result = arr match {
case Array(0) => "0"
case Array(1, 0) => "Array(1, 0)"
case Array(x, y) => "Array: " + x + ", " + y //匹配两元素数组
case Array(0, _*) => "以0开头的数组"
case Array(x, 1, z) => "中间为1的三元素数组"
case _ => "something else"
}
println(result)
}P130【130_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(四)_匹配列表】08:56
// 4. 匹配列表
// 方式一
for (list <- List(
List(0),
List(1, 0),
List(0, 0, 0),
List(1, 1, 0),
List(88),
List("hello")
)) {
val result = list match {
case List(0) => "0"
case List(x, y) => "List(x, y): " + x + ", " + y
case List(0, _*) => "List(0, ...)"
case List(a) => "List(a): " + a
case _ => "something else"
}
println(result)
}
// 方式二
val list1 = List(1, 2, 5, 7, 24)
val list = List(24)
list match {
case first :: second :: rest => println(s"first: $first, second: $second, rest: $rest")
case _ => println("something else")
}P131【131_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(五)_匹配元组(一)_基本用法】06:20
// 5. 匹配元组
for (tuple <- List(
(0, 1),
(0, 0),
(0, 1, 0),
(0, 1, 1),
(1, 23, 56),
("hello", true, 0.5)
)) {
val result = tuple match {
case (a, b) => "" + a + ", " + b
case (0, _) => "(0, _)"
case (a, 1, _) => "(a, 1, _) " + a
case (x, y, z) => "(x, y, z) " + x + " " + y + " " + z
case _ => "something else"
}
println(result)
}P132【132_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(五)_匹配元组(二)_变量声明】05:49
package chapter08
object Test03_MatchTupleExtend {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1. 在变量声明时匹配
val (x, y) = (10, "hello")
println(s"x: $x, y: $y")
val List(first, second, _*) = List(23, 15, 9, 78)
println(s"first: $first, second: $second")
val fir :: sec :: rest = List(23, 15, 9, 78)
println(s"first: $fir, second: $sec, rest: $rest")
}
}P133【133_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(五)_匹配元组(三)_for推导式中变量】07:30
package chapter08
object Test03_MatchTupleExtend {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
println("=====================1. 在变量声明时匹配")
// 1. 在变量声明时匹配
val (x, y) = (10, "hello")
println(s"x: $x, y: $y")
val List(first, second, _*) = List(23, 15, 9, 78)
println(s"first: $first, second: $second")
val fir :: sec :: rest = List(23, 15, 9, 78)
println(s"first: $fir, second: $sec, rest: $rest")
println("=====================2. for推导式中进行模式匹配")
// 2. for推导式中进行模式匹配
val list: List[(String, Int)] = List(("a", 12), ("b", 35), ("c", 27), ("a", 13))
// 2.1 原本的遍历方式
for (elem <- list) {
println(elem._1 + " " + elem._2)
}
println("-----------------------")
// 2.2 将List的元素直接定义为元组,对变量赋值
for ((word, count) <- list) {
println(word + ": " + count)
}
println("-----------------------")
// 2.3 可以不考虑某个位置的变量,只遍历key或者value
for ((word, _) <- list)
println(word)
println("-----------------------")
// 2.4 可以指定某个位置的值必须是多少
for (("a", count) <- list) {
println(count)
}
}
}P134【134_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(六)_匹配对象】10:15
package chapter08
object Test04_MatchObject {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val student = new Student("alice", 18)
//针对对象实例的内容进行匹配
val result = student match {
case Student("alice", 18) => "alice, 18"
case _ => "Else"
}
println(result)
}
}
//定义类
class Student(val name: String, val age: Int)
//定义伴生对象
object Student {
def apply(name: String, age: Int): Student = new Student(name, age)
//必须实现一个unapply方法,用来对对象属性进行拆解
def unapply(student: Student): Option[(String, Int)] = {
if (student == null) {
None
} else {
Some((student.name, student.age))
}
}
}P135【135_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(三)_模式匹配的不同用法(七)_样例类】04:04
package chapter08
object Test05_MatchCaseClass {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val student = Student1("alice", 18)
//针对对象实例的内容进行匹配
val result = student match {
case Student1("alice", 18) => "Alice, 18"
case _ => "Else"
}
println(result) //Alice, 18
}
}
//定义样例类
case class Student1(name: String, age: Int)P136【136_尚硅谷_Scala_模式匹配(四)_偏函数】15:50
package chapter08
object Test06_PartialFunction {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val list: List[(String, Int)] = List(("a", 12), ("b", 35), ("c", 27), ("a", 13))
// 1. map转换,实现key不变,value2倍
val newList = list.map(tuple => (tuple._1, tuple._2 * 2))
// 2. 用模式匹配对元组元素赋值,实现功能
val newList2 = list.map(
tuple => {
tuple match {
case (word, count) => (word, count * 2)
}
}
)
// 3. 省略lambda表达式的写法,进行简化
val newList3 = list.map {
case (word, count) => (word, count * 2)
}
println(newList) //List((a,24), (b,70), (c,54), (a,26))
println(newList2) //List((a,24), (b,70), (c,54), (a,26))
println(newList3) //List((a,24), (b,70), (c,54), (a,26))
// 偏函数的应用,求绝对值
// 对输入数据分为不同的情形:正、负、0
val positiveAbs: PartialFunction[Int, Int] = {
case x if x > 0 => x
}
val negativeAbs: PartialFunction[Int, Int] = {
case x if x < 0 => -x
}
val zeroAbs: PartialFunction[Int, Int] = {
case 0 => 0
}
def abs(x: Int): Int = (positiveAbs orElse negativeAbs orElse zeroAbs) (x)
println(abs(-67)) //67
println(abs(35)) //35
println(abs(0)) //0
}
}第09章-异常
P137【137_尚硅谷_Scala_异常处理】08:14
package chapter09plus
object Test01_Exception {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
try {
val n = 10 / 0
} catch {
case e: ArithmeticException => {
println("发生算术异常!")
}
case e: Exception => {
println("发生一般异常!")
}
} finally {
println("处理结束!")
}
}
}第10章-隐式转换
P138【138_尚硅谷_Scala_隐式转换(一)_基本概念和类型】06:54
当编译器第一次编译失败的时候,会在当前的环境中查找能让代码编译通过的方法,用于将类型进行转换,实现二次编。
P139【139_尚硅谷_Scala_隐式转换(二)_隐式函数和隐式类】07:57
package chapter09plus
object Test02_Implicit {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val new12 = new MyRichInt(12)
println(new12.myMax(15))
// 1. 隐式函数
implicit def convert(num: Int): MyRichInt = new MyRichInt(num)
println(12.myMax(15))
println("============================")
// 2. 隐式类
implicit class MyRichInt2(val self: Int) {
// 自定义比较大小的方法
def myMax2(n: Int): Int = if (n < self) self else n
def myMin2(n: Int): Int = if (n < self) n else self
}
println(12.myMin2(15))
println("============================")
// 3. 隐式参数
implicit val str: String = "alice"
// implicit val str2: String = "alice2"
implicit val num: Int = 18
def sayHello()(implicit name: String): Unit = {
println("hello, " + name)
}
def sayHi(implicit name: String = "atguigu"): Unit = {
println("hi, " + name)
}
sayHello
sayHi
// 简便写法
def hiAge(): Unit = {
println("hi, " + implicitly[Int])
}
hiAge()
}
}
// 自定义类
class MyRichInt(val self: Int) {
// 自定义比较大小的方法
def myMax(n: Int): Int = if (n < self) self else n
def myMin(n: Int): Int = if (n < self) n else self
}P140【140_尚硅谷_Scala_隐式转换(三)_隐式参数】09:38
package chapter09plus
object Test02_Implicit {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 3. 隐式参数
implicit val str: String = "alice"
// implicit val str2: String = "alice2"
implicit val num: Int = 18
def sayHello()(implicit name: String): Unit = {
println("hello, " + name)
}
def sayHi(implicit name: String = "atguigu"): Unit = {
println("hi, " + name)
}
sayHello
sayHi
// 简便写法
def hiAge(): Unit = {
println("hi, " + implicitly[Int])
}
hiAge()
}
}
第11章-泛型
P141【141_尚硅谷_Scala_泛型(一)_概念和意义】05:56
P142【142_尚硅谷_Scala_泛型(二)_逆变和协变】06:40
package chapter09plus
object Test03_Generics {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1. 协变和逆变
val child: Parent = new Child
//val childList: MyCollection[Parent] = new MyCollection[Child]
val childList: MyCollection[SubChild] = new MyCollection[Child]
}
}
// 定义继承关系
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent {}
class SubChild extends Child {}
// 定义带泛型的集合类型
class MyCollection[-E] {}P143【143_尚硅谷_Scala_泛型(三)_上下限】06:14
package chapter09plus
object Test03_Generics {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 2. 上下限
def test[A <: Child](a: A): Unit = {
println(a.getClass.getName)
}
test[SubChild](new SubChild)
}
}
// 定义继承关系
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent {}
class SubChild extends Child {}
// 定义带泛型的集合类型
class MyCollection[-E] {}第12章-总结
12.1 开发环境
要求掌握必要的 Scala 开发环境搭建技能。
12.2 变量和数据类型
掌握 var 和 val 的区别掌握数值类型(Byte、Short、Int、Long、Float、Double、Char)之间的转换关系
12.3 流程控制
掌握 if-else、for、while 等必要的流程控制结构,掌握如何实现 break、continue 的功能。
12.4 函数式编程
掌握高阶函数、匿名函数、函数柯里化、闭包、函数参数以及函数至简原则。
12.5 面向对象
掌握 Scala 与 Java 继承方面的区别、单例对象(伴生对象)、构造方法、特质的用法及功能。
12.6 集合
掌握常用集合的使用、集合常用的计算函数。
12.7 模式匹配
掌握模式匹配的用法
12.8 下划线
掌握下划线不同场合的不同用法
12.9 异常
掌握异常常用操作即可
12.10 隐式转换
掌握隐式方法、隐式参数、隐式类,以及隐式解析机制
12.11 泛型
掌握泛型语法