Prometheus系统 – Exporter原理
为什么我们需要Exporter?
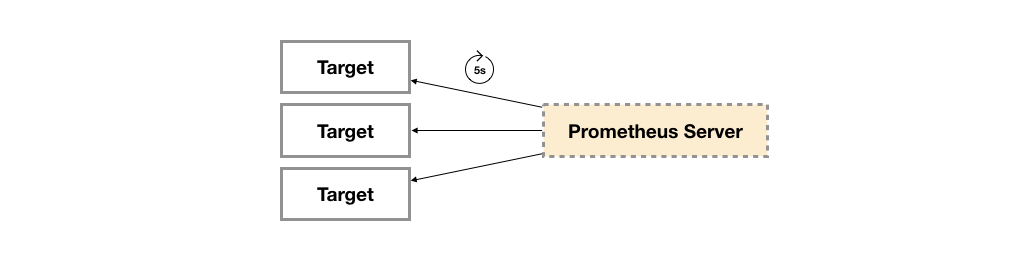
广义上讲所有可以向Prometheus提供监控样本数据的程序都可以被称为一个Exporter。而Exporter的一个实例称为target,如下所示,Prometheus通过轮询的方式定期从这些target中获取样本数据:
Prometheus 已经成为云原生应用监控行业的标准,在很多流行的监控系统中都已经实现了 Prometheus的监控接口,例如 etcd、Kubernetes、CoreDNS等,它们可以直接被Prometheus监控,但大多数监控对象都没办法直接提供监控接口,主要原因有:
- 很多系统在Prometheus诞生之前的很多年就已经发布了,例如MySQL和Redis等。
- 它们本身不支持HTTP接口,例如对于硬件性能指标,操作系统并没有原生的HTTP接口可以获取。
- 考虑到安全性,稳定性以及代码耦合等因素的影响,软件作者并不愿意将监控代码加入现有的代码中。
这些都导致无法通过一个规范解决所有监控问题。在此背景之下,Exporter 应运而生。Exporter 是一个采集监控数据并通过 Prometheus 监控规范对外提供数据的组件。除了官方实现的Exporter如Node Exporter、HAProxy Exporter、MySQLserver Exporter,还有很多第三方实现如Redis Exporter和RabbitMQ Exporter等。
Exporter分类
- 社区提供的:
- 例如:Node Exporter,MySQL Exporter,Fluentd Exporter
- 官方文档链接:https://prometheus.io/docs/instrumenting/exporters/
- 用户自定义的:
- 用户可以基于Prometheus提供的Client Library创建自己的Exporter程序。
- 这里给出Client Go的链接:https://github.com/prometheus/client_golang
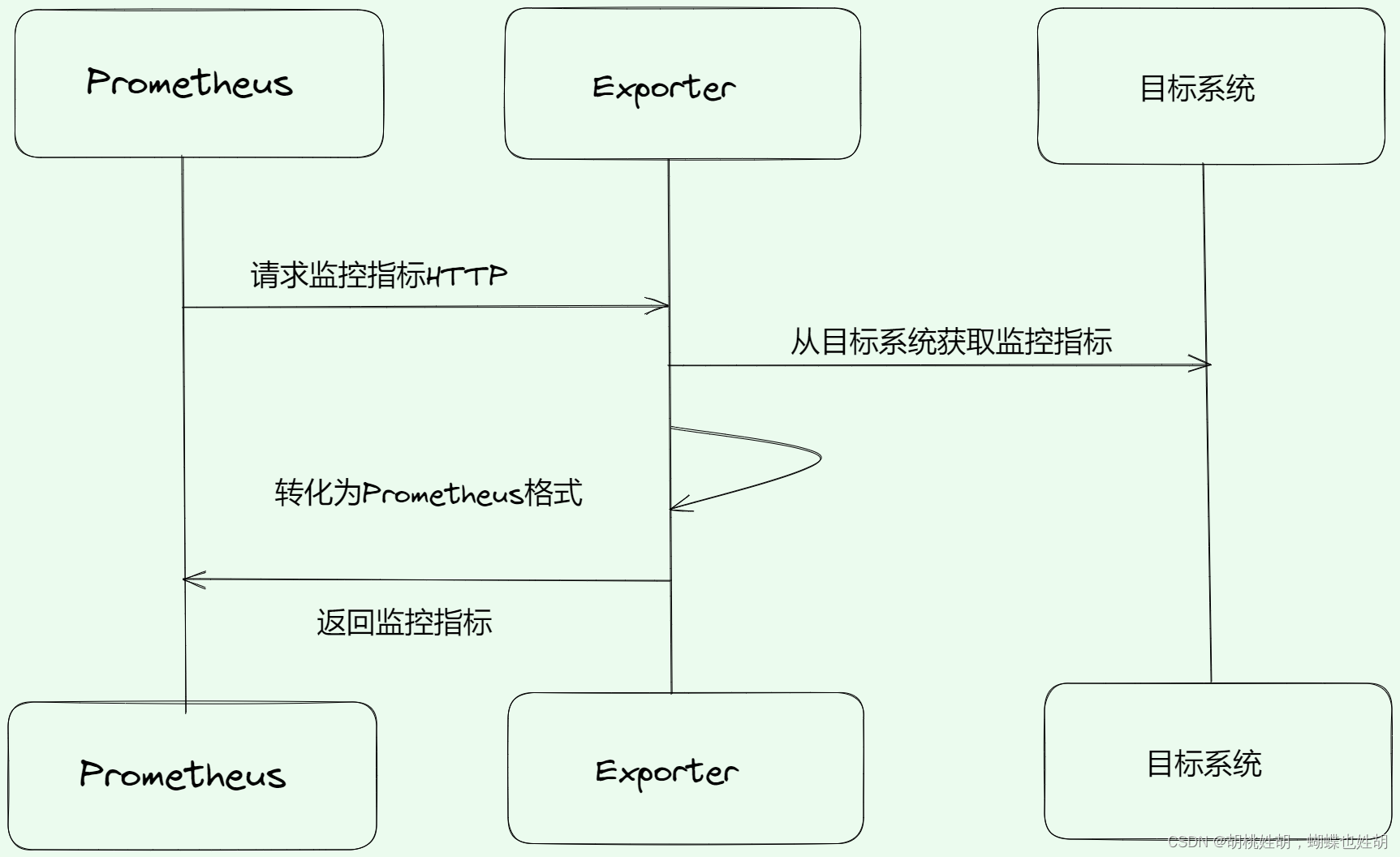
Exporter获取监控数据的方式
Exporter主要通过被监控对象提供的监控相关的接口获取监控数据,主要有如下几种方式:
- HTTP/HTTPS方式。例如RabbitMQ exporter通过RabbitMQ的HTTPS接口获取监控数据。
- TCP方式。例如Redis exporter通过Redis提供的系统监控相关命令获取监控指标,MySQL server exporter通过MySQL开发的监控相关的表获取监控指标。
- 本地文件方式。例如Node exporter通过读取proc文件系统下的文件,计算得到整个操作系统的状态。
- 标准协议方式。
Exporter规范
Prometheus 在面对众多繁杂的监控对象时并没有采用逐一适配的方式,而是制定了一套独特的监控数据规范,符合这套规范的监控数据都可以被Prometheus统一采集、分析和展现。
所有的Exporter程序都需要按照Prometheus的规范,返回监控的样本数据。以Node Exporter为例,当访问/metrics地址时会返回以下内容:
# HELP node_cpu Seconds the cpus spent in each mode.
# TYPE node_cpu counter
node_cpu{cpu="cpu0",mode="idle"} 362812.7890625
# HELP node_load1 1m load average.
# TYPE node_load1 gauge
node_load1 3.0703125
Exporter返回的样本数据,主要由三个部分组成:样本的一般注释信息(HELP),样本的类型注释信息(TYPE)和样本。Prometheus会对Exporter响应的内容逐行解析:
- 如果当前行以# HELP开始,Prometheus将会按照以下规则对内容进行解析,得到当前的指标名称以及相应的说明信息:
# HELP <metrics_name> <doc_string> - 如果当前行以# TYPE开始,Prometheus会按照以下规则对内容进行解析,得到当前的指标名称以及指标类型:
# TYPE <metrics_name> <metrics_type> - 除了# 开头的所有行都会被视为是监控样本数据。 每一行样本需要满足以下格式规范:
metric_name [
"{" label_name "=" `"` label_value `"` { "," label_name "=" `"` label_value `"` } [ "," ] "}"
] value [ timestamp ]
自定义Exporter
官方给出了example可以给我们参考:
https://github.com/prometheus/client_golang/blob/main/examples/random/main.go
现在我们来解析一下:
-
定义指标
rpcDurations = prometheus.NewSummaryVec( prometheus.SummaryOpts{ Name: "rpc_durations_seconds", Help: "RPC latency distributions.", Objectives: map[float64]float64{0.5: 0.05, 0.9: 0.01, 0.99: 0.001}, }, []string{"service"}, ) -
注册指标:
prometheus.MustRegister(rpcDurations) -
记录监控样本数据:
go func() { for { v := rand.Float64() * *uniformDomain rpcDurations.WithLabelValues("uniform").Observe(v) time.Sleep(time.Duration(100*oscillationFactor()) * time.Millisecond) } }() -
暴露接口
http.Handle("/metrics", promhttp.HandlerFor( prometheus.DefaultGatherer, promhttp.HandlerOpts{ // Opt into OpenMetrics to support exemplars. EnableOpenMetrics: true, }, )) log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(*addr, nil)) -
观察监控指标
# HELP rpc_durations_seconds RPC latency distributions. # TYPE rpc_durations_seconds summary rpc_durations_seconds{service="uniform",quantile="0.5"} 4.2852774516474985e-05 rpc_durations_seconds{service="uniform",quantile="0.9"} 0.00012093205759592392 rpc_durations_seconds{service="uniform",quantile="0.99"} 0.00012093205759592392 rpc_durations_seconds_sum{service="uniform"} 0.0002537090545263203 rpc_durations_seconds_count{service="uniform"} 4
Node Exporter解析
-
初始化注册采集
// NodeCollector implements the prometheus.Collector interface. type NodeCollector struct { Collectors map[string]Collector logger log.Logger }NodeCollector是采集器的集合,Collectors是包含了各种采集器的集合,每个采集器在启动的时候都会将自身注册到这个Collector中。
// collector/meminfo.go func init() { registerCollector("meminfo", defaultEnabled, NewMeminfoCollector) } -
注册给Prometheus
func (h *handler) innerHandler(filters ...string) (http.Handler, error) { nc, err := collector.NewNodeCollector(h.logger, filters...) r := prometheus.NewRegistry() r.Register(nc); } -
采集指标
-
遍历Collectors,执行采集动作。
// Collect implements the prometheus.Collector interface. func (n NodeCollector) Collect(ch chan<- prometheus.Metric) { wg := sync.WaitGroup{} wg.Add(len(n.Collectors)) for name, c := range n.Collectors { go func(name string, c Collector) { execute(name, c, ch, n.logger) wg.Done() }(name, c) } wg.Wait() } func execute(name string, c Collector, ch chan<- prometheus.Metric, logger log.Logger) { begin := time.Now() err := c.Update(ch) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(scrapeDurationDesc, prometheus.GaugeValue, duration.Seconds(), name) ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric(scrapeSuccessDesc, prometheus.GaugeValue, success, name) } -
具体采集指标实现Update接口(例如:meminfo.go)
-
Update方法传入一个只写(write only)的单向管道,首先通过getMemInfo获取内存信息,然后将内存信息发送到管道中。
// Update calls (*meminfoCollector).getMemInfo to get the platform specific // memory metrics. func (c *meminfoCollector) Update(ch chan<- prometheus.Metric) error { var metricType prometheus.ValueType memInfo, err := c.getMemInfo() if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("couldn't get meminfo: %w", err) } level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "Set node_mem", "memInfo", memInfo) for k, v := range memInfo { if strings.HasSuffix(k, "_total") { metricType = prometheus.CounterValue } else { metricType = prometheus.GaugeValue } ch <- prometheus.MustNewConstMetric( prometheus.NewDesc( prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, memInfoSubsystem, k), fmt.Sprintf("Memory information field %s.", k), nil, nil, ), metricType, v, ) } return nil } func (c *meminfoCollector) getMemInfo() (map[string]float64, error) { ... return map[string]float64{ "active_bytes": ps * float64(vmstat.active_count), "compressed_bytes": ps * float64(vmstat.compressor_page_count), "inactive_bytes": ps * float64(vmstat.inactive_count), "wired_bytes": ps * float64(vmstat.wire_count), "free_bytes": ps * float64(vmstat.free_count), "swapped_in_bytes_total": ps * float64(vmstat.pageins), "swapped_out_bytes_total": ps * float64(vmstat.pageouts), "total_bytes": float64(total), "swap_used_bytes": float64(swap.xsu_used), "swap_total_bytes": float64(swap.xsu_total), }, nil }
-
-
-
查看结果:
# HELP node_memory_active_bytes Memory information field active_bytes. # TYPE node_memory_active_bytes gauge node_memory_active_bytes 5.08428288e+09 # HELP node_memory_swapped_in_bytes_total Memory information field swapped_in_bytes_total. # TYPE node_memory_swapped_in_bytes_total counter node_memory_swapped_in_bytes_total 3.73191360512e+11