🎉🎉🎉点进来你就是我的人了
博主主页:🙈🙈🙈戳一戳,欢迎大佬指点!
人生格言:当你的才华撑不起你的野心的时候,你就应该静下心来学习!欢迎志同道合的朋友一起加油喔🦾🦾🦾
目标梦想:进大厂,立志成为一个牛掰的Java程序猿,虽然现在还是一个🐒嘿嘿
谢谢你这么帅气美丽还给我点赞!比个心
目录
一.单向链表的实现
1. MySingleList的大概实现框架
2. addFirst--头插
3. addLast--尾插
4. addIndex--任意位置插入
5. contains--查找是否包含关键字key
6. remove--删除第一次出现的key
7. removeAllkey--删除所有key
8. (1)求单链表的长度;(2)打印单链表;(3)清除单链表
双向链表的简单介绍
二、双向链表的实现
1.基本框架的构建
2.打印链表
3.查找链表长度
4.头插法
5.尾插法
6.任意位置插入
7.查找是否存在关键词key
8.删除第一次出现的关键词key
9.删除所有关键词key
10、清空链表
三. 缺陷与区别(ArrayList&LinkedList)
链表的简单介绍
链表是一种在物理上非连续的存储结构。在单向链表中,每一个节点都是一个对象,其中包含了数据和引用两部分,通过引用指向下一个节点。这种结构相比线性存储结构要复杂,并且由于增加了指针(引用)域导致内存开销更大,但它不像数组那样需要预先知道数据规模,可以充分利用计算机的内存空间。
一.单向链表的实现
首先我们和ArrayList一样,将MySingleList单独定义为一个Java文件,然后每一个结点我们将它定义成一个静态内部类,这样就方便我们访问结点的成员,,还是和ArrayList一样,我们再定义一个Test类用来测试我们的单链表,写一个函数可以测试一下
 无头单向非循环链表的实现:
无头单向非循环链表的实现:
1. MySingleList的大概实现框架
public class MySingleList {
static class ListNode {
public int value;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//简单的创建单链表
public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(22);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(23);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
this.head = listNode1;
}
public ListNode head;
public void addFirst(int data){}
public void addLast(int data){}
public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
public boolean contains(int key){return false;}
public void remove(int key){}
public void removeAllKey(int key){}
public int size(){return -1;}
public void display(){}
public void clear(){}
}2. addFirst--头插
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}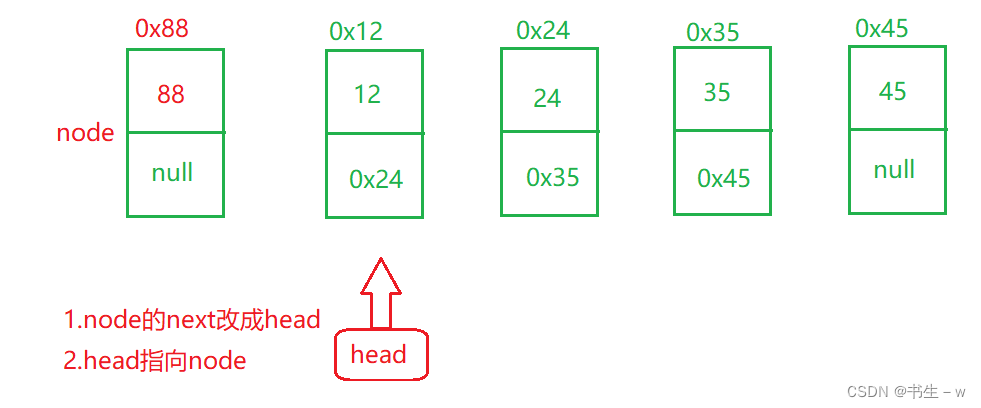
头插没啥细节点,以上图做辅助理解,我就不多赘述了,,
3. addLast--尾插
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//1.链表为空
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
//2.链表不为空
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}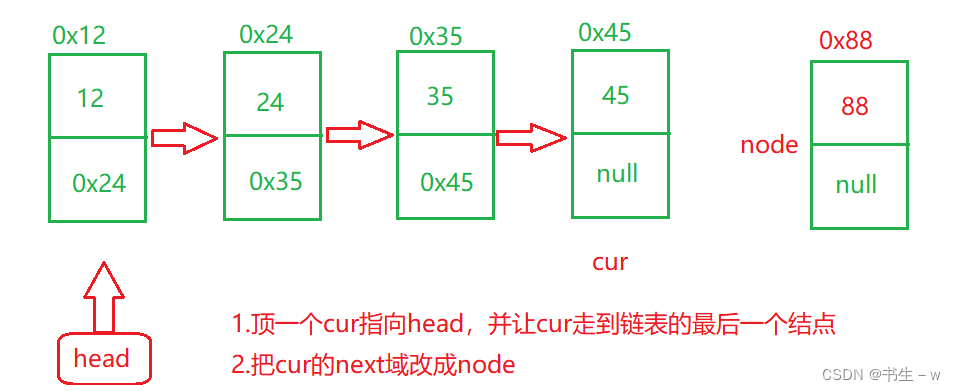
这里要注意链表为空的时候,只需要将head指向node即可;
4. addIndex--任意位置插入
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws MySingleListIndexOutOfException{
//1.先检查插入位置是否合法
checkAddIndex(index);
//2.分两种情况:1.头插 2.中间位置和尾插
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findAddIndexSubOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
private void checkAddIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > this.size()) {
throw new MySingleListIndexOutOfException("任意位置插入时,index不合法!");
}
}
//找到待插入位置的前一个结点
private ListNode findAddIndexSubOne(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(index - 1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
任意位置插的注意事项:1.先要判断下标是否合法;2.要分两种情况。
5. contains--查找是否包含关键字key
public boolean contains(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return false;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.value == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}6. remove--删除第一次出现的key
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
//1.判断有无结点
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
//2.删第一个
if(this.head.value == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
//3.删后面的
ListNode cur = this.head;
cur = removeSubOne(key,cur);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("链表中没有这个元素!");
return;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
private ListNode removeSubOne(int key, ListNode cur) {
while(cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.value == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
删除函数的注意事项:1.判空 2.分两种情况:删头和删剩下的,
7. removeAllkey--删除所有key
//方法一:时间复杂度O(N^2)
public void removeAllKey1(int key) {
//1.判断有无结点
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
//处理中间和尾巴
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
//removeSubOne函数在上一个删除方法里头
cur = removeSubOne(key,cur);
if(cur != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
}
//处理头
if(this.head.value == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}
//方法二:时间复杂度O(N),只遍历一遍链表
public void removeAllKey2(int key){
//特殊情况,首结点的值为key的处理情况(这里我们选择处理方式二)
//处理方式一,直接将位于链表前面所有值为key的结点删除,更新头结点
// while(head.value == key) {
// head = head.next;
// }
if(head == null) {
return;
}
Node pre = head;//前指针
Node cur = head.next;//游标
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.value == key) {
//删除当前cur结点
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
//不删除当前cur结点
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//处理方式二,在整个链表删除(结点值为key的)完毕后直接将首结点(值为key)更新
if(head.value == key) {
head= head.next;
}
}方法一:调用前写过的removeSubOne方法
1.如果先处理头,则需要写成循环,因为当链表所有结点都是待删除的情况时,一个if条件语句处理不了
2.while循环里面的条件不能写成cur.next == null,因为removeSubOne函数如果没找到待删除 的结点,它返回的是一个null,如果写成cur.next != null,则可能会报空指针异常
方法二:只遍历一遍链表,时间复杂度O(N)
使用前后指针解决这个问题, 前指针指向值为key的结点的前驱结点, 而后指针用来标识是否某个结点的值为key。

接下来就是几个简单的函数,也很重要,大家都能看得懂:
8. (1)求单链表的长度;(2)打印单链表;(3)清除单链表
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public void display() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear() {
this.head = null;
}这里解释一下遍历链表循环的结束条件:(head不能动,否则打印一次就找不到头结点了)
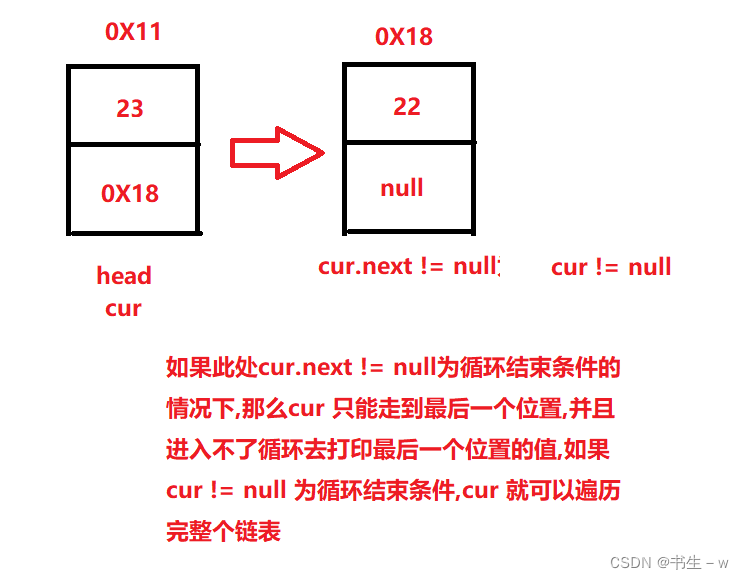
这里说说清除函数,我这种方式是比较暴力,也可以用温柔的方式:
用cur结点保存head的next,然后将head的val和next不断置为0或空,然后两个"指针"不断往后走

双向链表的简单介绍
双向链表,顾名思义和单向链表很相似,均为链表,两者之间的操作也十分相近,最明显的不同之处就是双向链表的单个结点带有两个指针域,分别指向前后两个元素。
二、双向链表的实现
1.基本框架的构建
节点的结构如图:

首先,在实现各项操作前,应该首先实现结点的构建,以静态内部类来实现。
代码如下:
//实现静态内部类,用于实现结点
static class ListNode{
public int val;
//定义存放头尾结点的域
public ListNode next;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
接下来,我们需要了解应该实现哪些不同的方法,如下:
1.打印链表
2.查找链表长度
3.头插法
4.尾插法
5.任意位置插入
6.查找是否包含关键词key
7.删除第一次出现的key结点
8.删除全部key结点
9.清空链表
注:
首先定义出 head 指针和 tail 指针,分别指向头尾。
public ListNode head;
public ListNode tail;
下面,我将会详细进行逐一实现。
2.打印链表
public void display(){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
3.查找链表长度
public int size(){
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
4.头插法
简单分析:
这里有两个需要考虑的地方。
1.当链表起始时为空时
2.当链表有元素时
代码如下:
public void addFirst(int data){
//申请一个新的节点
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//当不存在元素时
if(head == null){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
//当存在元素时
head.prev = node;
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
}
详细分析:
这里主要分析情况 2。
分析如图:
5.尾插法
简单分析:
同样,这里也有两个需要考虑的地方。
1.当链表为空时。
2.当链表中存在元素时。
代码实现:
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
tail.next = node;
node.prev = tail;
tail = node;
}
}
详细分析
这里主要分析情况 2 。
6.任意位置插入
简单分析
这里有需要考虑的三个地方。
1.插入的位置 index 是否合法
2.插入的 index 位置是否在头尾
3.插入的 index 位置位于一般位置
代码如下:
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//1.判断index的合法性
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
System.out.println("index不合法");
throw new IndexWrongFulException("index不合法");
}
//2.判断是头插还是尾插
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
//3.找到index位置的结点地址
ListNode cur = find(index);
cur.prev.next = node;
node.next = cur;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
注:
1.这里判断合法性使用了异常判断类
代码如下:
public class IndexWrongFulException extends RuntimeException{
public IndexWrongFulException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
2.在寻找 index 位置时,定义了 find 方法,
代码如下:
private ListNode find(int index){
ListNode cur = head;
while(index != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
详细分析:
这里主要分析一般情况下在链表中间插入的情况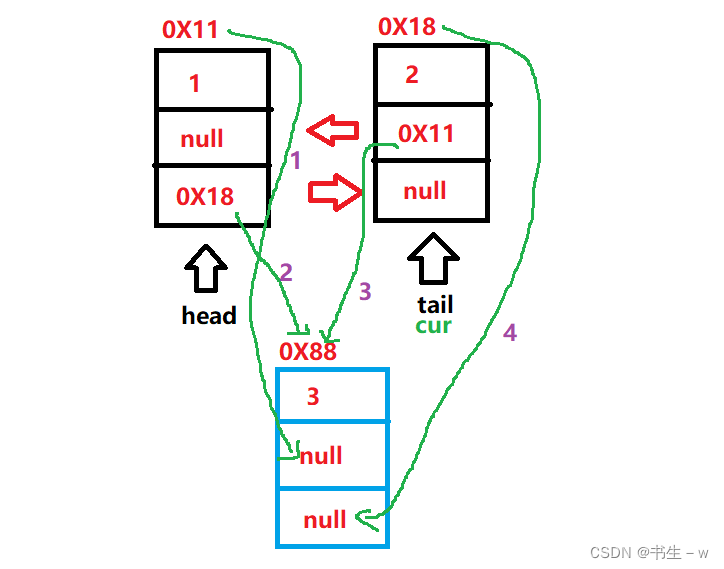
注:紫色数字为指针顺序。
7.查找是否存在关键词key
简单分析:
这个方法难度不大,只需要遍历寻找即可。
代码如下:
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
8.删除第一次出现的关键词key
简单分析:
这里有三个地方需要考虑。
1.当要删除的结点为一个单独的头结点
2.要删除的节点恰好为尾部结点
3.要删除的结点的位置为链表中的一般位置
代码如下:
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//循环寻找 key 的值
if(cur.val == key){
//当要删除的值是头节点
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
//判断删除的是不是单独的一个头节点
if(head != null){
head.prev = null;
}else{
tail = null;
}
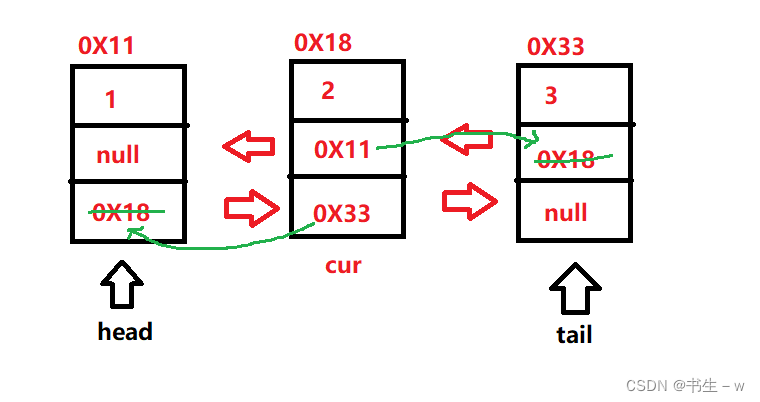
}else{
//一般情况删除
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
//判断删除的是否为尾部结点
if(cur.next != null){
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else{
this.tail = cur.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
详细分析:
1.删除头节点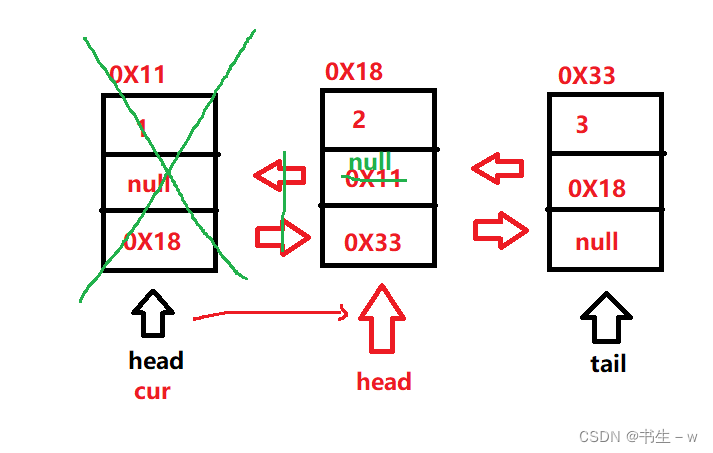
2.删除中间节点
3.删除尾部结点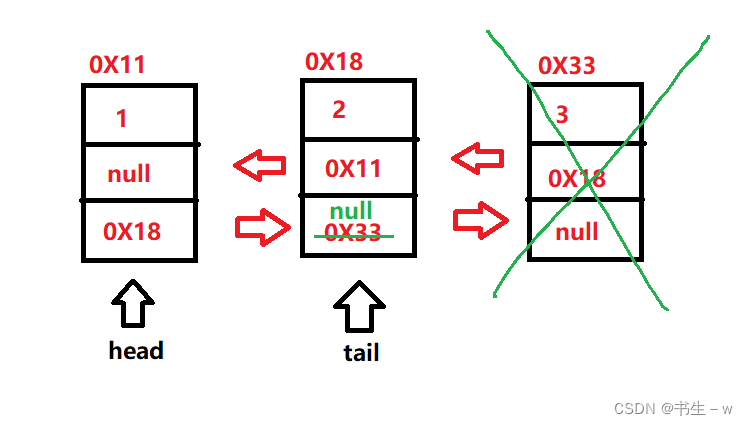
9.删除所有关键词key
简单分析:
这个方法实现非常简单,只要将上一个方法中的 return 删除即可。
代码实现:
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
if(head != null){
head.prev = null;
}else{
tail = null;
}
}else{
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next != null){
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else{
this.tail = cur.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
10、清空链表
简单分析:
双向链表的清空并非是简单的将 head 和 tail 置为 null ,而是要将所有结点的指向全部置为 null
代码如下:
public void clear(){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur.prev = null;
cur =curNext;
}
}
至此,所有的方法实现结束。
三. 缺陷与区别(ArrayList&LinkedList)
我们之前学了顺序表,但是在某些方面,它存在着许多不足,由于其底层是一段连续的空间,当ArrayList任意位置插入或删除元素的时候,就需要将后续元素整体往前或者往后移动,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入删除比较多的场景,而这些问题链表都可以解决。
区别:
| 不同点 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上连续 | 逻辑上连续,物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1) | 不支持O(N) |
| 头插 | 需要移动元素,效率低O(N) | 只需要修改引用的指向O(1) |
| 插入 | 空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 频繁访问+随机存取 | 任意位置插入+频繁删除 |






![[HAOI2011]Problem b(莫比乌斯反演)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8894d21b08bb478c8b4b1a617f0eaaa0.png)