文章目录
- 前言
- Midiapipe关键点检测
- stgcn 姿态评估
- 效果
前言
冒个泡,年少无知吹完的牛皮是要还的呀。
那么这里的话要做的一个东西就是一个人体的姿态判断,比如一个人是坐着还是站着还是摔倒了,如果摔倒了我们要做什么操作,之类的。
不过这里比较可惜的就是这个midiapipe 它里面的Pose的话是只有一个pose的也就是单目标的一个检测,所以距离我想要的一个效果是很难受的,不过这个dome还是挺好玩的。
实现效果如下:

Midiapipe关键点检测
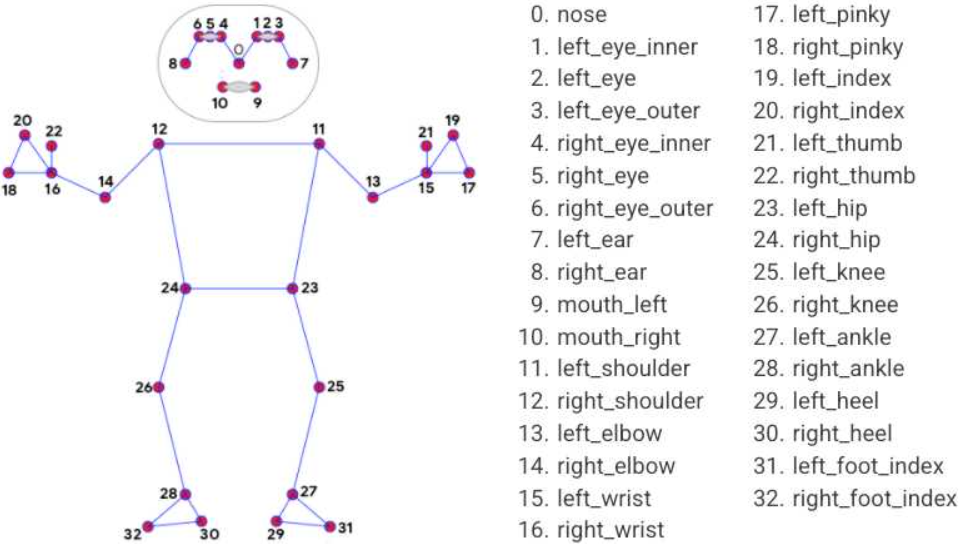
这个dome的核心之一,就是这个检测到人体的一个关键点,
import time
from collections import deque
import cv2
import numpy as np
import mediapipe as mp
from stgcn.stgcn import STGCN
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
# 人体关键点检测模块
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles
mp_pose = mp.solutions.pose
# 人脸模块
mpFace = mp.solutions.face_detection
faceDetection = mpFace.FaceDetection(min_detection_confidence=0.5)
KEY_JOINTS = [
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.NOSE,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.LEFT_SHOULDER,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.RIGHT_SHOULDER,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.LEFT_ELBOW,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.RIGHT_ELBOW,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.LEFT_WRIST,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.RIGHT_WRIST,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.LEFT_HIP,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.RIGHT_HIP,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.LEFT_KNEE,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.RIGHT_KNEE,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.LEFT_ANKLE,
mp_pose.PoseLandmark.RIGHT_ANKLE
]
POSE_CONNECTIONS = [(6, 4), (4, 2), (2, 13), (13, 1), (5, 3), (3, 1), (12, 10),
(10, 8), (8, 2), (11, 9), (9, 7), (7, 1), (13, 0)]
POINT_COLORS = [(0, 255, 255), (0, 191, 255), (0, 255, 102), (0, 77, 255), (0, 255, 0), # Nose, LEye, REye, LEar, REar
(77, 255, 255), (77, 255, 204), (77, 204, 255), (191, 255, 77), (77, 191, 255), (191, 255, 77), # LShoulder, RShoulder, LElbow, RElbow, LWrist, RWrist
(204, 77, 255), (77, 255, 204), (191, 77, 255), (77, 255, 191), (127, 77, 255), (77, 255, 127), (0, 255, 255)] # LHip, RHip, LKnee, Rknee, LAnkle, RAnkle, Neck
LINE_COLORS = [(0, 215, 255), (0, 255, 204), (0, 134, 255), (0, 255, 50), (77, 255, 222),
(77, 196, 255), (77, 135, 255), (191, 255, 77), (77, 255, 77), (77, 222, 255),
(255, 156, 127), (0, 127, 255), (255, 127, 77), (0, 77, 255), (255, 77, 36)]
POSE_MAPPING = ["站着","走着","坐着","躺下","站起来","坐下","摔倒"]
POSE_MAPPING_COLOR = [
(255,255,240),( 245,222,179),(244,164,96),( 210,180,140),
(255,127,80),(255,165,79),( 255,48,48)
]
# 为了检测动作的准确度,每30帧进行一次检测
ACTION_MODEL_MAX_FRAMES = 30
class FallDetection:
def __init__(self):
self.action_model = STGCN(weight_file='./weights/tsstg-model.pth', device='cpu')
self.joints_list = deque(maxlen=ACTION_MODEL_MAX_FRAMES)
def draw_skeleton(self, frame, pts):
l_pair = POSE_CONNECTIONS
p_color = POINT_COLORS
line_color = LINE_COLORS
part_line = {}
pts = np.concatenate((pts, np.expand_dims((pts[1, :] + pts[2, :]) / 2, 0)), axis=0)
for n in range(pts.shape[0]):
if pts[n, 2] <= 0.05:
continue
cor_x, cor_y = int(pts[n, 0]), int(pts[n, 1])
part_line[n] = (cor_x, cor_y)
cv2.circle(frame, (cor_x, cor_y), 3, p_color[n], -1)
# cv2.putText(frame, str(n), (cor_x+10, cor_y+10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1)
for i, (start_p, end_p) in enumerate(l_pair):
if start_p in part_line and end_p in part_line:
start_xy = part_line[start_p]
end_xy = part_line[end_p]
cv2.line(frame, start_xy, end_xy, line_color[i], int(1*(pts[start_p, 2] + pts[end_p, 2]) + 3))
return frame
def cv2_add_chinese_text(self, img, text, position, textColor=(0, 255, 0), textSize=30):
if (isinstance(img, np.ndarray)): # 判断是否OpenCV图片类型
img = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 创建一个可以在给定图像上绘图的对象
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 字体的格式,opencv不支持中文,需要指定字体
fontStyle = ImageFont.truetype(
"./fonts/MSYH.ttc", textSize, encoding="utf-8")
draw.text(position, text, textColor, font=fontStyle)
return cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def detect(self):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# cap.set(3, 540)
# cap.set(4, 960)
# cap.set(5,30)
image_h = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)
image_w = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)
frame_num = 0
print(image_h, image_w)
with mp_pose.Pose(
min_detection_confidence=0.7,
min_tracking_confidence=0.5) as pose:
while cap.isOpened():
fps_time = time.time()
frame_num += 1
success, image = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Ignoring empty camera frame.")
continue
# 提高性能,这里是做那个姿态的一个推理
image.flags.writeable = False
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
results = pose.process(image)
if results.pose_landmarks:
# 识别骨骼点
image.flags.writeable = True
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
landmarks = results.pose_landmarks.landmark
joints = np.array([[landmarks[joint].x * image_w,
landmarks[joint].y * image_h,
landmarks[joint].visibility]
for joint in KEY_JOINTS])
# 人体框
box_l, box_r = int(joints[:, 0].min())-50, int(joints[:, 0].max())+50
box_t, box_b = int(joints[:, 1].min())-100, int(joints[:, 1].max())+100
self.joints_list.append(joints)
# 识别动作
action = ''
clr = (0, 255, 0)
# 30帧数据预测动作类型
if len(self.joints_list) == ACTION_MODEL_MAX_FRAMES:
pts = np.array(self.joints_list, dtype=np.float32)
out = self.action_model.predict(pts, (image_w, image_h))
#
index = out[0].argmax()
action_name = POSE_MAPPING[index]
cls = POSE_MAPPING_COLOR[index]
action = '{}: {:.2f}%'.format(action_name, out[0].max() * 100)
print(action)
# 绘制骨骼点和动作类别
image = self.draw_skeleton(image, self.joints_list[-1])
image = cv2.rectangle(image, (box_l, box_t), (box_r, box_b), (255, 0, 0), 1)
image = self.cv2_add_chinese_text(image, f'当前状态:{action}', (box_l + 10, box_t + 10), clr, 40)
else:
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
image = cv2.putText(image, f'FPS: {int(1.0 / (time.time() - fps_time))}',
(50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('Pose', image)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
FallDetection().detect()
stgcn 姿态评估
首先的话,他这个时空图神经网络,我是没有研究过的,这玩意就是啥呢,就是把pose传入然后一通运算,然后就可以得到一个动作以及所属类别,也就是说这玩意是一个分类的图网络。这部分的话我不是很熟悉,这是我的盲区,所以我这里就把这个当作黑盒处理了。那么同样的这部分代码也是直接在Github上面cv过来,然后集成到这个项目里面。
是的,算法的运用开发和我们正常的开发其实区别不大,重新训练任务只是调参,适当调整网络模型,以及训练数据即可,颠覆性的改动=重新设计算法。
这部分代码并不多,我就直接贴出来了:
按顺序从上到下
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from stgcn.Utils import Graph
class GraphConvolution(nn.Module):
"""The basic module for applying a graph convolution.
Args:
- in_channel: (int) Number of channels in the input sequence data.
- out_channels: (int) Number of channels produced by the convolution.
- kernel_size: (int) Size of the graph convolving kernel.
- t_kernel_size: (int) Size of the temporal convolving kernel.
- t_stride: (int, optional) Stride of the temporal convolution. Default: 1
- t_padding: (int, optional) Temporal zero-padding added to both sides of
the input. Default: 0
- t_dilation: (int, optional) Spacing between temporal kernel elements. Default: 1
- bias: (bool, optional) If `True`, adds a learnable bias to the output.
Default: `True`
Shape:
- Inputs x: Graph sequence in :math:`(N, in_channels, T_{in}, V)`,
A: Graph adjacency matrix in :math:`(K, V, V)`,
- Output: Graph sequence out in :math:`(N, out_channels, T_{out}, V)`
where
:math:`N` is a batch size,
:math:`K` is the spatial kernel size, as :math:`K == kernel_size[1]`,
:math:`T_{in}/T_{out}` is a length of input/output sequence,
:math:`V` is the number of graph nodes.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
t_kernel_size=1,
t_stride=1,
t_padding=0,
t_dilation=1,
bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
out_channels * kernel_size,
kernel_size=(t_kernel_size, 1),
padding=(t_padding, 0),
stride=(t_stride, 1),
dilation=(t_dilation, 1),
bias=bias)
def forward(self, x, A):
x = self.conv(x)
n, kc, t, v = x.size()
x = x.view(n, self.kernel_size, kc//self.kernel_size, t, v)
x = torch.einsum('nkctv,kvw->nctw', (x, A))
return x.contiguous()
class st_gcn(nn.Module):
"""Applies a spatial temporal graph convolution over an input graph sequence.
Args:
- in_channels: (int) Number of channels in the input sequence data.
- out_channels: (int) Number of channels produced by the convolution.
- kernel_size: (tuple) Size of the temporal convolving kernel and
graph convolving kernel.
- stride: (int, optional) Stride of the temporal convolution. Default: 1
- dropout: (int, optional) Dropout rate of the final output. Default: 0
- residual: (bool, optional) If `True`, applies a residual mechanism.
Default: `True`
Shape:
- Inputs x: Graph sequence in :math: `(N, in_channels, T_{in}, V)`,
A: Graph Adjecency matrix in :math: `(K, V, V)`,
- Output: Graph sequence out in :math: `(N, out_channels, T_{out}, V)`
where
:math:`N` is a batch size,
:math:`K` is the spatial kernel size, as :math:`K == kernel_size[1]`,
:math:`T_{in}/T_{out}` is a length of input/output sequence,
:math:`V` is the number of graph nodes.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
stride=1,
dropout=0,
residual=True):
super().__init__()
assert len(kernel_size) == 2
assert kernel_size[0] % 2 == 1
padding = ((kernel_size[0] - 1) // 2, 0)
self.gcn = GraphConvolution(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size[1])
self.tcn = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels,
out_channels,
(kernel_size[0], 1),
(stride, 1),
padding),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.Dropout(dropout, inplace=True)
)
if not residual:
self.residual = lambda x: 0
elif (in_channels == out_channels) and (stride == 1):
self.residual = lambda x: x
else:
self.residual = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=(stride, 1)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x, A):
res = self.residual(x)
x = self.gcn(x, A)
x = self.tcn(x) + res
return self.relu(x)
class StreamSpatialTemporalGraph(nn.Module):
"""Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks.
Args:
- in_channels: (int) Number of input channels.
- graph_args: (dict) Args map of `Actionsrecognition.Utils.Graph` Class.
- num_class: (int) Number of class outputs. If `None` return pooling features of
the last st-gcn layer instead.
- edge_importance_weighting: (bool) If `True`, adds a learnable importance
weighting to the edges of the graph.
- **kwargs: (optional) Other parameters for graph convolution units.
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(N, in_channels, T_{in}, V_{in})`
- Output: :math:`(N, num_class)` where
:math:`N` is a batch size,
:math:`T_{in}` is a length of input sequence,
:math:`V_{in}` is the number of graph nodes,
or If num_class is `None`: `(N, out_channels)`
:math:`out_channels` is number of out_channels of the last layer.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, graph_args, num_class=None,
edge_importance_weighting=True, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
# Load graph.
graph = Graph(**graph_args)
A = torch.tensor(graph.A, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=False)
self.register_buffer('A', A)
# Networks.
spatial_kernel_size = A.size(0)
temporal_kernel_size = 9
kernel_size = (temporal_kernel_size, spatial_kernel_size)
kwargs0 = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if k != 'dropout'}
self.data_bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(in_channels * A.size(1))
self.st_gcn_networks = nn.ModuleList((
st_gcn(in_channels, 64, kernel_size, 1, residual=False, **kwargs0),
st_gcn(64, 64, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs),
st_gcn(64, 64, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs),
st_gcn(64, 64, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs),
st_gcn(64, 128, kernel_size, 2, **kwargs),
st_gcn(128, 128, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs),
st_gcn(128, 128, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs),
st_gcn(128, 256, kernel_size, 2, **kwargs),
st_gcn(256, 256, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs),
st_gcn(256, 256, kernel_size, 1, **kwargs)
))
# initialize parameters for edge importance weighting.
if edge_importance_weighting:
self.edge_importance = nn.ParameterList([
nn.Parameter(torch.ones(A.size()))
for i in self.st_gcn_networks
])
else:
self.edge_importance = [1] * len(self.st_gcn_networks)
if num_class is not None:
self.cls = nn.Conv2d(256, num_class, kernel_size=1)
else:
self.cls = lambda x: x
def forward(self, x):
# data normalization.
N, C, T, V = x.size()
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous() # (N, V, C, T)
x = x.view(N, V * C, T)
x = self.data_bn(x)
x = x.view(N, V, C, T)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
x = x.view(N, C, T, V)
# forward.
for gcn, importance in zip(self.st_gcn_networks, self.edge_importance):
x = gcn(x, self.A * importance)
x = F.avg_pool2d(x, x.size()[2:])
x = self.cls(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
return x
class TwoStreamSpatialTemporalGraph(nn.Module):
"""Two inputs spatial temporal graph convolutional networks.
Args:
- graph_args: (dict) Args map of `Actionsrecognition.Utils.Graph` Class.
- num_class: (int) Number of class outputs.
- edge_importance_weighting: (bool) If `True`, adds a learnable importance
weighting to the edges of the graph.
- **kwargs: (optional) Other parameters for graph convolution units.
Shape:
- Input: :tuple of math:`((N, 3, T, V), (N, 2, T, V))`
for points and motions stream where.
:math:`N` is a batch size,
:math:`in_channels` is data channels (3 is (x, y, score)), (2 is (mot_x, mot_y))
:math:`T` is a length of input sequence,
:math:`V` is the number of graph nodes,
- Output: :math:`(N, num_class)`
"""
def __init__(self, graph_args, num_class, edge_importance_weighting=True,
**kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.pts_stream = StreamSpatialTemporalGraph(3, graph_args, None,
edge_importance_weighting,
**kwargs)
self.mot_stream = StreamSpatialTemporalGraph(2, graph_args, None,
edge_importance_weighting,
**kwargs)
self.fcn = nn.Linear(256 * 2, num_class)
def forward(self, inputs):
out1 = self.pts_stream(inputs[0])
out2 = self.mot_stream(inputs[1])
concat = torch.cat([out1, out2], dim=-1)
out = self.fcn(concat)
return torch.sigmoid(out)
import torch
import numpy as np
from .Models import TwoStreamSpatialTemporalGraph
from .Utils import normalize_points_with_size, scale_pose
class STGCN(object):
"""Two-Stream Spatial Temporal Graph Model Loader.
Args:
weight_file: (str) Path to trained weights file.
device: (str) Device to load the model on 'cpu' or 'cuda'.
"""
def __init__(self,
weight_file='./Models/TSSTG/tsstg-model.pth',
device='cuda'):
self.graph_args = {'strategy': 'spatial'}
self.class_names = ['Standing', 'Walking', 'Sitting', 'Lying Down',
'Stand up', 'Sit down', 'Fall Down']
self.num_class = len(self.class_names)
self.device = device
self.model = TwoStreamSpatialTemporalGraph(self.graph_args, self.num_class).to(self.device)
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weight_file, map_location=torch.device(device)))
self.model.eval()
def predict(self, pts, image_size):
"""Predict actions from single person skeleton points and score in time sequence.
Args:
pts: (numpy array) points and score in shape `(t, v, c)` where
t : inputs sequence (time steps).,
v : number of graph node (body parts).,
c : channel (x, y, score).,
image_size: (tuple of int) width, height of image frame.
Returns:
(numpy array) Probability of each class actions.
"""
pts[:, :, :2] = normalize_points_with_size(pts[:, :, :2], image_size[0], image_size[1])
pts[:, :, :2] = scale_pose(pts[:, :, :2])
pts = np.concatenate((pts, np.expand_dims((pts[:, 1, :] + pts[:, 2, :]) / 2, 1)), axis=1)
pts = torch.tensor(pts, dtype=torch.float32)
pts = pts.permute(2, 0, 1)[None, :]
mot = pts[:, :2, 1:, :] - pts[:, :2, :-1, :]
mot = mot.to(self.device)
pts = pts.to(self.device)
out = self.model((pts, mot))
return out.detach().cpu().numpy()
### Reference from: https://github.com/yysijie/st-gcn/blob/master/net/utils/graph.py
import os
import torch
import numpy as np
class Graph:
"""The Graph to model the skeletons extracted by the Alpha-Pose.
Args:
- strategy: (string) must be one of the follow candidates
- uniform: Uniform Labeling,
- distance: Distance Partitioning,
- spatial: Spatial Configuration,
For more information, please refer to the section 'Partition Strategies'
in our paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.07455).
- layout: (string) must be one of the follow candidates
- coco_cut: Is COCO format but cut 4 joints (L-R ears, L-R eyes) out.
- max_hop: (int) the maximal distance between two connected nodes.
- dilation: (int) controls the spacing between the kernel points.
"""
def __init__(self,
layout='coco_cut',
strategy='uniform',
max_hop=1,
dilation=1):
self.max_hop = max_hop
self.dilation = dilation
self.get_edge(layout)
self.hop_dis = get_hop_distance(self.num_node, self.edge, max_hop)
self.get_adjacency(strategy)
def get_edge(self, layout):
if layout == 'coco_cut':
self.num_node = 14
self_link = [(i, i) for i in range(self.num_node)]
neighbor_link = [(6, 4), (4, 2), (2, 13), (13, 1), (5, 3), (3, 1), (12, 10),
(10, 8), (8, 2), (11, 9), (9, 7), (7, 1), (13, 0)]
self.edge = self_link + neighbor_link
self.center = 13
else:
raise ValueError('This layout is not supported!')
def get_adjacency(self, strategy):
valid_hop = range(0, self.max_hop + 1, self.dilation)
adjacency = np.zeros((self.num_node, self.num_node))
for hop in valid_hop:
adjacency[self.hop_dis == hop] = 1
normalize_adjacency = normalize_digraph(adjacency)
if strategy == 'uniform':
A = np.zeros((1, self.num_node, self.num_node))
A[0] = normalize_adjacency
self.A = A
elif strategy == 'distance':
A = np.zeros((len(valid_hop), self.num_node, self.num_node))
for i, hop in enumerate(valid_hop):
A[i][self.hop_dis == hop] = normalize_adjacency[self.hop_dis ==
hop]
self.A = A
elif strategy == 'spatial':
A = []
for hop in valid_hop:
a_root = np.zeros((self.num_node, self.num_node))
a_close = np.zeros((self.num_node, self.num_node))
a_further = np.zeros((self.num_node, self.num_node))
for i in range(self.num_node):
for j in range(self.num_node):
if self.hop_dis[j, i] == hop:
if self.hop_dis[j, self.center] == self.hop_dis[i, self.center]:
a_root[j, i] = normalize_adjacency[j, i]
elif self.hop_dis[j, self.center] > self.hop_dis[i, self.center]:
a_close[j, i] = normalize_adjacency[j, i]
else:
a_further[j, i] = normalize_adjacency[j, i]
if hop == 0:
A.append(a_root)
else:
A.append(a_root + a_close)
A.append(a_further)
A = np.stack(A)
self.A = A
#self.A = np.swapaxes(np.swapaxes(A, 0, 1), 1, 2)
else:
raise ValueError("This strategy is not supported!")
def get_hop_distance(num_node, edge, max_hop=1):
A = np.zeros((num_node, num_node))
for i, j in edge:
A[j, i] = 1
A[i, j] = 1
# compute hop steps
hop_dis = np.zeros((num_node, num_node)) + np.inf
transfer_mat = [np.linalg.matrix_power(A, d) for d in range(max_hop + 1)]
arrive_mat = (np.stack(transfer_mat) > 0)
for d in range(max_hop, -1, -1):
hop_dis[arrive_mat[d]] = d
return hop_dis
def normalize_digraph(A):
Dl = np.sum(A, 0)
num_node = A.shape[0]
Dn = np.zeros((num_node, num_node))
for i in range(num_node):
if Dl[i] > 0:
Dn[i, i] = Dl[i]**(-1)
AD = np.dot(A, Dn)
return AD
def normalize_undigraph(A):
Dl = np.sum(A, 0)
num_node = A.shape[0]
Dn = np.zeros((num_node, num_node))
for i in range(num_node):
if Dl[i] > 0:
Dn[i, i] = Dl[i]**(-0.5)
DAD = np.dot(np.dot(Dn, A), Dn)
return DAD
def normalize_points_with_size(xy, width, height, flip=False):
"""Normalize scale points in image with size of image to (0-1).
xy : (frames, parts, xy) or (parts, xy)
"""
if xy.ndim == 2:
xy = np.expand_dims(xy, 0)
print(xy[:, :, 1].min(), xy[:, :, 1].max())
xy[:, :, 0] /= width
xy[:, :, 1] /= height
print('preprocess')
print(xy[:, :, 0].min(), xy[:, :, 0].max())
print(xy[:, :, 1].min(), xy[:, :, 1].max())
if flip:
xy[:, :, 0] = 1 - xy[:, :, 0]
return xy
def scale_pose(xy):
"""Normalize pose points by scale with max/min value of each pose.
xy : (frames, parts, xy) or (parts, xy)
"""
if xy.ndim == 2:
xy = np.expand_dims(xy, 0)
xy_min = np.nanmin(xy, axis=1)
xy_max = np.nanmax(xy, axis=1)
for i in range(xy.shape[0]):
xy[i] = ((xy[i] - xy_min[i]) / (xy_max[i] - xy_min[i])) * 2 - 1
return xy.squeeze()
这里还有一个权重,这个是人家官方那里下载的哈。
此外这里还有个字体:
然后就没有了。
效果
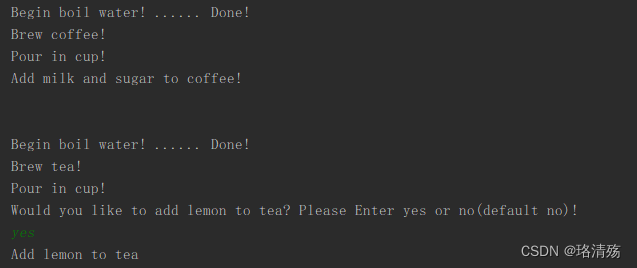
最后的话,就可以看到这样的一个效果了:

这里的话帧数还是比较低的,因为是纯cpu跑的,不过综合效果来看,当每满30帧时,它去判断姿态其实不会由明显卡顿,可能帧数会下降一些,但是就几帧。
当然局限很明显,就是不适合多目标的检测,还是单目标的。