目录
1、缘起
2、案例描述
3、案例分析
4、代码清单 1
5、代码清单 2
6、总结
1、缘起
最近学习完了 C++ 语言的结构体相关知识点,如 结构体数组,结构体指针,结构体嵌套结构体 和 结构体做函数参数。本篇博客围绕着这些知识点,编写了一个这些知识点的综合应用案例,希望能够对这些知识点加深印象和灵活运用。
2、案例描述
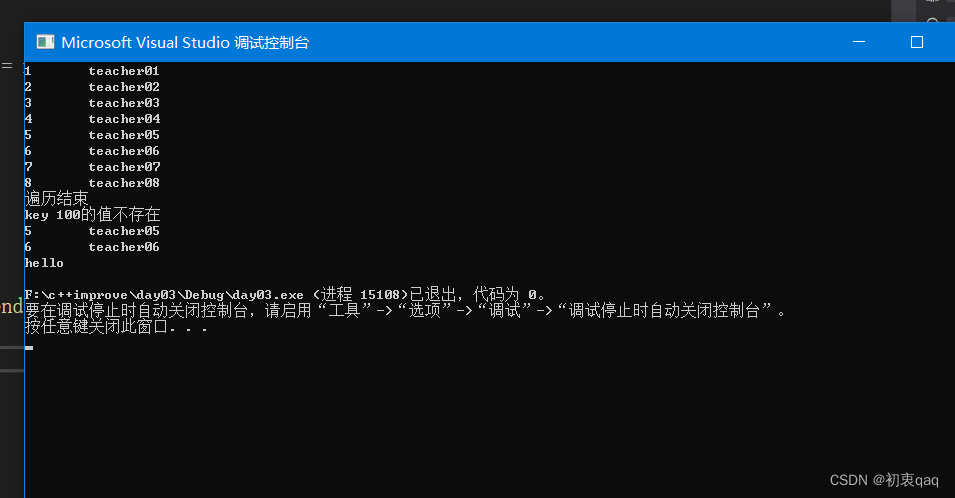
学校正在做毕设项目,每名老师带领 5 个学生,总共有 3 名老师,需求如下:
设计学生和老师的结构体,其中在老师的结构体中,有老师姓名和一个存放 5 名学生的数组作为其成员。学生的成员有姓名和考试分数,创建数组存放 3 名老师,通过函数给每个老师及所带的学生赋值。最终打印出老师数据以及老师所带的学生数据。
3、案例分析

老师的结构体中,包含了学生的结构体,这里涉及了 结构体嵌套结构体 的相关知识点。每名老师名下都有 5 名学生,把这 5 名学生都放在存放在一个数组中,这里是涉及了 结构体数组 的相关知识点。
4、代码清单 1
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//函数声明
void AllocateSpace(struct Teacher t_arr[], int len);
void PrintInfo(struct Teacher t_arr[], int len);
//定义一个学生的结构体
struct Student
{
string name;
int score = 0;
};
//定义一个老师的结构体
struct Teacher
{
string name;
struct Student stu_arr[5];
};
int main()
{
//1、定义一个老师的结构体数组
struct Teacher t_arr[5];
//2、通过函数给 3 名老师的信息赋值,并给老师带的学生信息赋值
int len = sizeof(t_arr) / sizeof(t_arr[0]);
AllocateSpace(t_arr,len);
//3、打印所有老师及所带的学生的信息
PrintInfo(t_arr,len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//给老师和学生赋值的函数
void AllocateSpace(struct Teacher t_arr[],int len)
{
//随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//将学生的分数设为随机值
int x1 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x2 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x3 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x4 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x5 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x6 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x7 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x8 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x9 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x10 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x11 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x12 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x13 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x14 = rand() % 61 + 40;
int x15 = rand() % 61 + 40;
//给老师开始赋值
t_arr[0].name = "张老师";
t_arr[1].name = "薛老师";
t_arr[2].name = "李老师";
//张老师的学生信息
t_arr[0].stu_arr[0].name = "张三";
t_arr[0].stu_arr[0].score = x1;
t_arr[0].stu_arr[1].name = "李四";
t_arr[0].stu_arr[1].score = x2;
t_arr[0].stu_arr[2].name = "王五";
t_arr[0].stu_arr[2].score = x3;
t_arr[0].stu_arr[3].name = "赵六";
t_arr[0].stu_arr[3].score = x4;
t_arr[0].stu_arr[4].name = "吴七";
t_arr[0].stu_arr[4].score = x5;
//薛老师的学生信息
t_arr[1].stu_arr[0].name = "张三";
t_arr[1].stu_arr[0].score = x6;
t_arr[1].stu_arr[1].name = "李四";
t_arr[1].stu_arr[1].score = x7;
t_arr[1].stu_arr[2].name = "王五";
t_arr[1].stu_arr[2].score = x8;
t_arr[1].stu_arr[3].name = "赵六";
t_arr[1].stu_arr[3].score = x9;
t_arr[1].stu_arr[4].name = "吴七";
t_arr[1].stu_arr[4].score = x10;
//李老师的学生信息
t_arr[2].stu_arr[0].name = "张三";
t_arr[2].stu_arr[0].score = x11;
t_arr[2].stu_arr[1].name = "李四";
t_arr[2].stu_arr[1].score = x12;
t_arr[2].stu_arr[2].name = "王五";
t_arr[2].stu_arr[2].score = x13;
t_arr[2].stu_arr[3].name = "赵六";
t_arr[2].stu_arr[3].score = x14;
t_arr[2].stu_arr[4].name = "吴七";
t_arr[2].stu_arr[4].score = x15;
}
//打印老师和学生的信息的函数
void PrintInfo(struct Teacher t_arr[], int len)
{
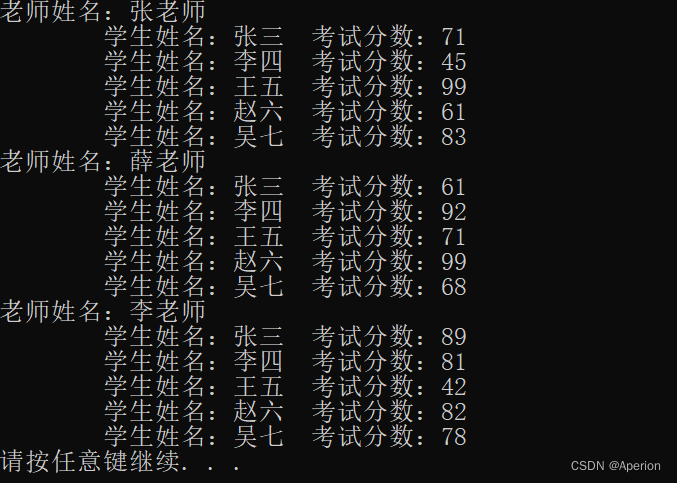
//第一个老师的信息
cout << "老师姓名:" << t_arr[0].name << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[0].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[0].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[1].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[1].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[2].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[2].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[3].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[3].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[4].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[0].stu_arr[4].score << endl;
//第二个老师的信息
cout << "老师姓名:" << t_arr[1].name << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[0].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[0].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[1].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[1].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[2].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[2].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[3].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[3].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[4].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[1].stu_arr[4].score << endl;
//第三个老师的信息
cout << "老师姓名:" << t_arr[2].name << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[0].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[0].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[1].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[1].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[2].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[2].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[3].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[3].score << endl;
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[4].name << " ";
cout << "考试分数:" << t_arr[2].stu_arr[4].score << endl;
}
5、代码清单 2
上文代码实在是太暴力了,接下来对上述代码进行优化。但不可否认的是,暴力解决法确实很实用。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void AllocateSpace(struct Teacher t_arr[], int len);
void PrintInfo(struct Teacher t_arr[], int len);
//定义一个学生的结构体类型
struct Student
{
string name;
int score = 0;
};
//定义一个老师的结构体类型
struct Teacher
{
string name;
struct Student stu_arr[5];
};
int main()
{
//设置随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1、定义一个 3 名老师的结构体数组
struct Teacher t_arr[3];
//2、定义一个给老师和学生的信息赋值的函数
int len = sizeof(t_arr) / sizeof(t_arr[0]);
AllocateSpace(t_arr,len);
//3、定义一个打印老师和学生的信息的函数
PrintInfo(t_arr,len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//打印老师和学生的信息
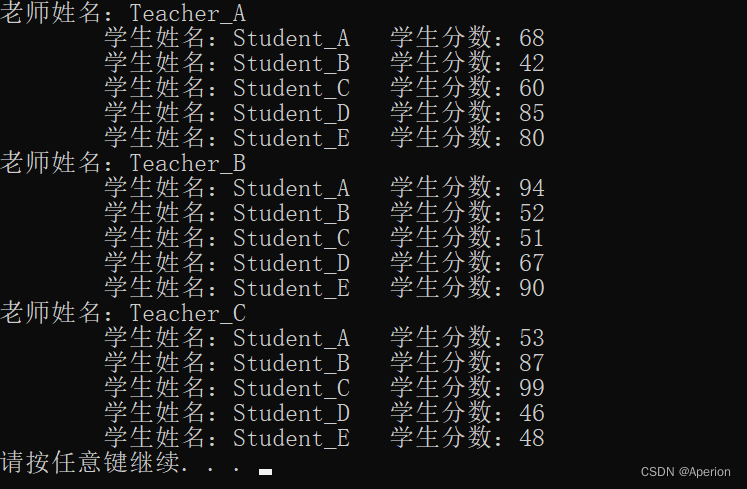
void PrintInfo(struct Teacher t_arr[],int len)
{
//输出老师的相关信息
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << "老师姓名:" << t_arr[i].name << endl;
//输出学生的相关信息
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
cout << "\t学生姓名:" << t_arr[i].stu_arr[j].name << " ";
cout << "学生分数:" << t_arr[i].stu_arr[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
//给老师和学生的信息赋值
void AllocateSpace(struct Teacher t_arr[],int len)
{
string name_seed = "ABCDE";
//给老师开始赋值
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
t_arr[i].name = "Teacher_";
t_arr[i].name += name_seed[i];
//通过循环给每名老师所带的学生赋值
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
//设置一个随机数,使得学生的分数随机
int random = rand() % 61 + 40;
t_arr[i].stu_arr[j].name = "Student_";
t_arr[i].stu_arr[j].name += name_seed[j];
t_arr[i].stu_arr[j].score = random;
}
}
}
6、总结
对于一个任务需求,最重要的是先把它的功能实现,然后在对其代码进行优化。暴力解决方案确实是有点不优雅,但确实是很实用。
本期的分享总结就到这里了,如果有疑问的小伙伴,我们在评论区交流嗷,笔者必回,我们下期再见啦 !