@Transactional注解
@Transactional是spring中声明式事务管理的注解配置方式。@Transactional注解可以帮助我们标注事务开启、提交、者回滚、事务传播、事务隔离、超时时间等操作。
而@EnableTransactionManagement是开启Spring 事务的入口。
@EnableTransactionManagement 标注启动事务管理
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
// TODO 重点:事务注册入口类
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
/**false:使用JDK代理;true:使用CGLIB代理*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**事务通知的方式*/
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
}
@EnableTransactionManagement注解引入了TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector根据AdviceMode 类型使用对应的事务管理配置。
public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> {
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
// 这里导入了两个类,重点看 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration,这里注入了事务切面。
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}
private String determineTransactionAspectClass() {
return (ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", getClass().getClassLoader()) ?
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.JTA_TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME :
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
}
}
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration都做了那些事情呢?
- 实例化
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类,在AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization中使用此类判断当前beanClass是否作为事务类进行增强; - 实例化
TransactionInterceptor类,事务开启、挂起、提交等操作; - 实例化
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类,用于解析@Transactional注解,实际由SpringTransactionAnnotationParser解析,解析生成RuleBasedTransactionAttribute。
@Configuration
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
/**
* 实例化事务切面
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
// 事务切面类
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
// TODO 事务属性解析类
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
// 事务拦截器
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
使用BeanPostProcessor处理@Transactional注释
@Transactional,作用是定义代理植入点。代理对象创建的通过BeanPostProcessor的实现类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法来实现。
/**AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,生成bean代理*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
// 如果是FactoryBean,cacheKey是 &+beanName拼接而成,如果benaName为空,则是beanClass。
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// TODO 必要时包装给定的bean,即是否有资格被代理。
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
/**如果需要才会代理,否则直接返回bean*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// TODO 重点:如果有需要增强,就创建代理对象,这里会循环此类中所有的方法,如果有增强匹配到类中的方法,就会将增强对象封装到list中。
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// TODO 重点:创建代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
/**根据bean找对应的切面Advisor*/
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
// 这里封装了匹配的增强方法的Advisor对象,包括PointCut expression、aspectName等信息。
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
/**查找有资格处理beanClass的切面Advisor*/
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//查找到所有的增强方法,封装成Advisor对象。这里查找了两种增强,一种是实现了Advisor的实例,一种是带有@Aspect注解的bean实例中定义的增强方法。
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 根据每个增强中的切点表达式,进行匹配,筛选出合适的增强实例列表。
// 事务处理:
// @Transactional 注解将匹配到 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,
// BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 类包含 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut用于匹配@Transactional 注解
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
// 对增强方法进行排序,可以不看。
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
Advisor切面判断是否增强beanClass
相关类概述
在展开前,先了解几个类功能:
Pointcut:“切点”,它是用来匹配连接点 Join point 的,可以说"Pointcut"表示的是"Join point"的集合。Advice:“通知”,表示 Aspect 在特定的 Join point 采取的操作。包括 “around”, “before” and “after 等Advisor:“通知者”,它持有 Advice,是 Spring AOP 的一个基础接口。Advisor 可以获取到 Advice。PointcutAdvisor为Advisor子接口可以获取到Pointcut和Advice。
Pointcut概述
事务使用Pointcut使用TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut:
/**BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor#pointcut*/
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
/**TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 类,
用于判断类或者方法是否存在@Transactional注解,
并且生成TransactionAttribute*/
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PlatformTransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
// 匹配方法,判断方法是否有@Transaction注解
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
}
Advice 概述
Advice大体上分为了三类:BeforeAdvice、MethodInterceptor、AfterAdvice。
MethodInterceptor 是功能最强大的,它能够处理 BeforeAdvice、AroundAdvice、AfterAdvice、ThrowsAdvice、@Valid方法参数校验、@Async异步等
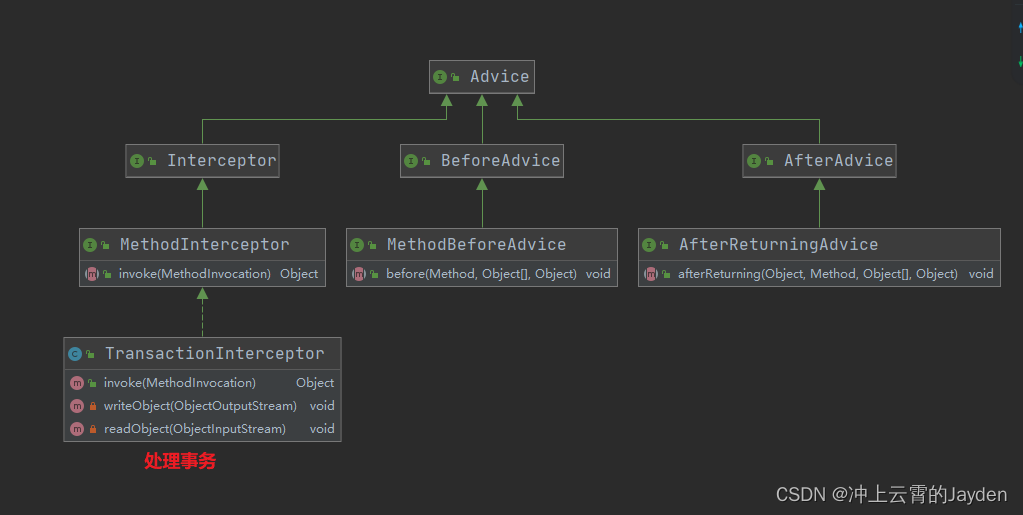
Advisor概述
事务使用BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类,类图如下: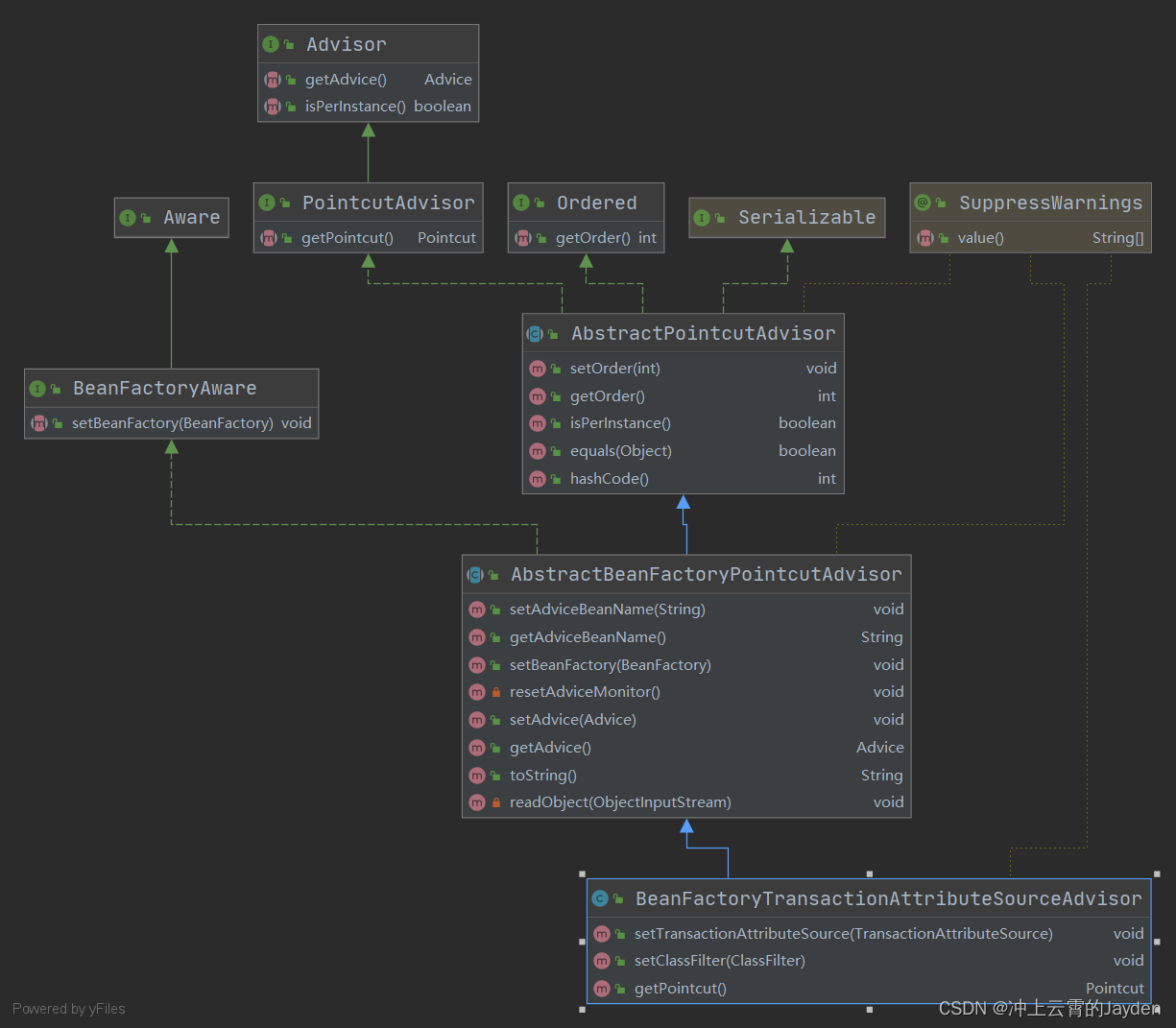
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实现了PointcutAdvisor,使用Pointcut匹配方法、类上是否存在@Transactional。
beanClass是否需要增强?
如何判断一个Advisor是否支持目标类,如果支持那么解析@Transactional生成RuleBasedTransactionAttribute并且缓存。
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute:
作为TransactionAttribute实现,用于保存@Transactional注解配置的数据。
/**AopUtils方法,返回参数提供的Advisor中能支持clazz的Advisor*/
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 先处理IntroductionAdvisor类型的增强
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
// 再处理其他类型的增强
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 我们自定义的切面,就会走到这里,使用已经封装的PointcutAdvisor,根据切点表达式进行匹配,具体的匹配过程,不用看。
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
/**判断Advisor是否支持targetClass*/
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
//切点表达式匹配。
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
/**
1.获取targetClass、targetClass父类和接口的方法
2.使用Pointcut#getMethodMatcher提供的MethodMatcher匹配第1步中的方法
*/
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
// 这里做了切入点表达式的匹配,匹配通过的返回true,具体的匹配过程不用看,不是重点。
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
//事务中 introductionAwareMethodMatcher 实际上为 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#matches 检查方法是否有@Transaction注解,
如果有注解,生成TransactionAttribute实际生成RuleBasedTransactionAttribute*/
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PlatformTransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
// 匹配方法,判断方法是否有@Transactional注解
// tas 为 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
/**
解析@Transactional顺序:
当前method是否存在@Transactional
-》当前method所在类是否存在@Transactional
-》当前method的父类method是否存在@Transactional
-》当前method的父类是否存在@Transactional
解析到其中一个即可
*/
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// 获取事务注解属性
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// 先从缓存中拿。如果一个方法的事务注解信息被获取过,就会将其缓存到一个并发安全的map中。后面再获取就从这个缓存中获取。
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
// TODO 获取事务注解属性,放入缓存。
// We need to work it out.
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {// 放入缓存
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
//获取给定方法的全限定名,基本仅用于输出日志
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
//如果事务属性属于DefaultTransactionAttribute
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
//将结果存入缓存,再次遇到时不再解析
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
生成代理对象
生成代理对象入口:AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
/**AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy方法,创建代理对象*/
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 注意这个ProxyFactory,里面封装了 Advisors
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// TODO 重点:构建增强对象,这里会在原有的Advisor列表中,增加存在的MethodInterceptor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// TODO 重点:生成代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
/**ProxyFactory#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader)*/
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//根据目标对象是否有接口来判断采用什么代理方式,cglib代理还是jdk动态代理
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
/**ProxyCreatorSupport#createAopProxy*/
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
/**
DefaultAopProxyFactory#createAopProxy
生成cglib或者jdk代理
*/
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
// 如果目标类是一个接口,则使用JDK动态代理
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
// 使用cglib代理。
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
如果目标类实现了接口那么Spring使用JDK代理,否则是否cglib代理。