信号与系统1——Signals and Systems
- 一、Introduction
- 1. Signals and Systems信号与系统
- (1) Signal信号
- (2) System系统
- 2. Classification of Signals信号的分类
- (1) Continuous-time & discrete-time
- 1) Continuous-Time signal连续时间信号
- 2) Discrete-Time signal离散时间信号
- 3) Relationship关系
- (2) Even and odd signals偶奇信号
- 1) Even signals (偶信号)
- 2) Odd signals (奇信号)
- 3) Even-odd decomposition of x(t)奇偶分量
- 4) PRODUCT Rule
- 3. Operation on Signals信号运算
- (1) In Time Domain时域
- 1) Time Scaling时间展缩
- 2) Time Reflection时间反转
- 3) Time Shifting时移
- (2) In Amplitude幅度
- 1) Amplitude scaling幅度缩放
- 2) Addition加
- 3) Multiplication乘
- 4) Differentiation 微分
- 5) Integration 积分
- (3) Precedence Rule步骤
- 二、Basic Time Signals基本时间信号
- 1. Exponential Signals指数信号
- (1) Continuous-time
- (2) Discrete-time
- 2. Sinusoidal Signals正弦信号
- (1) Continuous-time
- (2) Discrete-time
- (3) Relation Between Sinusoidal and Complex Exponential Signals
- 1) Complex exponential signal
- 2) Discrete-time case
- 3) Two-dimensional representation of the complex exponential e^jΩn^ for Ω = Π/4 and n = 0, 1...
- (4) Exponential Damped (衰减) Sinusoidal Signals
- 3. Step Functions阶跃信号
- (1) Continuous-time
- (2) Discrete-time
- (3) Properties
- 1) 相乘特性(单边特性)
- 2) 表示作用区间
- 3) 积分
- 4. Impulse Functions冲激信号
- (1) Discrete-time
- (2) Continuous-time
- (3) Properties of impulse function
- 1) Even function偶函数
- 2) Sifting property时移特性
- 3) Time-scaling property展缩特性
- 4) Sampling property取样特性
- 5) 相乘特性
- 6) Derivatives
- 7) 与u(t)的关系
- 三、Systems Classification and Properties系统分类和性质
- 1. System Representation
- 2. Continuous-time and Discrete-time Systems
- (1) Continuous-time
- (2) Discrete-time
- (3) Moving-average system
- (4) Representation of discrete-time operations
- 3. Systems with and without memory
- (1) without memory
- (2) with memory
- 4. Causal and Non-causal systems
- (1) Causal
- (2) Non-causal
- 5. Linear and Nonlinear systems
- (1) Linear
- (2) Nonlinear
- 6. Time-variant and Time-invariant Systems
- (1) Time-invariant
- (2) Condition for time-invariant system
- 7. Stable systems
- 8. Feedback systems
- 9. Invertibility(可逆性) systems
- (1) Continuous-time system
- (2) Output of the second system
- (3) Condition for invertible system
一、Introduction
1. Signals and Systems信号与系统
(1) Signal信号
A signal is formally defined as a function of one or more variables that conveys information on the
nature of a physical phenomenon.
(2) System系统
A system is formally defined as an entity that manipulates one or more signals to accomplish a function, thereby yielding new signals.

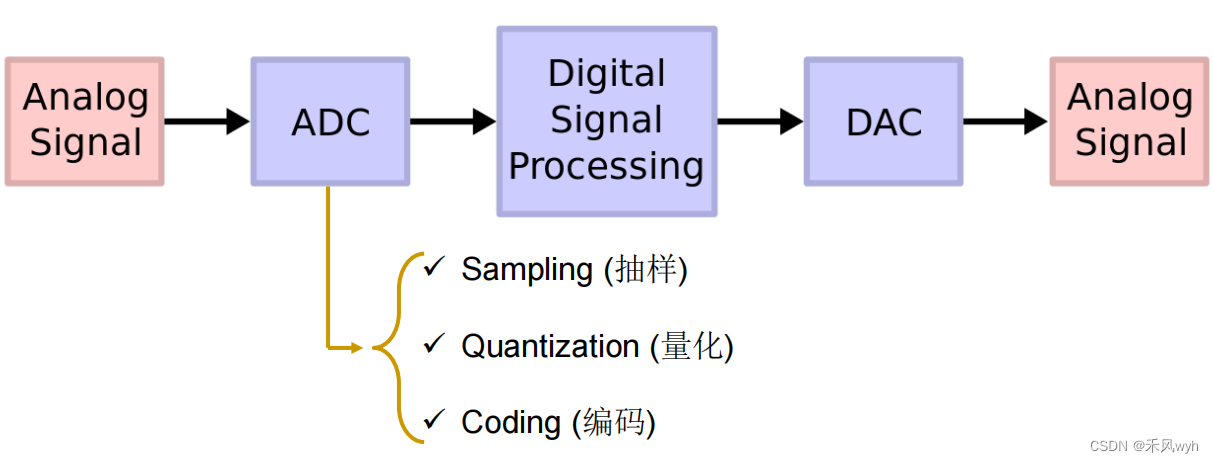
2. Classification of Signals信号的分类
(1) Continuous-time & discrete-time
1) Continuous-Time signal连续时间信号
A continuous-time signal is defined for all time t, except at some discontinuous point.
2) Discrete-Time signal离散时间信号
A continuous-time signal is defined only at discrete instants of time.
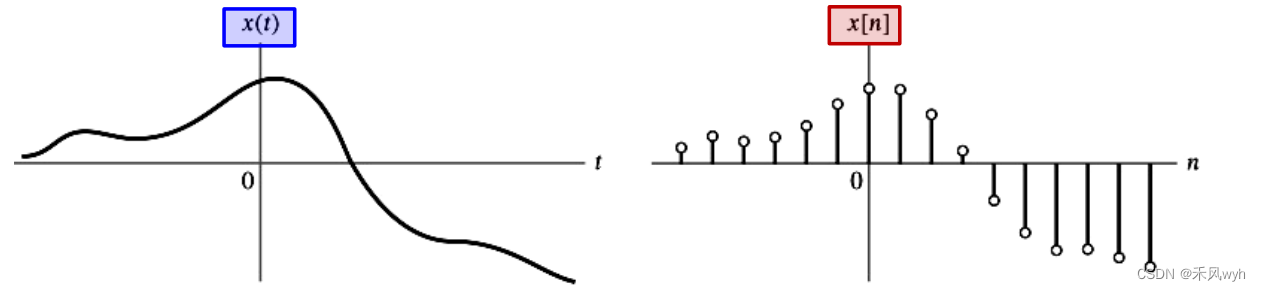
3) Relationship关系
· A discrete-time signal is often derived from a continuous-time signal by sampling (抽样) it at a uniform rate (nT)
x[n]=
x
(
t
)
∣
t
=
n
T
x(t)|_{t=nT}
x(t)∣t=nT=x(nT)
T: sampling period, n: an integer
Continuous-time signals: x(t)
Discrete-time signals: x[n]=x(n
T
s
T_s
Ts), n=0,
±
\pm
± 1,
±
\pm
± 2,
…
\ldots
…
(2) Even and odd signals偶奇信号
1) Even signals (偶信号)
Symmetric about vertical axis: x (-t) = x (t), x [-n] = x [n] for all t
2) Odd signals (奇信号)
Antisymmetric about origin: x (-t) = - x (t), x [-n] = x [n] for all t
3) Even-odd decomposition of x(t)奇偶分量
x (t)=
x
e
x_e
xe(t)+
x
o
x_o
xo(t) where
x
e
x_e
xe(-t) =
x
e
x_e
xe(t),
x
o
x_o
xo(-t) = -
x
o
x_o
xo(t)
→
\rightarrow
→
x
e
x_e
xe(t)=
1
2
\frac{1}{2}
21[x(t)+x(-t)]
→
\rightarrow
→
x
o
x_o
xo(t)=
1
2
\frac{1}{2}
21[x(t)-x(-t)]
4) PRODUCT Rule
ODD
×
\times
× ODD
→
\rightarrow
→ EVEN
EVEN
×
\times
× EVEN
→
\rightarrow
→ EVEN
EVEN
×
\times
× ODD
→
\rightarrow
→ ODD
ODD
×
\times
× EVEN
→
\rightarrow
→ ODD
∫
−
T
T
x
(
t
)
d
t
\int_{-T}^Tx(t)dt
∫−TTx(t)dt=0 always of x(t) is ODD
=0 sometimes if x(t) is EVEN
∫
−
T
T
x
(
t
)
d
t
\int_{-T}^Tx(t)dt
∫−TTx(t)dt=2
∫
0
T
x
(
t
)
d
t
\int_{0}^Tx(t)dt
∫0Tx(t)dt for x(t) EVEN
3. Operation on Signals信号运算
(1) In Time Domain时域
1) Time Scaling时间展缩
y(t) = x (at)
→
\rightarrow
→ a>1, compressed; 0<a<1, expanded
y[n] =x [kn] , k>0, k is an integer
→
\rightarrow
→some values lost
2) Time Reflection时间反转
y(t)=x(-t) → \rightarrow →The signal y(t) represents a reflected version of x(t) about t=0
3) Time Shifting时移
y(t)=x(t-
t
0
t_0
t0)
→
\rightarrow
→
t
0
t_0
t0>0, 右移(shift towards right) ;
t
0
t_0
t0<0, 左移(shift towards left)
y[n]=x[n-m]
→
\rightarrow
→ m>0, 右移(shift towards right) ;m<0, 左移(shift towards left)
(2) In Amplitude幅度
1) Amplitude scaling幅度缩放
x(t)
→
\rightarrow
→ y(t)=cx(t)
x[n]
→
\rightarrow
→ y[n]=cx[n]
2) Addition加
y(t) =
x
1
x_1
x1(t) +
x
2
x_2
x2(t)
y[n] =
x
1
x_1
x1[n] +
x
2
x_2
x2[n]
3) Multiplication乘
y(t) =
x
1
x_1
x1(t)
x
2
x_2
x2(t)
y[n] =
x
1
x_1
x1[n]
x
2
x_2
x2[n]
4) Differentiation 微分
y(t) = d d t \frac{d}{dt} dtdx(t)
5) Integration 积分
y(t) = ∫ − ∞ t x ( τ ) d τ \int_{-∞}^tx(τ)dτ ∫−∞tx(τ)dτ
(3) Precedence Rule步骤
1)f(t) → \rightarrow →f( α \alpha αt+ β \beta β)
f(t)
→
\rightarrow
→f(t+
β
\beta
β)
→
\rightarrow
→f(
α
\alpha
αt+
β
\beta
β)
→
\rightarrow
→ f(-
α
\alpha
αt+
β
\beta
β)
平移
→
\rightarrow
→ 展缩
→
\rightarrow
→ 反转
2)f( α \alpha αt+ β \beta β) → \rightarrow →f(t)
f(-
α
\alpha
αt +
β
\beta
β)
→
\rightarrow
→ f(
α
\alpha
αt+
β
\beta
β)
→
\rightarrow
→ f(t+
β
\beta
β)
→
\rightarrow
→ f(t)
反转
→
\rightarrow
→ 展缩
→
\rightarrow
→ 平移
二、Basic Time Signals基本时间信号
1. Exponential Signals指数信号
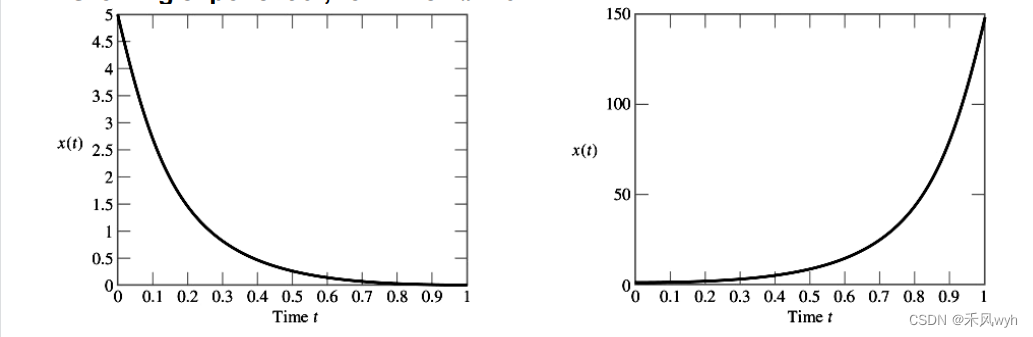
(1) Continuous-time
x(t) = Beαt, B and a are real parameters
a. Decaying exponential, for which α < 0
b. Growing exponential, for which α > 0
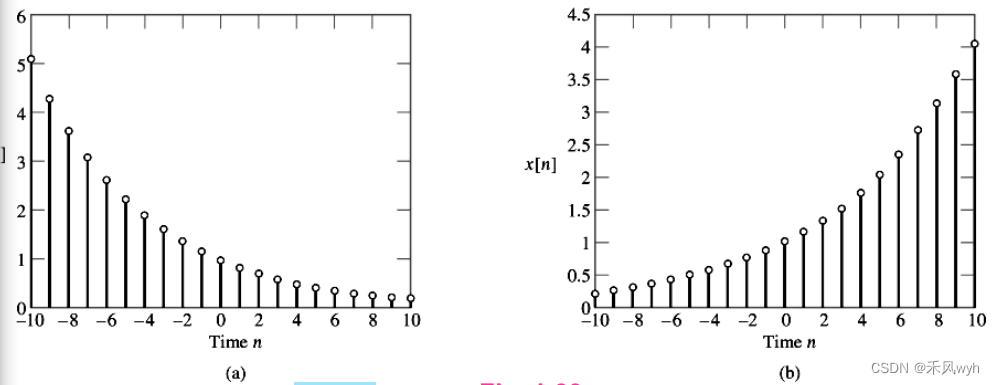
(2) Discrete-time
x[n]=Brn , r=e α
a. Decaying exponential, for which α < 0
b. Growing exponential, for which α > 0
2. Sinusoidal Signals正弦信号
(1) Continuous-time
x (t)=A cos (ωt+φ), T=
2
Π
ω
\frac{2Π}{ω}
ω2Π
x (t +T) = x(t)
(2) Discrete-time
x [n] =A cos (Ωn+φ)
Periodic condition: x [n + N] =A cos (Ωn+ΩN+φ)
→
\rightarrow
→ ΩN=2Πm or Ω=
2
Π
m
ω
\frac{2Πm}{ω}
ω2Πm
(3) Relation Between Sinusoidal and Complex Exponential Signals
1) Complex exponential signal
Euler’s identity:ejθ=cosθ+jsinθ
Complex exponential signal: Bejωt= A ejφejωt=A cos (ωt+φ)+j Asin (ωt+φ)
A cos (ωt+φ)= Re {Bejωt}
A sin (ωt+φ) = Im {Bejωt}
2) Discrete-time case
A cos (Ωn+φ) = Re {BejΩn}
A sin (Ωn+φ) = Im {BejΩn}
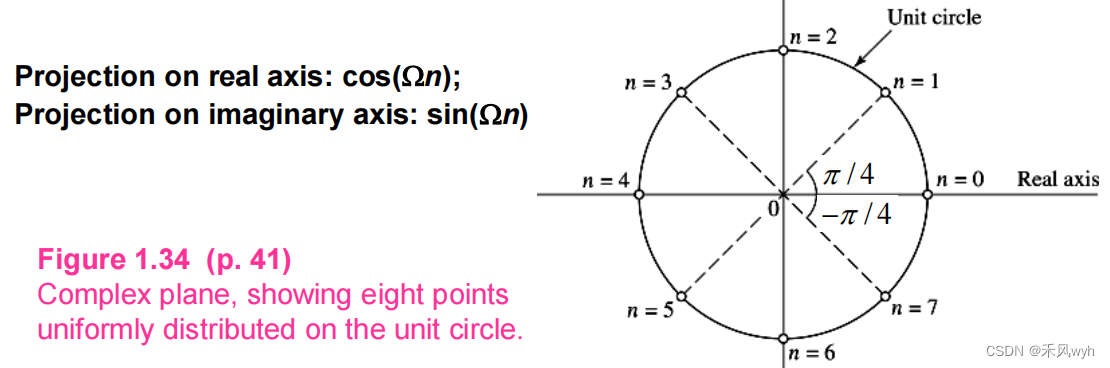
3) Two-dimensional representation of the complex exponential ejΩn for Ω = Π/4 and n = 0, 1…
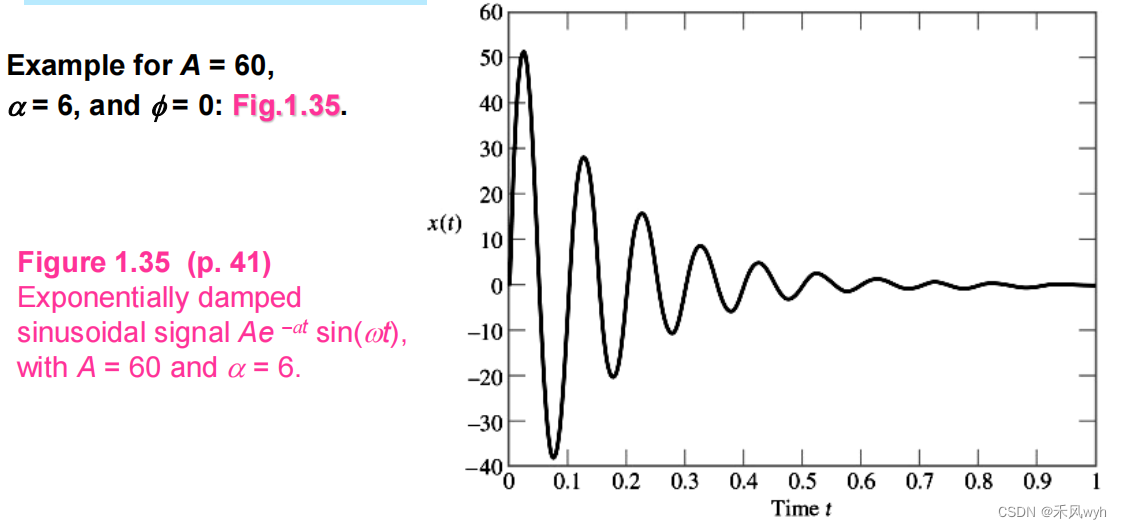
(4) Exponential Damped (衰减) Sinusoidal Signals
x(t)= A e-αt sin (ωt+φ), α>0
3. Step Functions阶跃信号
(1) Continuous-time
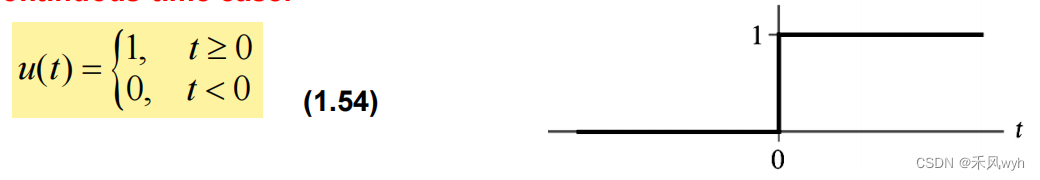
(2) Discrete-time
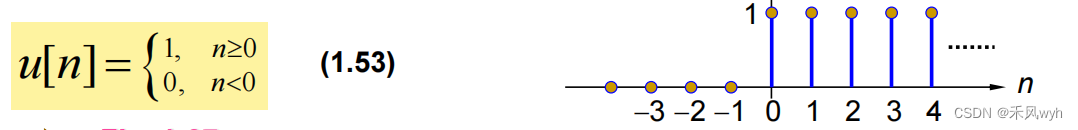
(3) Properties
1) 相乘特性(单边特性)
x(t)u(t)= { x(t) ,t>0
0,t<0
2) 表示作用区间
a. f(t)[u(t- t 1 t_1 t1)-u(t- t 2 t_2 t2)]
Rectangular pulse脉冲信号:p(t)=u(t+ 1 2 \frac{1}{2} 21)-u(t- 1 2 \frac{1}{2} 21)
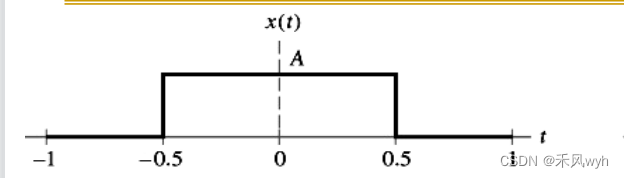
b. 加减
sgn(t) function符号函数
sgn(t)={1,t>0
-1, t<0
=u(t)-u(-t)
3) 积分
y(t) = ∫ − ∞ t u ( τ ) d τ \int_{-∞}^tu(τ)dτ ∫−∞tu(τ)dτ=tu(t)=r(t) → \rightarrow → 斜坡信号
4. Impulse Functions冲激信号
(1) Discrete-time
![[n]=1, n=0; 0, n≠0](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ba7e46f48dcc43ac98e36485ea35ad39.png)
(2) Continuous-time
δ
\delta
δ(t)=0 for t ≠0
∫
−
∞
∞
δ
(
t
)
d
t
\int_{-∞}^∞δ(t)dt
∫−∞∞δ(t)dt=1
(3) Properties of impulse function
1) Even function偶函数
δ \delta δ(-t)= δ \delta δ(t)
2) Sifting property时移特性
δ
\delta
δ(t-
t
0
t_0
t0) = 0, t ≠
t
0
t_0
t0
∫
−
∞
∞
δ
(
t
−
t
o
)
d
t
\int_{-∞}^∞δ(t-to)dt
∫−∞∞δ(t−to)dt=1
3) Time-scaling property展缩特性
δ \delta δ(at+b)= 1 a \frac{1}{a} a1 δ \delta δ(t+ b a \frac{b}{a} ab)
4) Sampling property取样特性
∫ − ∞ ∞ x ( τ ) δ ( t ) d t \int_{-∞}^∞x(τ)δ(t)dt ∫−∞∞x(τ)δ(t)dt=x(0)
x(t)* δ \delta δ(t- t 0 t_0 t0)= ∫ − ∞ ∞ x ( t ) δ ( t − t o ) d t \int_{-∞}^∞x(t)δ(t-to)dt ∫−∞∞x(t)δ(t−to)dt=x( t 0 t_0 t0)
x ( t ) δ ( t − t o ) x(t)δ(t-to) x(t)δ(t−to)=x( t 0 t_0 t0) δ \delta δ(t- t 0 t_0 t0)
∑ i = − ∞ ∞ \sum_{i=-∞}^∞ ∑i=−∞∞x(t) δ \delta δ(k)= x (0)
5) 相乘特性
x
(
t
)
δ
(
t
)
x(t)δ(t)
x(t)δ(t)=
x
(
0
)
δ
(
t
)
x(0)δ(t)
x(0)δ(t)
x
(
t
)
δ
(
t
−
t
o
)
x(t)δ(t-to)
x(t)δ(t−to)=
x
(
t
o
)
δ
(
t
−
t
o
)
x(to)δ(t-to)
x(to)δ(t−to)
6) Derivatives

7) 与u(t)的关系
δ(t) is the derivative of u(t): δ(t)= d d t u ( t ) \frac{d}{dt}u(t) dtdu(t)
u(t) is the integral of δ(t): u(t) = ∫ − ∞ t δ ( τ ) d τ \int_{-∞}^tδ(τ)dτ ∫−∞tδ(τ)dτ
u[n] = δ[n]+δ[n-1]+…= ∑ i = 0 ∞ \sum_{i=0}^∞ ∑i=0∞ δ \delta δ[n-k]= ∑ i = − ∞ n \sum_{i=-∞}^n ∑i=−∞n δ \delta δ[m]
δ[n]=u[n]-u[n-1]
三、Systems Classification and Properties系统分类和性质
1. System Representation

2. Continuous-time and Discrete-time Systems
(1) Continuous-time
y(t)=H{x(t)}
(2) Discrete-time
y[n]=H{x[n]}

(3) Moving-average system
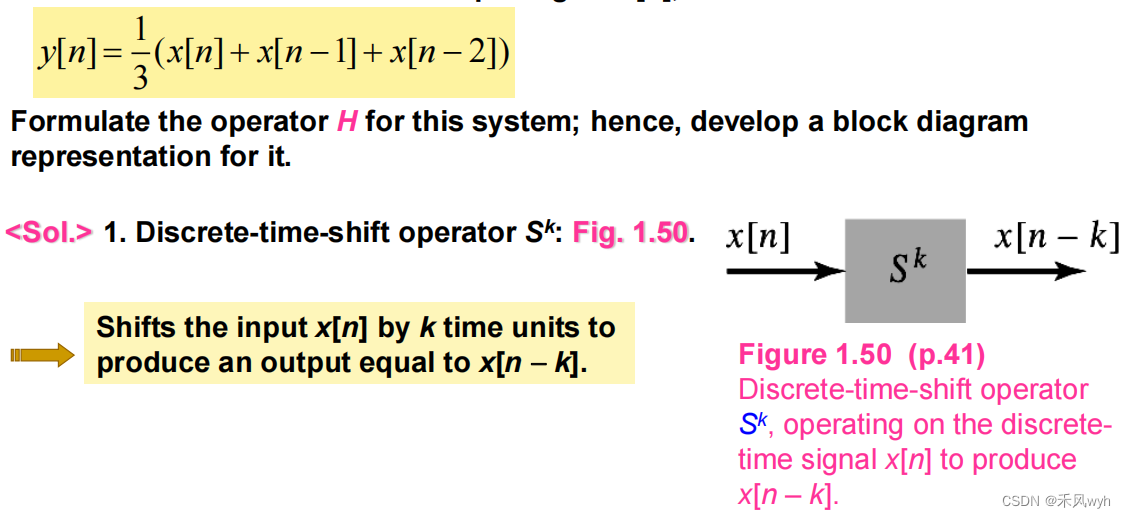
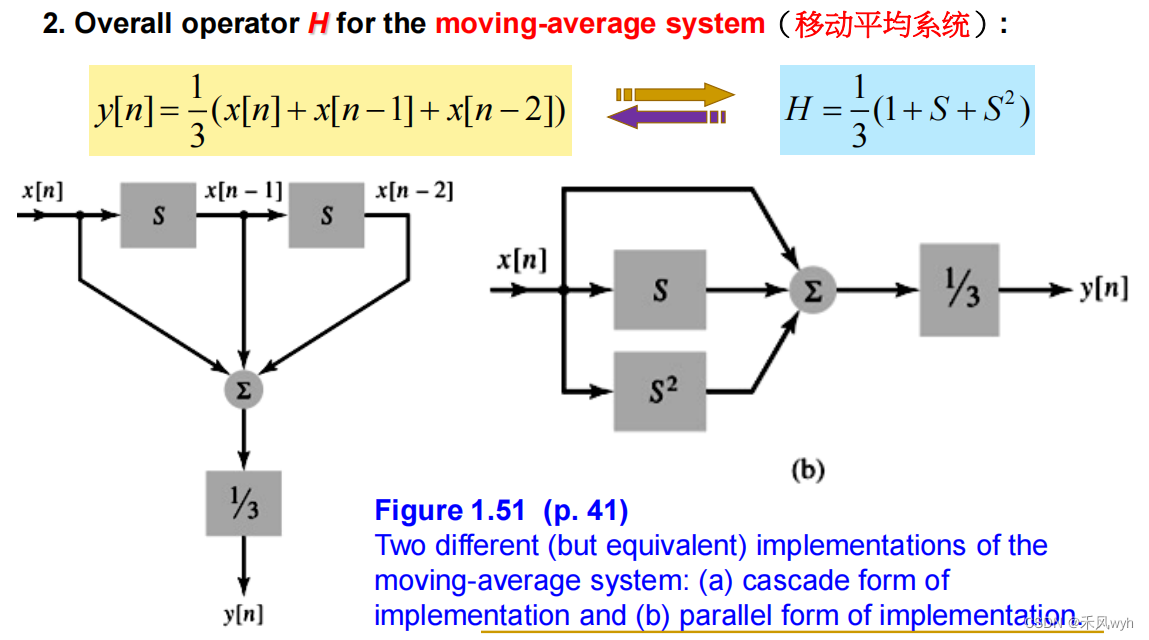
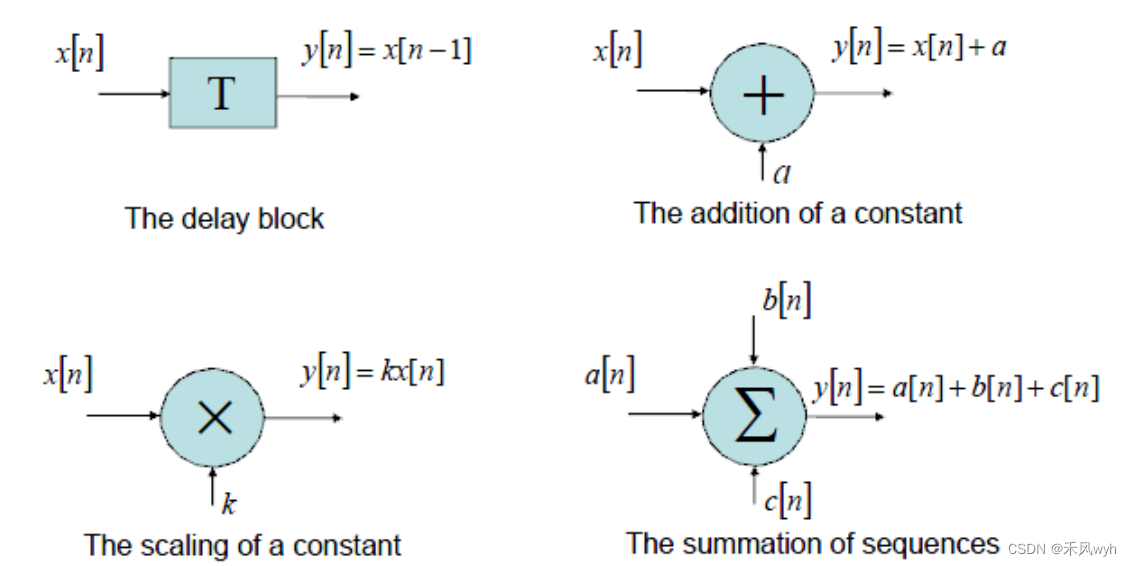
(4) Representation of discrete-time operations
3. Systems with and without memory
(1) without memory
A system is said to be memoryless if the output at any time depends on only the input at that same time.
(2) with memory
A system is said to be memory if the output at any time depends on only the input at past or in the future.
4. Causal and Non-causal systems
(1) Causal
A system is said to be causal if its present value of the output signal depends only on the present or past values of the input signal.
(2) Non-causal
A system is said to be noncausal if its output signal depends on one or more future values of the input signal.
5. Linear and Nonlinear systems
(1) Linear
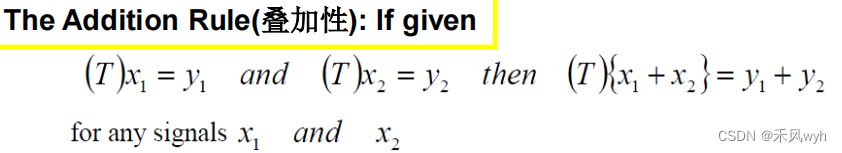

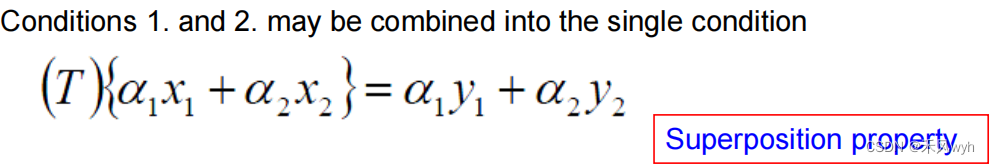
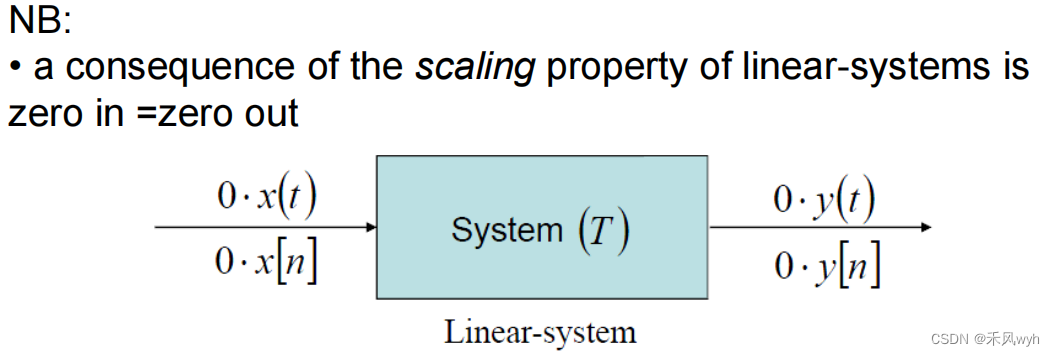
(2) Nonlinear
6. Time-variant and Time-invariant Systems
(1) Time-invariant

(2) Condition for time-invariant system
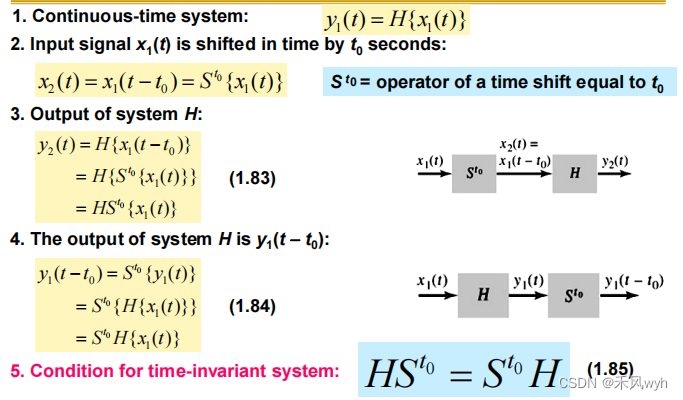
7. Stable systems
A system is bounded-input/bounded-output (BIBO,有界输入有界输出) stable if for any bounded input x defined by |x|≤
k
1
k_1
k1
The corresponding output y is also bounded defined by |y|≤
k
2
k_2
k2 where
k
1
k_1
k1 and
k
2
k_2
k2 are finite real constants
8. Feedback systems
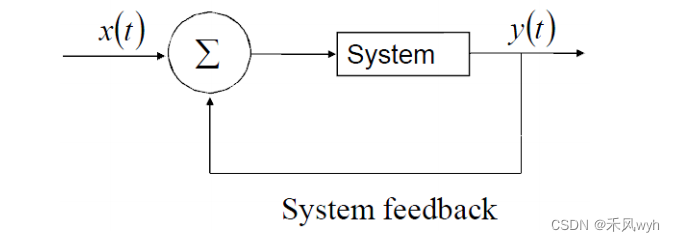
9. Invertibility(可逆性) systems
(1) Continuous-time system
x(t) = input; y(t) = output
H = first system operator; H
i
n
v
_{inv}
inv = second system operator
(2) Output of the second system
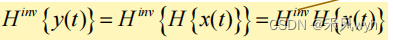
H
i
n
v
_{inv}
inv=inverse operator
(3) Condition for invertible system
H
i
n
v
_{inv}
inv H= I
I = identity operator (单位算符)






![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA实验教学过程管理平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a0c9c2426b3743619d880cd8dca1a29b.png)