目录
A. Yura's New Name(构造)
思路:
代码:
B. JoJo's Incredible Adventures(构造)
思路:
代码:
C. Constructive Problem(思维)
思路:
代码
D. The Butcher(思维,STL)
思路:
代码:
E. The Fox and the Complete Tree Traversal(构造,图的遍历)
思路:
代码:
A. Yura's New Name(构造)
After holding one team contest, boy Yura got very tired and wanted to change his life and move to Japan. In honor of such a change, Yura changed his name to something nice.
Fascinated by this idea he already thought up a name s consisting only of characters "_" and "^". But there's a problem — Yura likes smiley faces "^_^" and "^^". Therefore any character of the name must be a part of at least one such smiley. Note that only the consecutive characters of the name can be a smiley face.
More formally, consider all occurrences of the strings "^_^" and "^^" in the string s. Then all such occurrences must cover the whole string s, possibly with intersections. Forexample, in the string "^^__^_" the characters at positions 3,4,9,10 are not contained inside any smileys, and the other characters at positions 1,2,5,6,7 and 8 are contained inside smileys.
In one operation Jura can insert one of the characters "_" and "^" into his name s (you can insert it at any position in the string). He asks you to tell him the minimum number of operations you need to do to make the name fit Yura's criteria.
Input
Each test consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤100) —the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The first and only line of each test case contains a single string s (1≤|s|≤100), consisting of characters "_" and "^", — the name to change.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer — the minimum number of characters you need to add to the name to make it fit for Yura. If you don't need to change anything in the name, print 00.
Example
input
Copy
7
^______^
___^_^^^_^___^
^_
^
^_^^^^^_^_^^
___^^
_
output
5 5 1 1 0 3 2
Note
In the first test case, you can get the following name by adding 5 characters:
^_^_^_^_^_^_^
In the third test case, we can add one character "^" to the end of the name, then we get the name:
^_^
In the fourth test case, we can add one character "^" to the end of the name, then we get the name:
^^
In the fifth test case, all of the characters are already contained in smiley faces, so the answer is 0.
In the seventh test case, you can add one character "^" at the beginning of the name and one character "^" at the end of the name, then you get the name:
^_^
思路:
就是把每一个_两端都加上^,然后对一个字符特判
从头到尾扫过去,flag=0代表前面_没有^,1表示有
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
string s;
cin>>s;
int ans=0;
bool flag=0;
if(s=="^"){ //特判
cout<<1<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s[i]=='^'){ //标记当前有^
flag=1;
continue;
}
else{
if(flag==1){ //遇到_,标记清空
flag=0;
continue;
}
else{ //如果没标记说明要加一个^
ans++;
}
}
}
if(flag==0)ans++; //最后没有^的话要补一个
cout<<ans<<endl;
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. JoJo's Incredible Adventures(构造)
Did you think there was going to be a JoJo legend here? But no, that was me, Dio!
Given a binary string s of length n, consisting of characters 0 and 1. Let's build a square table of size n×n, consisting of 0 and 1 characters as follows.
In the first row of the table write the original string s. In the second row of the table write cyclic shift of the string s by one to the right. In the third row of the table, write the cyclic shift of line s by two to the right. And so on. Thus, the row with number k will contain a cyclic shift of string s by k to the right. The rows are numbered from 0 to n−1 top-to-bottom.
In the resulting table we need to find the rectangle consisting only of ones that has the largest area.
We call a rectangle the set of all cells (i,j)in the table, such that x1≤i≤x2and y1≤j≤y2for some integers 0≤x1≤x2<n and 0≤y1≤y2<n.
Recall that the cyclic shift of string s by k to the right is the string sn−k+1…sns1s2…sn−k. For example, the cyclic shift of the string "01011" by 00 to the right is the string itself "01011", its cyclic shift by 33 to the right is the string "01101".
Input
Each test consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤2⋅104) — the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The first and the only line of each test case contains a single binary string s (1≤|s|≤2⋅105), consisting of characters 0 and 1.
It is guaranteed that the sum of string lengths |s| over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105
Output
For each test case, output a single integer — the maximum area of a rectangle consisting only of ones. If there is no such rectangle, output 00.
Example
input
5
0
1
101
011110
101010
output
0 1 2 6 1
Note
In the first test case, there is a table 1×1 consisting of a single character 0, so there are no rectangles consisting of ones, and the answer is 00.
In the second test case, there is a table 1×1, consisting of a single character 1, so the answer is 11.
In the third test case, there is a table:
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
In the fourth test case, there is a table:
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
In the fifth test case, there is a table:
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Rectangles with maximum area are shown in bold.
思路:
给一个01串,错位排列成一个n*n矩阵,下一行是上一行右移一位形成的,找出矩阵中最大的1构成的矩形
我们将01串连续写两边,找新串的最长的连续的1的个数,如果为2*n说明全是1,否则一定小于n,然后排成一个等腰直角三角形,求包含的最大矩形,均值不等式即可
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
string s;
cin>>s;
ll siz=s.length();
s=s+s;
ll num=0;
ll cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s[i]=='1'){
cnt++;
num=max(cnt,num); //记录最多的连续1的个数
}
else cnt=0; //遇0清0
}
if(num==0){ //特判全是0
cout<<0<<endl;
return;
}
if(num==1){ //特判一个1
cout<<1<<endl;
return;
}
if(num>=siz){ //特判全是1
ll ans=siz*siz;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return;
}
num++;
ll ans=(num/2)*(num-num/2); //两者越接近,面积越大
cout<<ans<<endl;
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. Constructive Problem(思维)
As you know, any problem that does not require the use of complex data structures is considered constructive. You are offered to solve one of such problems.
You are given an array a of n non-negative integers. You are allowed to perform the following operation exactly once: choose some non-empty subsegment al,al+1,…,arof the array a and a non-negative integer k, and assign value k to all elements of the array on the chosen subsegment.
The task is to find out whether MEX(a)can be increased by exactly one by performing such an operation. In other words, if before the operation MEX(a)=m held, then after the operation it must hold that MEX(a)=m+1.
Recall that MEXMEX of a set of integers c1,c2,…,ck is defined as the smallest non-negative integer x which does not occur in the set c.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤50000) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤200000) — the number of elements of array .
The second line of each test case contains n integers a1,a2,…,an (0≤ai≤109) — elements of array a.
It is guaranteed that the sum n over all test cases does not exceed 200000.
Output
For each test case, print "Yes" if you can increase MEX(a) by exactly one by performing the operation from the statement exactly once, otherwise print "No".
You can output the answer in any case (upper or lower). For example, the strings "yEs", "yes", "Yes", and "YES" will be recognized as positive responses.
Example
input
4
3
1 2 1
4
0 2 2 0
4
3 2 0 2
1
0
output
Yes Yes No No
Note
In the first test case, MEX(a)=0 If you set all elements of a to 00, then MEXMEX of the resulting array will be 11, and thus will increase by one.
In the second test case, MEX(a)=1. If we assign a value of 1 to the elements of a on a subsegment from 22 to 33, we get an array [0,1,1,0] for which MEX is 2, and thus is increased by one compared to the original.
It can be shown that in the third and fourth test cases it is impossible to perform an operation so that the value of MEX(a)increases by exactly one.
思路:
给你一个数组,记录没出现过的最小自然数,看能不能选定一个区间,进行区间改变为某值,使没出现过的最小自然数加一
如果0没出现过,则全变为0
如果最小没出现过的数为n,一定是单调递增的等差数列,不可能使没出现的数变成n+1
如果最小没出现过的数+1也没出现过,把一个出现过的变成x即可
否则一定是x没出现,x+1出现,找x+1出现的第一个位置和最后一个位置,如果中间的所有小于x的数在其他位置都出现过,一定可以将区间全部改成x而最小没出现过的数不下降
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
ll n;
cin>>n;
vector<ll>a(n+1),b(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i]; //a用来对应原来的位置
b[i]=a[i]; //b用来排序
}
sort(b.begin()+1,b.end());
if(b[1]!=0){ //如果0没出现过,全部置0
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
return;
}
int pos=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if((b[i]==b[i-1])||(b[i]==(b[i-1]+1)))continue;
pos=i; //pos为第一个间距大于1的位置
break; //x=b[pos-1]
}
if(pos==0){ //间距不大于1
cout<<((b[n]==n-1)?"NO\n":"YES\n"); //若间距为1则不行
return;
}
ll x1=b[pos-1],x2=b[pos]; //现为x1+1,目标x1+2
if(x1+2<x2){ //如果x+1没出现过,一定可以
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
return;
}
int ff=-1; //ff标记x+1在原数组中第一次出现的位置
set<ll>ss; //查看修改区间内的元素是否出现过
vector<ll>tmp; //储存修改区间内的元素
int pp=-1; //pp标记最后一次出现的位置
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(ff==-1){
if(a[i]==x2){ //找到第一个x+1
ff=i;
continue;
}
else{ //没出现过,放入集合
ss.insert(a[i]);
}
}
else{ //修改区间内
if(a[i]==x2){
pp=i;
continue;
}
else{ //储存区间内要判断的元素
tmp.push_back(a[i]);
}
}
}
if(pp==-1){ //只出现过一次,直接改成x
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=n;i>pp;i--){ //最后一次出现后面的元素也放入集合
ss.insert(a[i]);
}
bool flag=1;
for(int i=0;i<tmp.size();i++){
if(tmp[i]>x2)continue; //大于x2的不用管
if(ss.count(tmp[i]))continue;
flag=0; //如果有没出现过的比x小的数,一定不能修改
break;
}
cout<<((flag)?"YES\n":"NO\n");
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ll T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D. The Butcher(思维,STL)
Anton plays his favorite game "Defense of The Ancients 2" for his favorite hero — The Butcher. Now he wants to make his own dinner. To do this he will take a rectangle of height hℎ and width w, then make a vertical or horizontal cut so that both resulting parts have integer sides. After that, he will put one of the parts in the box and cut the other again, and so on.
More formally, a rectangle of size h×w can be cut into two parts of sizes x×w and (h−x)×w, where xis an integer from 11 to (h−1)(ℎ−1), or into two parts of sizes h×y and h×(w−y), where y is an integer from 11 to (w−1)
He will repeat this operation n−1 times, and then put the remaining rectangle into the box too. Thus, the box will contain n rectangles, of which n−1rectangles were put in the box as a result of the cuts, and the n-th rectangle is the one that the Butcher has left after all n−1 cuts.
Unfortunately, Butcher forgot the numbers hℎ and w, but he still has n rectangles mixed in random order. Note that Butcher didn't rotate the rectangles, but only shuffled them. Now he wants to know all possible pairs (h,w) from which this set of rectangles can be obtained. And you have to help him do it!
It is guaranteed that there exists at least one pair (h,w) from which this set of rectangles can be obtained.
Input
Each test consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤2⋅105) — the number of rectangles obtained.
The i-th of the next n lines contains two integers ai and bi (1≤ai,bi≤106) — the height and width of the i-th rectangle.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, on the first line output a single integer m — the number of pairs (h,w) denoting the sizes of rectangles from which the given rectangles can be obtained. Two rectangles are considered different if they have different heights or widths.
On each of the following m lines print output integers hi and wi— the height and width of the rectangle from which the given rectangles can be obtained. You can output the rectangles in any order.
Example
input
4
3
1 2
3 5
1 3
3
1 1
1 1
1 1
1
10 10
4
3 2
5 5
2 2
8 7
output
1 4 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 10 10 1 13 7
Note
In the first test case, Butcher could only have a rectangle of size 4×54×5. Then the cuts could look like this (first the green cut was made, then the red one):
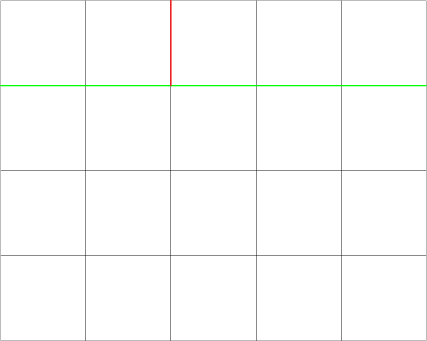
In the second test case, Butcher could have either a rectangle of 1×3 or 3×1. The cuts would have looked like this (first the green cut was made, then the red cut):
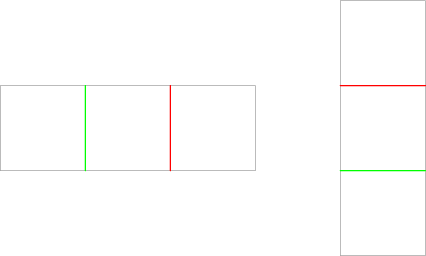
In the third test case, Butcher did not make any cuts, so the rectangle is 10×10.
思路:
给一个矩形,每次切一刀,然后拿其中一份继续切,一个切n-1刀,把切好的个矩形大乱,求原来没切时候的长和宽
找出切好的最大的长和最大的宽,其中一个一定是原来的长或原来的宽,若不能被总面积整除则一定不是。
然后判断以这两个值为长或宽的矩形能否切出这n个矩形即可
判断方法为,从最初的矩形开始,维护一个剩余的矩形,若矩形的长等于剩余矩形最长的长边或宽等于剩余矩形最宽的宽边时,切去这个最大的矩形,如果找不到可以切的矩形,则当前矩形不合法
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
bool check(vector<pair<ll,ll> >aa,ll w,ll d){
multiset<pair<ll,ll> >s1,s2; //把矩形储存起来并排序,方便每次找到最小的并删去
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
s1.insert(make_pair(aa[i].first,aa[i].second)); //s1按长度递增
s2.insert(make_pair(aa[i].second,aa[i].first)); //s2按宽度递增
}
bool flag=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
auto pos=prev(s1.end()); //pos为长度最长的矩形
if(pos->first==w){
d-=pos->second; //维护的矩形的宽度减去当前切出来矩形的宽度
s2.erase(s2.find(make_pair(pos->second,pos->first))); //在s2里找见并删去这个矩形
s1.erase(pos); //删去这个矩形
continue;
}
pos=prev(s2.end()); //pos为宽度最宽的矩形
if(pos->first==d){
w-=pos->second; //同理,切去长度
s1.erase(s1.find(make_pair(pos->second,pos->first)));
s2.erase(pos);
continue;
}
flag=0; //如果长度和宽度都不符合,切不出来n-1个矩形,不合法
break;
}
return flag;
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
ll sum=0;
vector<pair<ll,ll> >a(n+1);
ll max1=-1,max2=-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ll w,d;
cin>>w>>d;
sum+=w*d; //计算最初矩形的面积
max1=max(max1,w); //找见最大的长
max2=max(max2,d); //找见最大的宽
a[i]=make_pair(w,d);
}
set<pair<ll,ll> >ans;
if(sum%max1==0&&check(a,max1,sum/max1))ans.emplace(max1,sum/max1); //如果能构成矩形,则输出
if(sum%max2==0&&check(a,sum/max2,max2))ans.emplace(sum/max2,max2);
cout<<ans.size()<<endl; //输出答案
for(auto it:ans){
cout<<it.first<<' '<<it.second<<endl;
}
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E. The Fox and the Complete Tree Traversal(构造,图的遍历)
The fox Yae climbed the tree of the Sacred Sakura. A tree is a connected undirected graph that does not contain cycles.
The fox uses her magical powers to move around the tree. Yae can jump from vertex v to another vertex u if and only if the distance between these vertices does not exceed 22. In other words, in one jump Yae can jump from vertex v to vertex u if vertices v and u are connected by an edge, or if there exists such vertex w that vertices v and w are connected by an edge, and also verticesv and w are connected by an edge.
After Yae was able to get the sakura petal, she wondered if there was a cyclic route in the tree v1,v2,…,vn such that:
- the fox can jump from vertex vi to vertex vi+1,
- the fox can jump from vertex vn to vertex v1,
- all vi are pairwise distinct.
Help the fox determine if the required traversal exists.
Input
The first line contains one integer n (2≤n≤2⋅105) —the number of vertices of the tree.
Each of the following n−1 lines contains two integers u and v (1≤u,v≤n, u≠v) — vertices connected by an edge. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree.
Output
On the first line, print "Yes" (without quotes) if the required route of the tree exists, or "No" (without quotes) otherwise.
If the required tree traversal exists, on the second line print n integers of different integers v1,v2,…,vn (1≤vi≤n) — the vertices of the tree in traversal order.
If there are several correct traversals, output any of them.
Examples
input
5 1 2 1 3 3 4 3 5
output
Yes 4 5 1 2 3
input
3 1 2 1 3
output
Yes 1 2 3
input
15 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 3 6 3 7 4 8 4 9 5 10 5 11 6 12 6 13 7 14 7 15
output
No
Note
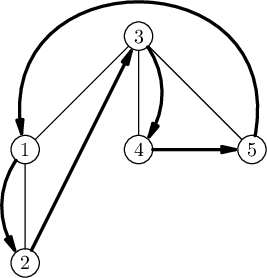
The tree from the first example is shown below. The bold arrows indicate the fox's route.
In the second example, any sequence of three different vertices is a correct route, because the fox can jump from any vertex to any vertex.
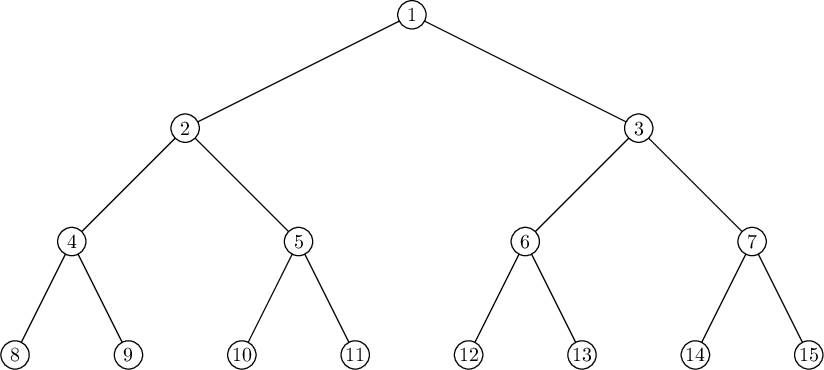
The tree from the third example is shown below. It can be shown that there is no required route for it.
思路:
给一颗n个点的树,从任意点开始,每步走1格或2格,问能不能n步走遍每一个点并能回到初始点
我们发现,删去所有的叶子结点后,剩下的部分一定是一条链,否则连着三条边的节点,一定最少走三遍,不可能n步走遍n个节点
我们先以任意点进行一遍bfs,找见离他最远的点,即最后链的一端
然后以这端开始,每次走两步,顺便走完第一步位置所连的叶子节点,走到另一端后,往回走一步,再两步两步地走回起始点,通过递归的性质实现,走回的路上顺便走完递归点的叶子结点
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<int>edge[200005];
int n;
int bfs(){
queue<int>q;
q.push(1); //以第一个点为起点
vector<int>dis(n+1,-1); //和点1的距离
dis[1]=0;
while(!q.empty()){
int tmp=q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto it:edge[tmp]){
if(dis[it]!=-1)continue; //已经算过不去更新
dis[it]=dis[tmp]+1; //否则用当前距离+1更新
q.push(it); //放入队列
}
} //找见所有点到点1的距离
return max_element(dis.begin()+1,dis.end())-dis.begin(); //返回距离点1最远点的标号
}
vector<int>ans;
void dfs(int pos,int fat){
for(auto i:edge[pos]){
if(i==fat||edge[i].size()==1)continue; //去掉其他点,找到链的下一个点
for(auto j:edge[i]){ //走两步,第二步
if(j==pos)continue; //不要走回去
if(edge[j].size()==1)ans.pb(j); //把叶子结点走完
}
for(auto j:edge[i]){ //沿着链的第二步
if(edge[j].size()==1||j==pos)continue; //不要走回来
//找到了第二步
ans.pb(j); //走这一步
dfs(j,i); //继续往下走
}
ans.pb(i); //往回反的时候,走一遍自己
}
for(auto i:edge[pos]){ //往回走的时候把自己的叶子结点走了
if(edge[i].size()==1)ans.pb(i);
}
return;
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
edge[u].push_back(v); //动态数组存边
edge[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ //判断删去叶子节点后是不是一条链
if(edge[i].size()==1)continue; //叶子节点删去
int cnt=0;
for(auto it:edge[i]){ //如果所连一条链,边数++
if(edge[it].size()>1)cnt++;
}
if(cnt>2){ //存在连着三个中间节点的节点,不是一条链
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return ;
}
}
int t=bfs(); //找出链的一端
ans.pb(t); //从第一个点开始走
dfs(t,-1); //从链的一端开始
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
for(auto it:ans){ //答案输出
cout<<it<<' ';
}
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
// cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}




![[Java Web]会话跟踪技术](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8e0cda9087a247b9ae40cf6b23c1275f.png)