一、概念
阻塞队列:从名字可以看出,他也是队列的一种,那么他肯定是一个先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构。与普通队列不同的是,它支持两个附加操作,即阻塞添加和阻塞删除方法。
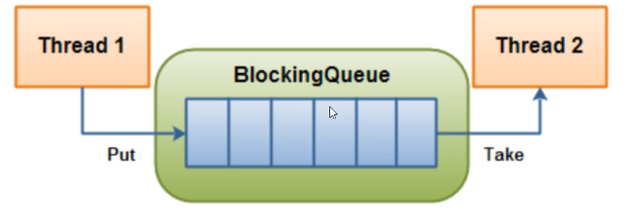
如上图,线程1往阻塞队列中添加元素,而线程2从阻塞队列中移除元素。而在这一系列操作必须符合以下规定:
阻塞添加:当阻塞队列是满时,往队列里添加元素的操作将被阻塞。
阻塞移除:当阻塞队列是空时,从队列中获取元素/删除元素的操作将被阻塞。
阻塞队列的好处
阻塞队列不用手动控制什么时候该被阻塞,什么时候该被唤醒,简化了操作。
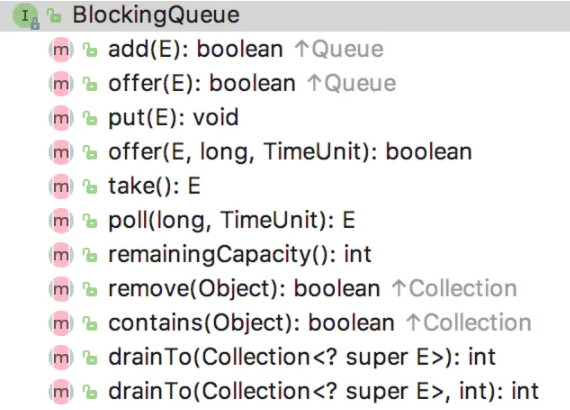
BlockingQueue的主要方法
二、分类
ArrayBlockingQueue:由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值为Integer.MAX_VALUE即2147483647)阻塞队列。
PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界队列。
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列。每个插入操作必须等到另一个线程调用移除操作,否则插入操作一直处于阻塞状态。
LinkedTransferQueue:由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
LinkedBlockingDeque:由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列。
三、BlockingQueue的核心方法
方法类型 | 抛出异常 | 返回布尔 | 阻塞 | 超时 |
插入 | add(E e) | offer(E e) | put(E e) | offer(E e,Time,TimeUnit) |
移除 | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(Time,TimeUnit) |
队首 | element() | peek() | 无 | 无 |
抛出异常是指当队列满时,再次插入会抛出异常(如果队列未满,插入返回值未true);
返回布尔是指当队列满时,再次插入会返回false;
阻塞是指当队列满时,再次插入会被阻塞,直到队列取出一个元素,才能插入。
超时是指当一个时限过后,才会插入或者取出。
1、抛出异常组
当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里add插入元素会抛IllegalStateException: Queue full
当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里remove移除元素会抛NoSuchElementException
代码案例:
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 插入
System.out.println("插入");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
// Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
// blockingQueue.add("d");
// 检查
System.out.println("检查");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.element());
// 移除
System.out.println("移除");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
}
}2、返回布尔值组
offer插入方法,成功true,失败false
poll移除方法,成功返回出队列的元素,队列里面没有就返回null
代码案例:
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 插入
System.out.println("插入");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));
// 检查
System.out.println("检查");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());
// 移除
System.out.println("移除");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println("检查");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());
}
}输出结果:
插入
true
true
true
false
检查
a
移除
a
b
c
null
检查
null3、阻塞和超时控制
阻塞
当阻塞队列满时,生产者线程继续往队列里put元素,队列会一直阻塞生产线程直到put数据或者响应中断退出。
当阻塞队列空时,消费者线程试图从队列里take元素,队列会一直阻塞消费者线程直到队列可用。
代码案例:
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 插入
System.out.println("插入");
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("a");
System.out.println("=======================");
blockingQueue.put("a");
// 移除
System.out.println("移除");
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
}
}超时退出
当阻塞队列满时,队列会阻塞生产者线程一定时间,超过限时后生产者线程会退出。
代码案例:
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 插入
System.out.println("插入");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("=======================" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("=======================" + System.currentTimeMillis());
// 移除
System.out.println("移除");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("=======================" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("=======================" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
4、同步SynchronousQueue队列
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列。每个插入操作必须等到另一个线程调用移除操作,否则插入操作一直处于阻塞状态。
代码案例:
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + blockingQueue.take());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + blockingQueue.take());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "BBB").start();
}
}输出结果:
AAA put 1
BBB 1
AAA put 2
BBB 2
AAA put 3
BBB 3