文章目录
- Vuex
- 概述
- 安装
- 单向数据流
- Vuex核心概念
- State
- mapState 辅助函数
- 扩展运算符
- Getter
- mapGetters 辅助函数
- Mutation
- 提交载荷
- 提交载荷对象
- 对象风格提交
- 使用常量替代mutation事件类型
- Action
- 异步分发
- Module
- 命名空间
Vuex
概述
Vuex 是一个状态管理库,用于管理 Vue.js 应用程序中的共享状态。它可以帮助你在应用程序中保持数据的一致性和可预测性。
Vuex包括以下几个核心概念:
- state:存储应用程序的状态数据。
- getters:提供一种计算派生状态的方式,类似于Vue.js中的计算属性。
- mutations:用于修改状态的方法,但是只能进行同步操作。
- actions:用于提交mutations,可以进行异步操作。
- modules:将store拆分为模块,每个模块都有自己的state、getters、mutations和actions。
Vuex 官方文档
安装
npm install vuex@next --save
单向数据流
<script >
export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.count++;
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<button @click="count++">{{ count }}</button>
</template>
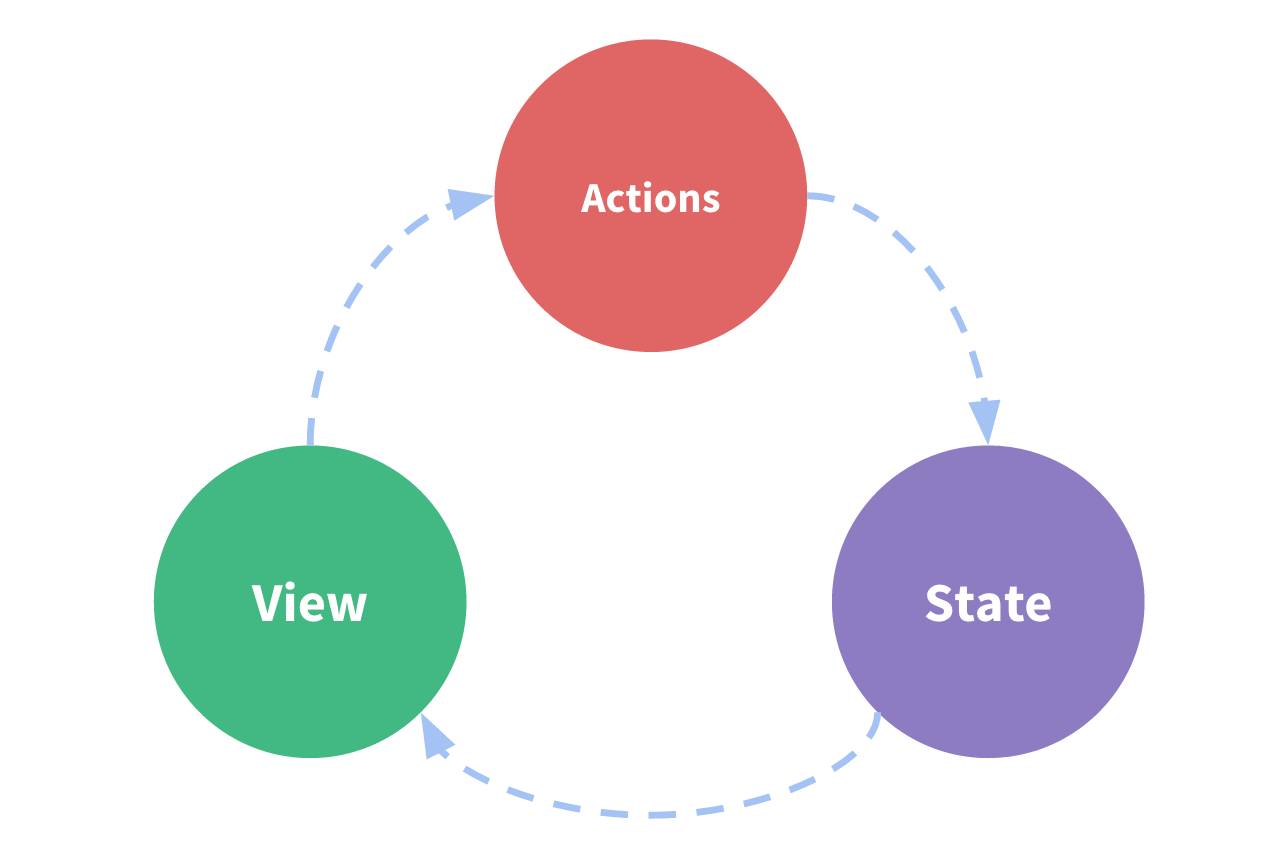
这是一个单向数据流:
- 状态:驱动应用的数据源。
- 视图:以声明方式将状态映射到视图。
- 操作:响应在视图上的操作导致的状态变化。
但是,当我们的应用遇到多个组件共享状态时,单向数据流的简洁性很容易被破坏:
- 多个视图依赖于同一状态。
- 来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态。
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。确实是如此——如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex。一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
Vuex核心概念
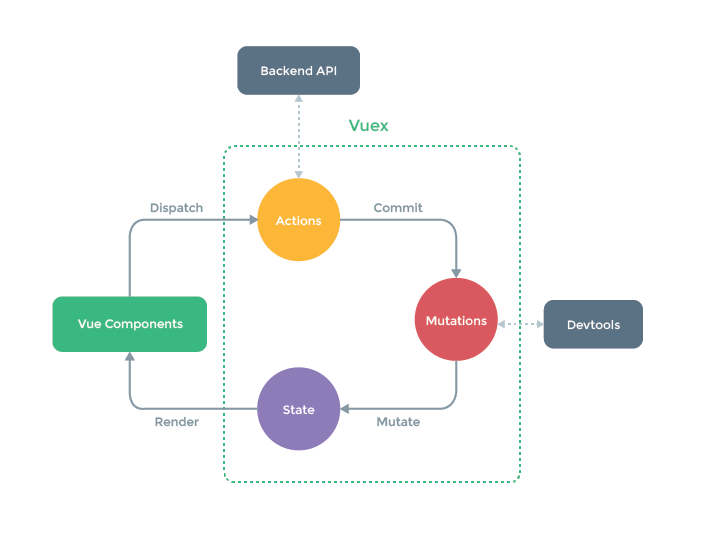
每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。
Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同:
- Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
- 你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
State
用于存储应用程序的状态数据。
- 在Vue组件中,通过
this.$store访问store实例。 - 通过
$store.state获取状态对象。 - Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。
支持Vuex
import store from "./store";
const app = createApp(App);
// 将 store 实例作为插件安装
app.use(store);
app.mount("#app");
定义store对象
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count: 0,
};
}
});
export default store;
使用store
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<!-- 不推荐 -->
<button @click="$store.state.count++">修改count</button>
</template>
mapState 辅助函数
使用mapState辅助函数可以简化代码,如:将{{ $store.state.count }}简化为{{ count }}。
<script >
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
//mapState传对象
computed: mapState({
//简化代码:
//方式一;使用箭头函数
// count: state => state.count,
//方式二:字符串参数,等价于`state => state.count`
count: "count"
})
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="$store.state.count++">修改count</button>
</template>
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组:
<script >
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
//mapState传数组
computed: mapState(["count", "msg"])
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<button @click="$store.state.count++">修改count</button>
</template>
扩展运算符
computed属性在Vue组件中只能有一个,可以使用对象扩展运算符兼容局部计算属性。
<script >
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {
num: 10
}
//对象扩展运算符
computed: {
addNum() {
return this.num + 5;
},
...mapState(["count", "msg"])
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<p>{{ addNum }}</p>
<button @click="$store.state.count++">修改count</button>
</template>
Getter
提供一种计算派生状态的方式,类似于Vue.js中的计算属性,例如对列表进行过滤并计数。
从 Vue 3.0 开始,getter的结果不再像计算属性一样会被缓存起来。
定义store对象
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
msg: "hello world",
};
},
getters: {
reverseMsg(state) {
return state.msg.split("").reverse().join("");
},
reverseMsgLength(state, getters) {
return getters.reverseMsg.length;
},
}
});
export default store;
在Vue中使用
<template>
<p>{{ $store.getters.reverseMsg }}</p>
<p>{{ $store.getters.reverseMsgLength }}</p>
</template>
mapGetters 辅助函数
可以通过mapGetters辅助函数将getter映射到计算属性中。
<script >
import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {
num: 10
}
},
computed: {
addNum() {
return this.num + 5;
},
...mapState(["count", "msg"]),
...mapGetters(["reverseMsg", "reverseMsgLength"])
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>{{ $store.getters.reverseMsg }}</p>
<p>{{ $store.getters.reverseMsgLength }}</p>
<p>{{ reverseMsg }}</p>
<p>{{ reverseMsgLength }}</p>
</template>
Mutation
用于修改状态的方法,但是只能进行同步操作。
- 使用
$store.commit()方法触发mutation函数。
定义store对象
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count: 0
};
},
mutations: {
//修改状态的方法
increment(state) {
state.count++;
},
},
});
export default store;
在Vue中使用
<script >
export default {
methods: {
increment() {
//使用`$store.commit`触发方法
this.$store.commit("increment");
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="increment">修改count</button>
</template>
提交载荷
你可以向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的载荷(payload)。
在store对象中定义
mutations: {
add(state, num) {
state.count += num;
},
},
使用
<script >
export default {
data() {
return {
num: 10
}
},
methods: {
add() {
this.$store.commit("add", 5);
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="add">修改num</button>
</template>
提交载荷对象
在store对象中定义
mutations: {
add2(state, payload) {
state.count += payload.num;
},
}
使用
<script >
export default {
methods: {
add2() {
this.$store.commit("add2", { num: 10 });
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="add2">修改num</button>
</template>
对象风格提交
this.$store.commit({
type: "add",
num: 20
})
使用常量替代mutation事件类型
定义mutation-type.js文件
export const ADD = "add";
在store对象中使用
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import { ADD } from "../mutation-type";
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count: 0
};
},
mutations: {
[ADD](state, num) {
state.count += num;
}
},
});
export default store;
Action
用于提交mutations,可以进行异步操作。
- 使用
$store.dispatch()方法触发actions中定义的函数。
在store对象中定义
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count: 0
};
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
}
},
actions: {
increment(context) {
context.commit("increment");
},
},
});
export default store;
在Vue中使用
<script >
export default {
methods: {
increment2() {
this.$store.dispatch("increment");
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="increment2">修改num(actions)</button>
</template>
**使用参数解构简化代码 **
actions: {
increment({ commit }) {
commit("increment");
},
},
异步分发
在store对象中定义
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count: 0,
};
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
}
},
actions: {
incrementAsync({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit("increment");
}, 1000);
},
},
});
export default store;
在Vue中使用
<script >
export default {
methods: {
incrementAsync() {
this.$store.dispatch("incrementAsync")
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>count: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="incrementAsync">修改num(异步)</button>
</template>
Module
将store拆分为模块,每个模块都有自己的state、getters、mutations和actions。
新建user模块
const user = {
state() {
return {
userName: "xiaoming",
};
},
getters: {
userNameAge(state, getters, rootState) {
return state.userName + " 18岁";
},
},
mutations: {
updateUserName(state) {
state.userName = "小明";
},
},
};
export default user;
添加子模块
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import user from "./user";
const store = createStore({
modules: {
user,
},
});
export default store;
访问user模块
<script >
export default {
methods: {
changeUserName() {
console.log(this.$store);
this.$store.commit("updateUserName");
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>{{ $store.state.user.userName }}</p>
<button @click="changeUserName">修改userName</button>
<p>{{ $store.getters.userNameAge }}</p>
</template>
命名空间
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
新建Student的store对象
const student = {
namespaced: true, //开启命名空间
state() {
return {
userName: "xiaohei",
};
},
getters: {
userNameAge(state, getters, rootState) {
return state.userName + " 8岁";
},
},
mutations: {
updateStudentName(state) {
state.userName = "小黑";
},
},
};
export default student;
在Vue3中使用
<script >
export default {
methods: {
changeStudentName() {
this.$store.commit("student/updateStudentName");
}
}
</script>
<template>
<h2>student模块</h2>
<p>{{ $store.state.student.userName }}</p>
<button @click="changeStudentName">修改studentName</button>
<p>{{ $store.getters["student/userNameAge"] }}</p>
</template>