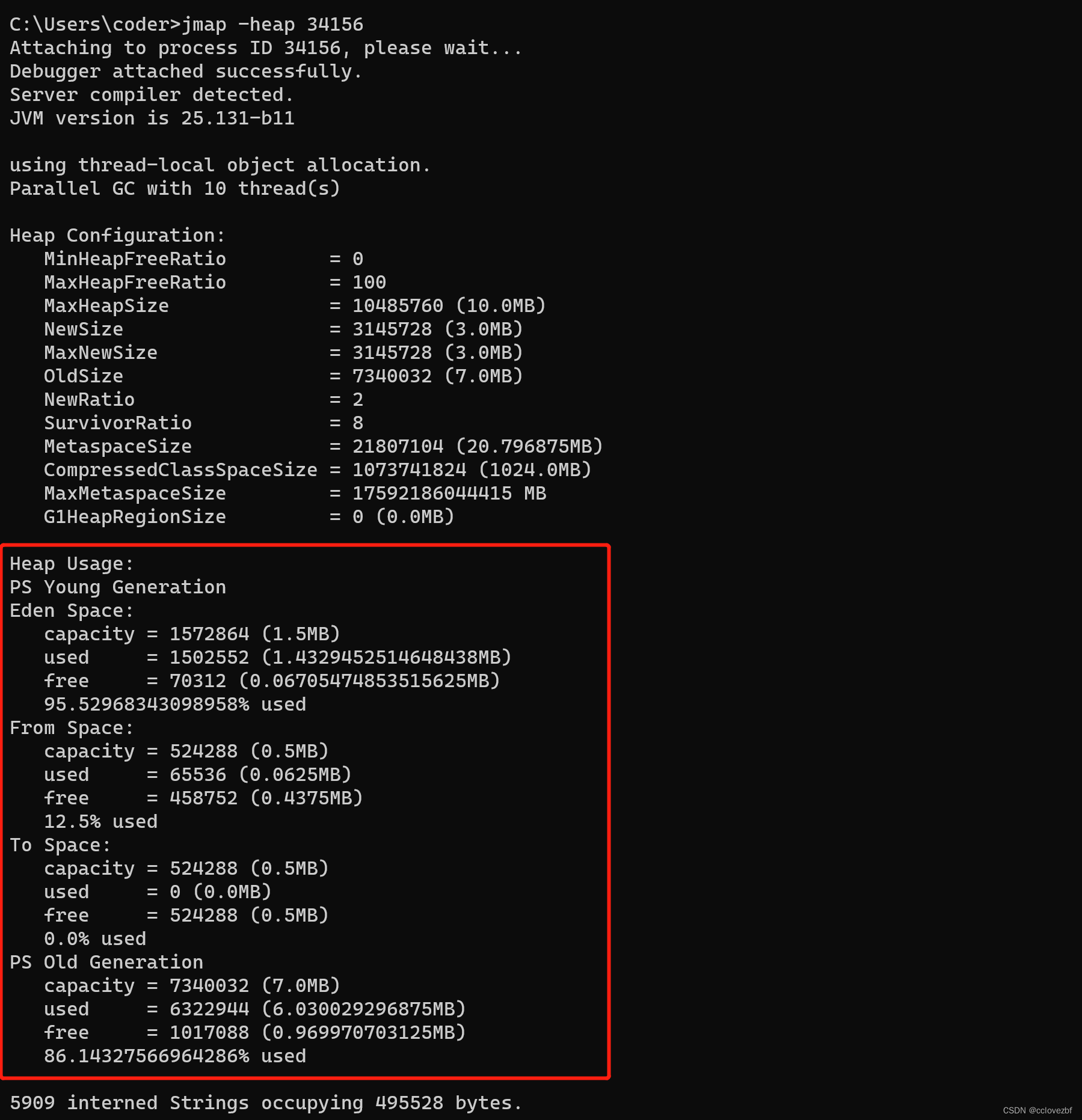
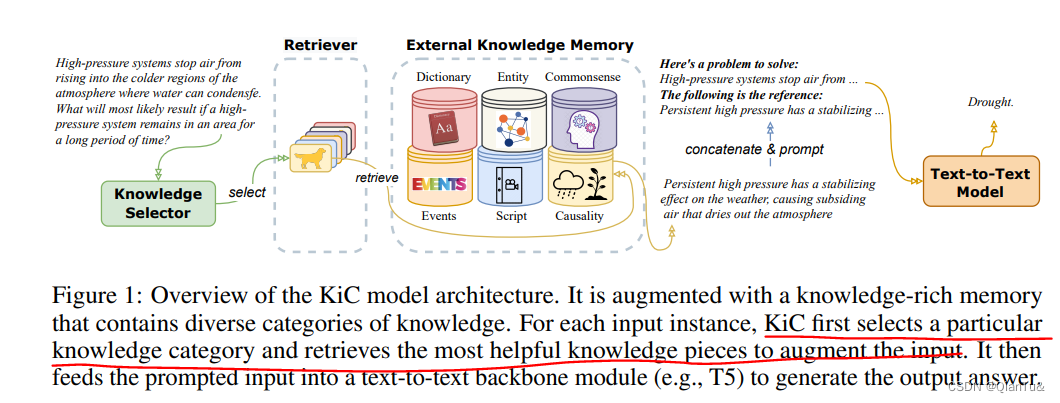
处理解析JWT时的异常
由于解析JWT是在过滤器中执行的,而过滤器是整个服务器端中最早接收到所有请求的组件,此时,控制器等其它组件尚未运行,则不可以使用此前的“全局异常处理器”来处理解析JWT时的异常(全局异常处理器只能处理控制器抛出的异常),也就是说,在过滤器中只能使用try...catch语法来处理异常!
为了便于表示需要响应到客户端的结果,仍推荐使用JsonResult封装相关信息,而响应到客户端的结果应该是JSON格式的,则需要将JsonResult对象转换成JSON格式的字符串!
在项目中添加fastjson依赖项,此依赖项可以实现Java对象与JSON格式的字符串的相互转换:
<!-- fastjson:实现对象与JSON的相互转换 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.75</version>
</dependency>
在处理异常之前,还应该在ServiceCode中补充相关的业务状态码,例如:
ERR_JWT_EXPIRED(60000),
ERR_JWT_MALFORMED(60100),
ERR_JWT_SIGNATURE(60200),
然后,调整JwtAuthorizationFilter中解析JWT的代码片段:
Claims claims = null;
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8");
try {
claims = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(secretKey)
.parseClaimsJws(jwt)
.getBody();
} catch (SignatureException e) {
String message = "非法访问!";
log.warn("解析JWT时出现SignatureException,响应消息:{}", message);
JsonResult<Void> jsonResult
= JsonResult.fail(ServiceCode.ERR_JWT_SIGNATURE, message);
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
printWriter.println(JSON.toJSONString(jsonResult));
printWriter.close();
return;
} catch (MalformedJwtException e) {
String message = "非法访问!";
log.warn("解析JWT时出现MalformedJwtException,响应消息:{}", message);
JsonResult<Void> jsonResult
= JsonResult.fail(ServiceCode.ERR_JWT_MALFORMED, message);
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
printWriter.println(JSON.toJSONString(jsonResult));
printWriter.close();
return;
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
String message = "您的登录信息已过期,请重新登录!";
log.warn("解析JWT时出现ExpiredJwtException,响应消息:{}", message);
JsonResult<Void> jsonResult
= JsonResult.fail(ServiceCode.ERR_JWT_EXPIRED, message);
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
printWriter.println(JSON.toJSONString(jsonResult));
printWriter.close();
return;
}
关于认证信息中的“当事人”
认证信息中的“当事人”可以通过@AuthenticationPrincipal注入到方法(控制器的方法)的参数中,在访求处理过程中,可能需要获取“当事人”的ID、用户名等数据,所以,应该自定义数据类型表示“当事人”(Spring Security也希望你这样做,所以,在认证结果的信息中的“当事人”被声明为Object类型)!
在项目的根包下创建security.LoginPrincipal类:
package cn.tedu.csmall.passport.security;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 当事人类型,就是成功通过认证的用户信息类型
*
* @author java@tedu.cn
* @version 0.0.1
*/
@Data
public class LoginPrincipal implements Serializable {
/**
* 当事人ID
*/
private Long id;
/**
* 当事人用户名
*/
private String username;
}
然后,调整JwtAuthorizationFilter中的相关代码:
Long id = claims.get("id", Long.class);
String username = claims.get("username", String.class);
log.debug("从JWT中解析得到的管理员ID:{}", id);
log.debug("从JWT中解析得到的管理员用户名:{}", username);
// 基于解析JWT的结果创建认证信息
LoginPrincipal principal = new LoginPrincipal();
principal.setId(id);
principal.setUsername(username);
// 暂不关心其它代码
在控制器中处理请求的方法的参数列表中,可以通过@AuthenticationPrincipal注入LoginPrincipal类型的参数,在处理请求的过程中,可以通过此参数获取当事人的具体数据:
@GetMapping("")
public JsonResult<List<AdminListItemVO>> list(
// ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓ 自定义的当事人类型
@ApiIgnore @AuthenticationPrincipal LoginPrincipal loginPrincipal) {
log.debug("开始处理【查询管理员列表】的请求,参数:无");
log.debug("当事人:{}", loginPrincipal);
log.debug("当事人的ID:{}", loginPrincipal.getId());
log.debug("当事人的用户名:{}", loginPrincipal.getUsername());
List<AdminListItemVO> list = adminService.list();
return JsonResult.ok(list);
}
关于权限
目前,当管理员登录成功后,服务器端生成的JWT中并不包含此管理员的权限信息,所以,此管理员后续携带JWT提交请求时,服务器端也无法根据此JWT直接获取管理员的权限列表,更加不能把正确的权限列表存入到SecurityContext中的认证信息中,所以,无法检查管理员的权限!
可以在管理员登录成功后,将此管理员的权限列表也写入到JWT中!
**注意:**由于权限列表并不是一般的字面值数据,生成到JWT中后,将无法还原回原本的集合类型!应该先将权限列表转换成JSON格式的字符串,后续,再根据此JSON数据还原回原本的列表!
在AdminServiceImpl中的login()方法中调整:
// 将通过认证的管理员的相关信息存入到JWT中
// 准备生成JWT的相关数据
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + durationInMinute * 60 * 1000);
AdminDetails principal = (AdminDetails) authenticationResult.getPrincipal();
Map<String, Object> claims = new HashMap<>();
claims.put("id", principal.getId());
claims.put("username", principal.getUsername());
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = principal.getAuthorities(); // 新增
String authoritiesJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(authorities); // 新增
claims.put("authoritiesJsonString", authoritiesJsonString); // 新增
然后,在JwtAuthorizationFilter中调整:
Long id = claims.get("id", Long.class);
String username = claims.get("username", String.class);
String authoritiesJsonString = claims.get("authoritiesJsonString", String.class); // 新增
log.debug("从JWT中解析得到的管理员ID:{}", id);
log.debug("从JWT中解析得到的管理员用户名:{}", username);
log.debug("从JWT中解析得到的管理员权限列表JSON:{}", authoritiesJsonString);
// ========== 将原有的“山寨”权限的代码替换为以下代码 ==========
// 将JSON格式的权限列表转换成Authentication需要的类型(Collection<GrantedAuthority>)
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities =
JSON.parseArray(authoritiesJsonString, SimpleGrantedAuthority.class);
最后,在控制器中,可以继续使用@PreAuthroize注解检查权限!
**注意:**在API文档的调试中,需要使用新的JWT数据!
关于清空SecurityContext
目前,当使用有效的JWT提交请求后,即使下一次(间隔时间不能太久)不携带JWT再次提交请求,也是服务器端认可的!
这是因为:当使用有效的JWT提交请求后,JwtAuthorizationFilter会将此JWT中的信息创建为Authentication对象,并将此Authentication保存到SecurityContext中!而SecurityContext是基于Session的,所以,在Session未过期之前,即使后续的请求没有携带JWT,Spring Security仍能从Session中找到SecurityContext中的Authentication对象,会视为此次访问与此前的访问是同一个客户端。
如果认为这是一种不合理的表现,可以在JwtAuthorizationFilter中,在执行过滤之初,就不由分说的**清空SecurityContext**即可!
// 清除SecurityContext中的数据
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
处理未登录的错误
当客户端没有携带JWT,却向需要通过认证的URL发起请求,默认将响应403错误,这种问题需要在Spring Security的配置类中的void configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中进行配置:
// 处理“需要通过认证,但是实际上未通过认证就发起的请求”导致的错误
http.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(new AuthenticationEntryPoint() {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
String message = "未检测到登录,请登录!(在开发阶段,看到此提示时,请检查客户端是否携带了JWT向服务器端发起请求)";
JsonResult<Void> jsonResult = JsonResult.fail(ServiceCode.ERR_UNAUTHORIZED, message);
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
printWriter.println(JSON.toJSONString(jsonResult));
printWriter.close();
}
});
关于Spring Security的认证流程
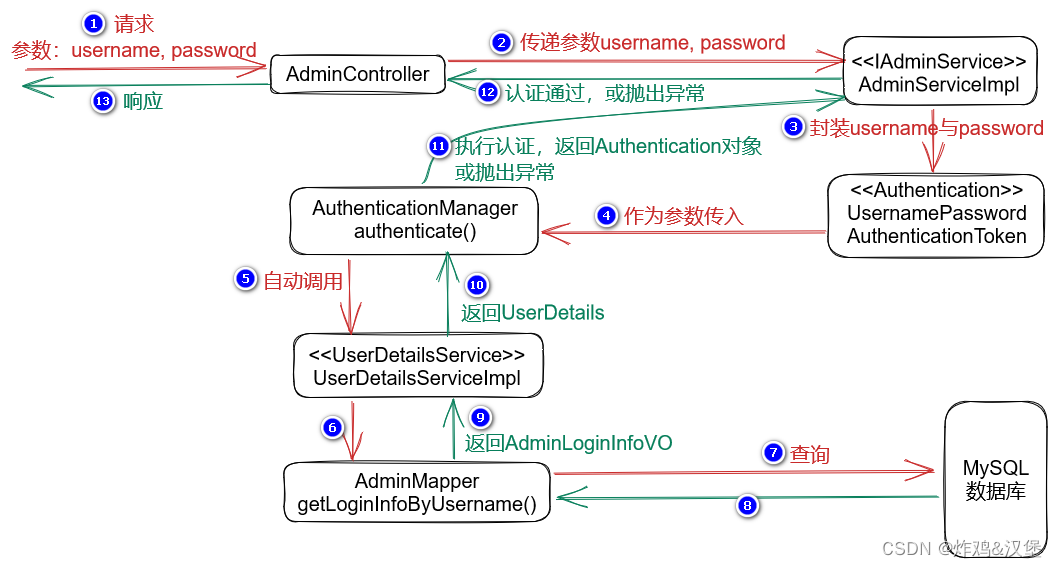
使用axios携带JWT发起请求
当需要携带JWT发起请求时,根据业内惯例,JWT应该放在请求头的Authorization属性中,则使用axios时需要自定义请求头,其语法是:
// 以下调用的create()表示创建一个axios实例,此函数的参数是一个对象,用于表示新创建的axios的参数
this.axios
.create({
'headers': {
'Authorization': jwt
}
})
.get(); // 与此前使用相同,在此处调用get()或post()发起请求
关于复杂请求的预检机制导致的跨域问题
在使用了Spring Security框架的项目中,当客户端携带JWT向服务器端发起异步请求,默认会出现跨域访问的错误(即使在服务器端通过Spring MVC配置类允许跨域,此问题依然存在),可以在Spring Security的配置类中的void configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中添加配置,以解决此问题:
http.cors();
出现此问题的根本原因在于:如果客户端提交的请求自定义了请求头中的特定属性(例如配置了请求头中的Authorization属性),此请求会被视为“复杂请求”,客户端的浏览器会先向服务器端的此URL发起OPTIONS类型的请求执行“预检(PreFlight)”,如果预检不通过,则不允许提交原本尝试提交的请求。
所以,可以在Spring Security的配置类中,对所有OPTIONS类型的请求“放行”,即可解决此问题:
http.authorizeRequests() // 配置URL的访问控制
// 重要,以下2行代码表示:对所有OPTIONS类型的请求“放行”
.mvcMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**")
.permitAll()
.mvcMatchers(urls)
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated();
或者,通过http.cors();也可以解决此问题,此方法的本质是启用了Spring Security自带的CorsFilter过滤器,此过滤器会对OPTIONS请求放行。