MyBatis 中使用XML映射文件
什么是XML映射
使用注解的映射SQL的问题:
- 长SQL需要折行,不方便维护
- 动态SQL查询拼接复杂
- 源代码中的SQL,不方便与DBA协作
MyBatis建议使用XML文件映射SQL才能最大化发挥MySQL的功能
- 统一管理SQL, 方便协作
- 不需要 “ ” + 等语法,方便“长”SQL
- 方便处理动态SQL连接
参考连接: https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html
HelloWorld
开发步骤:
- 创建项目(不要使用Spring Boot 3!), 选择依赖:
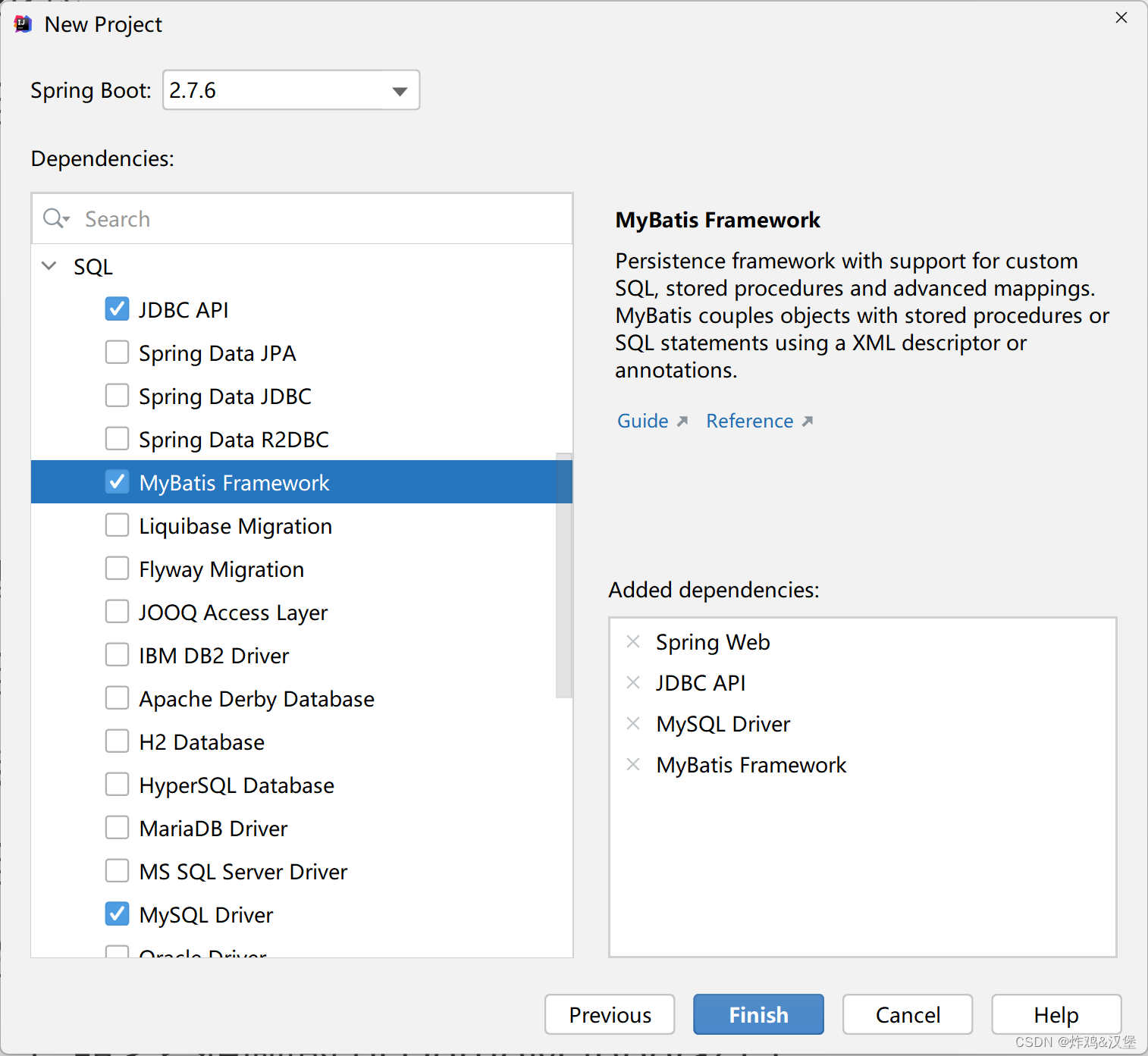
-
配置application.properties, 设置数据库连接
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bootdb?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&rewriteBatchedStatements=true spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root # 设定 mapper xml 文件的位置, classpath 就是指 resources 位置 mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mappers/*.xml # 查看MyBatis执行的SQL logging.level.cn.tedu.boot2209.mapper=debug -
创建文件夹 /resources/mappers
-
添加一个XML文件,文件从doc.canglaoshi.org 下载
-
改名为 DemoMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- namespace 的值设定为被映射的包名.类名 --> <mapper namespace="cn.tedu.boot2209.mapper.DemoMapper"> <!-- select 元素用于映射查询语句到方法, id值必须和mapper接口中的方法名一致! 需要设定返回值类型resultType,类型与方法返回值类型一致 select 元素中定义SQL,SQL查询结果将自动映射到方法返回值, 不要使用分号结尾!!--> <select id="hello" resultType="java.lang.String"> SELECT 'Hello World!' </select> </mapper>
-
-
创建mapper.DemoMapper接口:
- 接口名和 xml文件的namespace 一致
- 方法名和xml文件的select元素的id一致
- 方法返回值类型和 resultType 的值一致
/** * 编写Mapper接口,用于映射SQL语句 */ @Mapper public interface DemoMapper { String hello(); } -
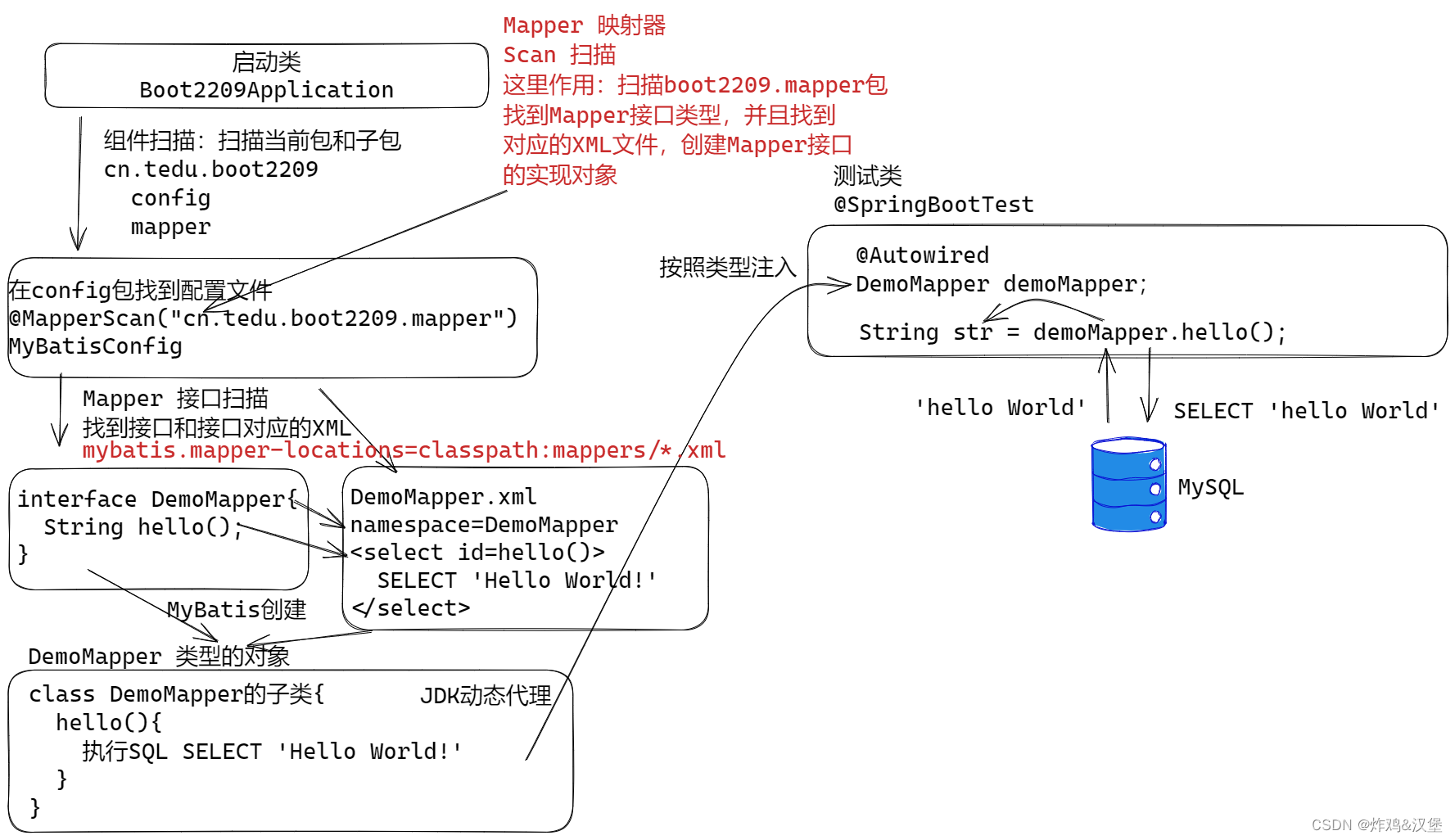
编写MyBatis配置文件 config.MyBatisConfig
- 包名、文件名,没有限制!
- 文件中使用 MapprScan 扫描 Mapper包:
/** * 创建一个配置文件,MyBatisConfig * 在配置文件中,启动Mapper接口扫描功能 * Mapper 接口扫描功能会自动创建 Mapper接口的实现对象(使用的JDK动态代理技术) */ @MapperScan(basePackages = "cn.tedu.boot2209.mapper") @Configuration public class MyBatisConfig { } -
测试案例: 测试结果说明,SQL被执行了,方法返回了SQL语句的结果
@SpringBootTest public class DemoMapperTests { @Autowired DemoMapper demoMapper; @Test void test(){ String str = demoMapper.hello(); System.out.println(str); } }
Spring Boot 中的配置类(配置文件)
@Configuration 用于声明新的配置文件类。
Spring Boot 中的主配置文件,就是Spring Boot 的启动类,可以作为配置文件使用。如果将全部配置信息放到主配置文件,就会很混乱。一般在开发中,将配置文件分开放置,相关的放到一起。
- MyBatis 放到一个文件中
- 安全配置放到一个文件中
- … …
创建一个配置包 config 管理全部的配置,然后创建MyBatis的配置类, 配置类需要标注 @Configuration
/**
* 创建一个配置文件,MyBatisConfig
* 在配置文件中,启动Mapper接口扫描功能
* Mapper 接口扫描功能会自动创建 Mapper接口的实现对象(使用的JDK动态代理技术)
*/
@MapperScan(basePackages = "cn.tedu.boot2209.mapper")
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
}
MyBatis XML映射文件工作原理
关于XML语法:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.tedu.boot2209.mapper.ProductMapper">
<select id="countProduct" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM product
</select>
</mapper>
- 处理节点:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>从来没有变过!- 可以省略,但是不建议省略!
- 文档定义: ”DOCTYPE“ 用于约定XML文件中的 元素、属性、嵌套关系
- 可以约束标签和属性
- 标签/标记:
<mapper>- 必须成对使用,有开启标签就必须结束标签:
<mapper></mapper>
- 必须成对使用,有开启标签就必须结束标签:
- 开始标签上可以定义属性:
id="countProduct"- 属性名不可以重复,属性无顺序
- XML文件只能有唯一的根元素!!!
- XML 可扩展的标记语言:
- 标签可以任意名称,标签名可以扩展
- 标签嵌套关系可以扩展,标签可以任意嵌套
- 属性可以扩展
- XML 中大小写敏感,不同!
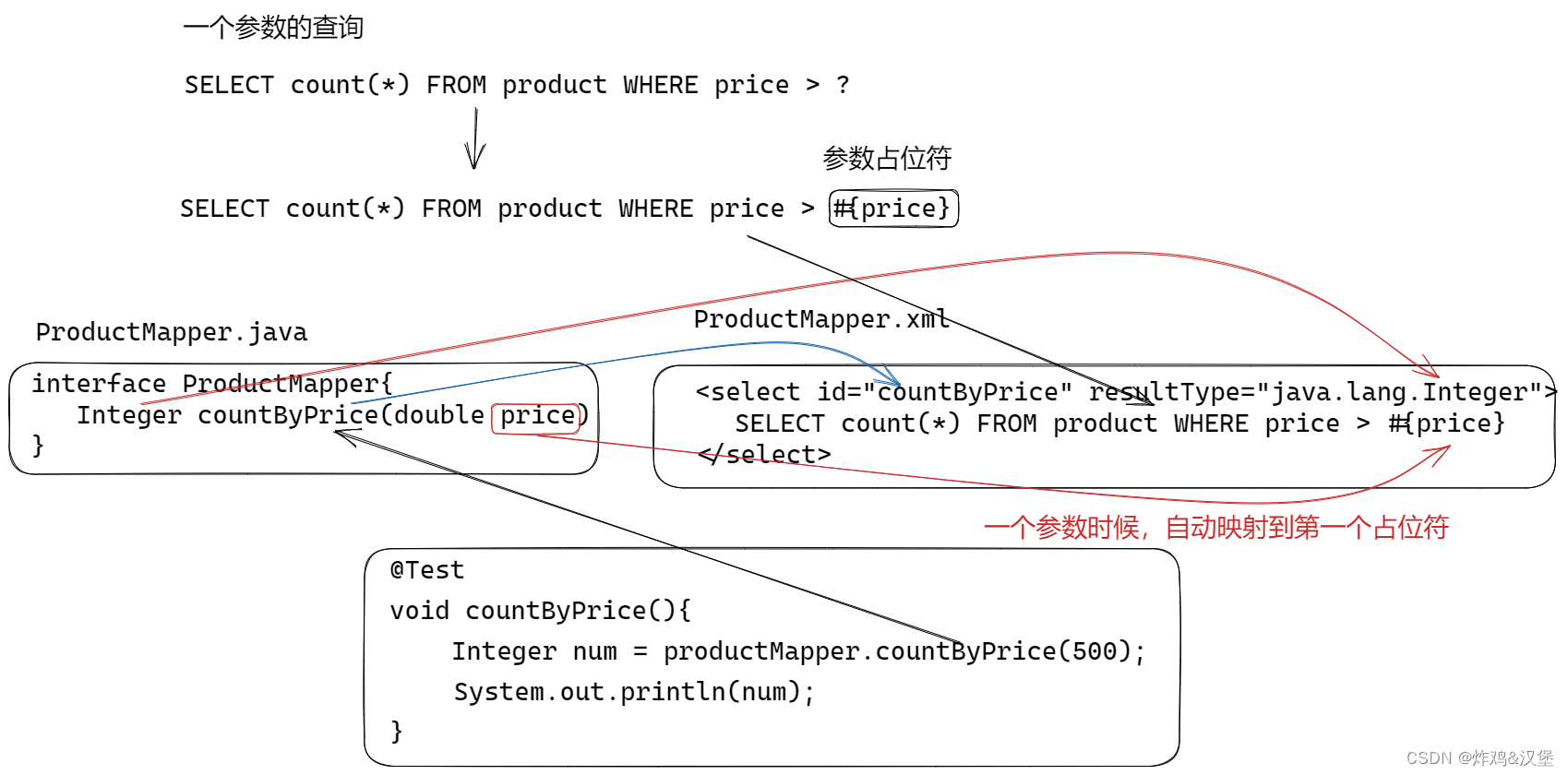
有参数的查询
处理一个参数查询
例子:
SELECT count(*) FROM product WHERE price > ?
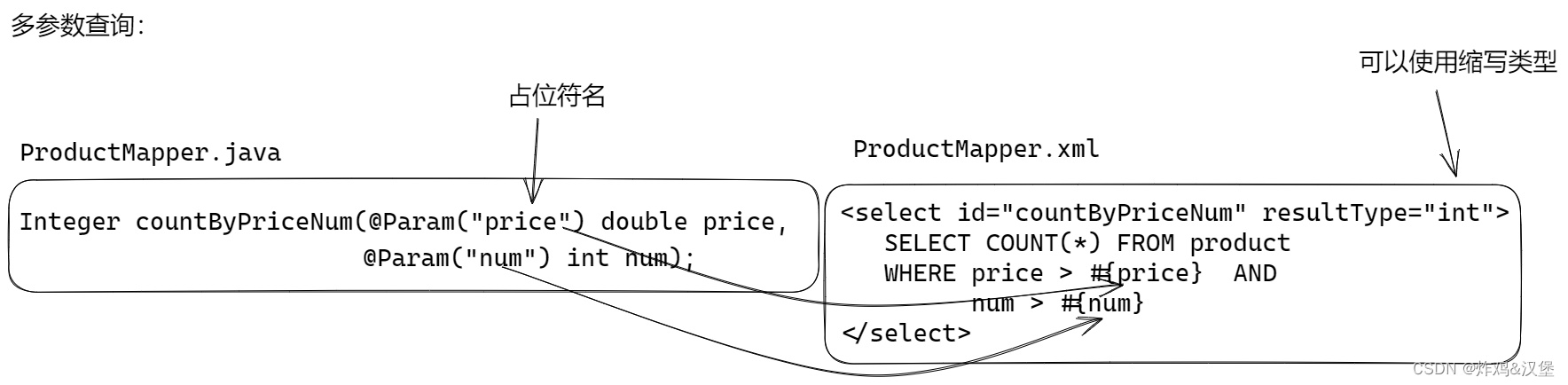
处理多个参数查询
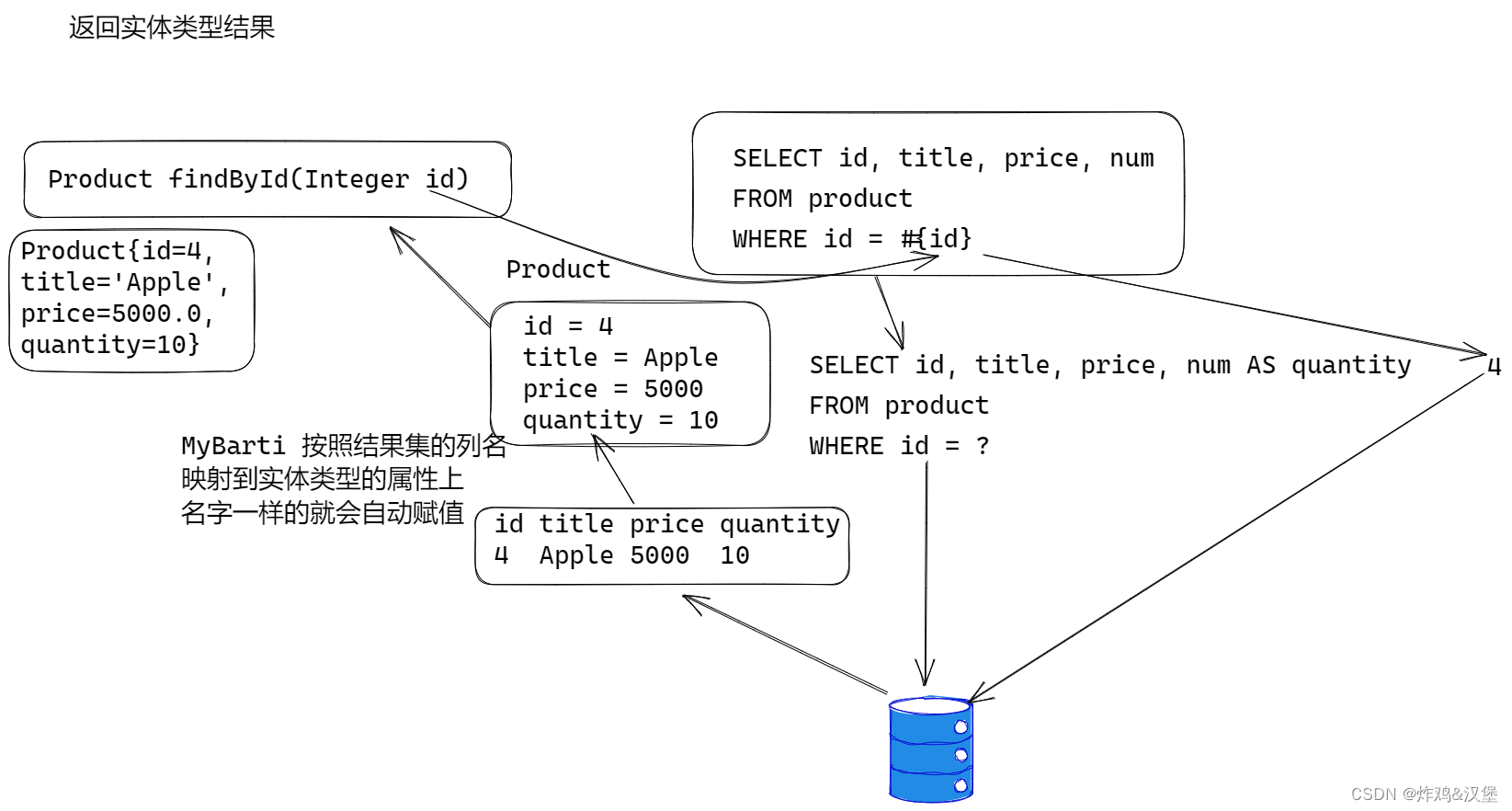
处理实体类型返回值
使用 Product 实体类作为返回值, 在resultType上指定实体类型就可以了
desc product;
+-------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| title | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| price | double(10,2) | YES | | NULL | |
| num | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
定义实体类型 Product
/**
* 产品实体类型
*/
public class Product {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private Double price;
private Integer quantity; //数量
public Product() {
}
public Product(Integer id, String title, Double price, Integer quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Integer getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
public void setQuantity(Integer quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", quantity=" + quantity +
'}';
}
}
编写ProductMapper接口方法
/**
* 根据ID返回一个对象
*/
Product findById(Integer id);
编写映射文件 ProductMapper.xml
<select id="findById" resultType="cn.tedu.boot2209.entity.Product">
SELECT id, title, price, num AS quantity
FROM product
WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
测试:ProductMapperTests
@Test
void findById(){
Product product = productMapper.findById(4);
System.out.println(product);
}
返回实体集合
在ProductMapper接口中添加方法:
/**
* 返回一组实体对象
* @param title %手机
* @return 匹配的一组对象
*/
List<Product> findByTitle(String title);
在 ProductMapper.xml 添加SQL语句:
<!-- 返回一组实体对象,必须有 resultType 值是返回集合中的元素类型-->
<select id="findByTitle" resultType="cn.tedu.boot2209.entity.Product">
SELECT id, title, price, num AS quantity
FROM product
WHERE title LIKE #{title}
</select>
测试方法 ProductMapperTests
@Test
void findByTitle(){
List<Product> products = productMapper.findByTitle("%手机");
for (Product product : products){
System.out.println(product);
}
}
插入和更新
使用变量传递参数
参数少,没有问题,但是参数多了以后就麻烦了,书写繁琐复杂
插入数据SQL:
INSERT INTO product (id, title, price, num ) VALUES (null, ?, ? ,?)
ProductMapper接口:插入、更新、删除方法只有一个默认返回int值,表示SQL影响行数
Integer saveProduct(@Param("title") String title,
@Param("price") Double price,
@Param("quantity") Integer quantity);
在MyBatis ProductMapper.xml:
<!-- insert 插入语句不需要定义 resultType,默认就有int返回值 -->
<insert id="saveProduct">
INSERT INTO product (id, title, price, num )
VALUES (null, #{title}, #{price}, #{quantity})
</insert>
测试:ProductMapperTests
@Test
void saveProduct(){
Integer n = productMapper.saveProduct("大力手机", 2000.0, 100);
System.out.println(n);
}
使用POJO对象打包传递参数
POJO 就是传统Java对象,实体对象 Product 对象就是 POJO。
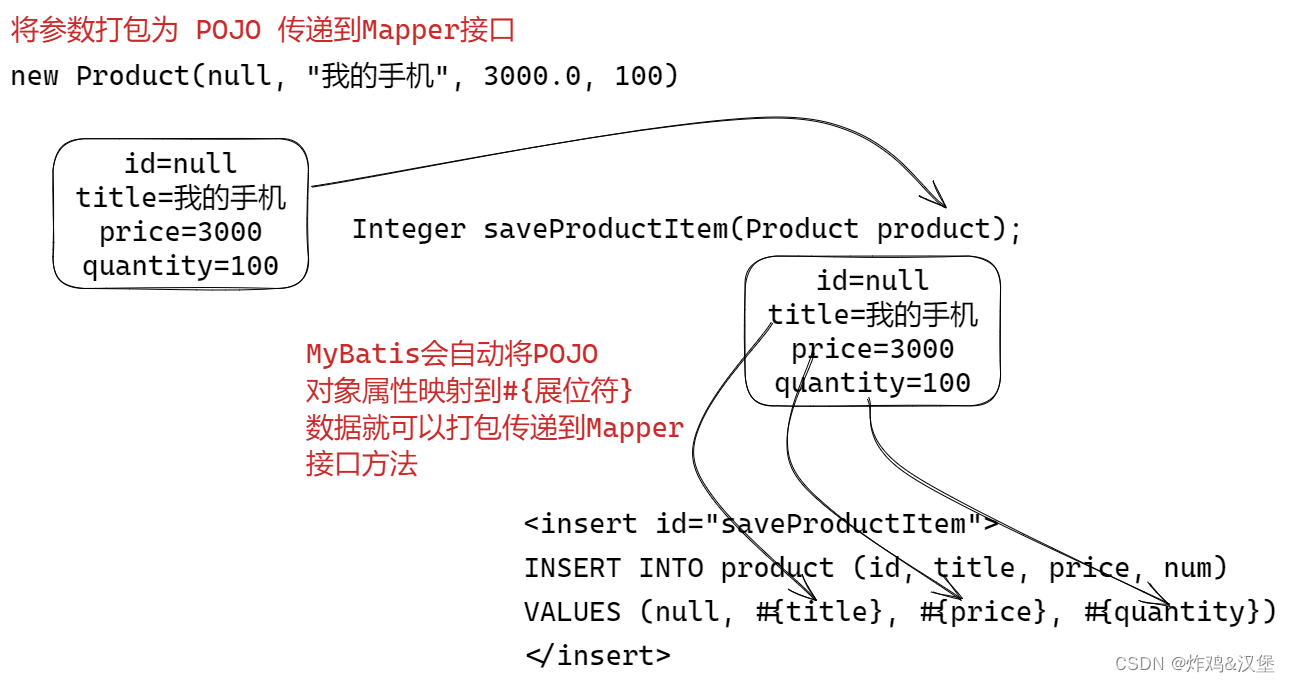
使用POJO对象作为Mapper方法参数: ProductMapper, 无需定义@Parm
Integer saveProductItem(Product product);
MyBatis 自动将POJO对象的属性, 映射传递到 #{占位符}
<!-- MyMatis 会自动的将 product 的属性 映射到#{title}, #{price}, #{quantity}
要求 #{title}, #{price}, #{quantity} 占位符必须和 product 的属性(getXXX)一致-->
<insert id="saveProductItem">
INSERT INTO product (id, title, price, num )
VALUES (null, #{title}, #{price}, #{quantity})
</insert>
测试
@Test
void saveProductItem(){
Product product = new Product(null, "大力手机", 2000.0, 100);
Integer n = productMapper.saveProductItem(product);
System.out.println(n);
}
返回自动增加的ID
使用POJO作为参数插入数据时候,可以返回自增的ID:
- useGeneratedKeys=“true” 使用生成的key
- keyProperty=“id” key 的属性名
<!-- useGeneratedKeys="true" 使用生成的key
keyProperty="id" key 的属性名 -->
<insert id="saveProductItem" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
INSERT INTO product (id, title, price, num)
VALUES (null, #{title}, #{price}, #{quantity})
</insert>
测试:
@Test
void saveProductItem(){
Product product = new Product(null, "他的手机", 3000.0, 100);
Integer n = productMapper.saveProductItem(product);
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println(product); //输出刚刚生成的 ID
}
更新数据 update
更新数据 SQL, 更新一行的全部数据:
UPDATE product SET title=?, price=?, num=? WHERE id=?
ProductMapper接口:
Integer updateProduct(Product product);
ProductMapper.xml:
<update id="updateProduct">
UPDATE product SET title=#{title}, price=#{price}, num=#{quantity}
WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
测试:
@Test
void updateProduct(){
Product product = new Product(12, "老虎的手机", 100.99, 10);
Integer num = productMapper.updateProduct(product);
System.out.println(product);
System.out.println(num);
}
MyBatis 动态SQL拼接
根据参加参数条件动态生成SQL,提示SQL效率。
动态SQL标签: if choose when for 等
/**
* 动态SQL更新
* @param product
* @return
*/
Integer updateProductPart(Product product);
XML:
<!-- 检查参数,动态拼接SQL -->
<!-- test="title != null" 检查title不为空,这拼接一段SQL title=#{title}
<set> 标签会自动删除多余的逗号 -->
<update id="updateProductPart">
UPDATE product
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title=#{title},
</if>
<if test="price != null">
price=#{price},
</if>
<if test="quantity != null">
num=#{quantity}
</if>
</set>
WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
测试:
@Test
void updateProductPart(){
Product product = new Product(10, null, 1500.0, null);
Integer num = productMapper.updateProductPart(product);
System.out.println(product);
System.out.println(num);
//一定要检查 SQL 处理结果!不是1,就是更新失败!!
}


![【 Java 组 】蓝桥杯省赛真题 [世纪末的星期] [幸运数] (持续更新中...)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20a7f1b58dfb4660b75d7f021c157d57.png#pic_center)