这场能题解写的感觉没多少其实(真的不是因为懒),既然有人想要题解,那么就随便写一下吧,其实大部分的题都有人写出来,感觉这场真的不需要。
A 题 题解
Count Interval AtCoder - abc233_d_霾まる的博客-CSDN博客
B题 题解
2021四川省icpc省赛H题 Nihongo wa Muzukashii Desu 日本語は難しいです!_霾まる的博客-CSDN博客
C题 题解:
线段树的典题,输入 去重 二分 线段树区间修改 最后求值即可。emmmmm,可能难在了 离散化去重的思想?还是线段树的板子? (本来想拉道线段树的板子,看看大家学的怎么样,拉的这道题没有达到效果,感觉这道题拉的挺失败的,应该拉道更板子的
(随机挑选一个代码看着比较顺眼的代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
int t;
int n,an;
int ans=0;
struct we{
int l,r;
}hh[100005];
int tr[400005];
bool v[10000000];
int b[400005];
void add(int l,int r,int x,int L,int R,int id){
if(L<=l&&R>=r){
tr[x]=id;
return;
}
if(tr[x]){
tr[x<<1]=tr[x];
tr[x<<1|1]=tr[x];
tr[x]=0;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid)add(l,mid,x<<1,L,R,id);
if(R>mid)add(mid+1,r,x<<1|1,L,R,id);
}
void cha(int x,int l,int r){
if(l==r){
if(v[tr[x]]==0&&tr[x]){
ans++;
v[tr[x]]=1;
}
return;
}
if(tr[x]){
tr[x<<1]=tr[x<<1|1]=tr[x];
tr[x]=0;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
cha(x<<1,l,mid);
cha(x<<1|1,mid+1,r);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie();
cout.tie();
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n;
memset(v,0,sizeof v);
memset(tr,0,sizeof tr);
an=0;
ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>hh[i].l>>hh[i].r;
b[++an]=hh[i].l;
b[++an]=hh[i].r;
}
sort(b+1,b+an+1);
an=unique(b+1,b+an+1)-b-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int l=lower_bound(b+1,b+an,hh[i].l)-b;
int r=lower_bound(b+1,b+an,hh[i].r)-b;
add(1,an,1,l,r,i);
}
cha(1,1,an);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}D题
The 2021 CCPC Guangzhou Onsited
是这场中的 H 签到题
题解的话,看这篇比较好,我觉得写的优雅 又 美丽
2021CCPC广州 H. Three Integers_h three integers__sky123_的博客-CSDN博客
E 题
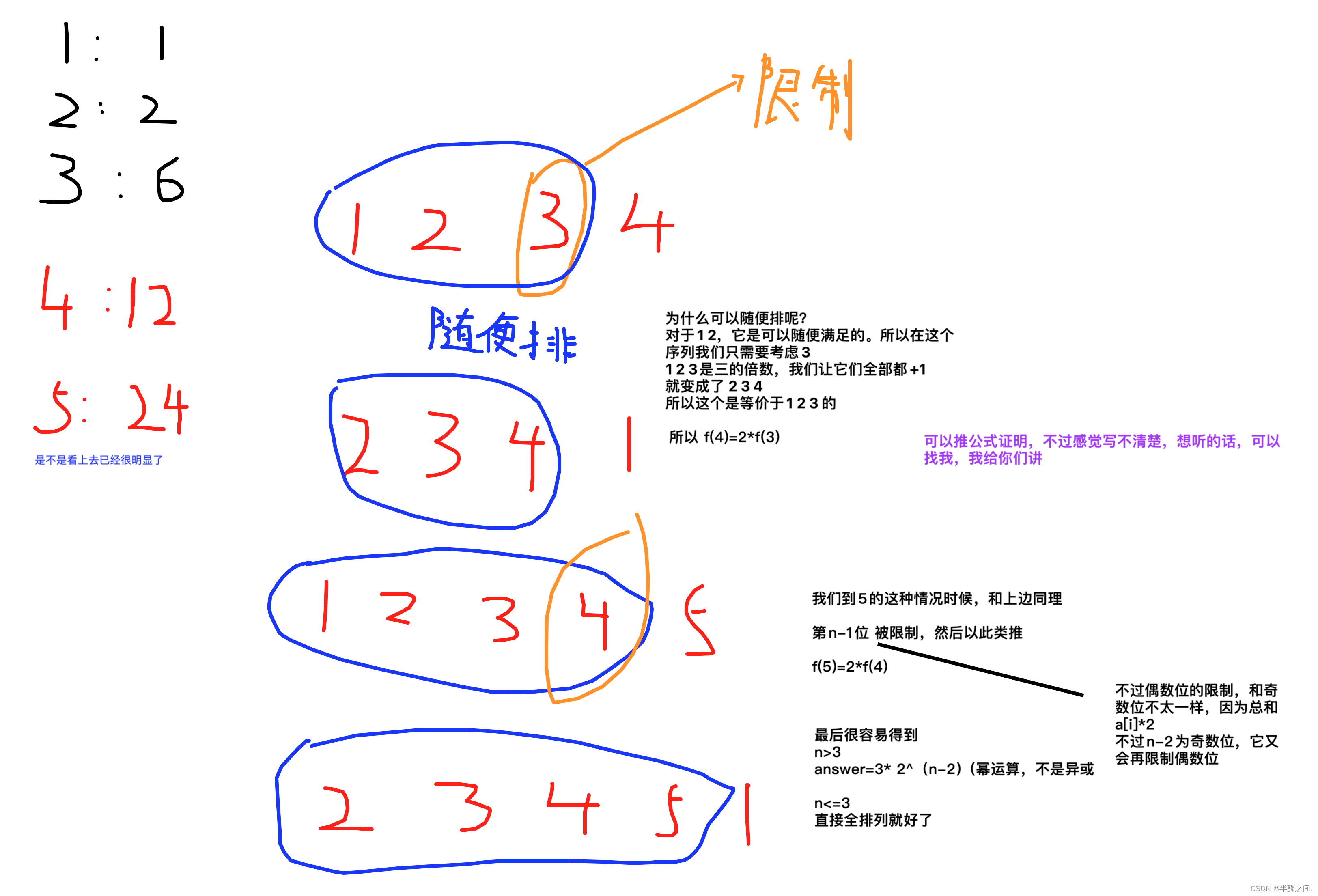
这题比D题还要简单,不过不知道为什么没有人写。
推结论的话,也很好推。不推结论的话,打表 或者 手模样例,最多到5,就能发现规律。可惜没有人写。(唉,这道题网上的题解感觉写的都挺烂,什么题解,还要我亲自动手写)
我们很容易推得
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
#include<stack>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
inline char nc() {
static char buf[1000000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1000000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++;
}
template <typename _Tp> inline void read(_Tp&sum) {
char ch = nc(); sum = 0;
while (!(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')) ch = nc();
while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') sum = (sum << 3) + (sum << 1) + (ch - 48), ch = nc();
}
inline __int128 read128(){
__int128 x = 0, f = 1;
char ch128 = getchar();
while(ch128 < '0' || ch128 > '9'){
if(ch128 == '-')
f = -1;
ch128 = getchar();
}
while(ch128 >= '0' && ch128 <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + ch128 - '0';
ch128 = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void print128(__int128 x){
if(x < 0){
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x > 9)
print128(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
//struct dian{
// double x,y;
//}A,B,C,D,E,F;//点
//cin>>A.x>>A.y>>B.x>>B.y>>C.x>>C.y>>D.x>>D.y>>E.x>>E.y>>F.x>>F.y;
//double len(dian x,dian y){
// return sqrt((x.x-y.x)*(x.x-y.x)+(x.y-y.y)*(x.y-y.y));
//}//两点之间距离
//double xj(dian x,dian y,dian z){
// x.x-=y.x;
// x.y-=y.y;
// z.x-=y.x;
// z.y-=y.y;
// return x.x*z.y-x.y*z.x;
//}//叉积
int n,t;
const ll N=998244353;
ll ksm(ll x,ll y){
ll oper=1;
while (y) {
if (y&1) {
oper=oper*x%N;
}
x=x*x%N;
y>>=1;
}
return oper;
}
void wanyurukong(){
cin>>n;
ll na=1;
if (n<=3) {
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
na*=i;
}
}
else{
na=3*ksm(2, n-2)%N;
}
cout<<na<<"\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
cin>>t;
while (t--) {
wanyurukong();
}
//wanyurukong
return 0;
}
F题
输出肯定是不行的。
我们直接手动模拟除法就好,除不了,就是乘10,然后小数点后推一位。然后细心一点就好了(直接放你们其中一个人AC代码了
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int c[1005];
int main()
{
int a,b,k;
cin>>a>>b>>k;
if(a==b)
{
cout<<1<<".";
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)cout<<0;
}
else
{
int z=0;
while(z<=k+1)
{
z++;
a*=10;
c[z]=a/b;
if(a>=b&&a!=0)a=a%b;
}
if(c[k+1]>=5)c[k]+=1;
cout<<0<<".";
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)cout<<c[i];
}
return 0;
}G 题
去年的ccpc河南省省赛的题,过了签到,过了这道题,再过一道树上MEX,罚时少一点,就可以金牌了。
题解:2022河南省CCPC省赛H题旋转水管_霾まる的博客-CSDN博客
H 题
吉林省赛 拓扑排序的板子题,应该是没人会的,可以都去学一下,这个类似于一种思想。
这道题的话,感觉没什么好说的。就是要确定的,所以我们从可以唯一确定的开始推,然后不断修改行列的状态,再找下一个唯一确定的,典型拓扑排序。
/*Looking! The blitz loop this planet to search way
Only my RAILGUN can shoot it 今すぐ
身体中を 光の速さで
駆け巡った確かな予感
掴め! 望むものなら残さず
輝ける自分らしさで
信じてるよ あの日の誓いを
この瞳に光る涙それさえも 強さになるから
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<tuple>
#include<numeric>
using namespace::std;
typedef long long ll;
inline char nc() {
static char buf[1000000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1000000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++;
}
template <typename _Tp> inline void read(_Tp&sum) {
char ch = nc(); sum = 0;
while (!(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')) ch = nc();
while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') sum = (sum << 3) + (sum << 1) + (ch - 48), ch = nc();
}
inline __int128 read128(){
__int128 x = 0, f = 1;
char ch128 = getchar();
while(ch128 < '0' || ch128 > '9'){
if(ch128 == '-')
f = -1;
ch128 = getchar();
}
while(ch128 >= '0' && ch128 <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + ch128 - '0';
ch128 = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void print128(__int128 x){
if(x < 0){
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if(x > 9)
print128(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
//struct dian{
// double x,y;
//}A,B,C,D,E,F;//点
//cin>>A.x>>A.y>>B.x>>B.y>>C.x>>C.y>>D.x>>D.y>>E.x>>E.y>>F.x>>F.y;
//double len(dian x,dian y){
// return sqrt((x.x-y.x)*(x.x-y.x)+(x.y-y.y)*(x.y-y.y));
//}//两点之间距离
//double xj(dian x,dian y,dian z){
// x.x-=y.x;
// x.y-=y.y;
// z.x-=y.x;
// z.y-=y.y;
// return x.x*z.y-x.y*z.x;
//}//叉积
int n;
int ff[1005][1005];
int h[1005],l[1005];
int s1[1005],s2[1005];
int enddh[1005],enddl[1005];
pair<int, int>jkl;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
cin>>n;
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
for (int j =1; j<=n; j++) {
cin>>ff[i][j];
if (ff[i][j]!=-1) {
h[i]++;
l[j]++;
s1[i]^=ff[i][j];
s2[j]^=ff[i][j];
}
}
}
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
cin>>enddh[i];
}
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
cin>>enddl[i];
}
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
for (int j =1; j<=n; j++) {
if (ff[i][j]==-1&&(h[i]==n-1||l[j]==n-1)) {
q.push({i,j});
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
jkl=q.front();q.pop();
if (h[jkl.first]==n-1) {
ff[jkl.first][jkl.second]=enddh[jkl.first]^s1[jkl.first];
}
if(l[jkl.second]==n-1){
ff[jkl.first][jkl.second]=enddl[jkl.second]^s2[jkl.second];
}
s2[jkl.second]^=ff[jkl.first][jkl.second];
s1[jkl.first]^=ff[jkl.first][jkl.second];
h[jkl.first]++;
l[jkl.second]++;
if ( l[jkl.second]==n-1) {
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
if (ff[i][jkl.second]==-1) {
q.push({i,jkl.second});
break;
}
}
}
if (h[jkl.first]==n-1) {
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
if (ff[jkl.first][i]==-1) {
q.push({jkl.first,i});
break;
}
}
}
}
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
for (int j =1; j<=n; j++) {
if (ff[i][j]==-1) {
printf("-1\n");return 0;
}
}
}
for (int i =1; i<=n; i++) {
for (int j =1; j<=n; j++) {
printf("%d ",ff[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}I 题
没什么好说的,就是树状数组的板子题。找一下 逆序对 就好,这道题甚至不需要离散化。
树状数组专题的第一道题 是需要 离散化的 找逆序对,按道理来说应该能直接写出来的。
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int t,x,y,n;
ll a[500005];
ll b[500005];
ll lowbit(ll x){
return x&(-x);
}
void add(ll x){
for(int i=x;i<=n;i+=lowbit(i)){
b[i]++;
}
}
ll cha(ll x){
ll ans=0;
for(int i=x;i>0;i-=lowbit(i)){
ans+=b[i];
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie();
cout.tie();
cin>>t;
while(t--){
memset(b,0,sizeof b);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
ll ans=0;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
// cout<<cha(a[i])<<"***\n";
ans+=cha(a[i]);
add(a[i]);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}本来预期 人均 5~6题,中间还感觉题拉简单了,后来发现 感觉 早了。
记得好好打专题+补题。