每天一题,防止痴呆
- 题目
- 示例
- 分析思路1
- 题解1
- 分析思路2
- 题解2
👉️ 力扣原文
题目
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1
输出: []
分析思路1
使用回溯算法:
使用了一个 start 变量来避免重复搜索。每次迭代从 start 开始,而不是从0开始。这是因为我们不需要在同一层次上搜索相同的元素,这会导致重复组合的出现。
此外,我们还进行了剪枝操作,即当候选数大于目标数时,我们停止搜索。这可以大大减少搜索空间,提高代码效率。
最后,我们使用了一个 result 列表来存储所有找到的组合。每当找到一个组合时,我们将其添加到结果列表中。
题解1
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 排序,便于剪枝
backtrack(candidates, target, 0, temp, result);
return result;
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int start, List<Integer> temp, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (target < 0) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] > target) { // 剪枝
break;
}
temp.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, temp, result); // 注意这里传入的参数
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
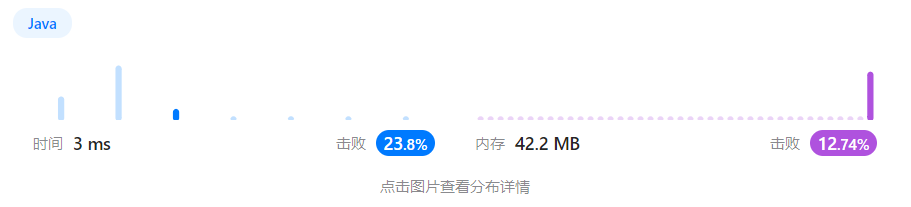
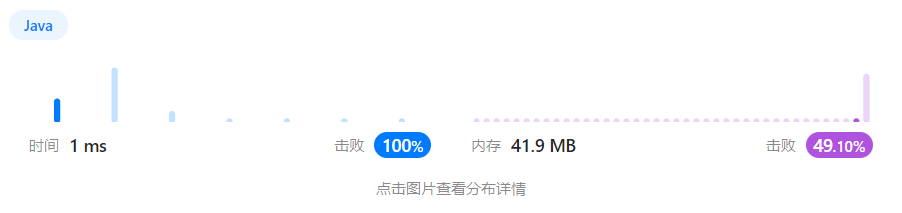
执行结果
分析思路2
动态规划:
使用了一个二维数组 dp 来存储中间结果,其中 dp[i] 表示数字和为 i 时的所有组合。初始时,dp[0] 存储一个空列表,表示数字和为 0 时只有一种组合,即不选任何数字。
接下来,对于每个数字 candidates[i],从 candidates[i] 开始枚举数字和 j,如果 dp[j - candidates[i]] 不为空,则将 dp[j - candidates[i]] 中的每个组合都加上 candidates[i],得到一个新的组合,将其加入到 dp[j] 中。这样,当枚举到 target 时,dp[target] 中存储的就是所有符合要求的组合。
最后,如果 dp[target] 为空,则返回一个空列表,否则返回 dp[target]。
题解2
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>>[] dp = new List[target + 1];
dp[0] = new ArrayList<>();
dp[0].add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
for (int j = candidates[i]; j <= target; j++) {
if (dp[j - candidates[i]] != null) {
if (dp[j] == null) {
dp[j] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (List<Integer> list : dp[j - candidates[i]]) {
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(list);
temp.add(candidates[i]);
dp[j].add(temp);
}
}
}
}
return dp[target] == null ? new ArrayList<>() : dp[target];
}
}
执行结果